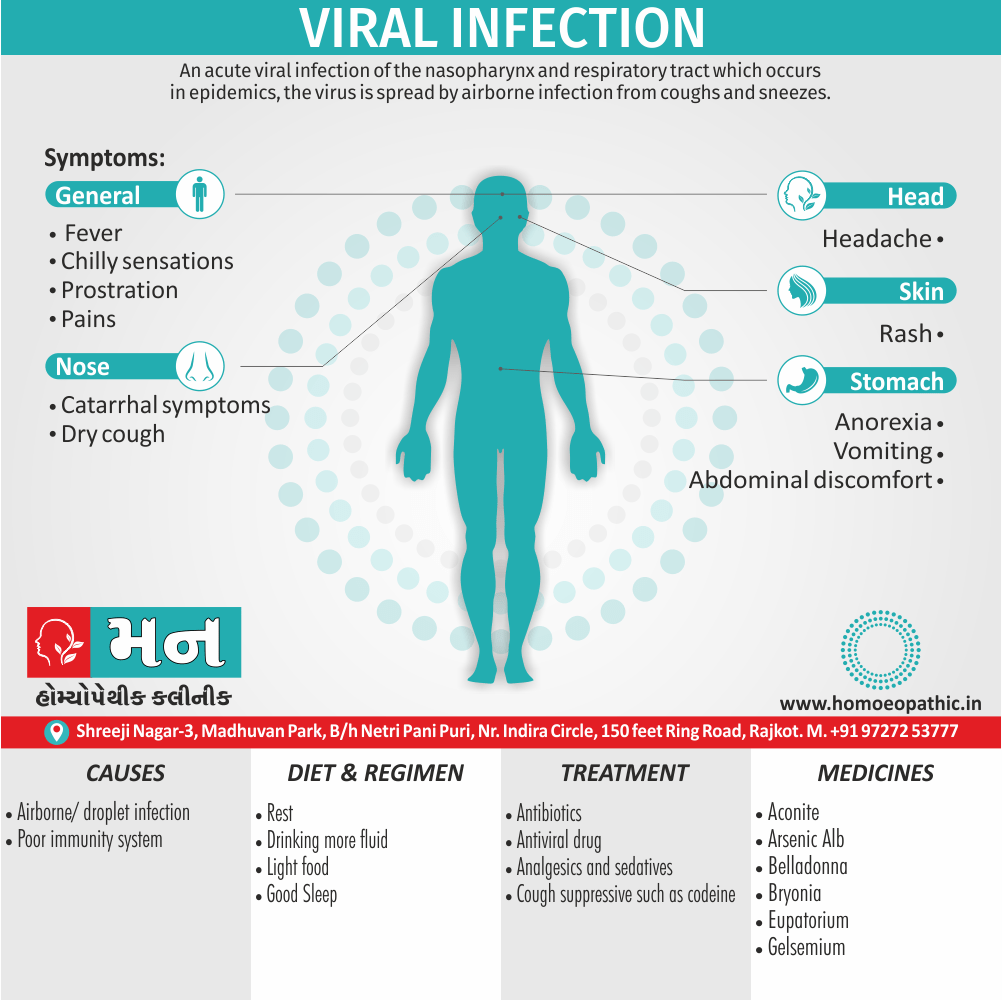
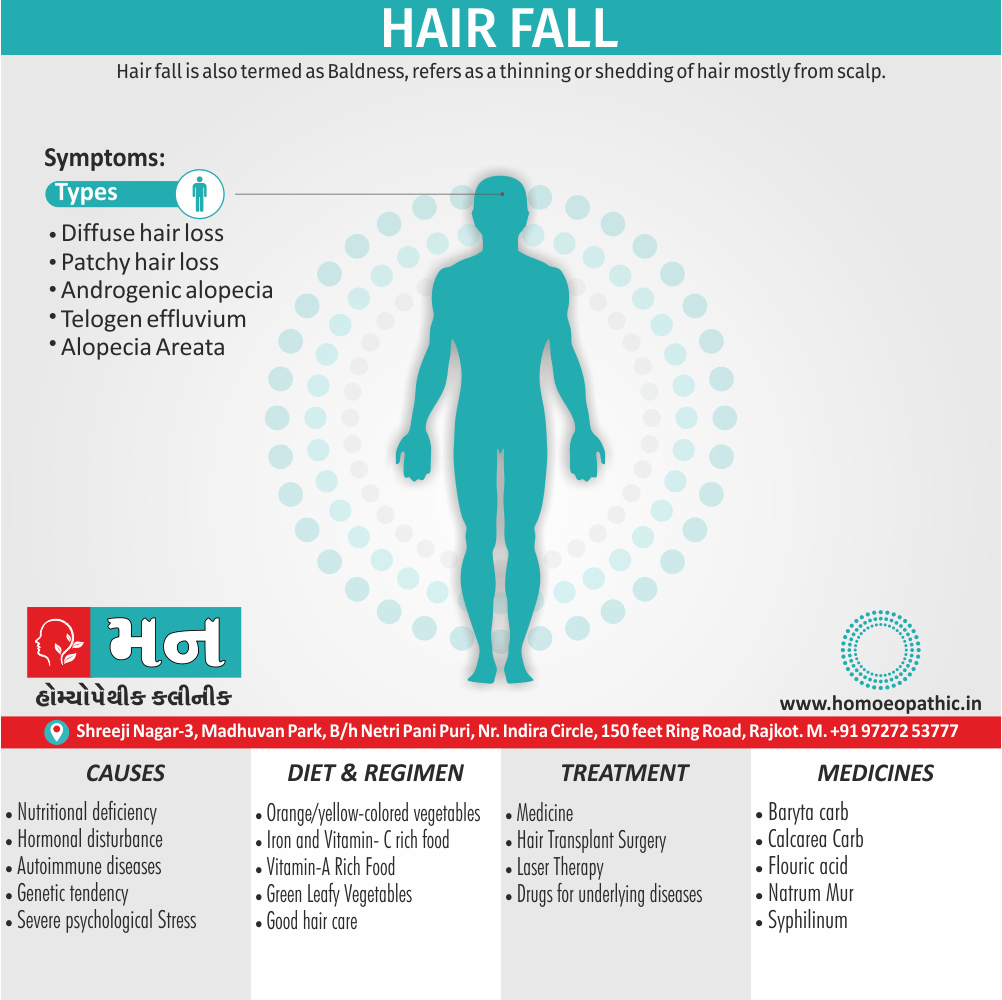
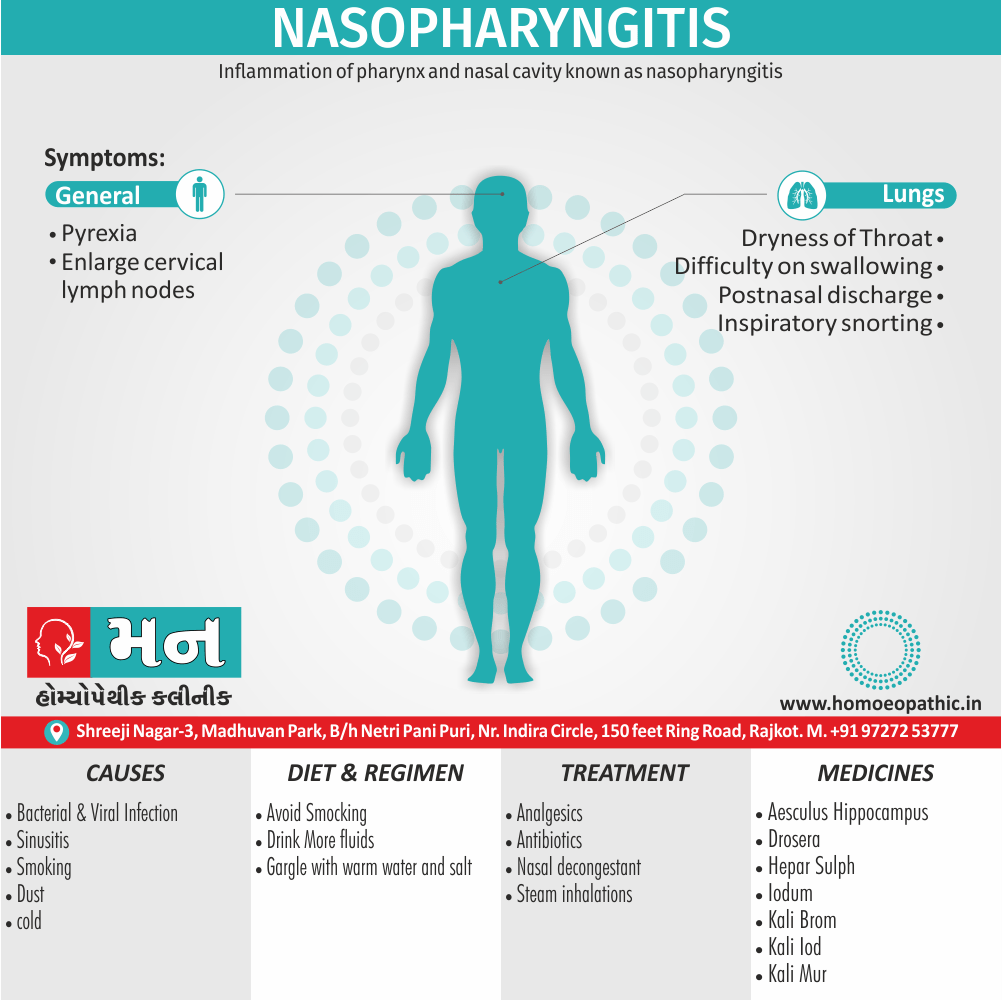
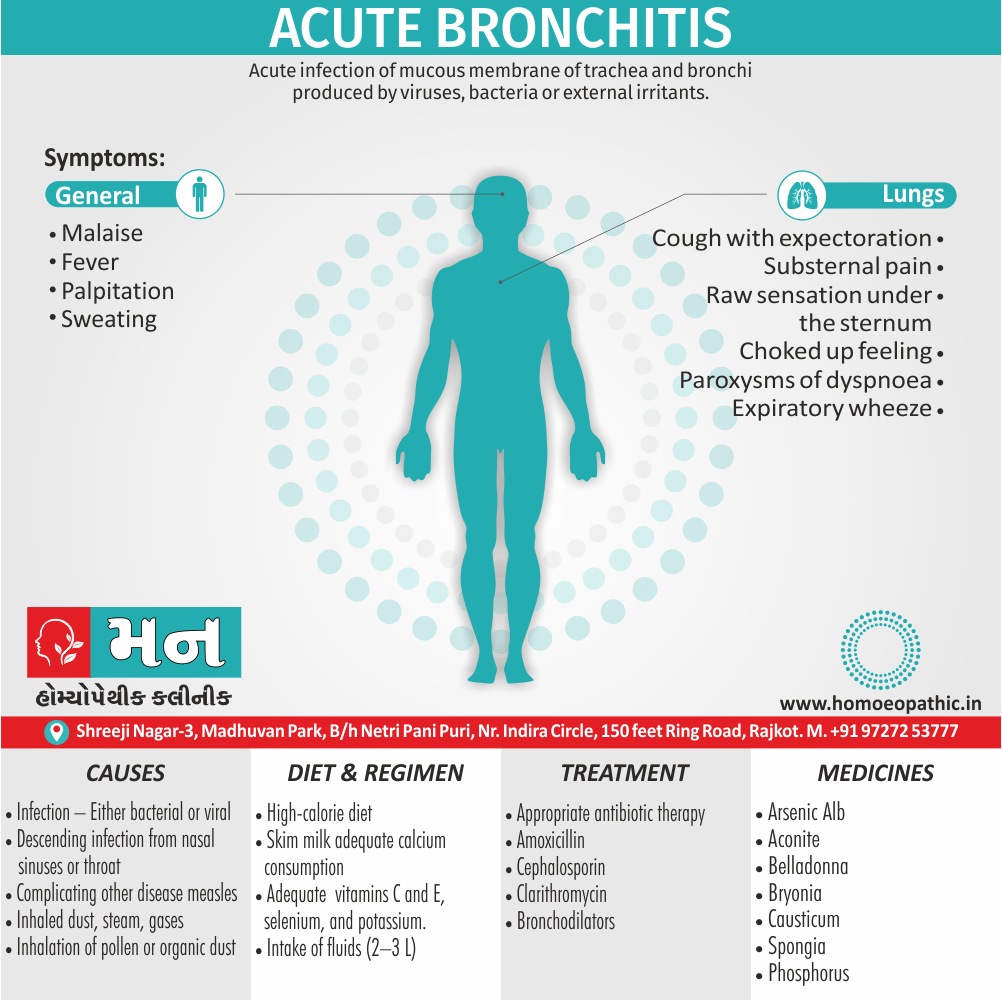
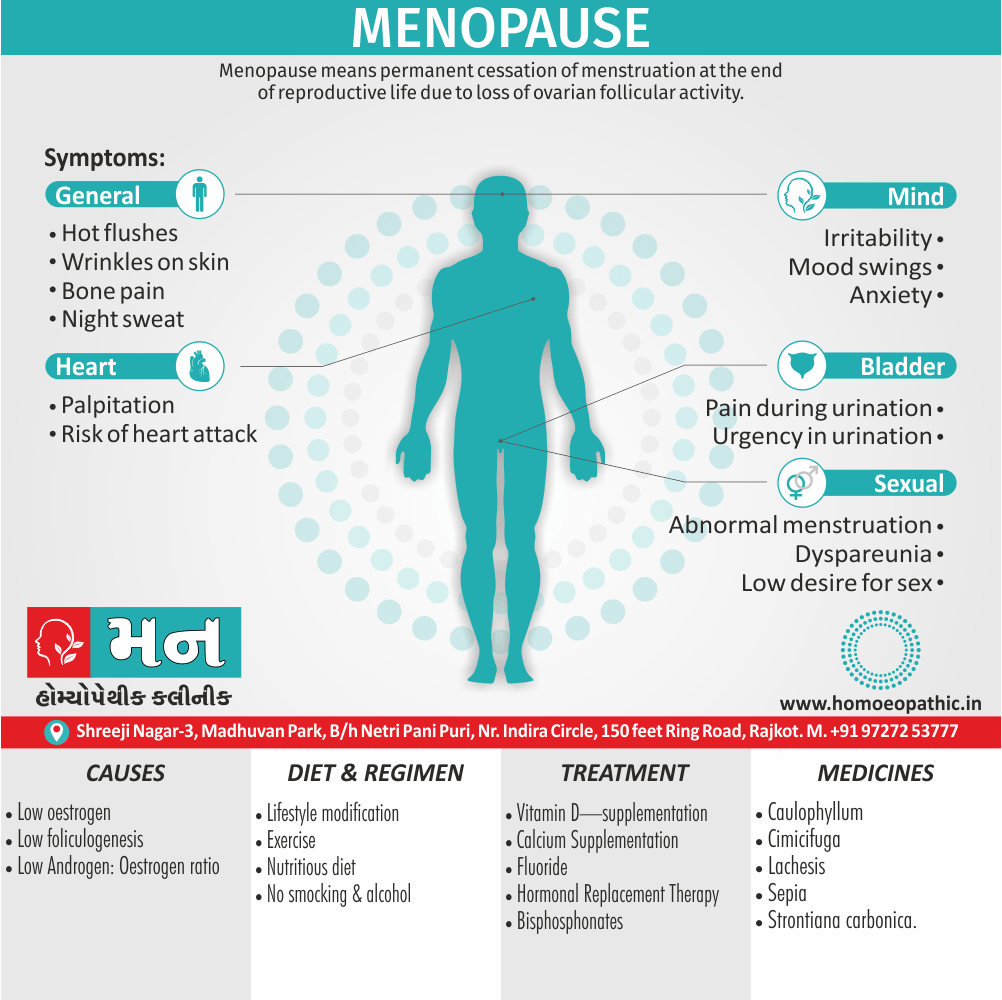
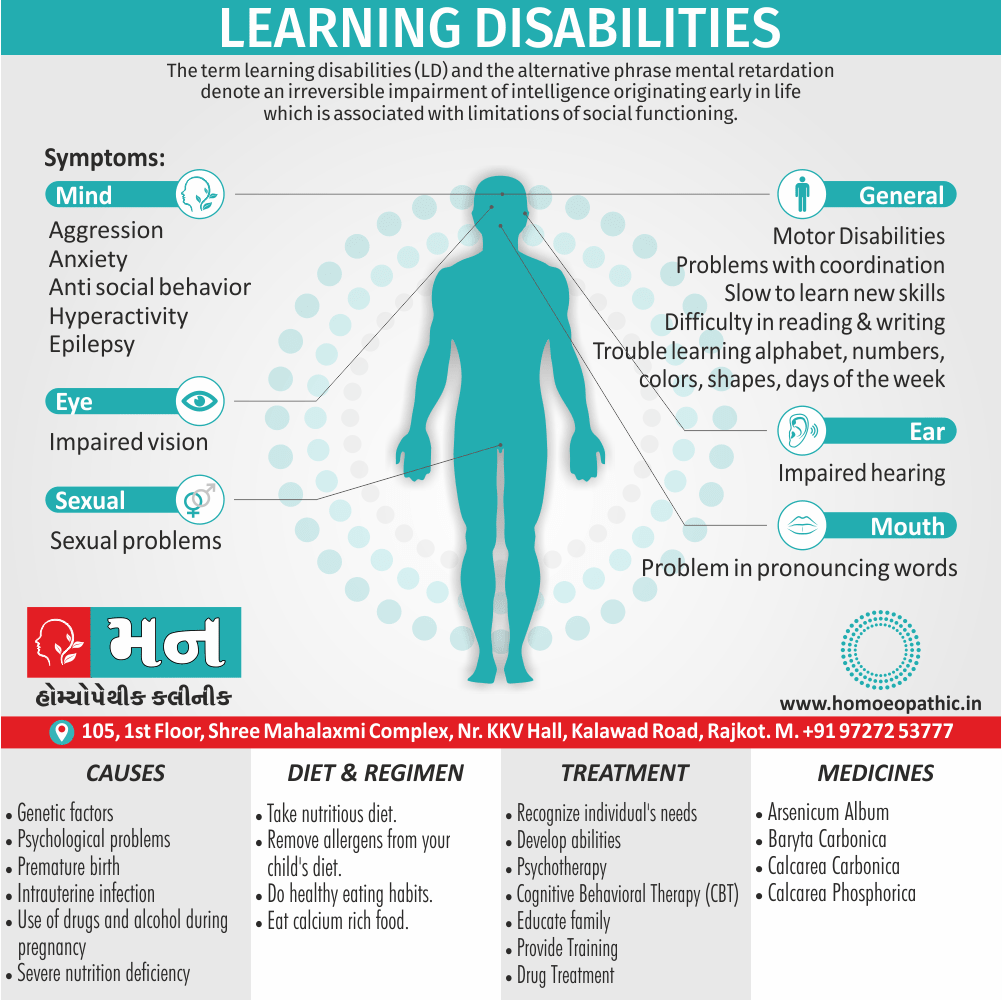
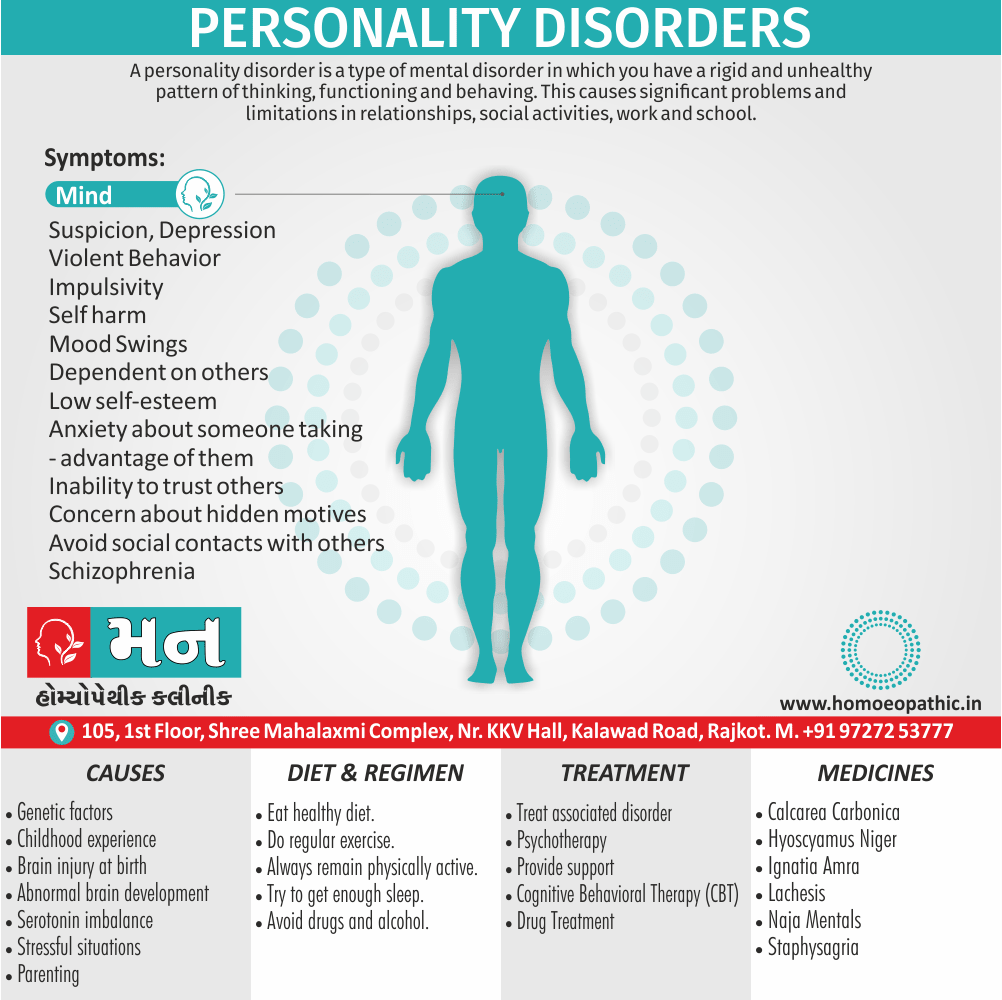
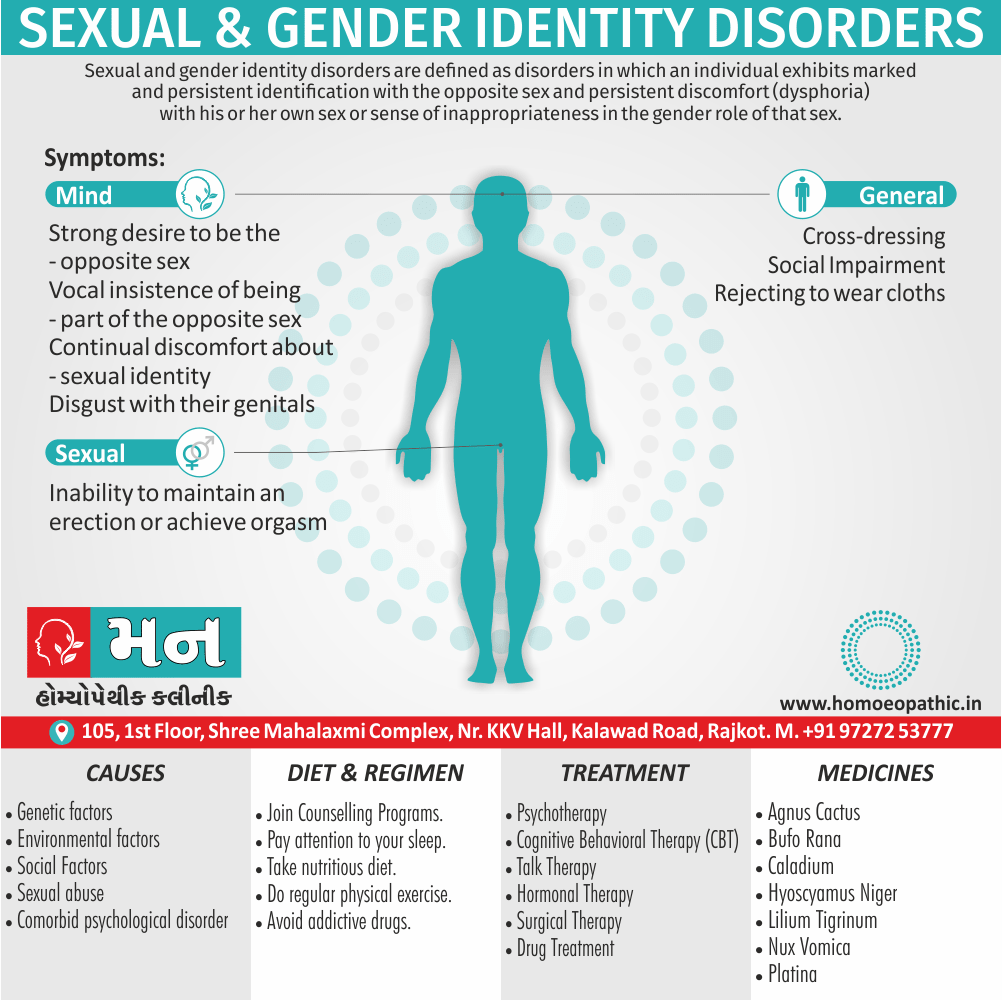
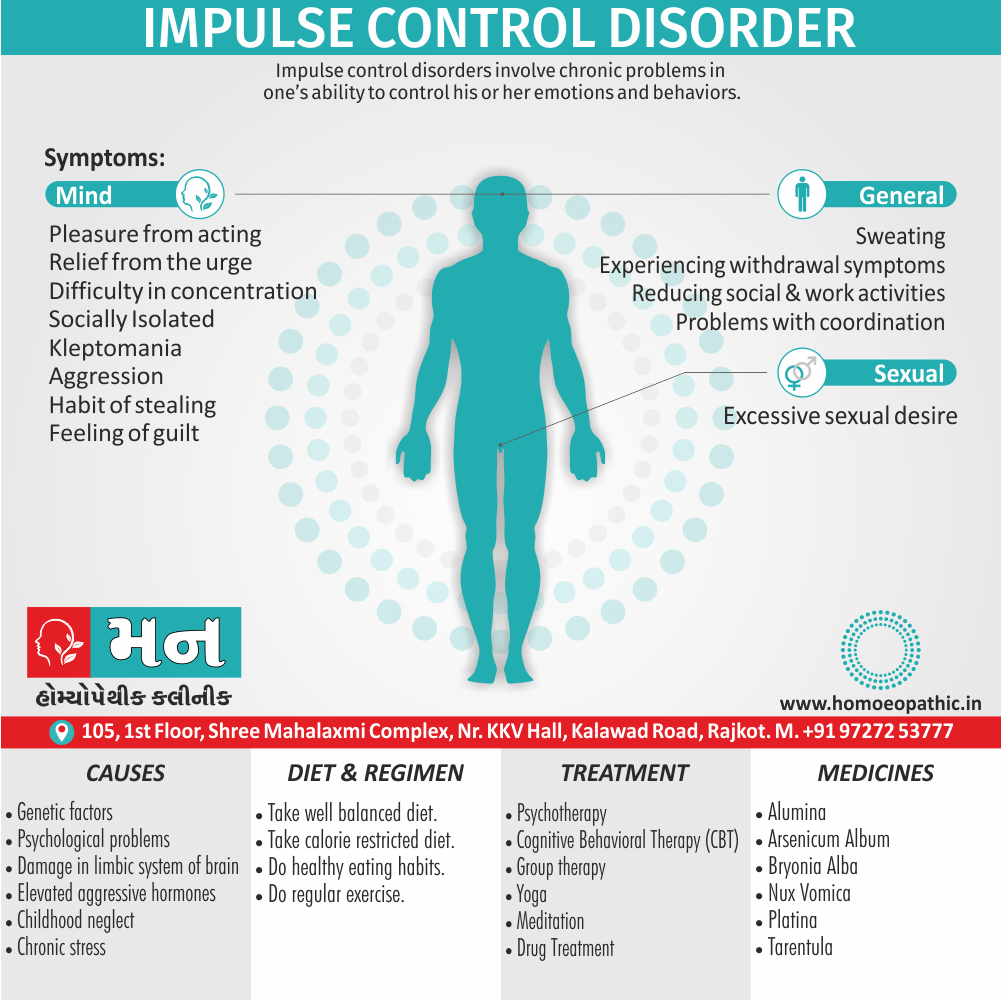
Disorders of Sexual Preference (Paraphilias)
Definition:
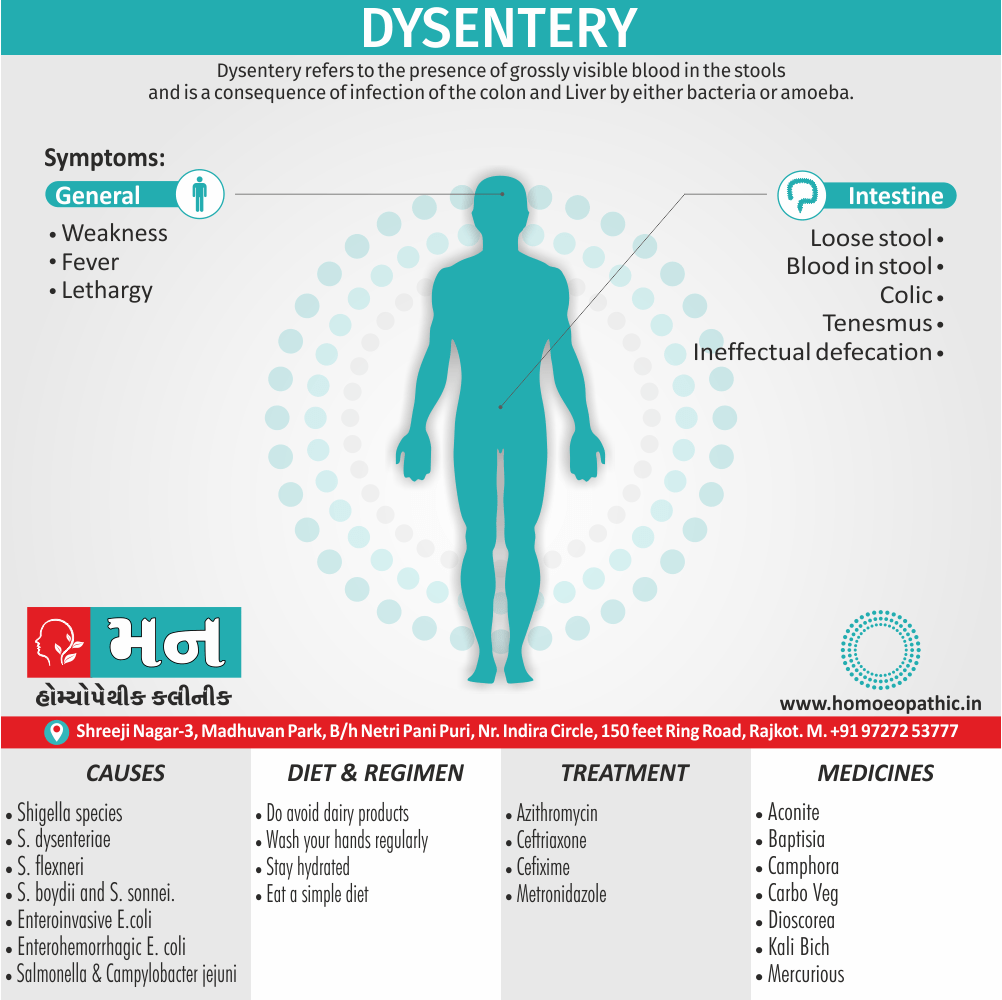
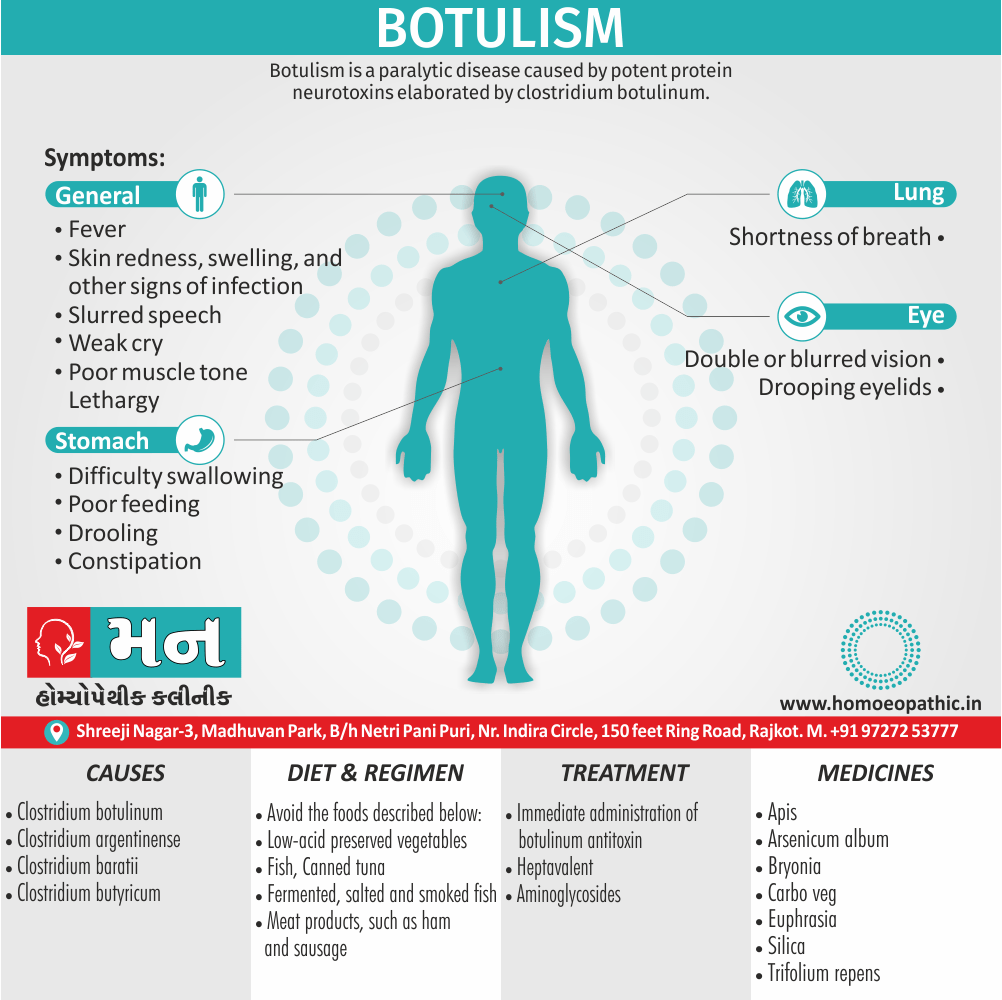
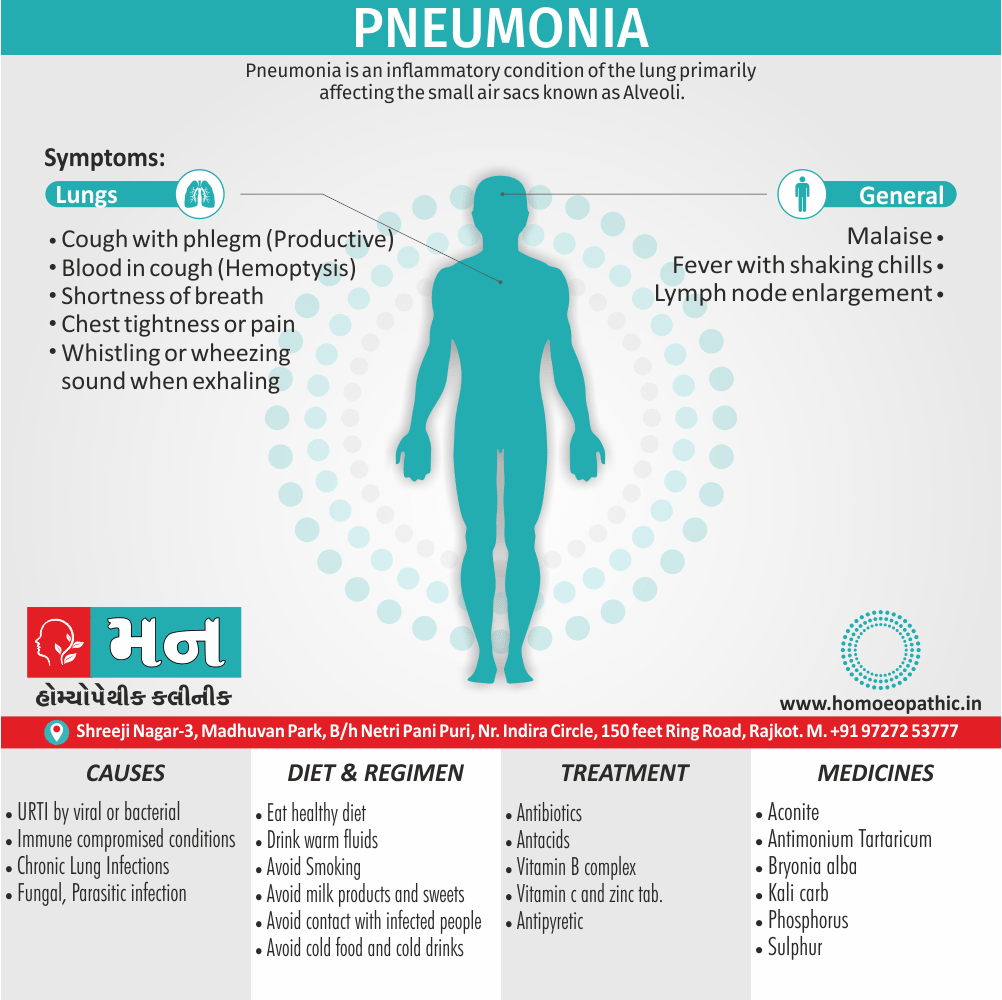
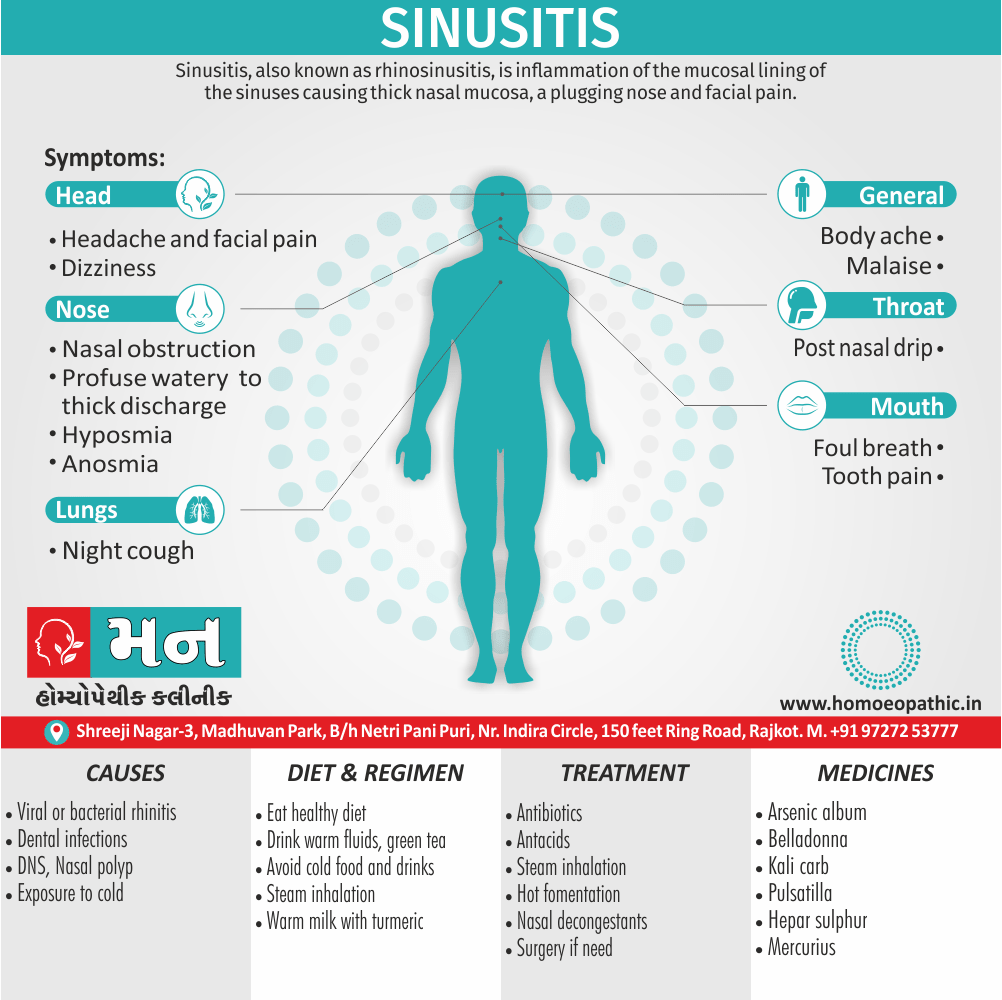
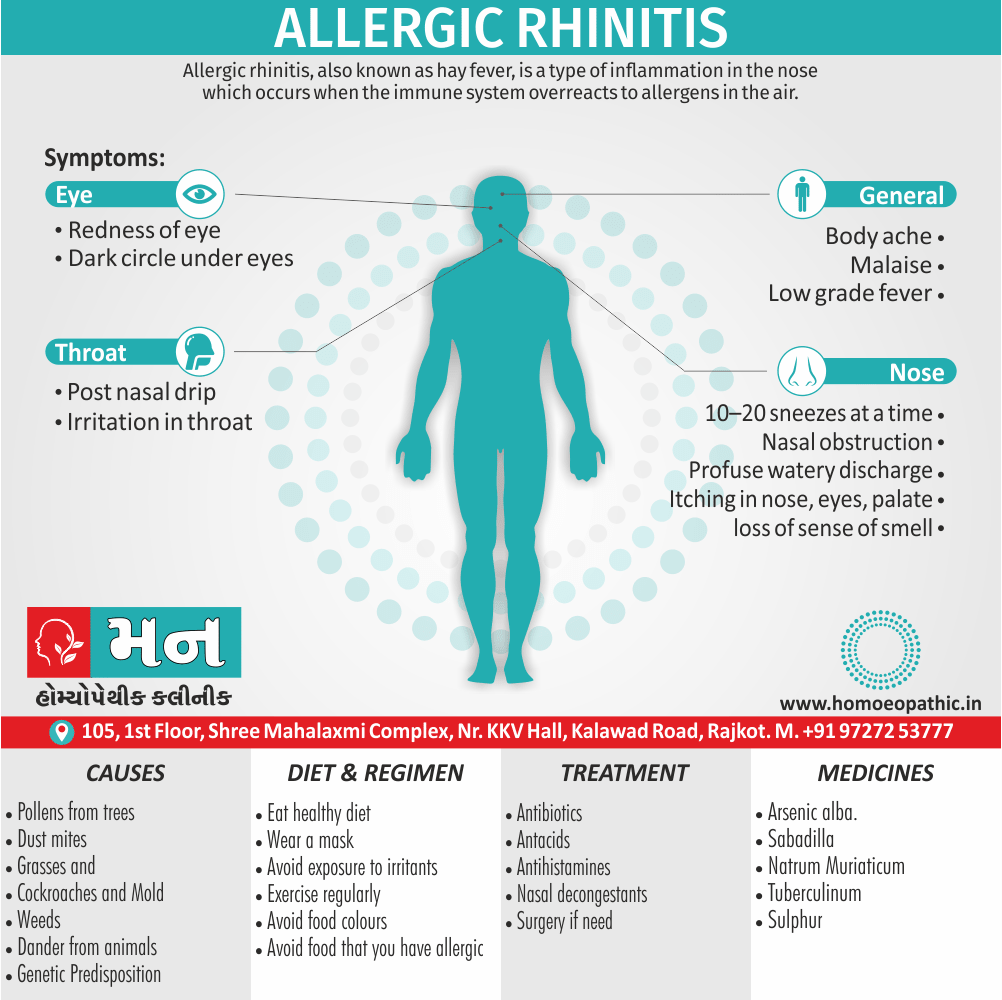
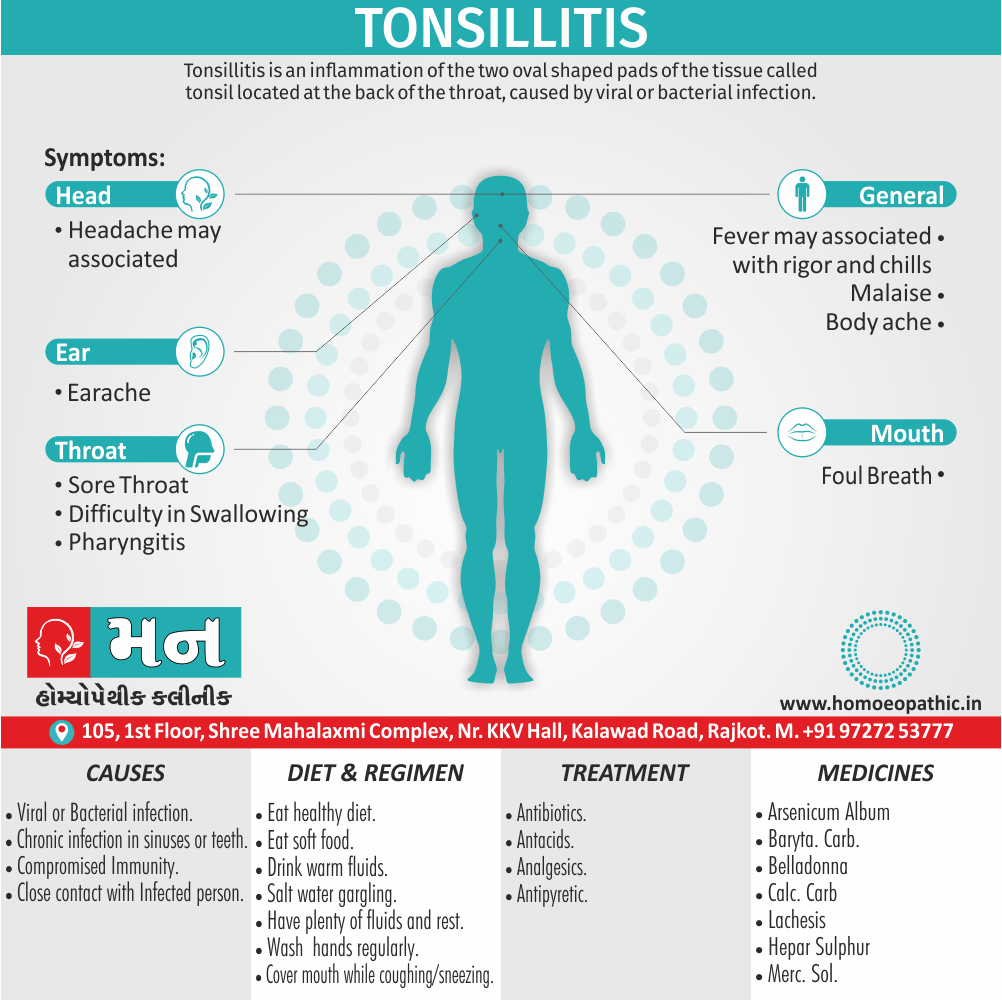
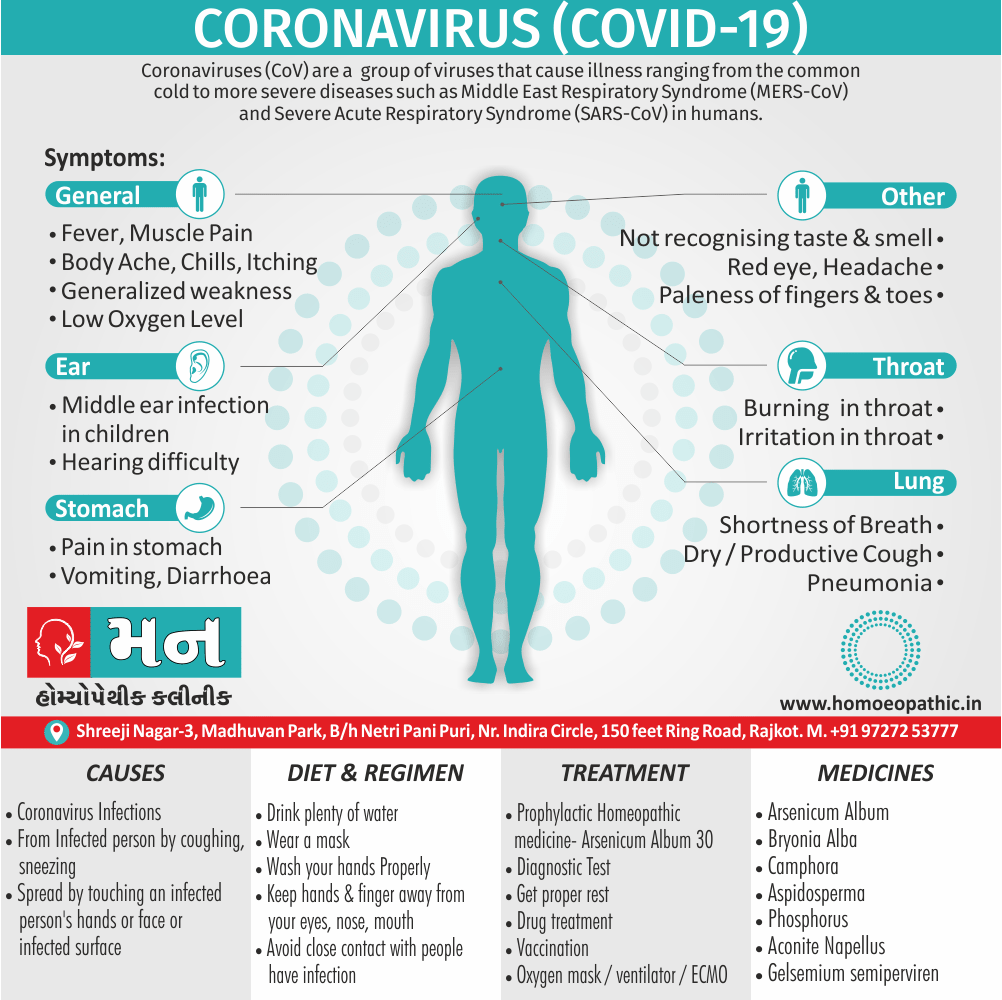
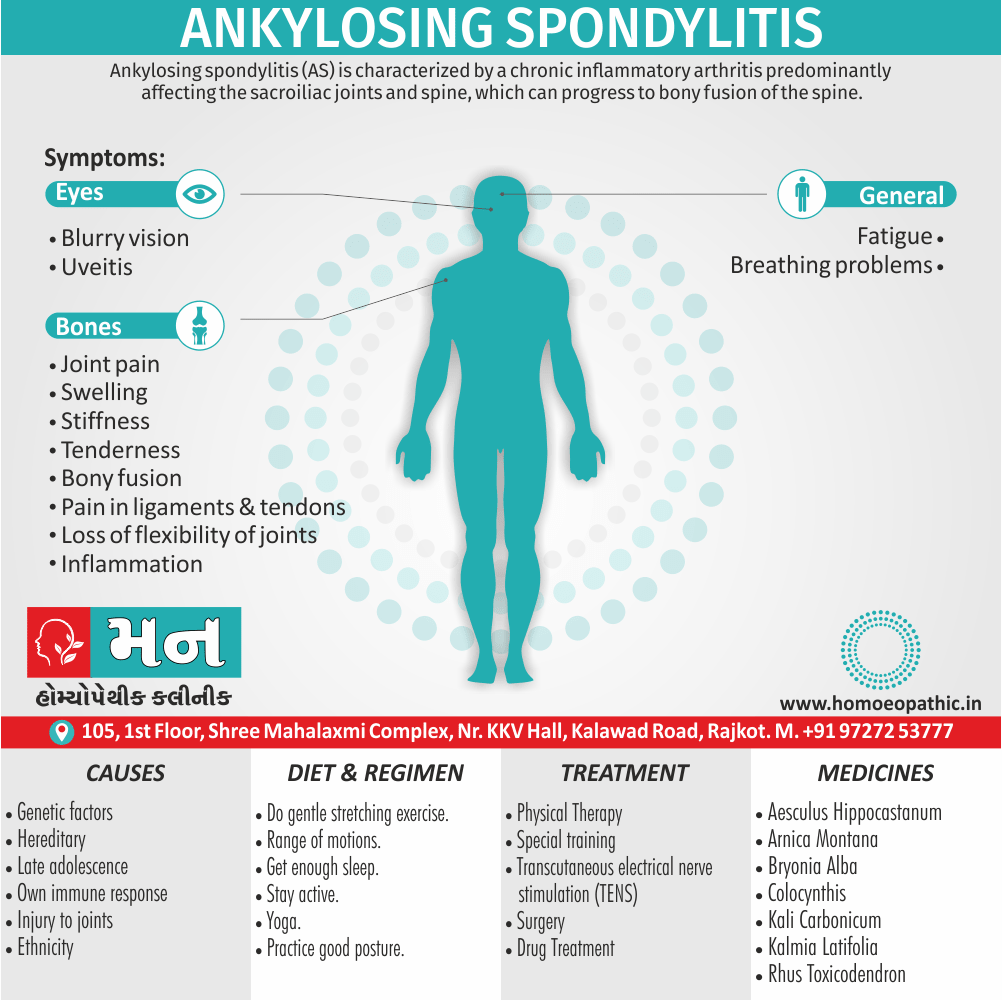
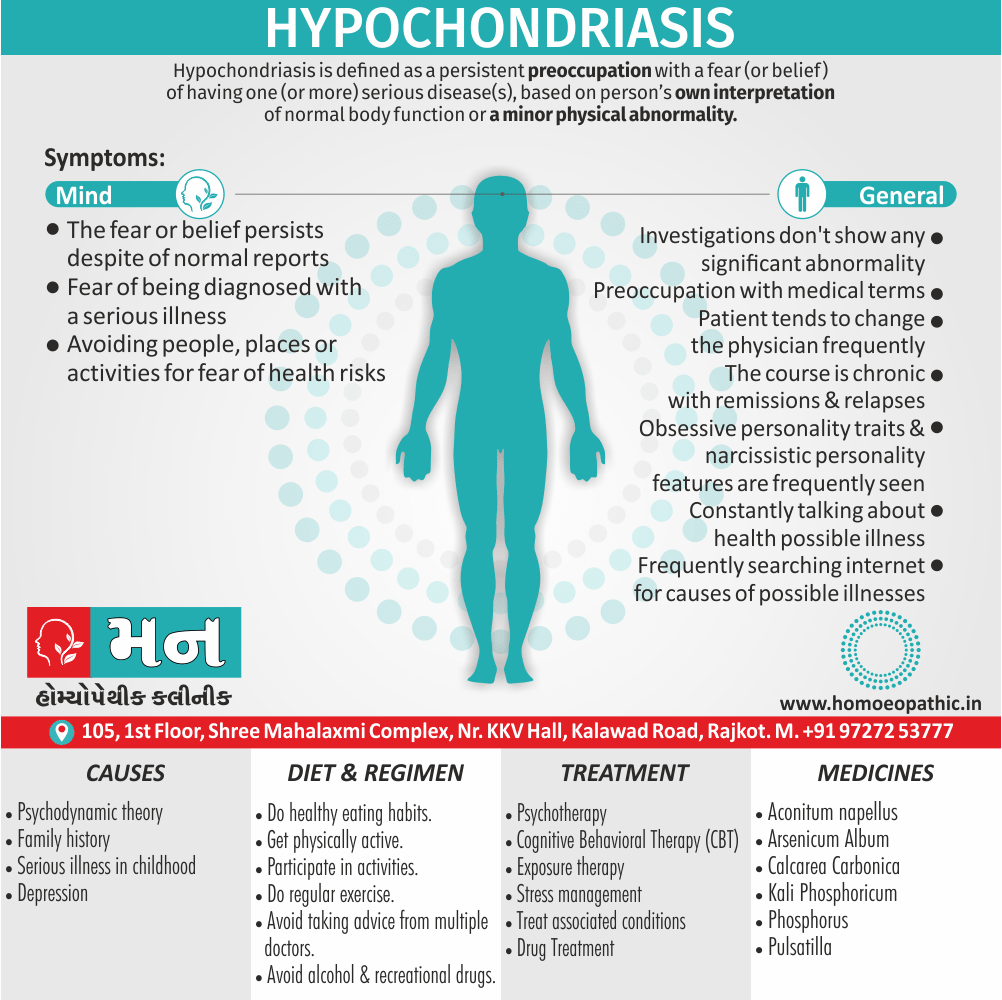
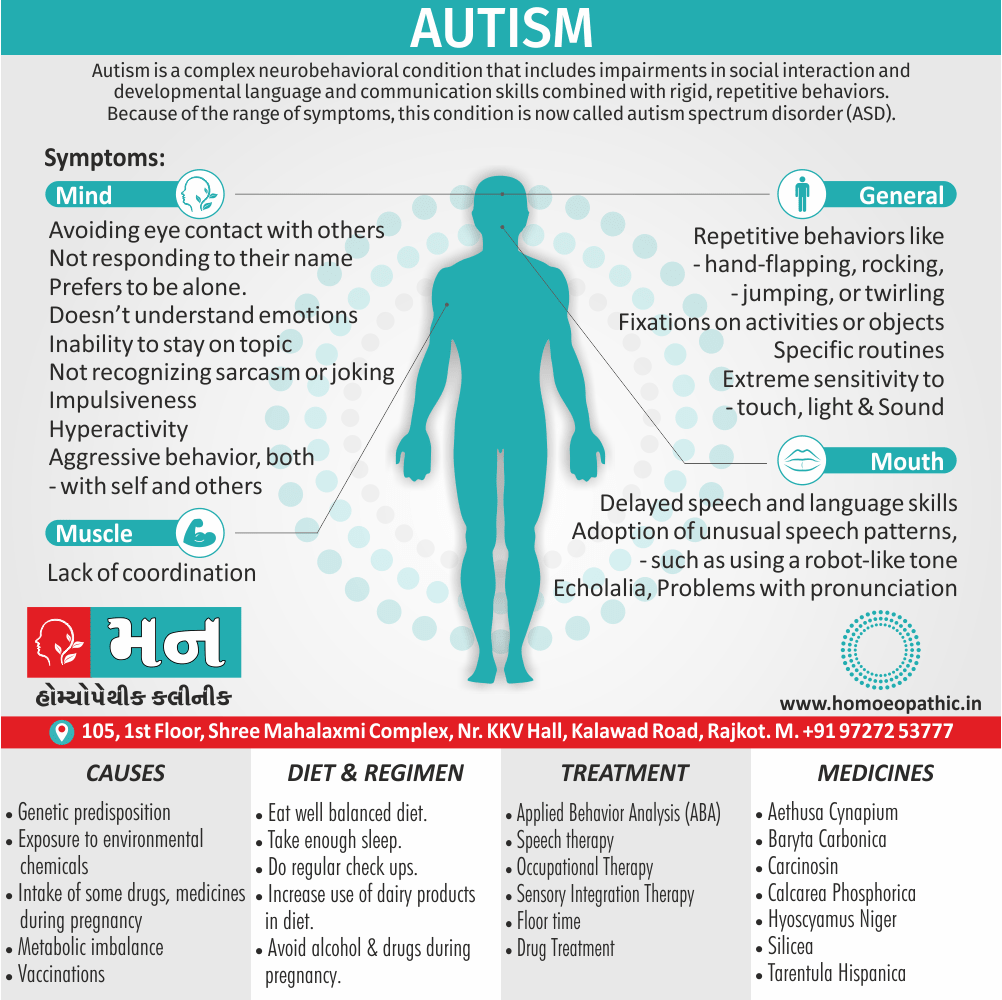
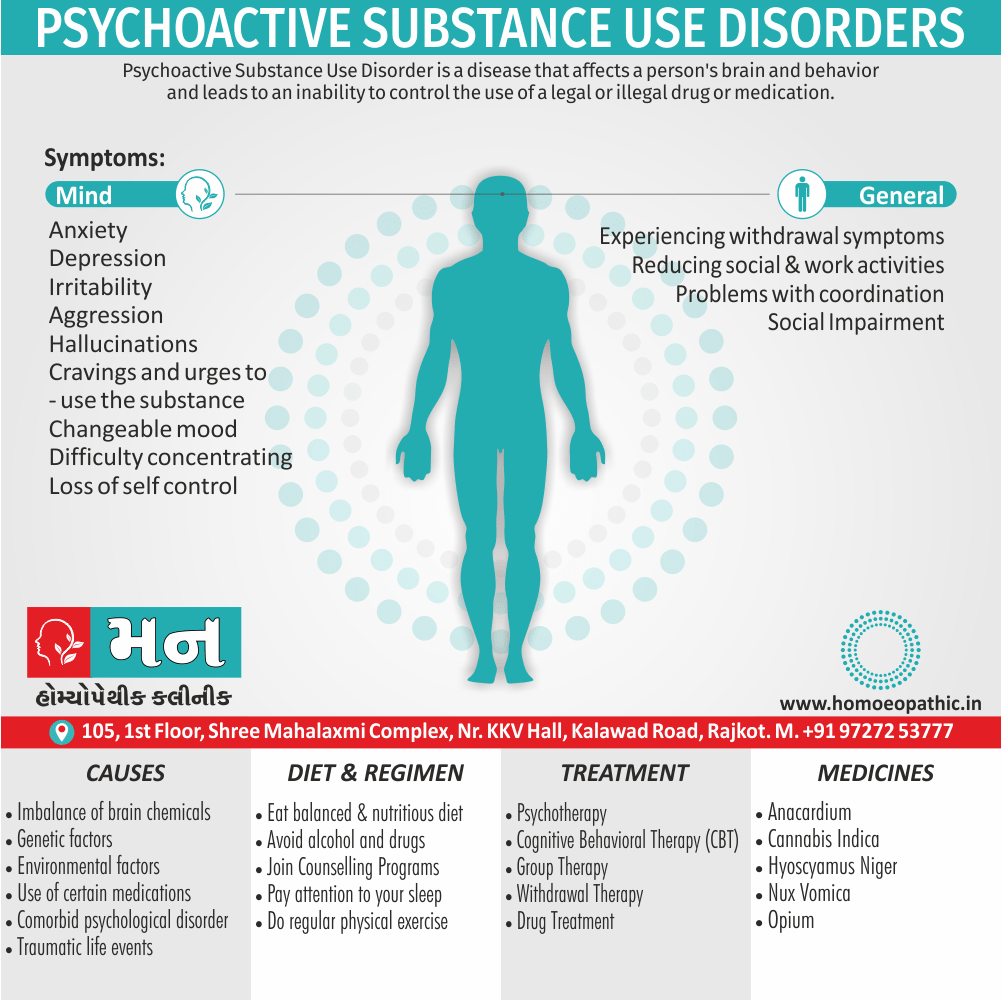
Paraphilias are disorders of sexual preference in which sexual arousal occurs persistently and significantly in response to objects which are not a part of normal sexual arousal (e.g. non human objects; suffering or humiliation of self and/or sexual partner; children or non consenting person). [2]
Disorders of sexual preference are sometimes know as paraphilias.
A Paraphilias can said to be abnormal by three criteria i.e.:
- Firstly; Most people in a society regard the sexual preference as abnormal.
- Secondly; The sexual preference can harmful to other people (e.g. sadistic sexual practices).
- Thirdly; The person with the preference suffers from its consequences (e.g. from a conflict between sexual preferences and moral standards). [1]
Disorders of Preference of the Sexual Object
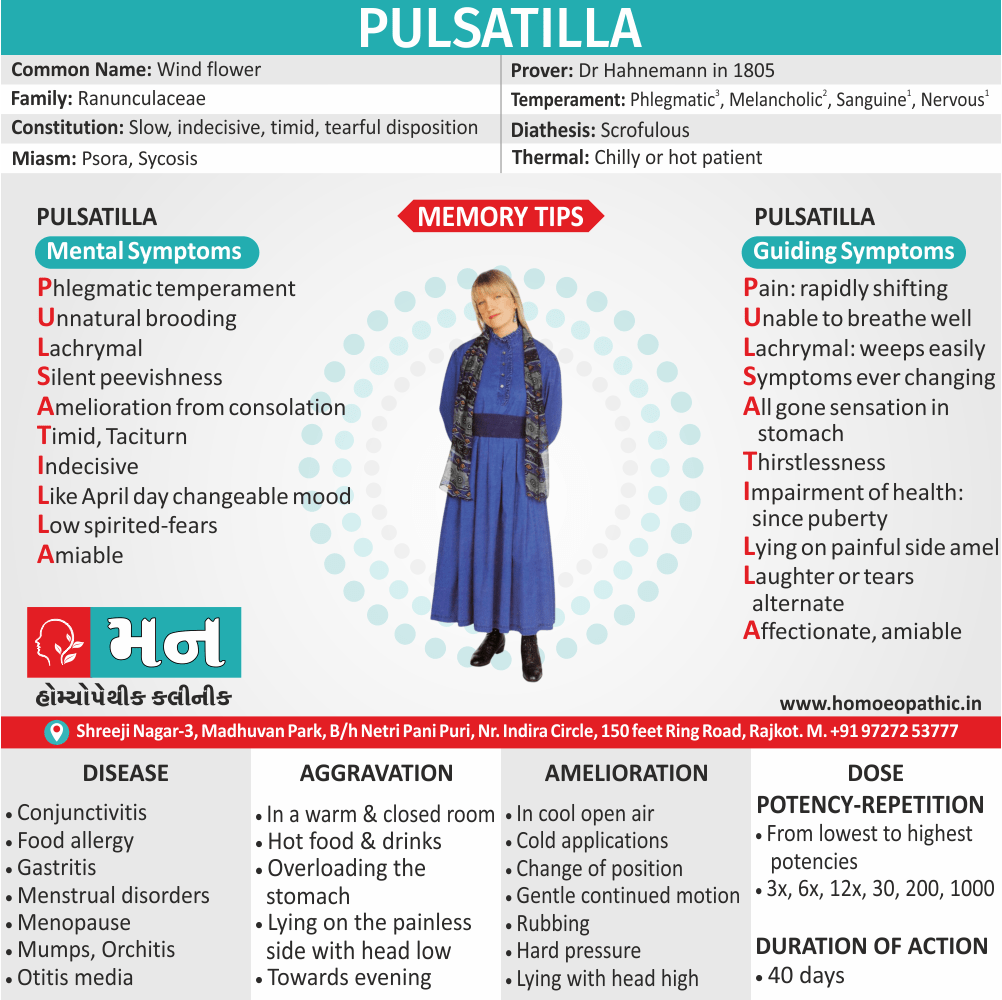
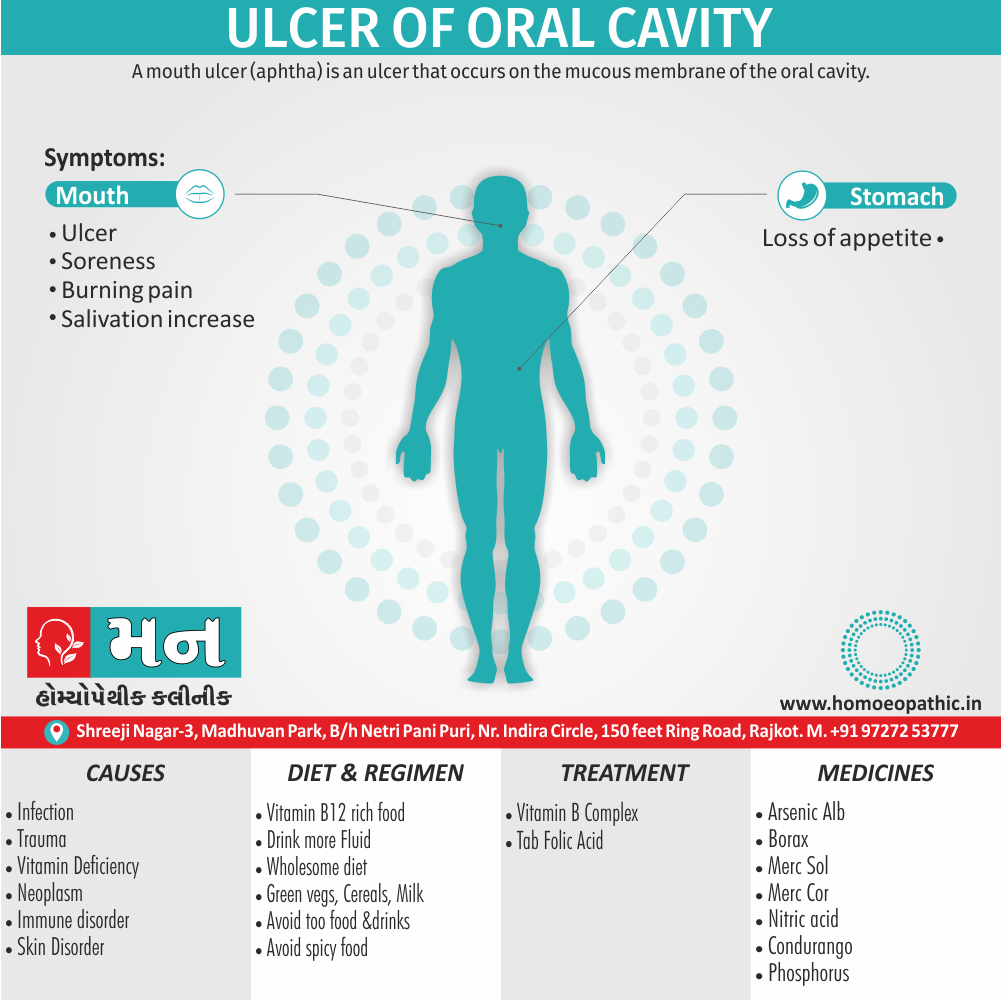
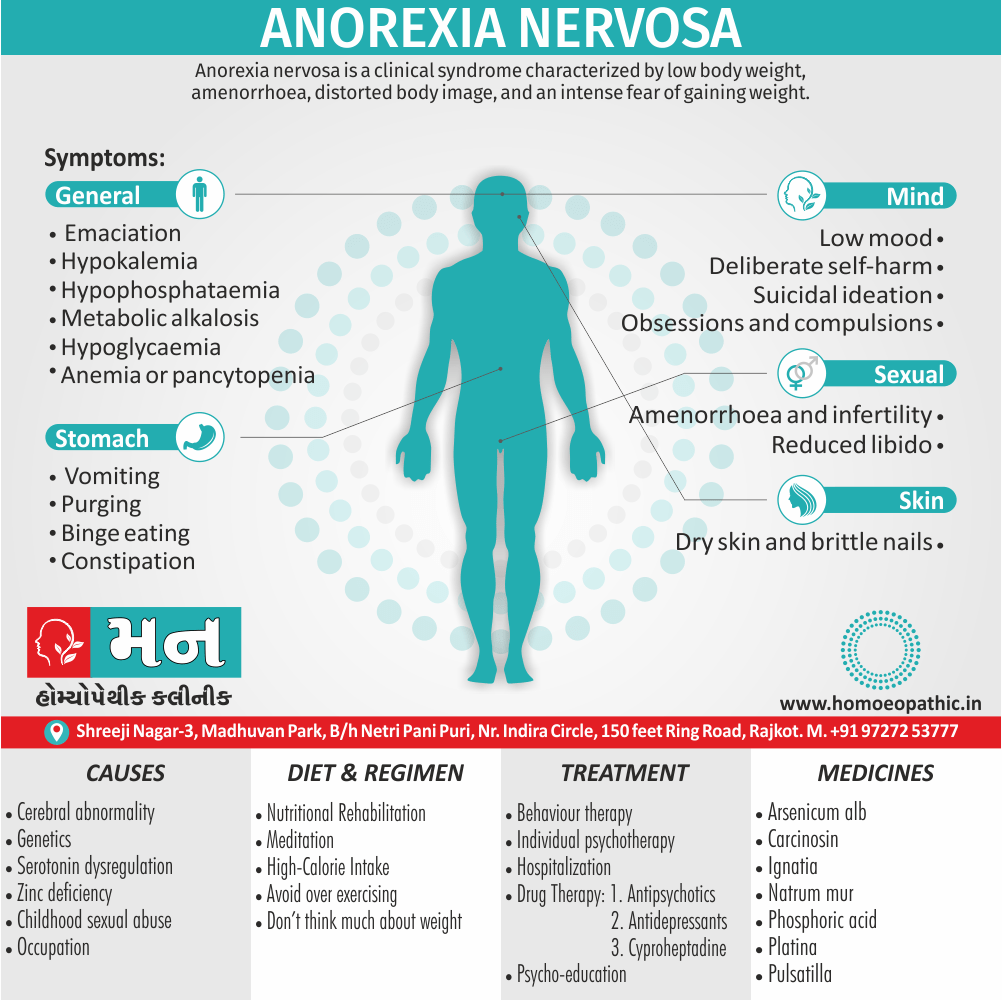
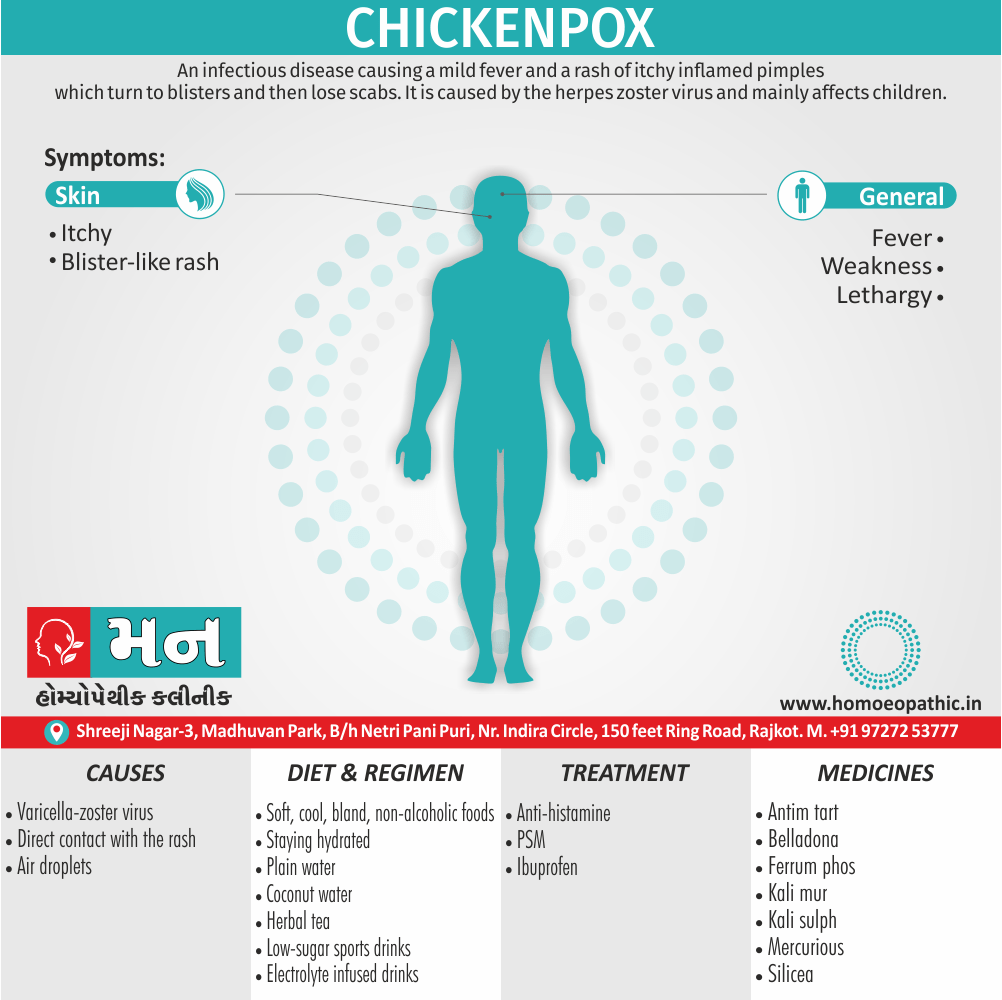
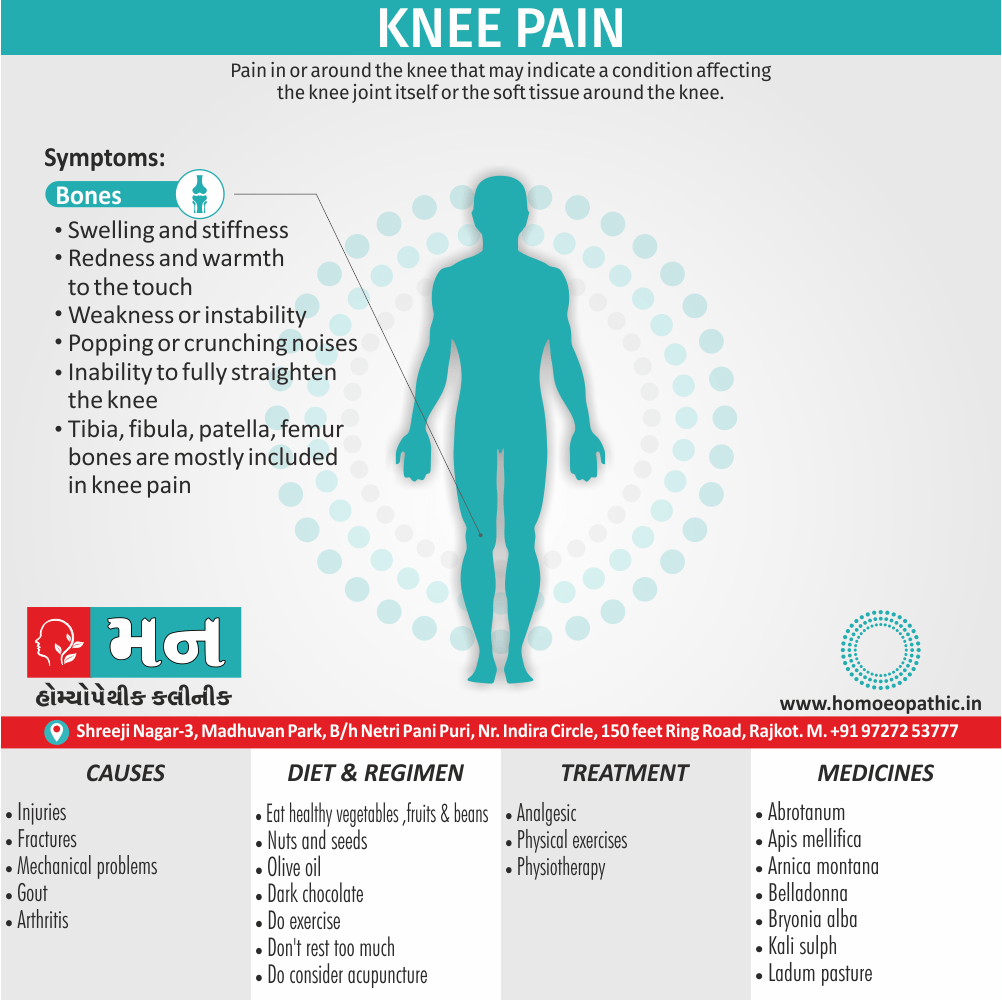
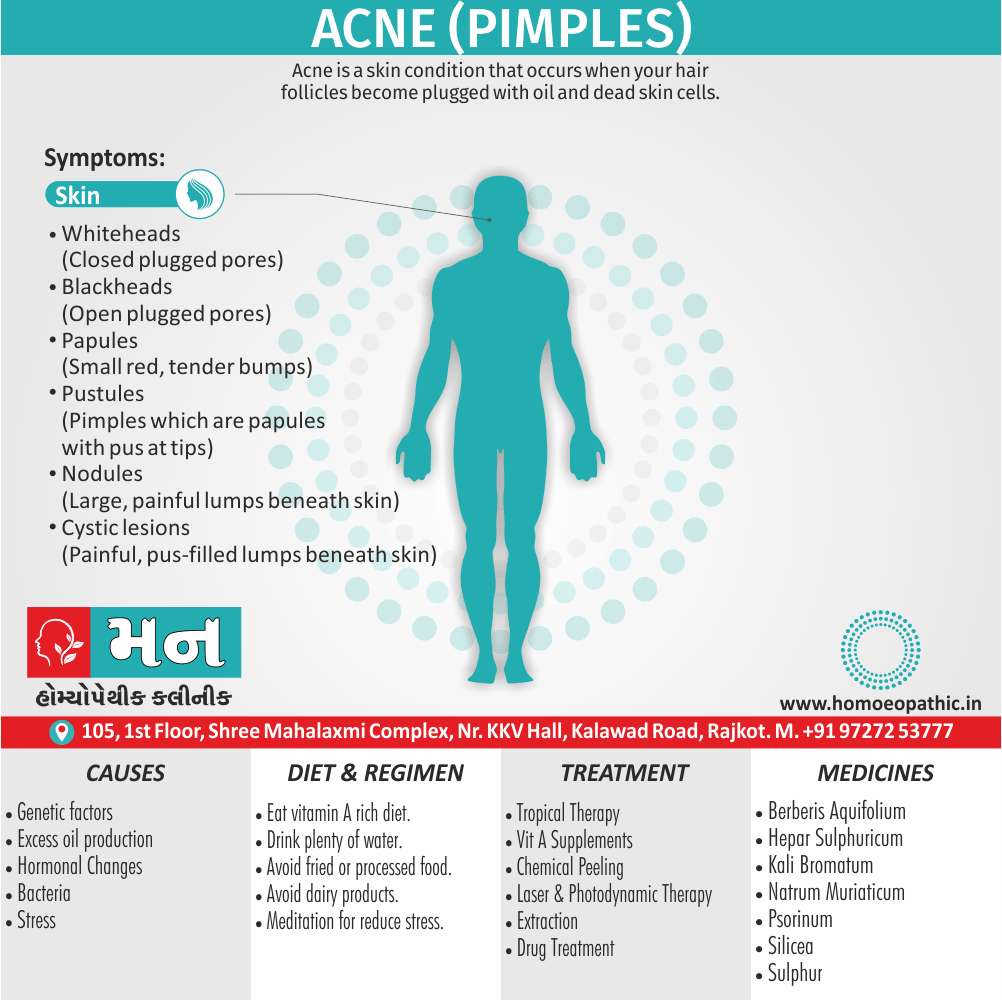
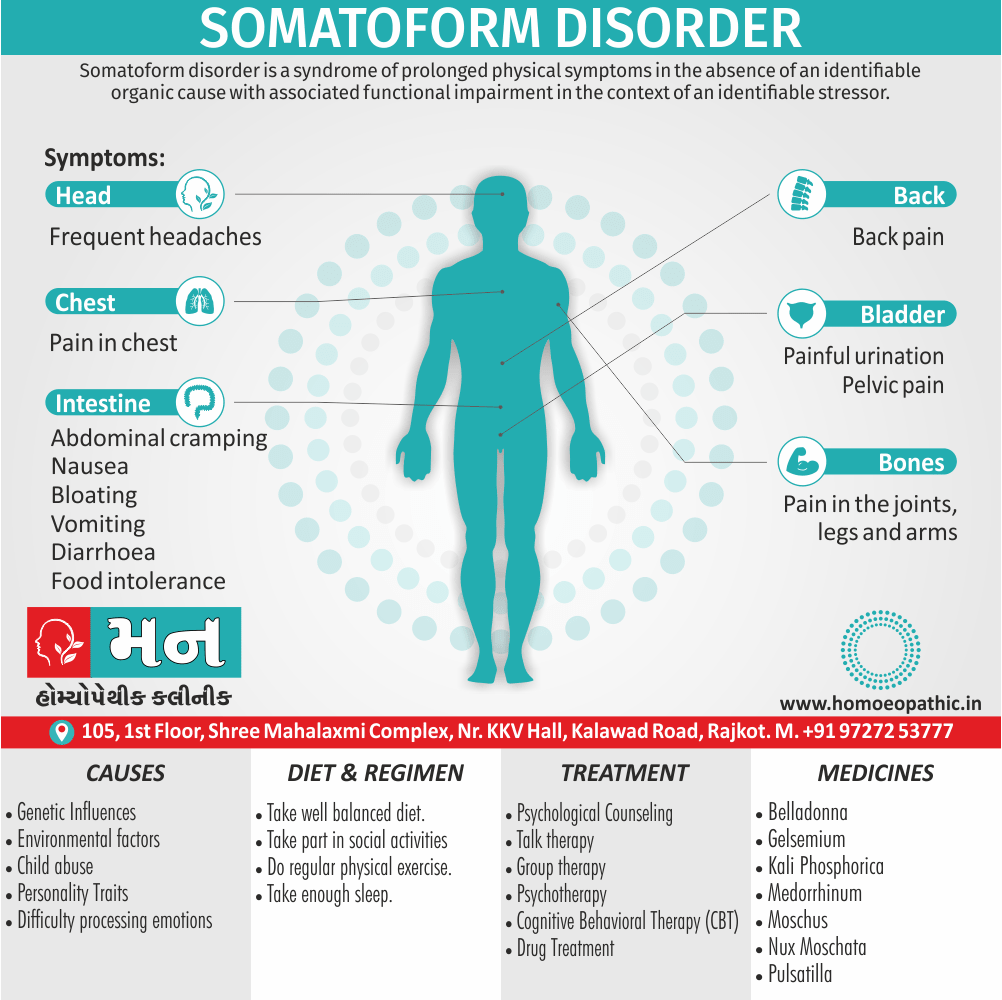
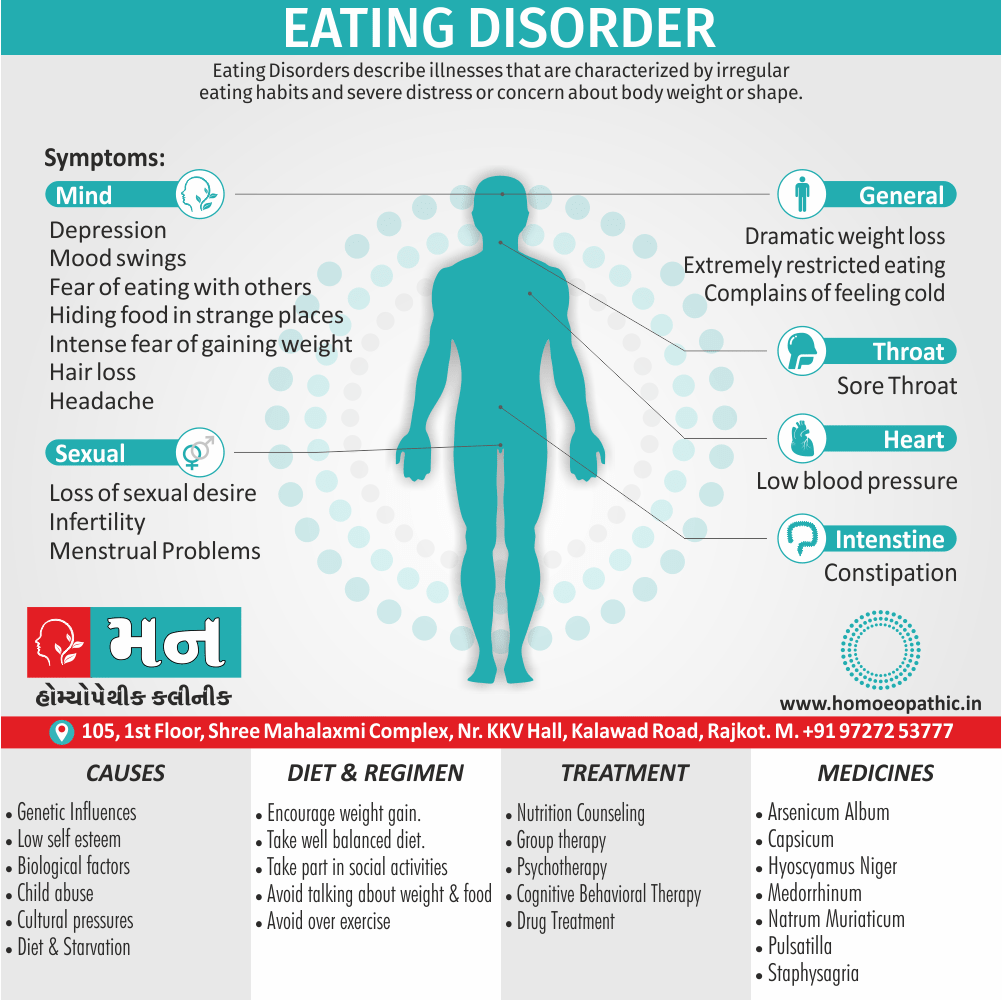
1. Fetishism:
- In fetishism, the sexual arousal occurs either solely or predominantly with a nonliving object, which is usually intimately associate with the human body.
- In this condition, an inanimate object is the prefer or only means of achieving sexual excitement. Additionally, Almost all fetishists are men and most are heterosexual.
- The word fetish means magical, i.e. the nonliving object ‘magically’ becomes phallic for that person.
- Fetishism is not diagnose if the sexual object is the wearing of clothes of opposite sex (in other words; fetishistic transvestism), the use of a human body part (masturbation), or the use of a genital-stimulating object (e.g. vibrator). [2]
- Among the many objects that can evoke arousal in different people, For example; rubber garments, women’s underclothes, also high-heeled shoes.
- Besides this; The smell and texture of these objects is often as important as their appearance in evoking sexual arousal. Some fetishists buy the objects, but others steal them and so come to the notice of the police.
- Lastly; Sometimes the behaviour is carry out with either a willing partner or with a paid prostitute, but often it is a solitary accompaniment of masturbation. [1]
2. Fetishistic Transvestism:
- The person actually or in fantasy wears clothes of the opposite sex (in other words; cross-dressing) for sexual arousal.
- Furthermore; This disorder occurs exclusively in heterosexual males.
- This disorder should differentiate from dual-role transvestism and trans exualism.
- In detail; It may be associated with fantasies of other males approaching the person who is in a female dress.
- Masturbation or rarely coitus is associated with cross-dressing to achieve orgasm.
- To be call a disorder, this should be a persistent and significant mode of sexual arousal in the person. [2]
- Crossdressing nearly always begins after puberty.
- All in all, At first, the clothes are worn only in private; a few people, however, go on to wear the clothes in public, usually hidden under male outer garments, but occasionally without precautions against discovery. [1]
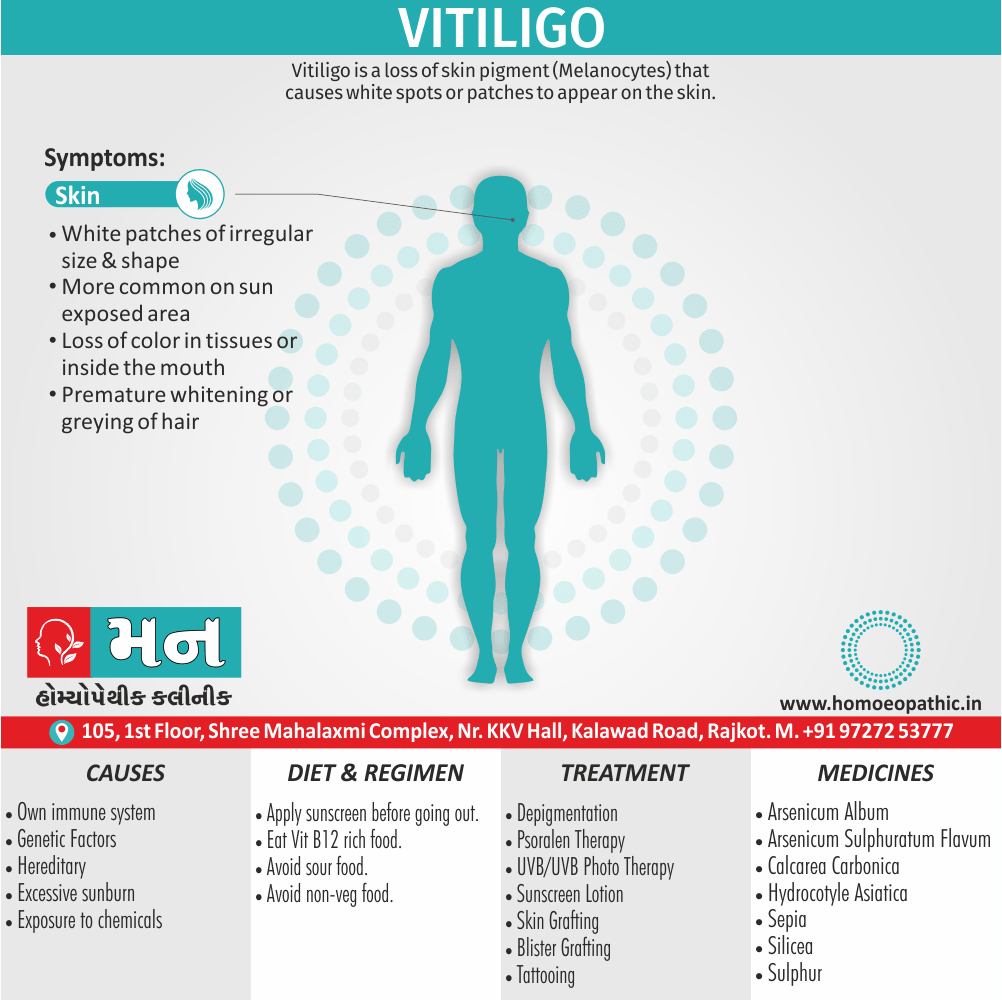
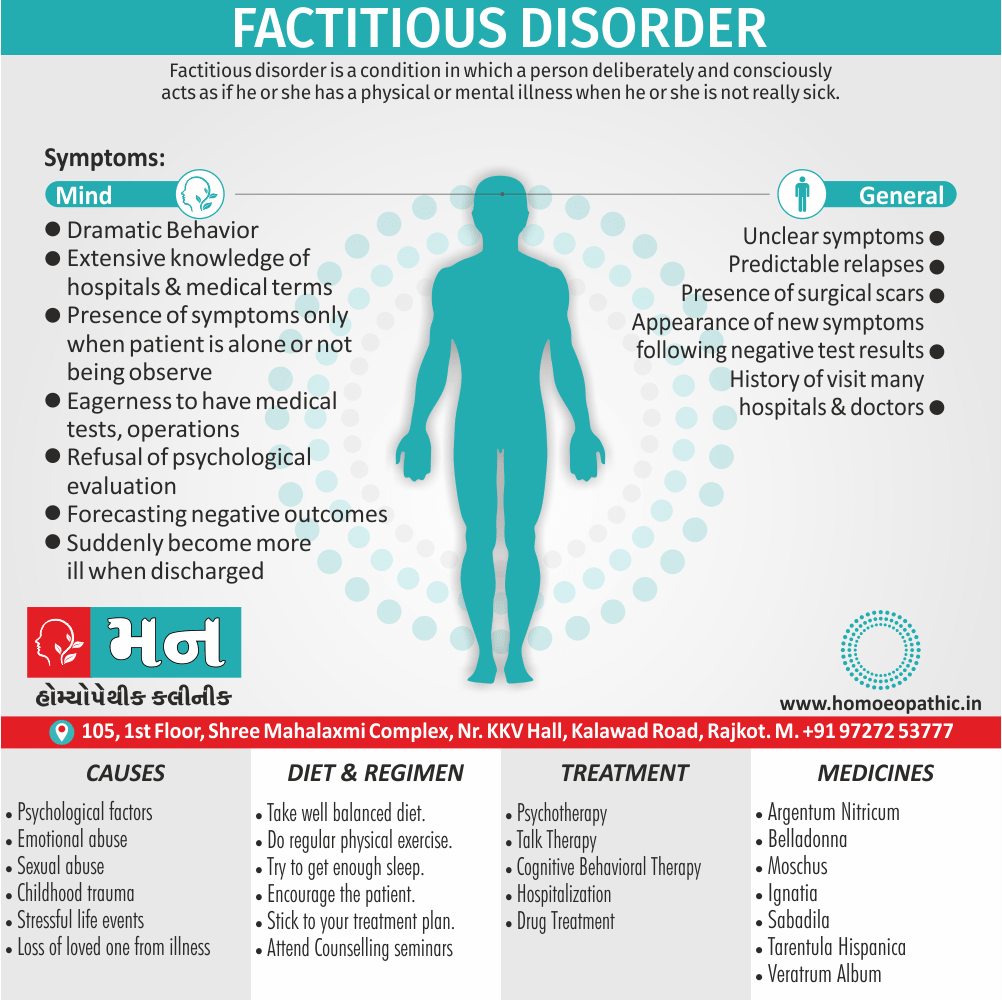
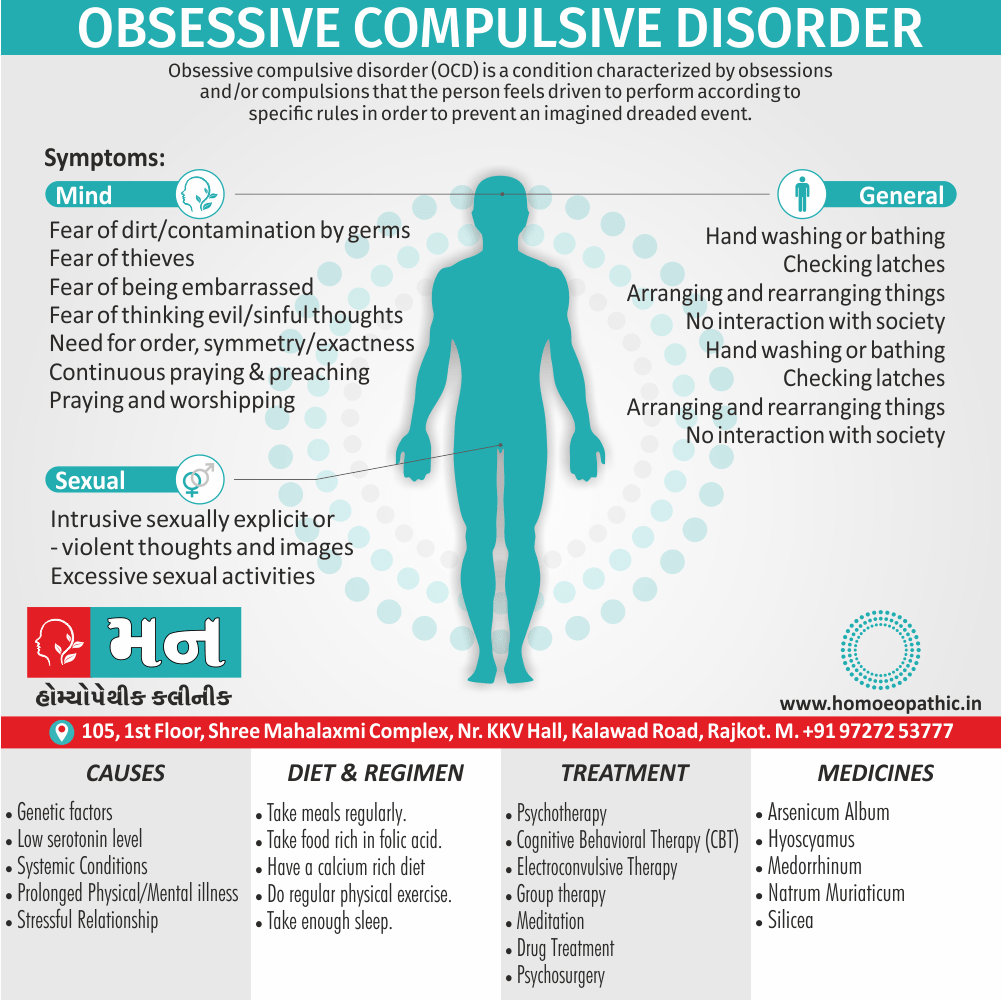
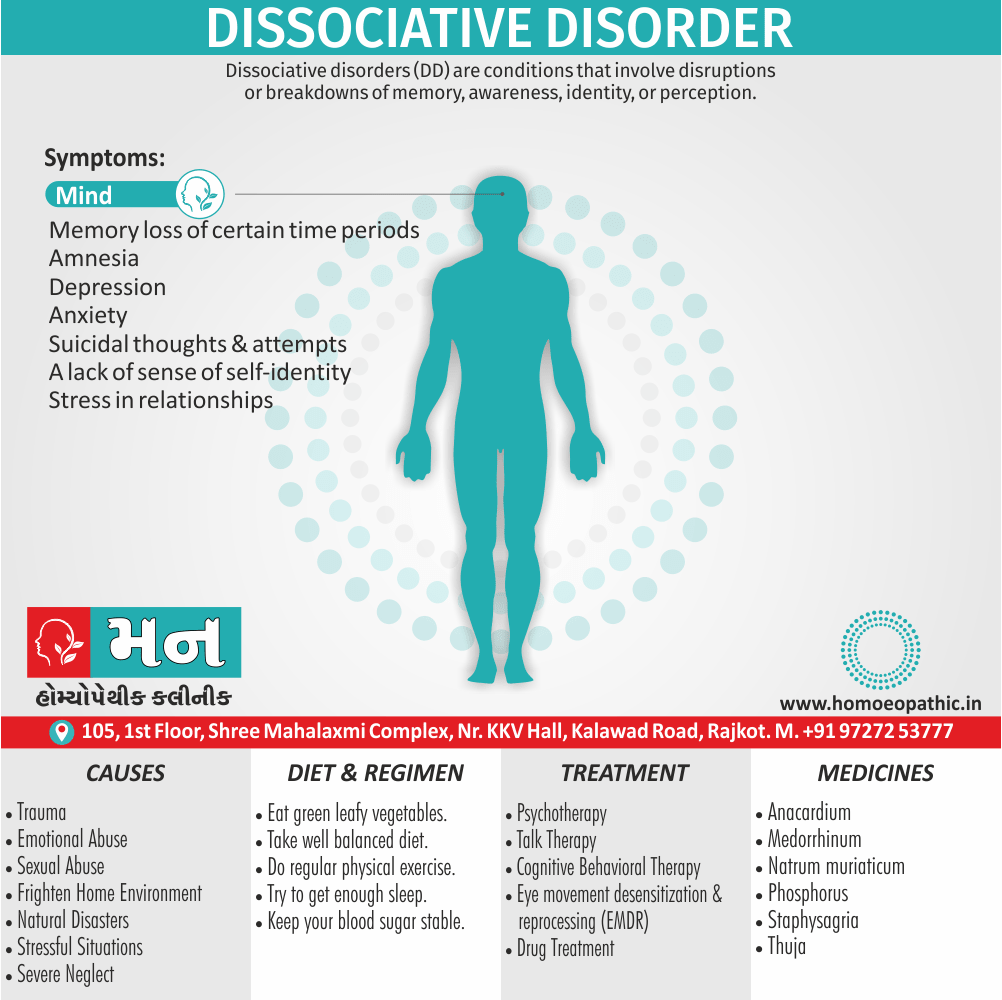
3. Paedophilia:
- Paedophilia is a persistent or recurrent involvement of an adult (age >16 years and at least 5 years older than the child) in sexual activity with prepubertal children, either heterosexual or homosexual.
- This may associate with sexual sadism.
- The paedophilic behaviour may either limited to incest or may spread to children outside the family.
- In most civilised societies, paedophilia is a serious offense also the convicted paedophile’s name remains on a sex offenders register in order to protect the society. [2]
- The sexual contact may involve fondling, masturbation, or full coitus with consequent injury to the child. [1]
The second group of disorders of sexual preference involves variations in the behaviour carried out to obtain sexual arousal.
Generally, the acts are direct towards other adults but sometimes towards children (e.g. by some exhibitionists or sadists).
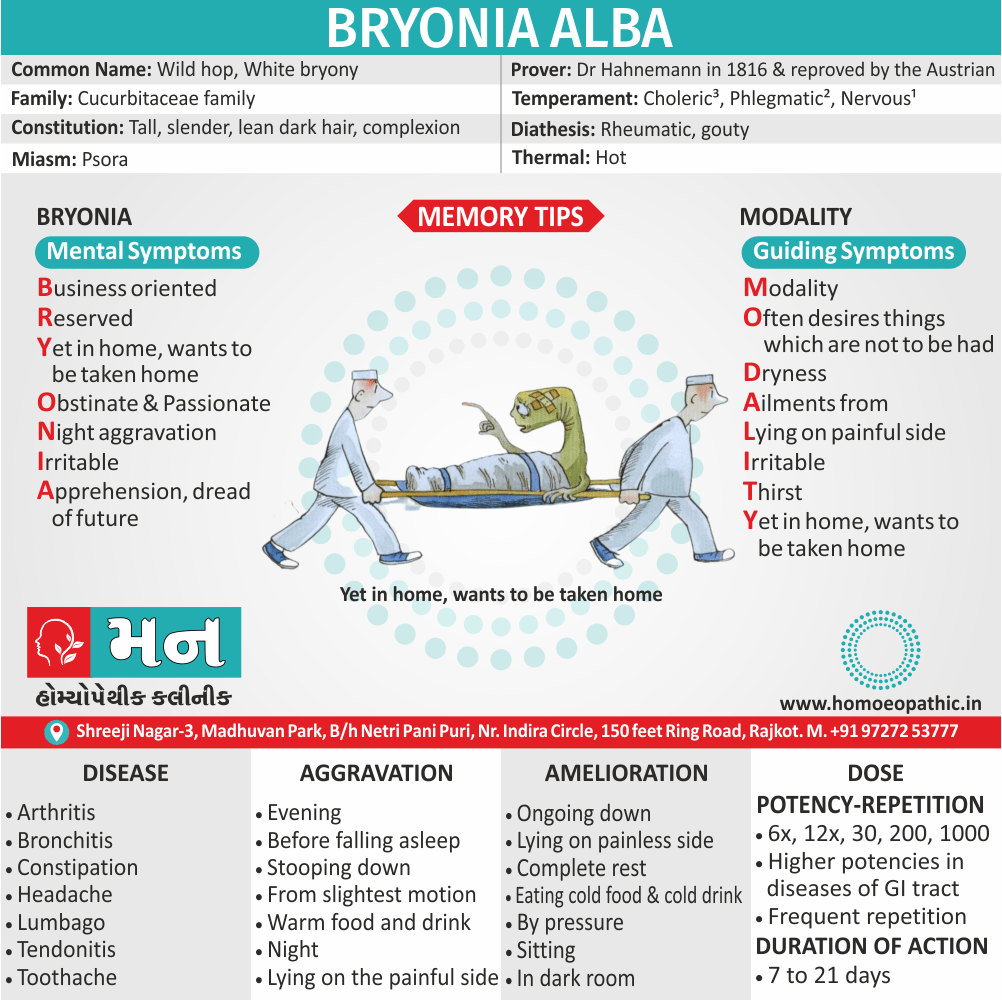
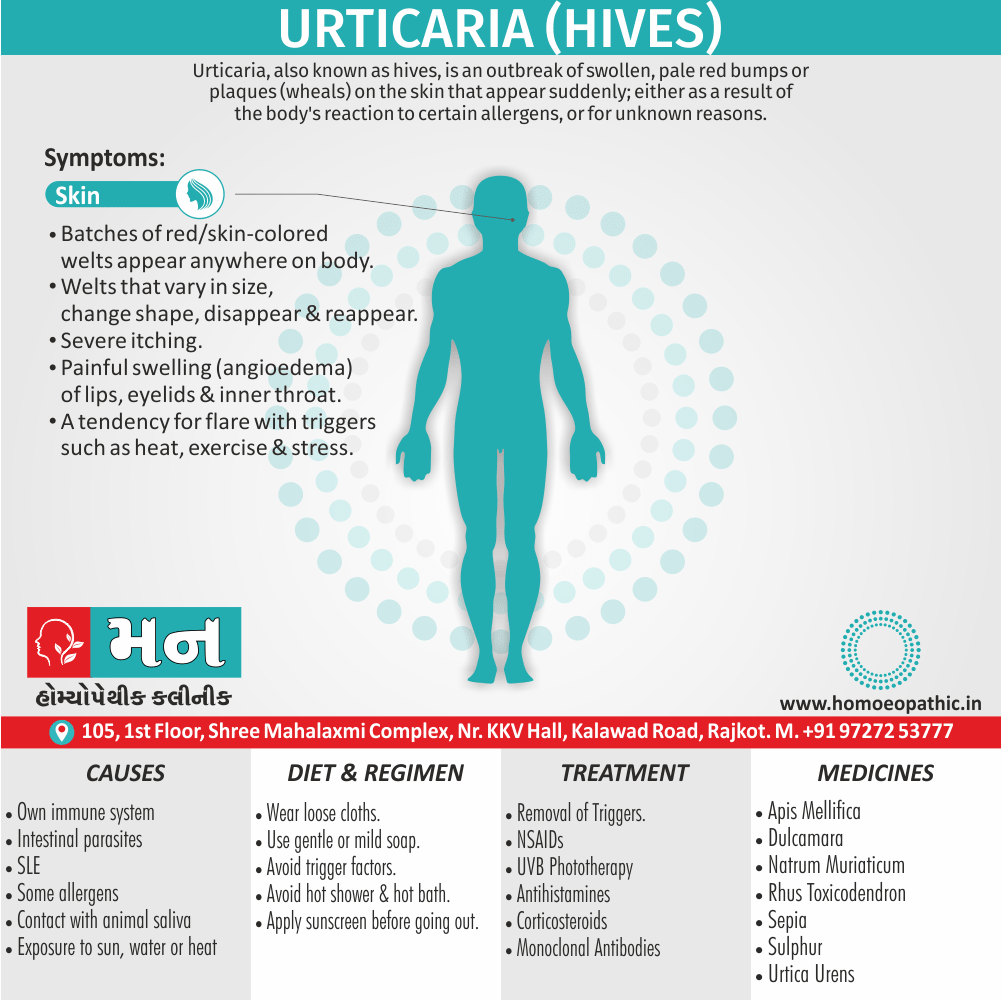
1. Exhibitionism:
- Exhibitionism is a persistent (or recurrent) and significant method of sexual arousal by the exposure of one’s genitalia to an unsuspecting stranger.
- This is often follow by masturbation to achieve orgasm. The disorder is almost exclusively see in males, and the ‘unsuspecting stranger’ is usually a female (child or adult). [2]
- The act of exposure is usually preceded by a period of mounting tension which is released by the act. Usually, the exhibitionist seeks to shock or surprise a female.
Most exhibitionists fall into two groups:
- The first consists of men with inhibited temperament who generally expose a flaccid penis also feel much guilt after the act.
- The second consists of men with aggressive personality traits who expose an erect penis while masturbating, also feel little guilt afterwards.
When exhibitionism begins in middle or late life the possibility of organic brain disorder, depressive disorder, or alcoholism should be considered since these conditions occasionally ‘release’ this pattern of behaviour.
In other people, the exhibitionism may start during a period of temporary stress.
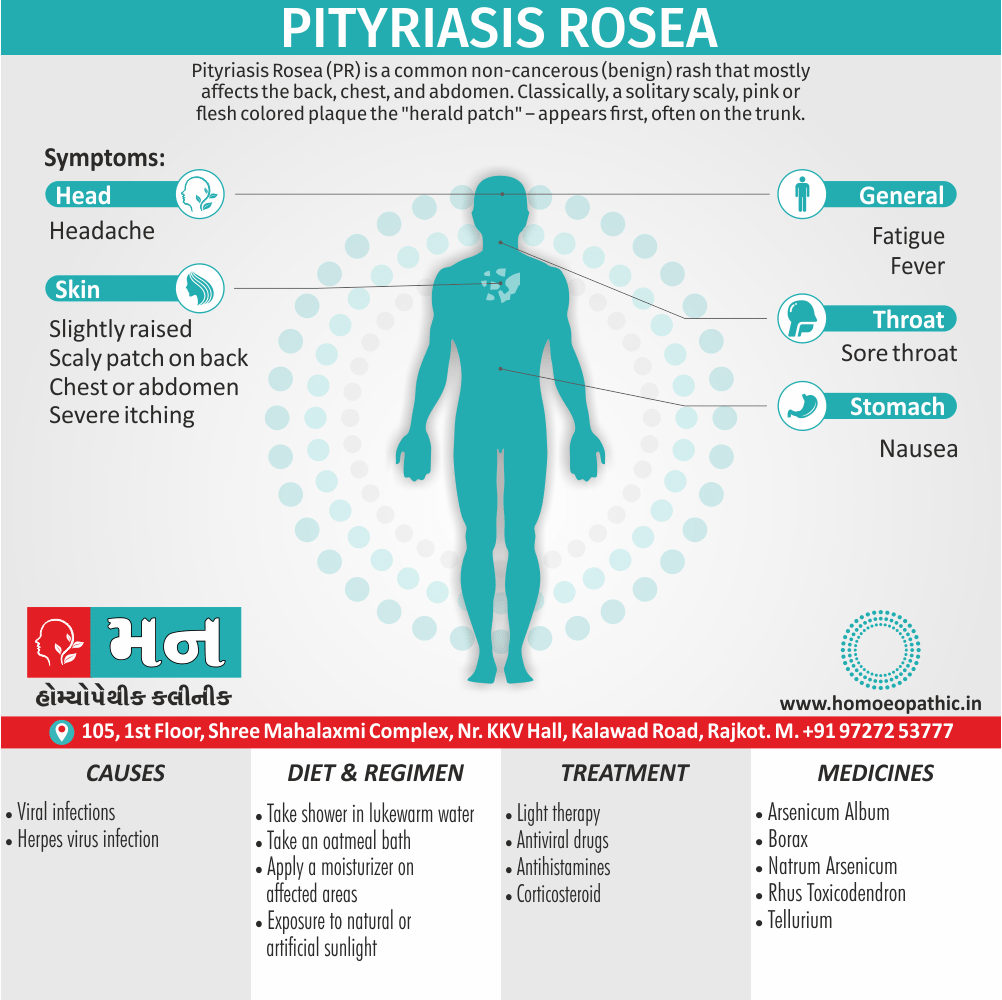
2. Voyeurism:
- This is a persistent or recurrent tendency to observe unsuspecting persons (usually of the other sex) naked, disrobing or engaged in sexual activity. [2]
- Most voyeurs are inhibit heterosexual men. Some voyeurs spy on couples who are having intercourse, others on women who are undressing or naked.
- This is often follow by masturbation to achieve orgasm without the observed person(s) being aware. [1]
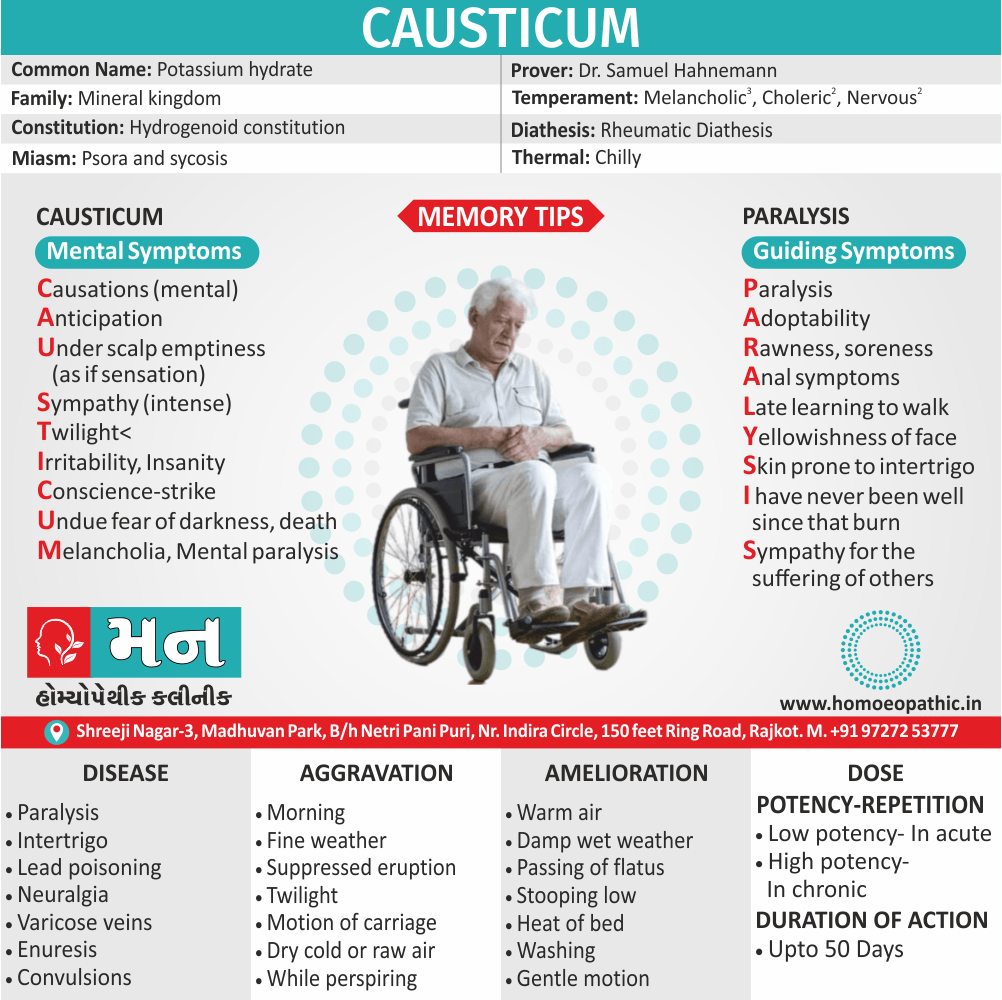
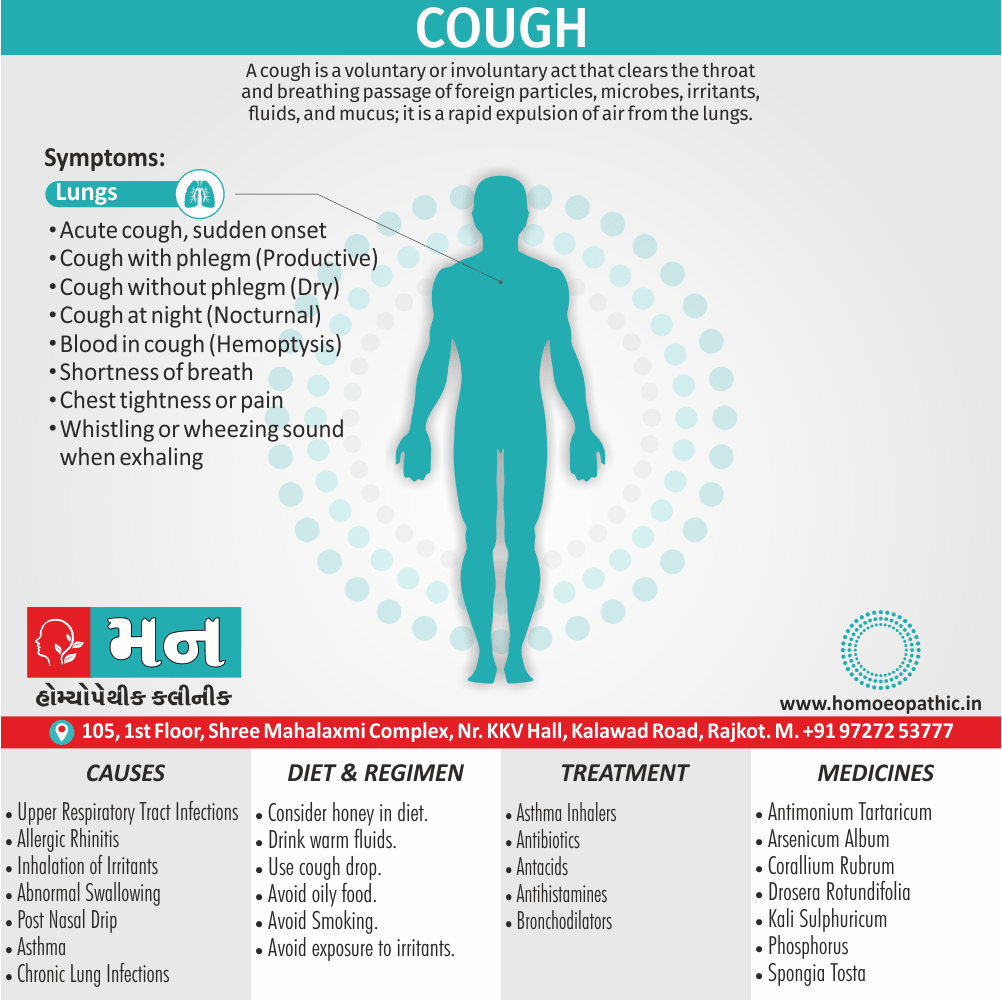
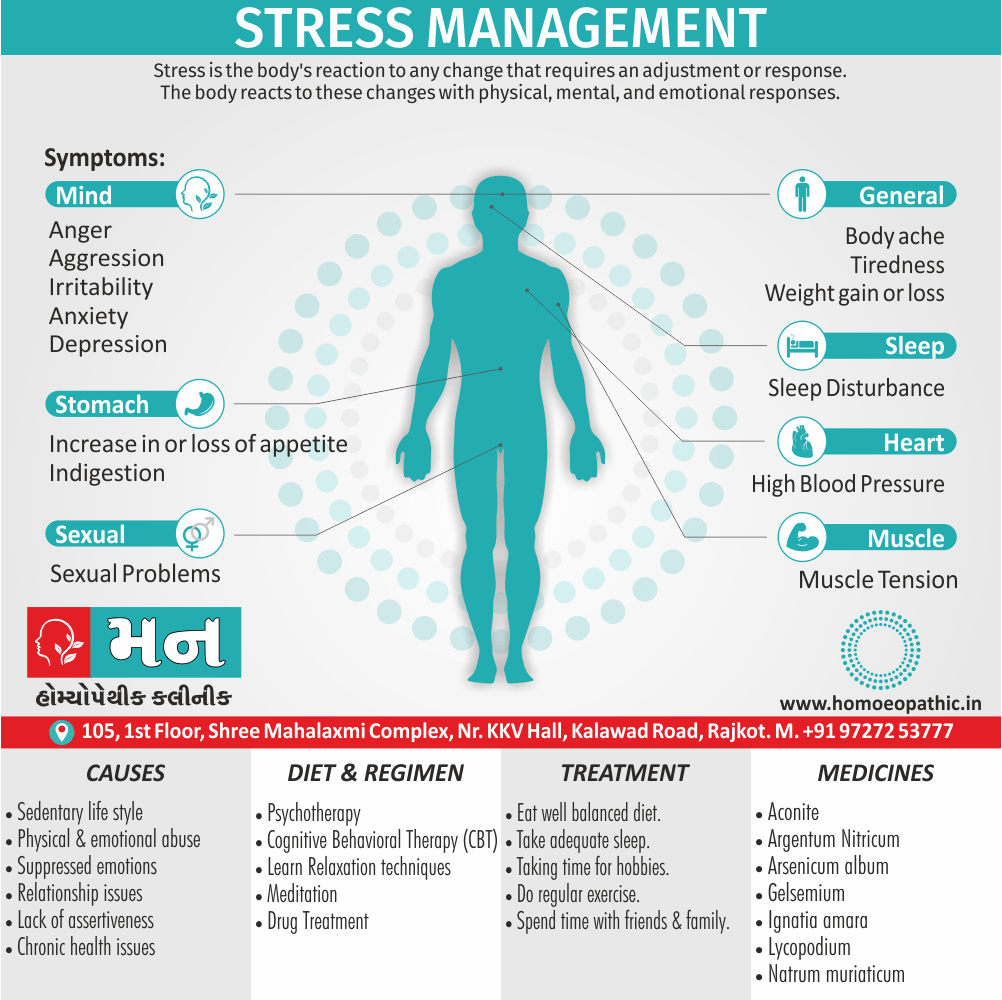
3. Sexual Sadism:
- In this disorder, the person (i.e. the ‘sadist’) is sexually arouse by physical and/or psychological humiliation, suffering or injury of the sexual partner (i.e. the ‘victim’).
- Most often the person inflicting the suffering is male, although this is not essential.
- The methods used range from restraining by tying, beating, burning, cutting, stabbing, to rape also even killing, but occasionally the acts cause serious injuries from which the partner may die. [2]
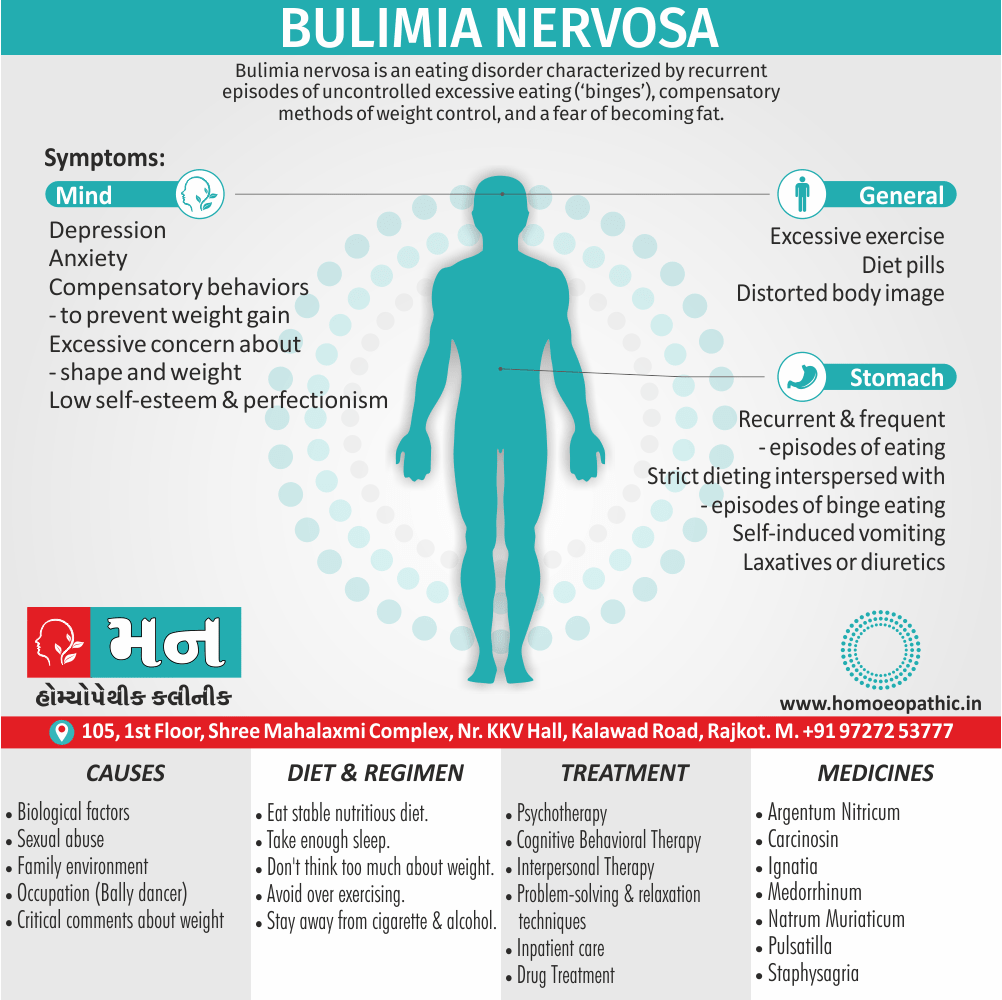
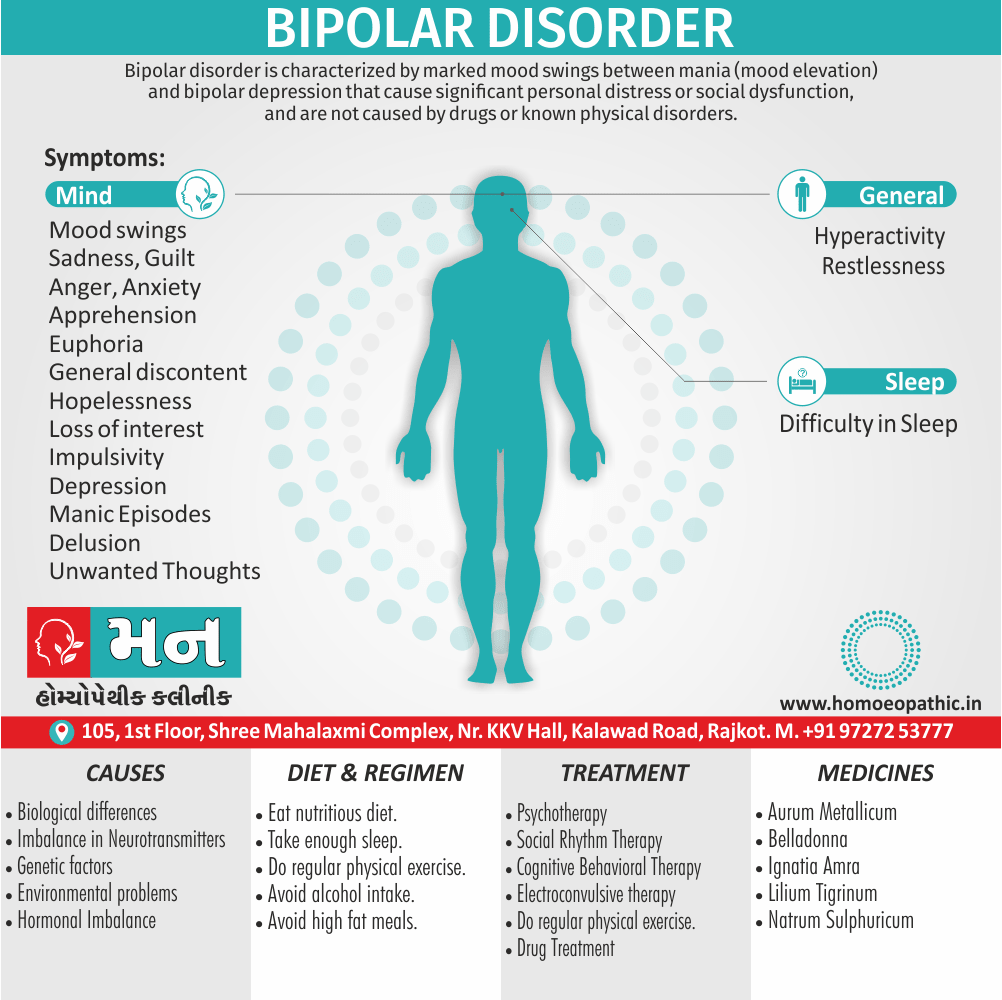
4.Sexual Masochism:
- Generally, This is just the reverse of sexual sadism.
- Here the person (the ‘masochist’) is sexually aroused by physical and/or psychological humiliation, suffering or injury inflicted on self by others (usually ‘sadists’).
- In detail; Most often the masochist is a female though any pattern is possible.
- The methods used are the same as the ones used in sexual sadism. Only there is a role reversal.
- To be called a disorder, this should be a persistent and significant mode of sexual arousal in the person. [2]
- Sexual sadism and sexual masochism are often seen in the same individual also are on a continuum; therefore they are classified together as sadomasochism in ICD-10.
- Besides this, Mild sadomasochistic behaviour is common and is considered to be part of the range of normal sexual activity.
- All in all; The disorder should be diagnosed only if sadomasochistic activity is the most important source of gratification or necessary for sexual stimulation. [1]
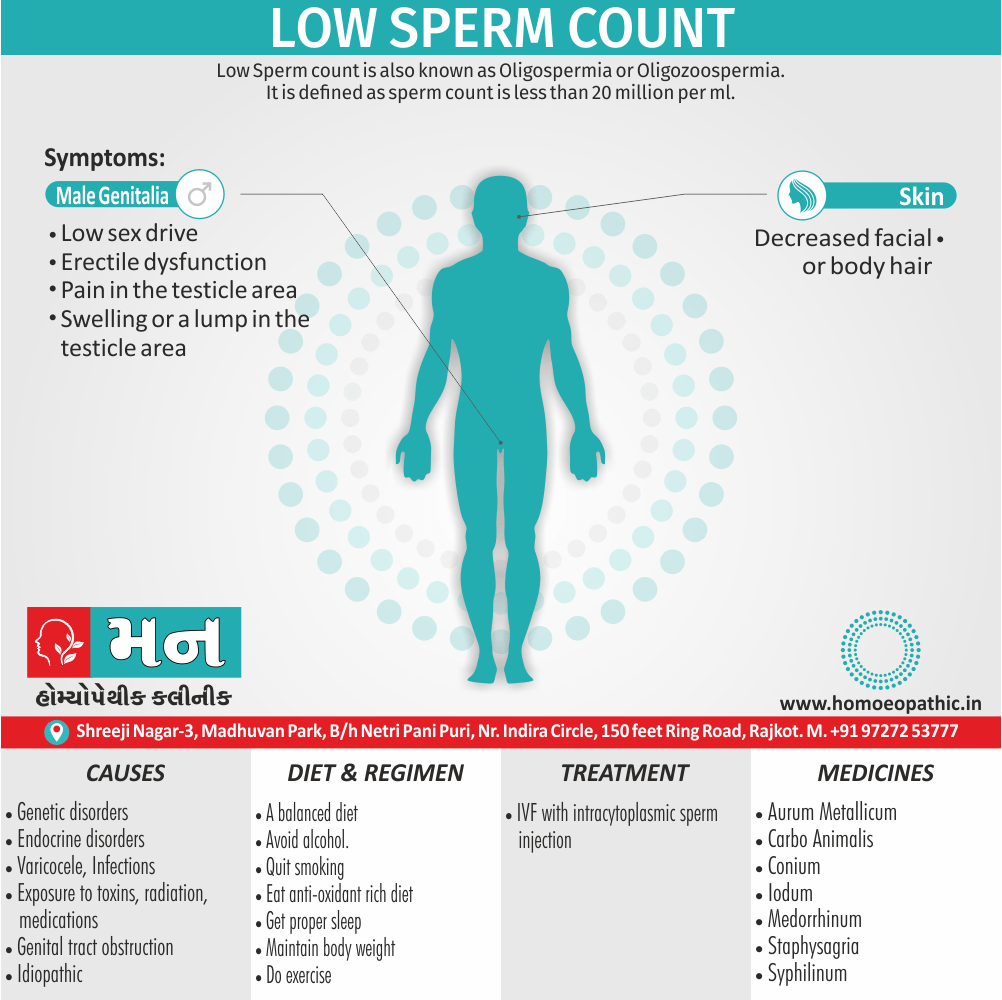
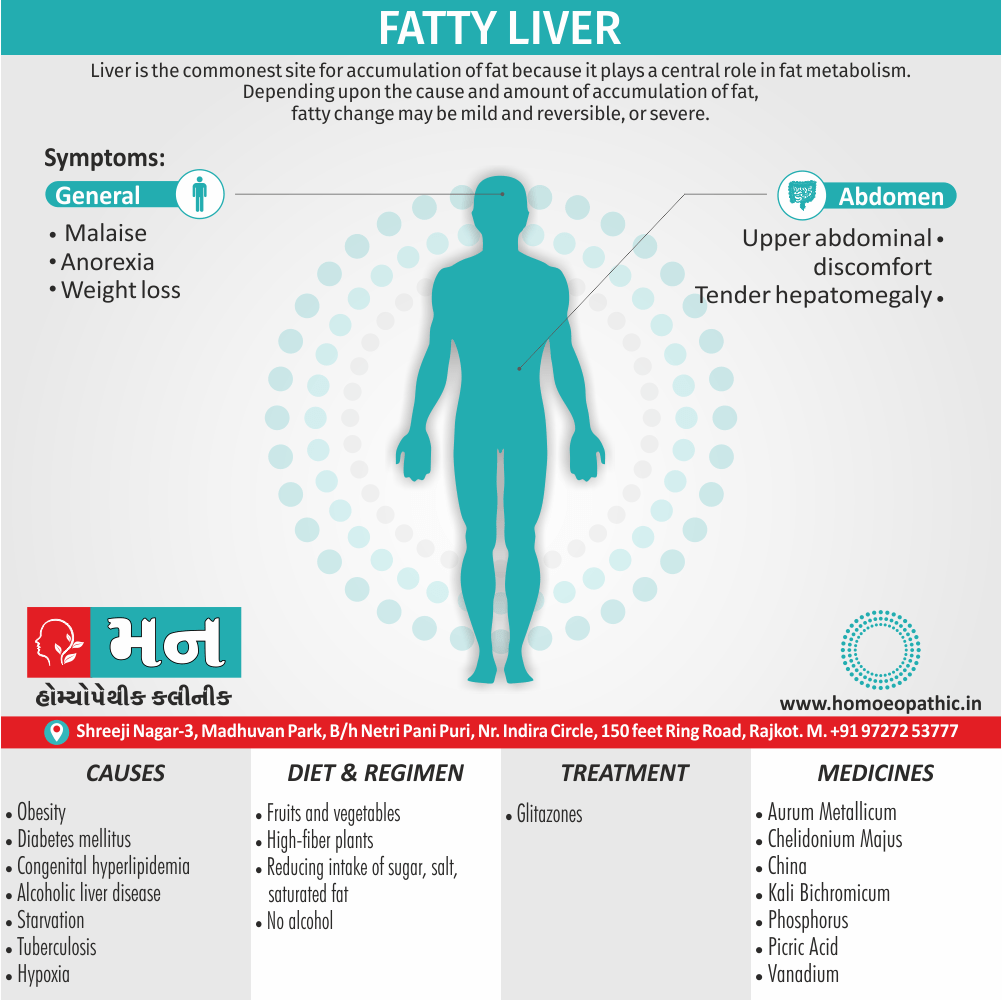
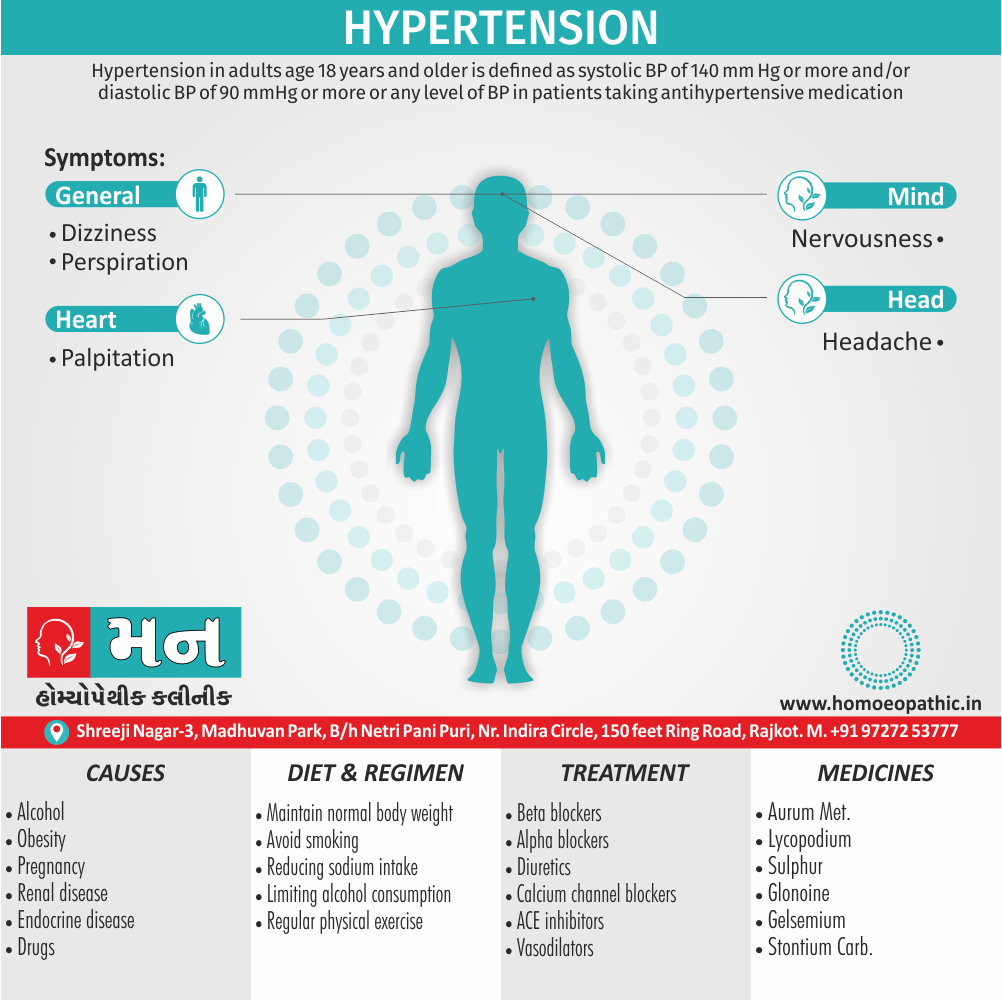
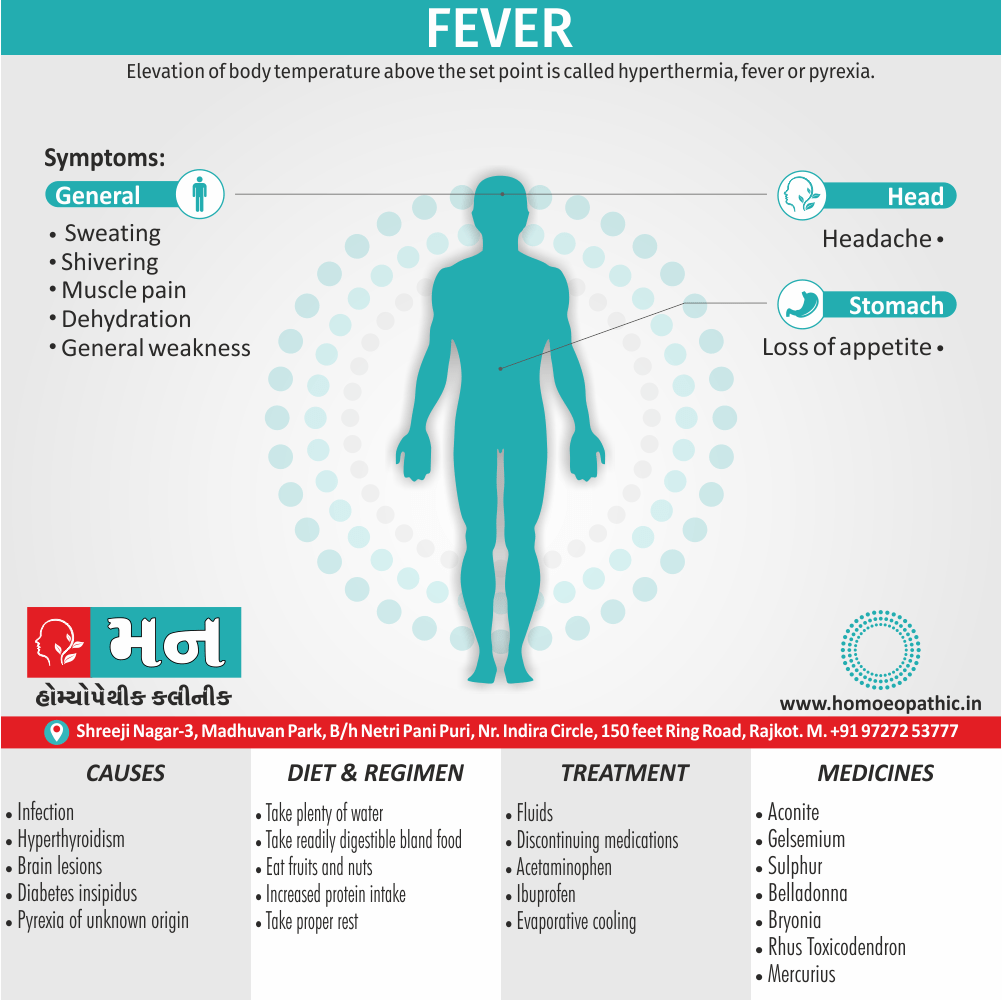
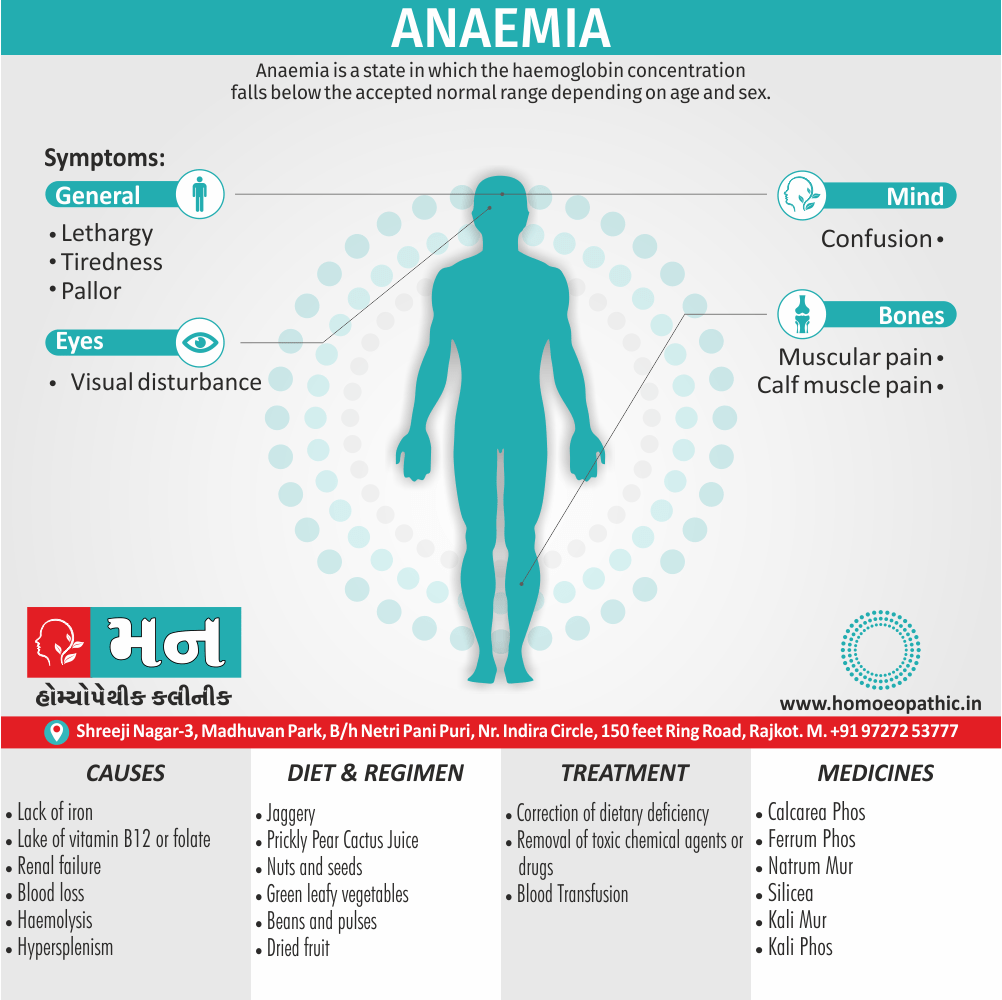
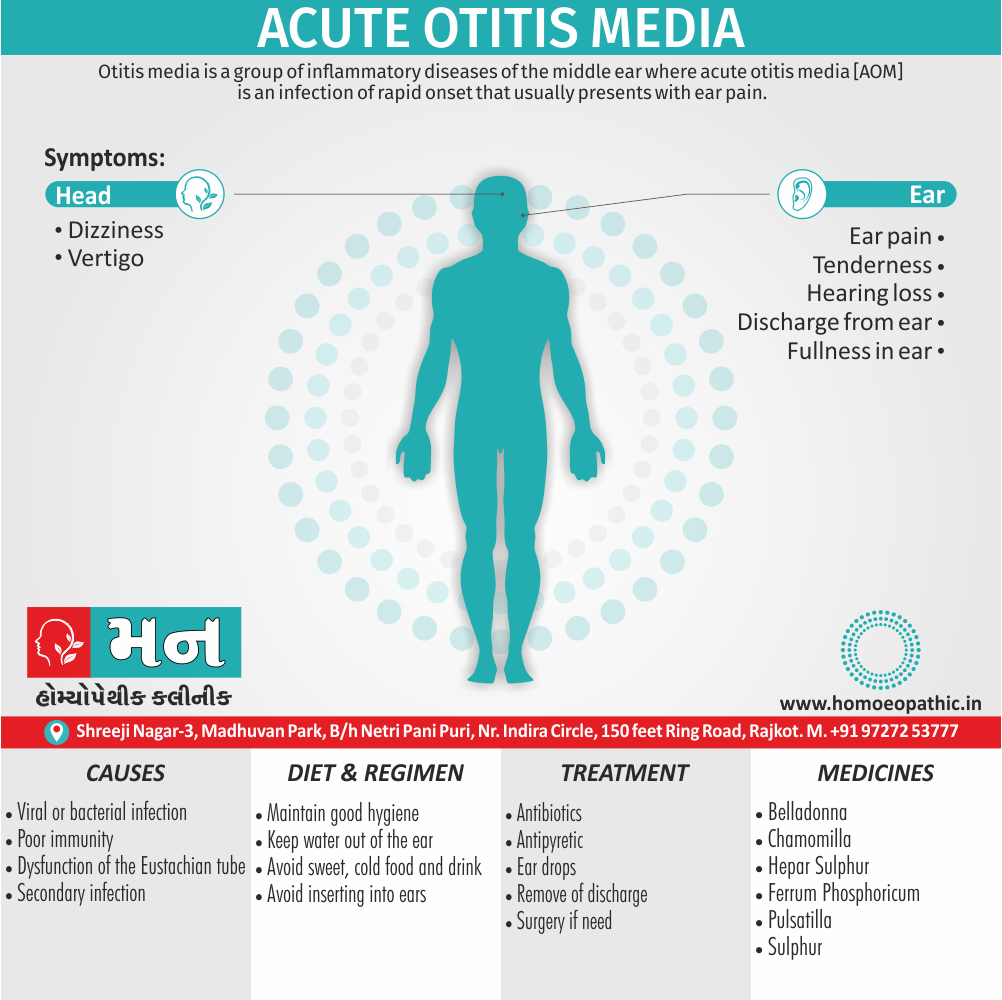
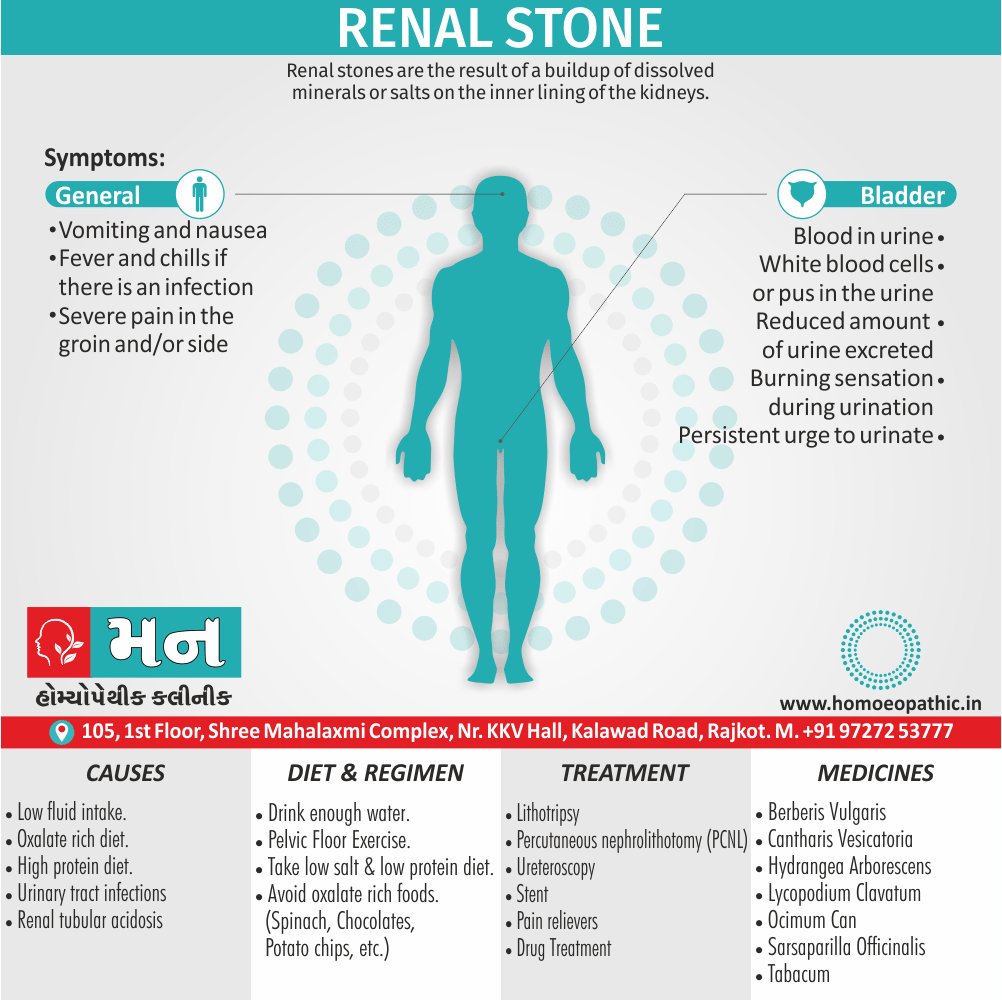
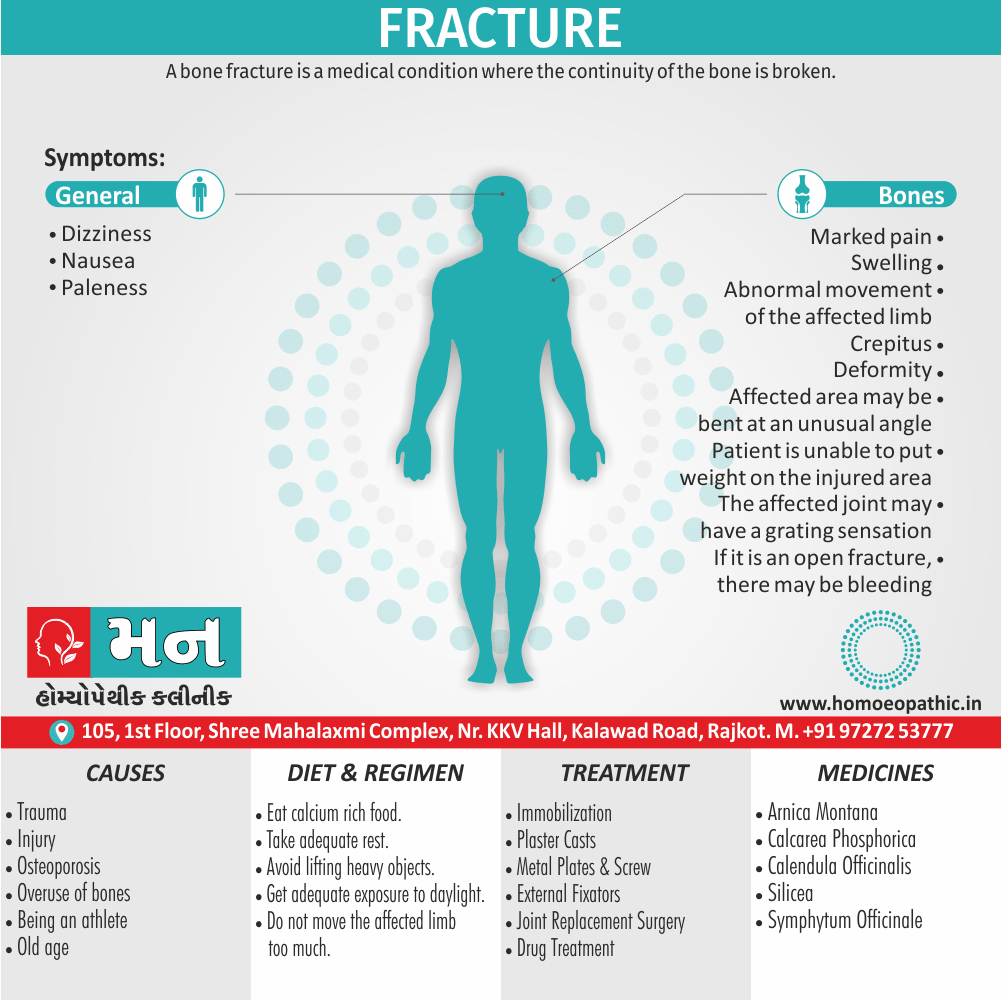
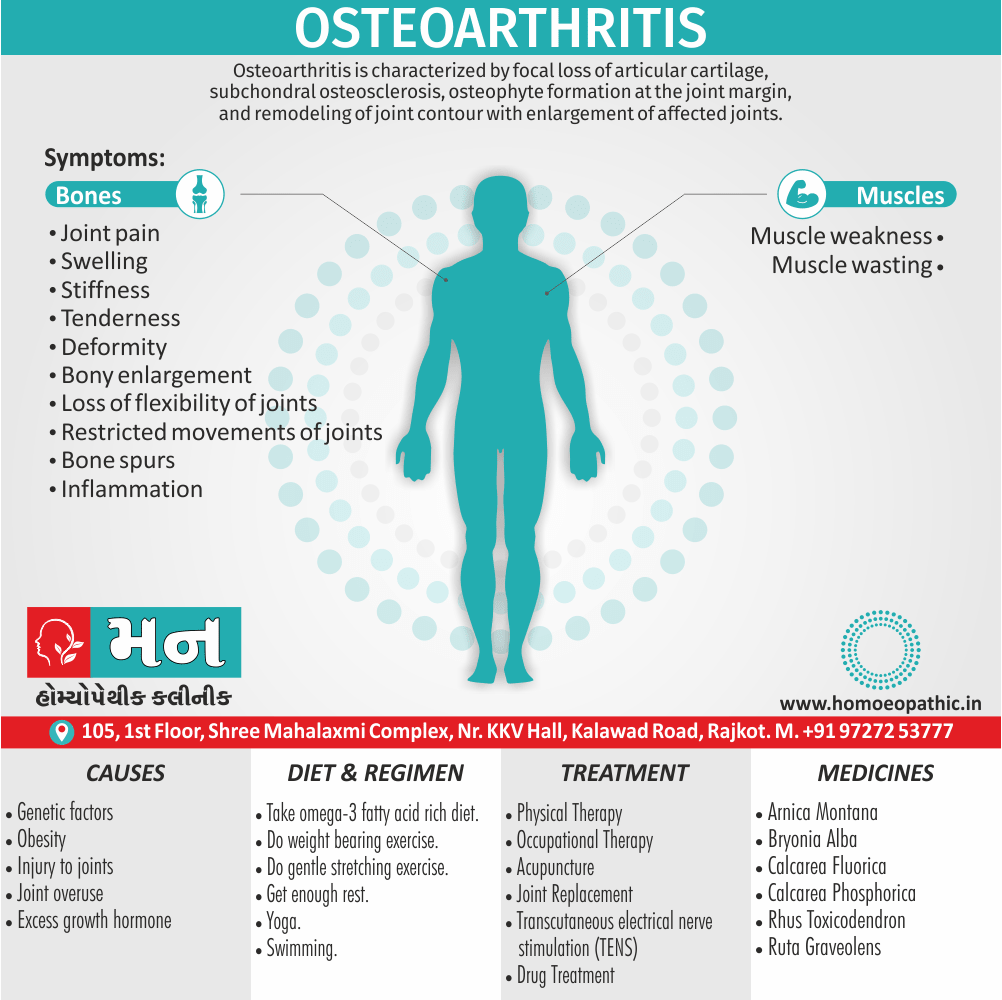
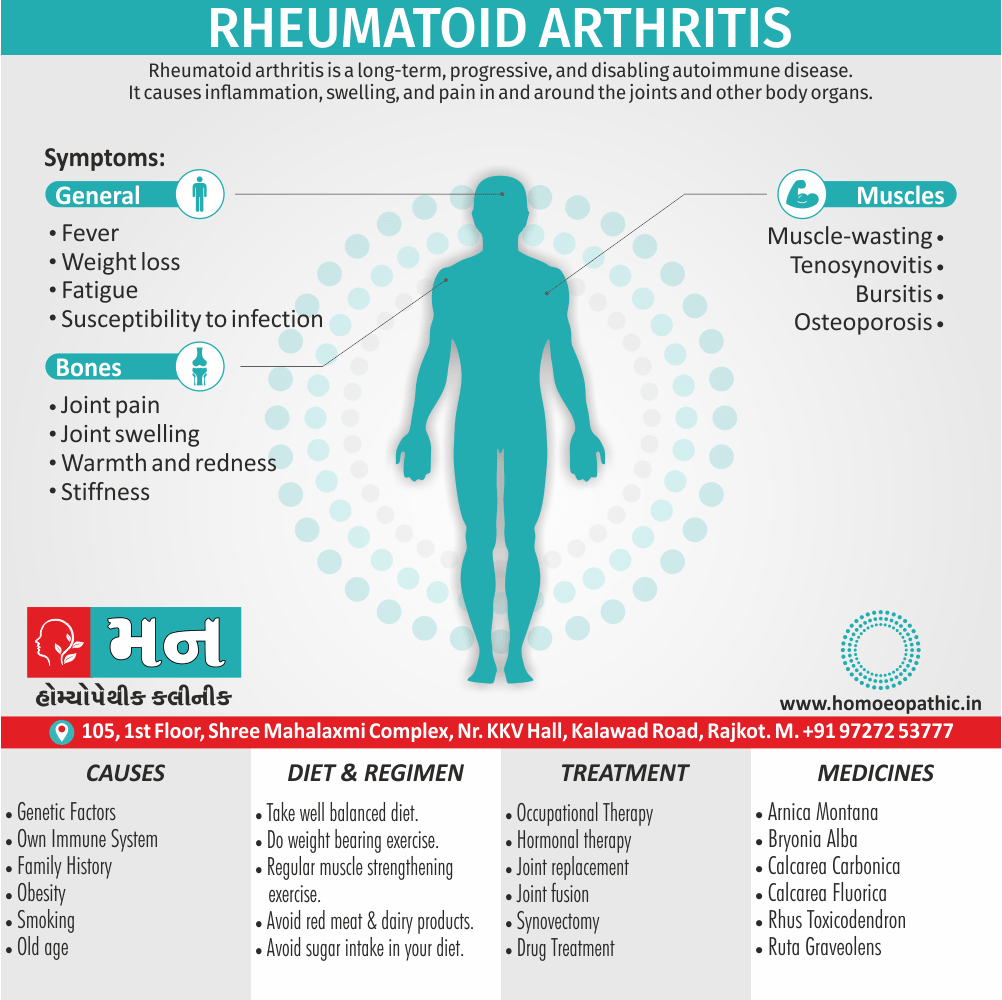
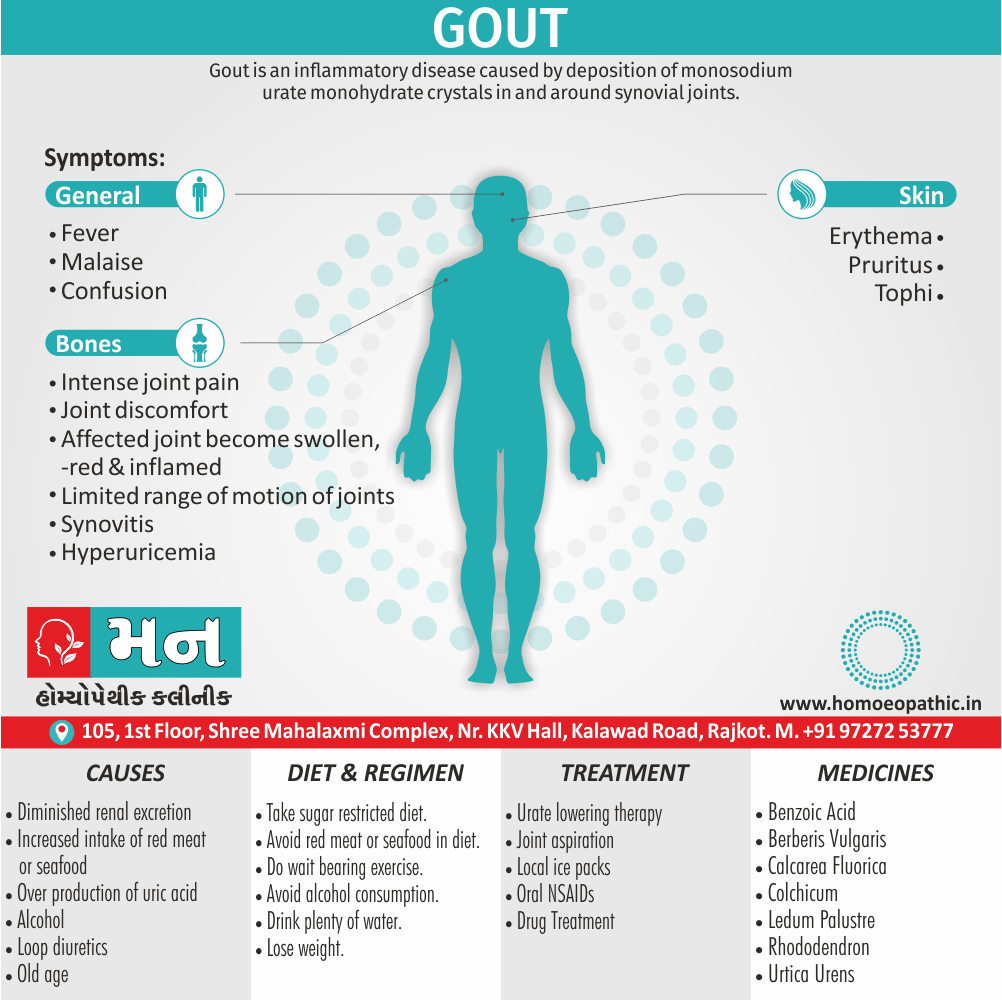
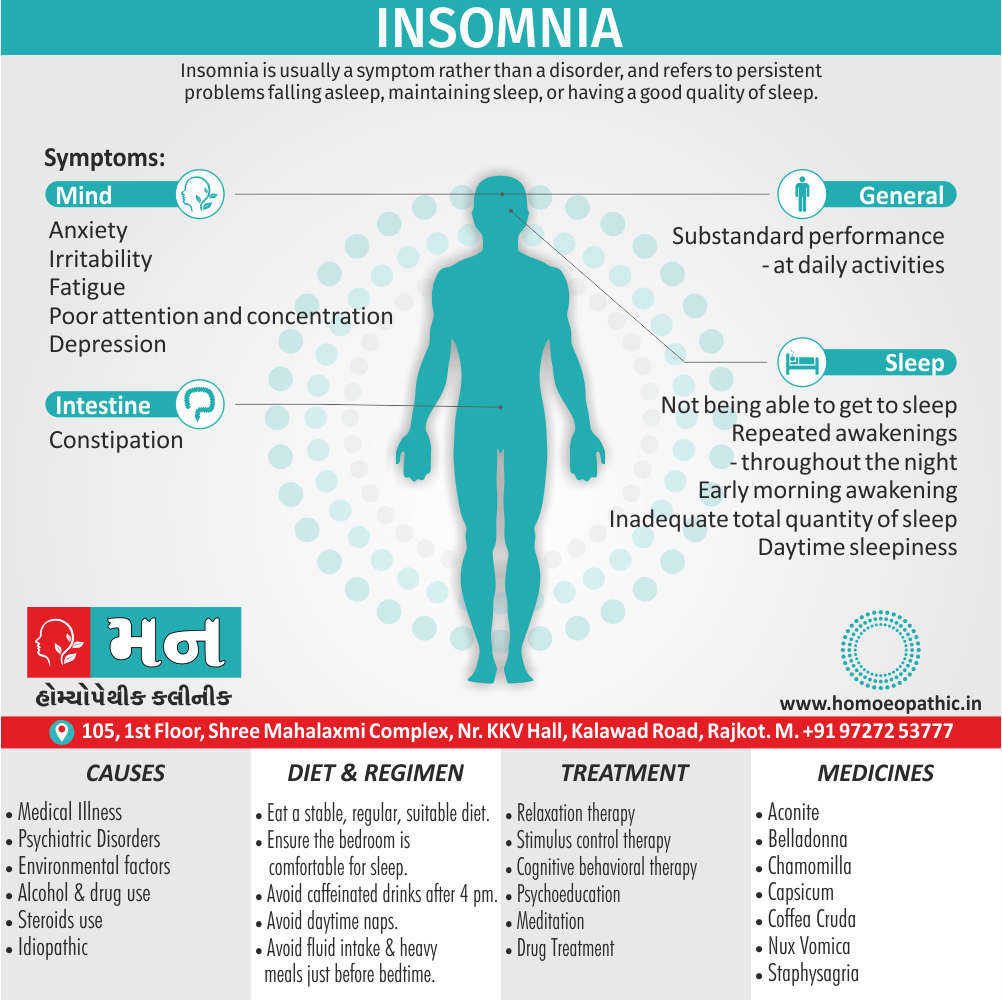
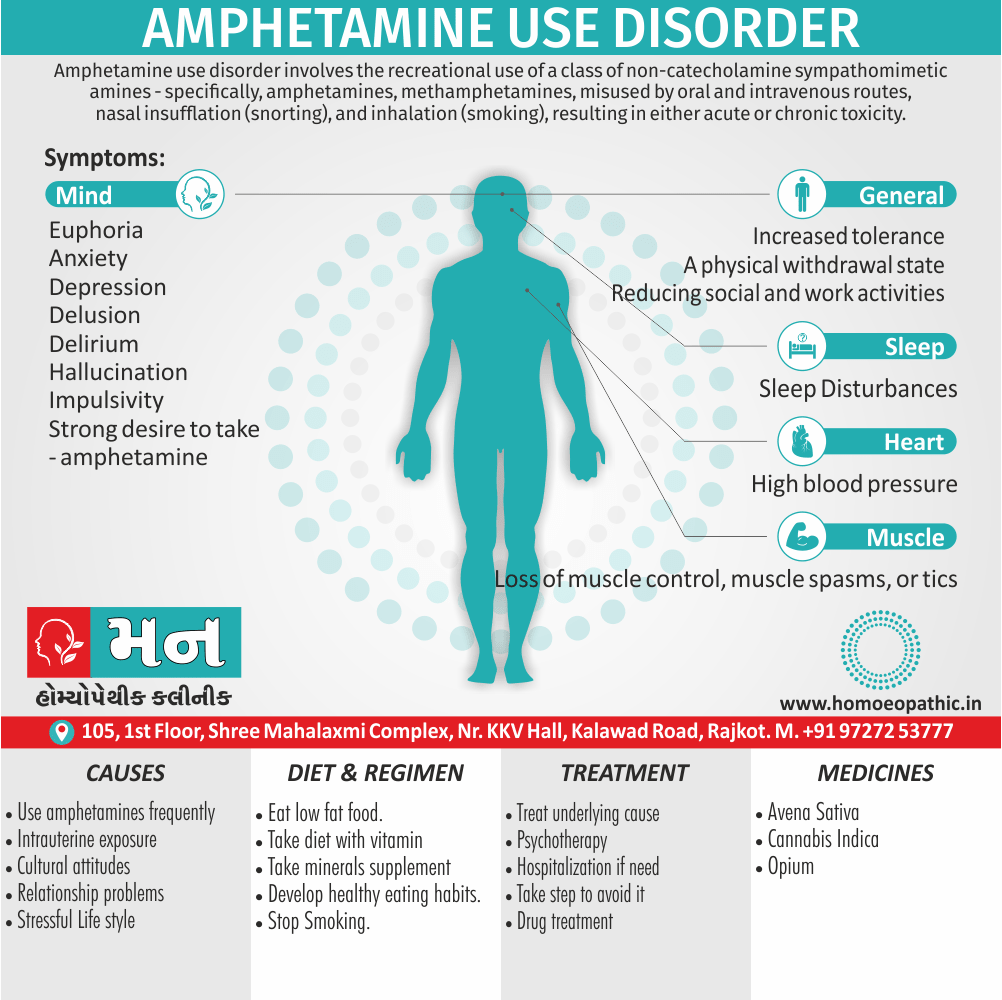
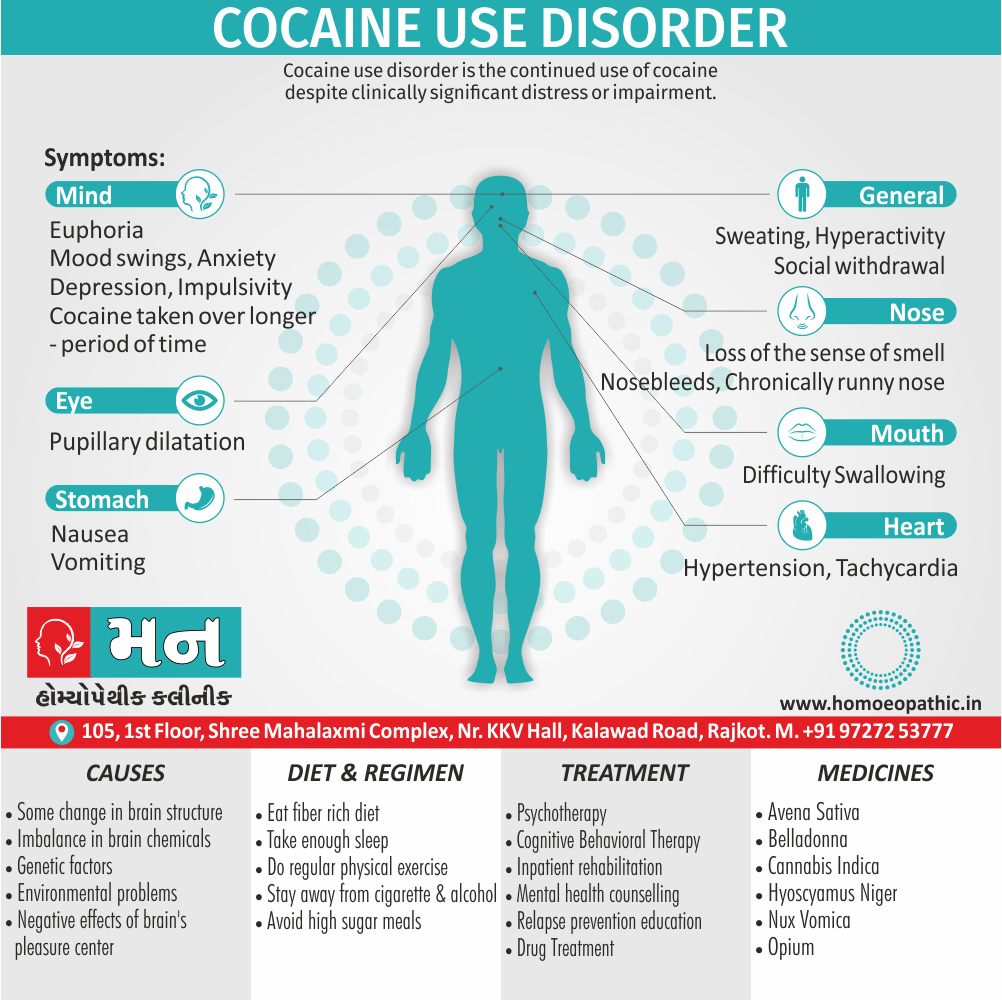
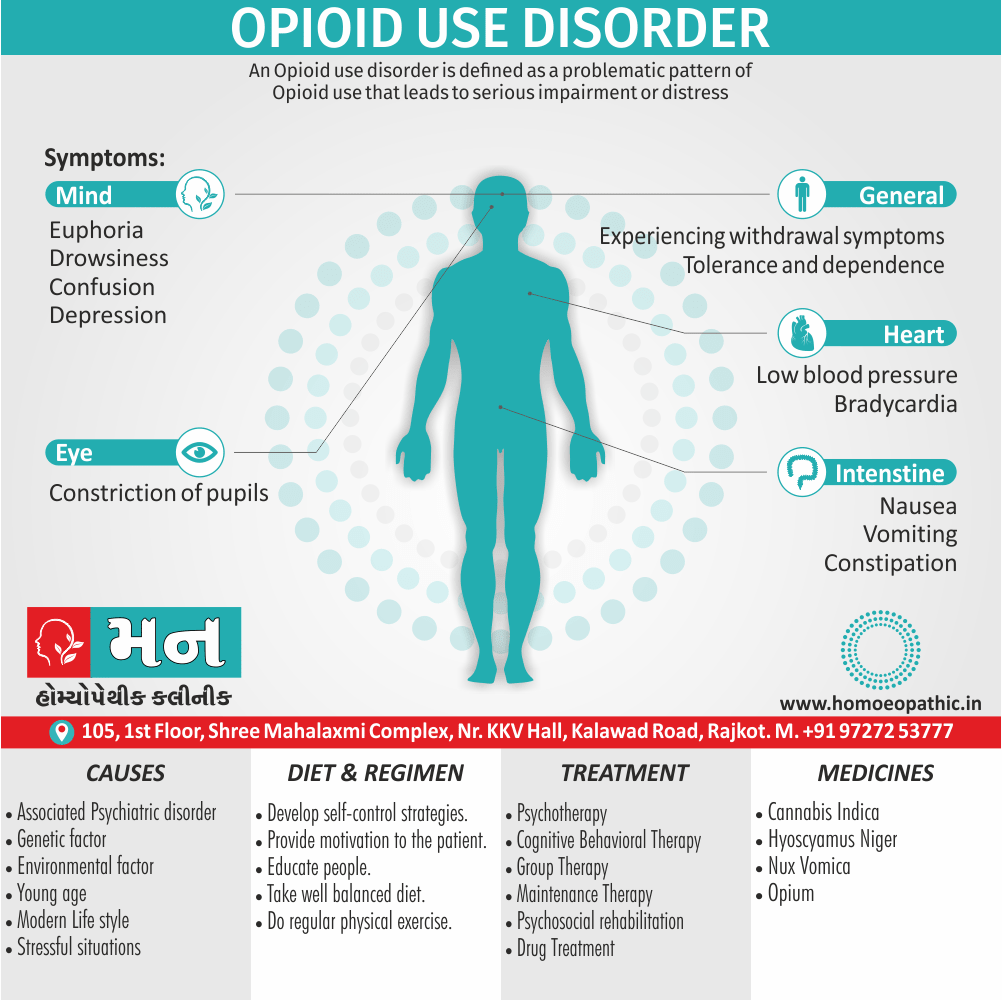
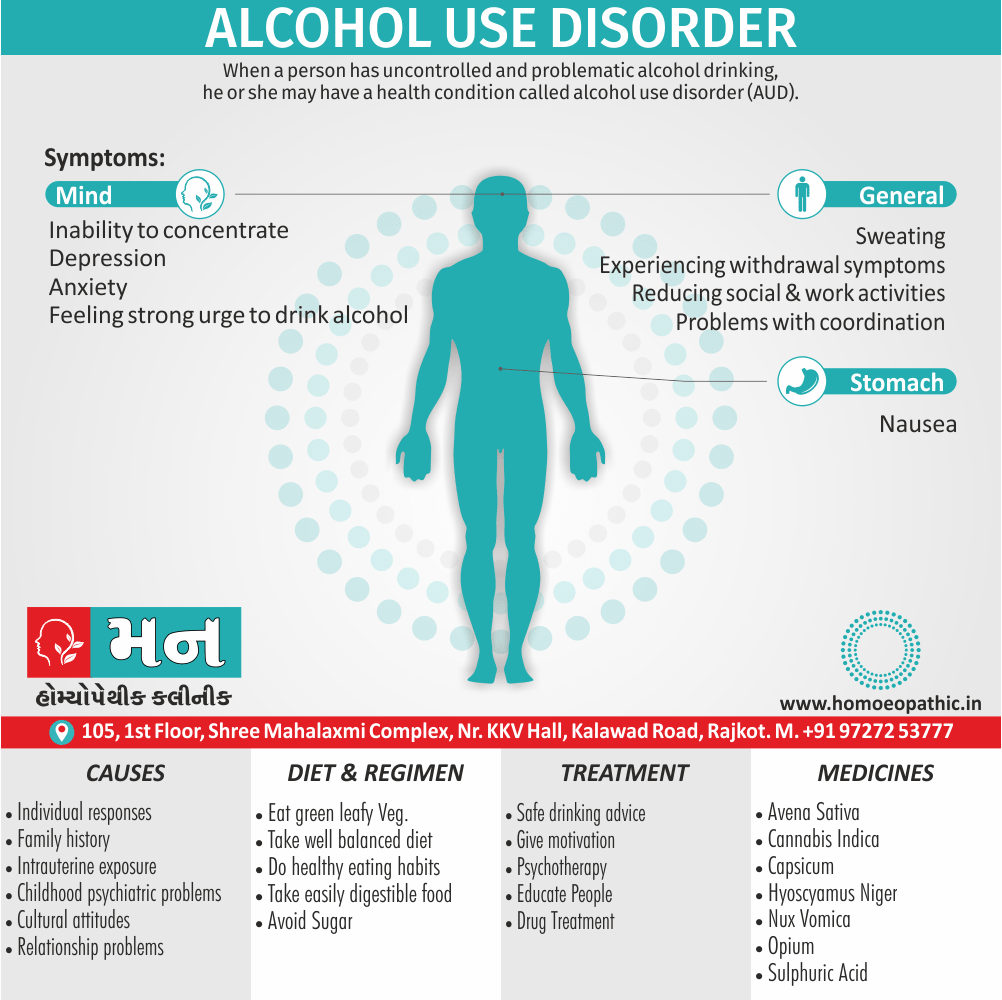
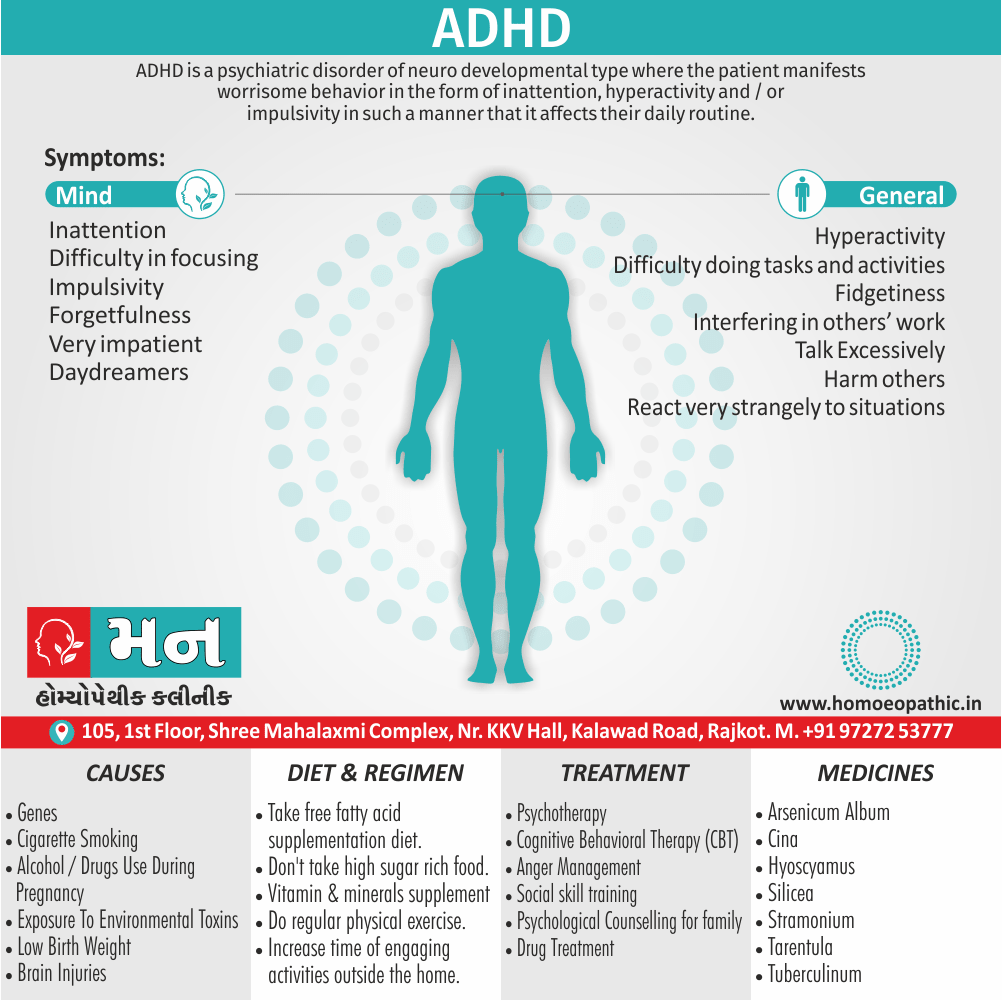
Causes of Disorders of Sexual Preference
Physical causes
- Many physical and / or medical conditions can cause problems with sexual function, these conditions include diabetes, heart and vascular (blood vessel) disease, neurological disorders, hormonal imbalances, chronic diseases such as kidney or liver failure, alcoholism, and drug abuse.
- Also, the side effects of some medications, including some antidepressants, can affect sexual function.
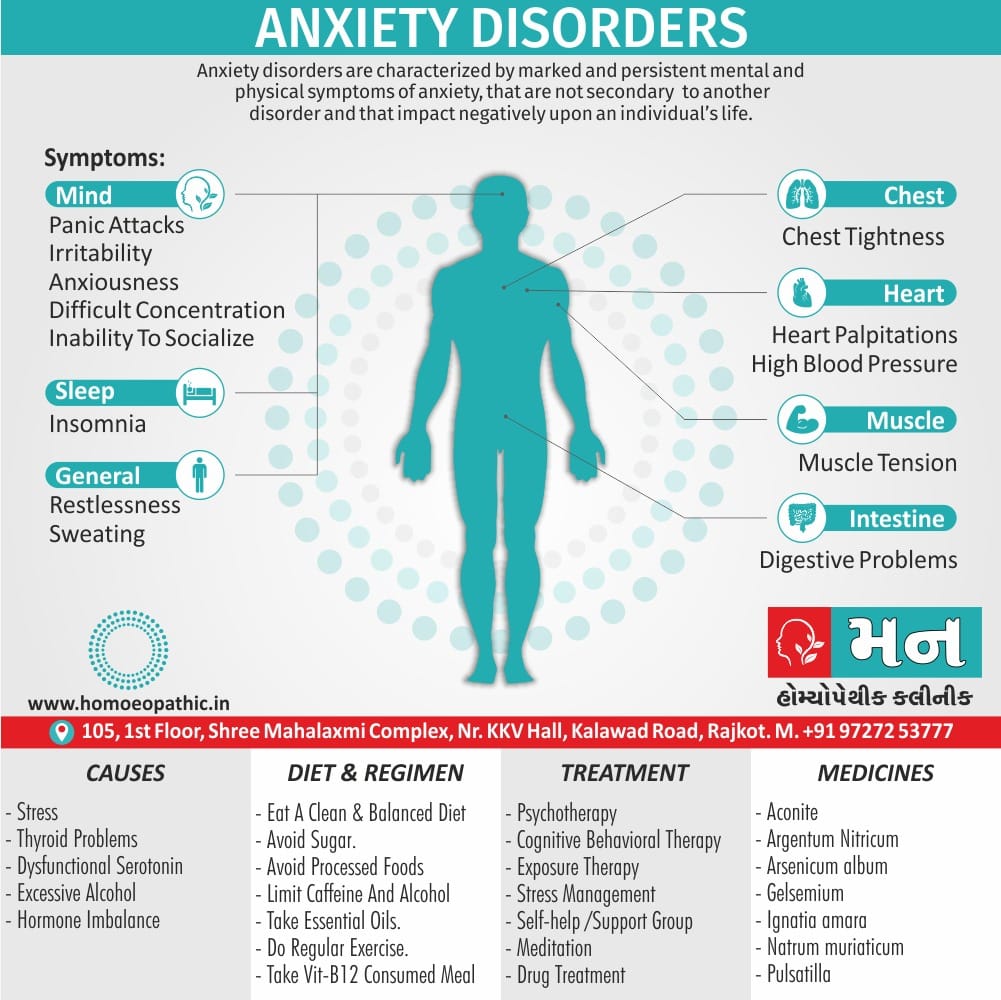
Psychological causes
- They include work-related stress and anxiety, concerns about sexual performance, marital or relationship problems, depression, feelings of guilt, concerns about body image, and the effects of past sexual trauma. (4)
Risk factors of Disorders of Sexual Preference
- Depression or anxiety
- Heart and blood vessel disease
- Neurological conditions, such as spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis
- Gynecological conditions, such as vulvovaginal atrophy, infections or lichen sclerosus
- Certain medications, such as antidepressants or high blood pressure medications
- Emotional or psychological stress, especially with regard to your relationship with your partner
- A history of sexual abuse (5)
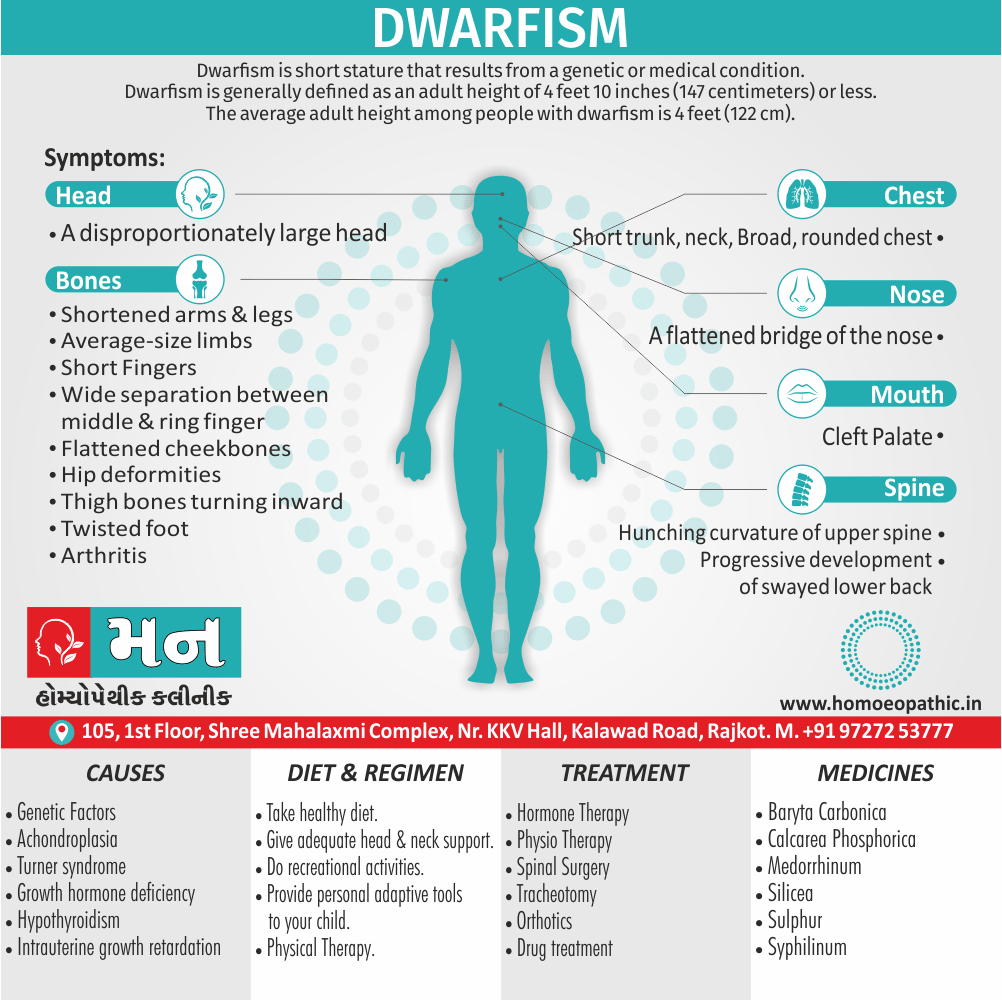
Pathophysiology of Disorders of Sexual Preference
- Disorders of sex development (DSD) are rare disorders occurring when there is a discordance between chromosomal, gonadal, or phenotypic sex.
- These occur in the presence of genetic mutations that affect one of the two major processes in sex development: sex determination or sex differentiation.
- In sex determination, the bipotential gonad is genetically programmed based on the sex chromosome complement to become either a testis or ovary.
- Sex differentiation occurs in the presence of a formed testis or ovary and is dependent upon the ability of the gonad to produce hormonal factors and/or the presence of the appropriate receptors in extragonadal tissues. (5)
Disorders of sexual preference are divide into i.e.:
1. Abnormalities of the sexual object:
- Sexual fetishism
- Transvestism
- Paedophilia
2. Abnormalities of the sexual act:
- Exhibitionism
- Voyeurism
- Sexual sadism
- Sexual masochism [1]
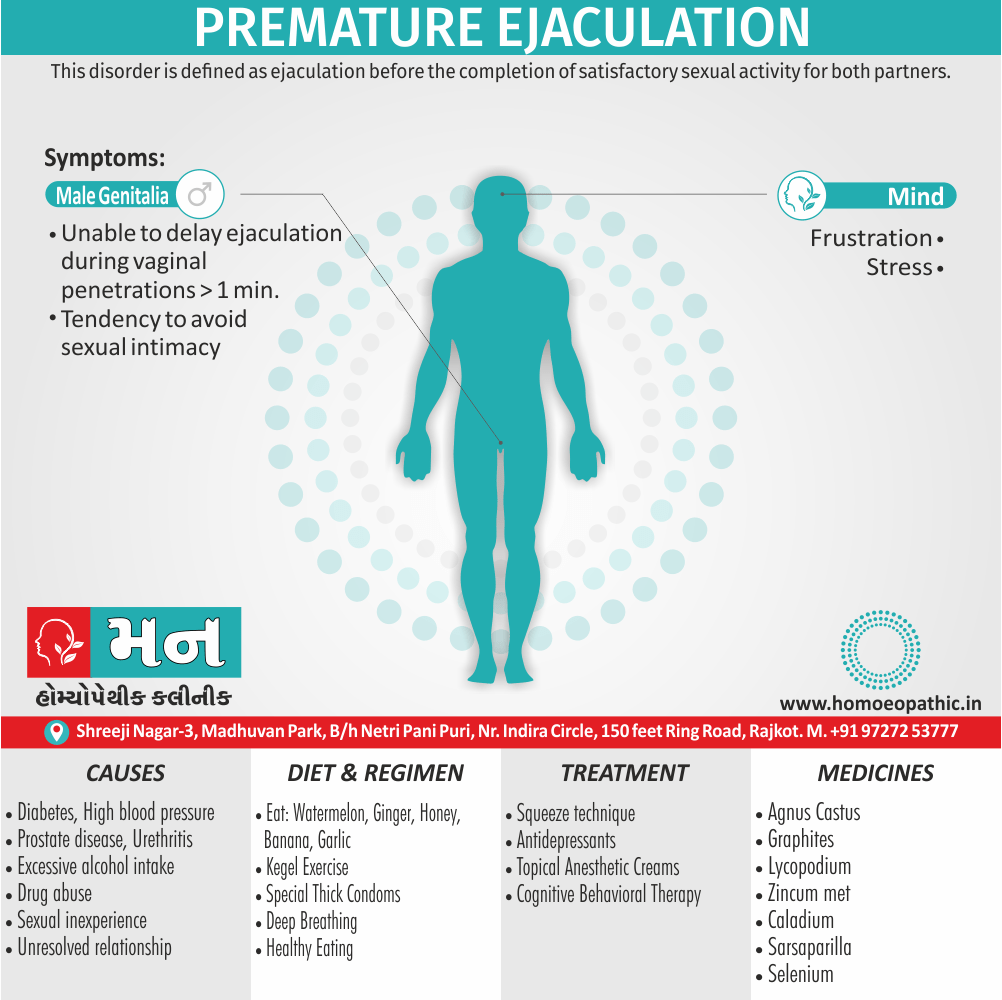
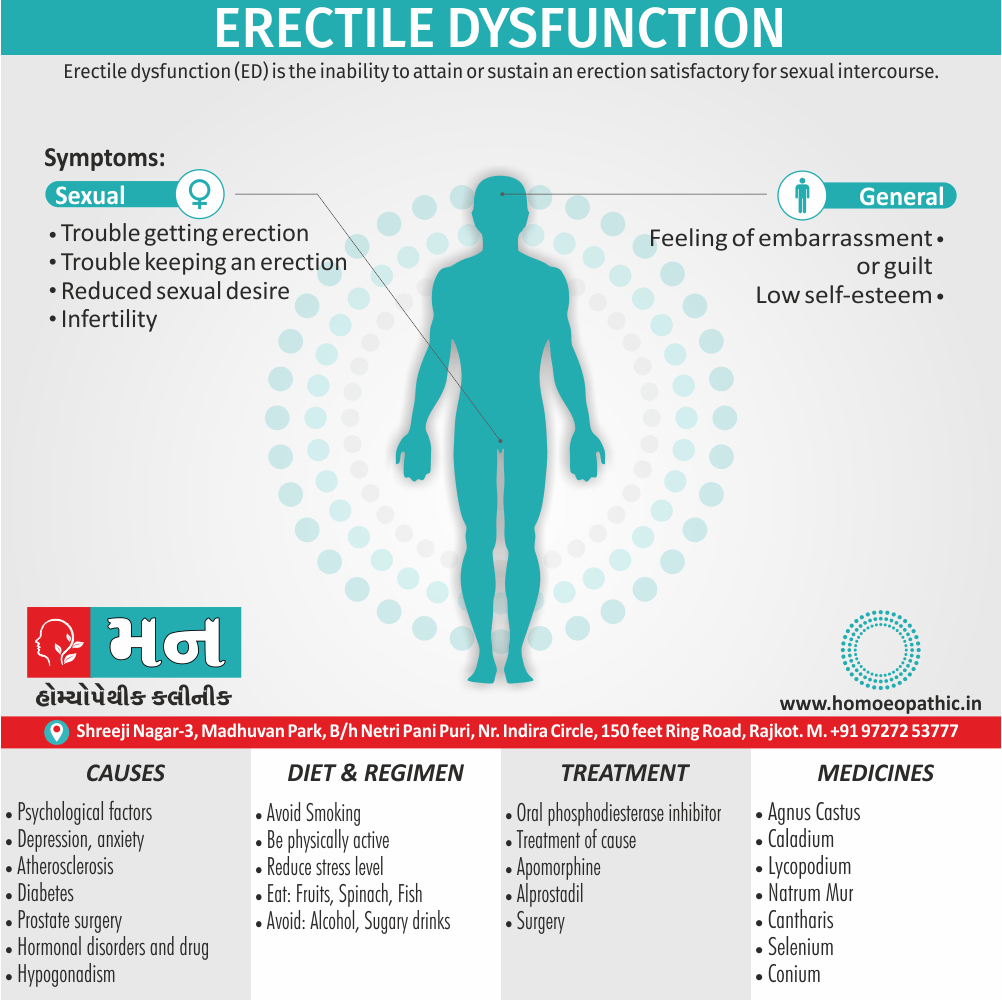
Sign & Symptoms of Disorders of Sexual Preference
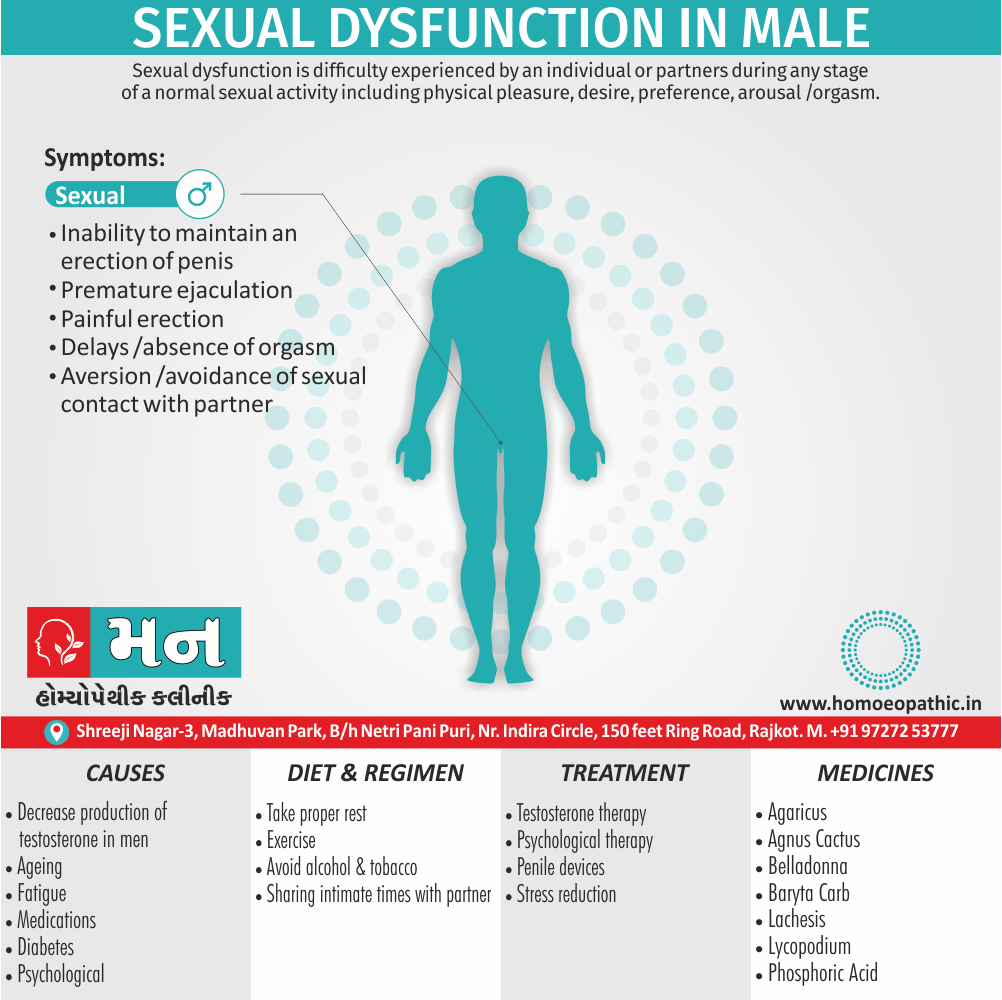
In men
- Inability to have an erection (erectile dysfunction).
- Absent or delayed ejaculation despite adequate sexual stimulation (delayed ejaculation).
- Inability to control the moment of ejaculation (premature or premature ejaculation).
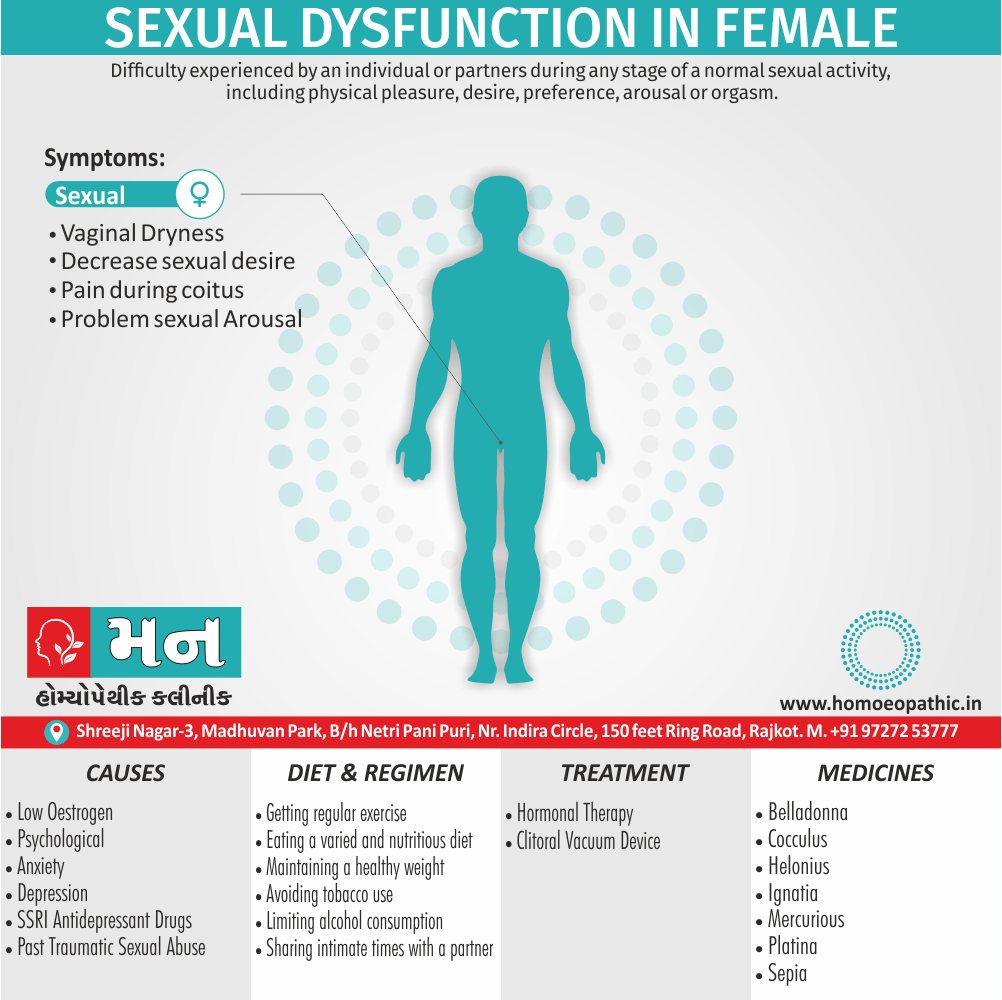
In women
- Inability to reach orgasm.
- Too little vaginal lubrication before and during intercourse.
- Inability to relax or stimulate the vaginal muscles to allow intercourse.
In men and women
- Lack of interest or desire for sex.
- Inability to get aroused
- Pain during sexual intercourse. (4)
Diagnosis of Disorders of Sexual Preference
Disorders of Sexual Preference in its basic form, it conducted with the use of disorders criteria defined in classification:
- The unusualness of content of sexual urge, pattern stability in time (more than 6 months) exhibiting behaviors in accordance with atypical urges, experiencing distress or impairment of social functioning in connection with Preference.(6)
Differential diagnosis of Disorders of Sexual Preference
-
5-Alpha-Reductase Deficiency
-
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
-
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
-
Denys-Drash Syndrome
-
Gender Identity
-
Genital Anomalies
-
Gonadoblastoma
-
Hypogonadism
-
Hypospadias
-
Menstruation Disorders in Adolescents
-
Microphallus
-
Pediatric Hydrocele and Hernia Surgery
-
Pediatric Hypopituitarism
-
Precocious Puberty (7)
Treatment Disorders of Sexual Preference:
Assessment of abnormalities of sexual preference:
- Identify the problem and its course
- Exclude associated mental disorder (especially depressive disorder, alcoholism, also dementia)
- Assess normal sexual functioning
- Consider the ‘role’ of the abnormal sexual behaviour
- Assess motivation for treatment [1]
Treatment:
Psychoanalysis and psychoanalytic psychotherapy i.e.:
This is of particular help if the patient psychologically minded and has good ego strength for therapy.
Behaviour therapy i.e.:
A version therapy is the treatment of choice in severe, distressing paraphilia, with the patient’s consent.
Drug therapy i.e.:
- Antipsychotics have sometimes use for severe or dangerous aggression associated with paraphilias.
- Benperidol was earlier believed to particularly useful but the claim has not substantiated, and the drug is not available in the market.
- Antiandrogens ( cyproterone acetate or medroxyprogesterone acetate) can use in paraphilias with excessive sexual activity. It have use to reduce sexual drive, especially in patients whose abnormal sexual behaviour is potentially dangerous to other people.
Other treatments i.e.:
Castration and psychosurgery are extremely rare choices these days. [2]
Homeopathic Treatment of Disorders of Sexual Preference
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
Which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improve with homeopathic medicines.
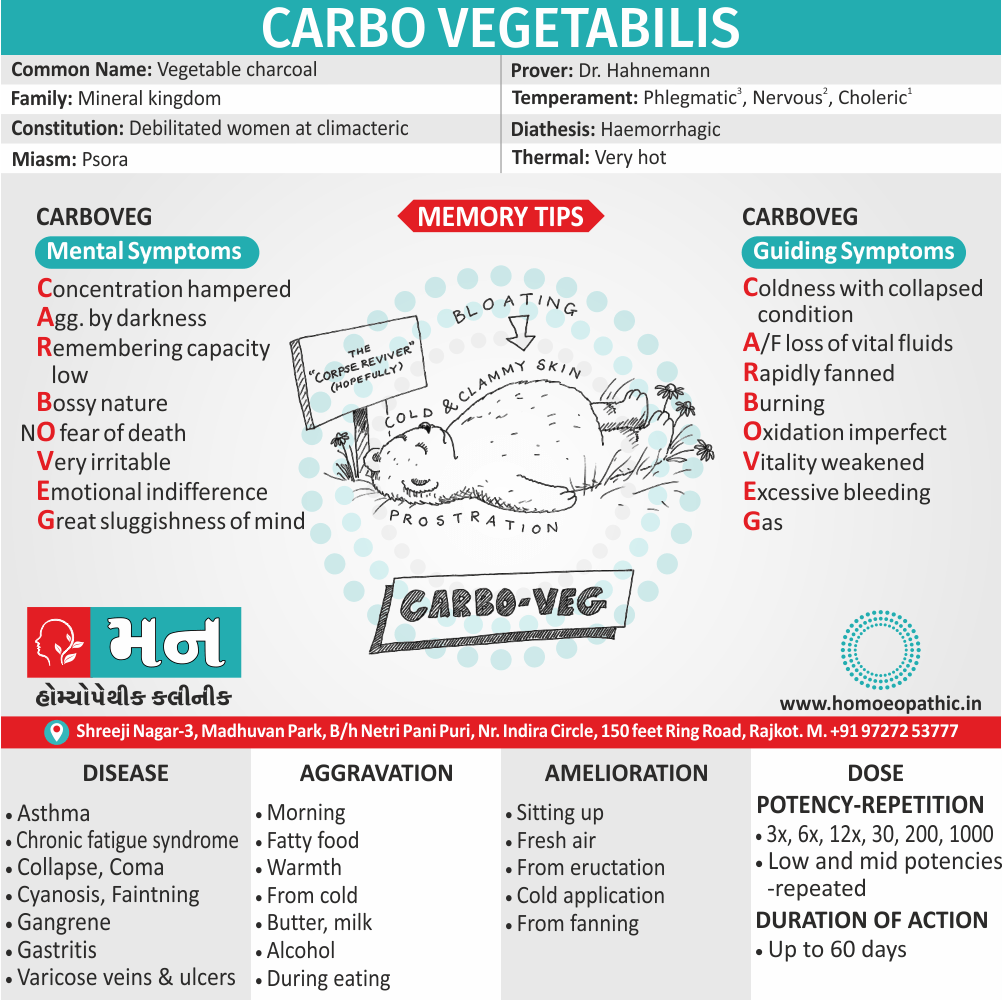
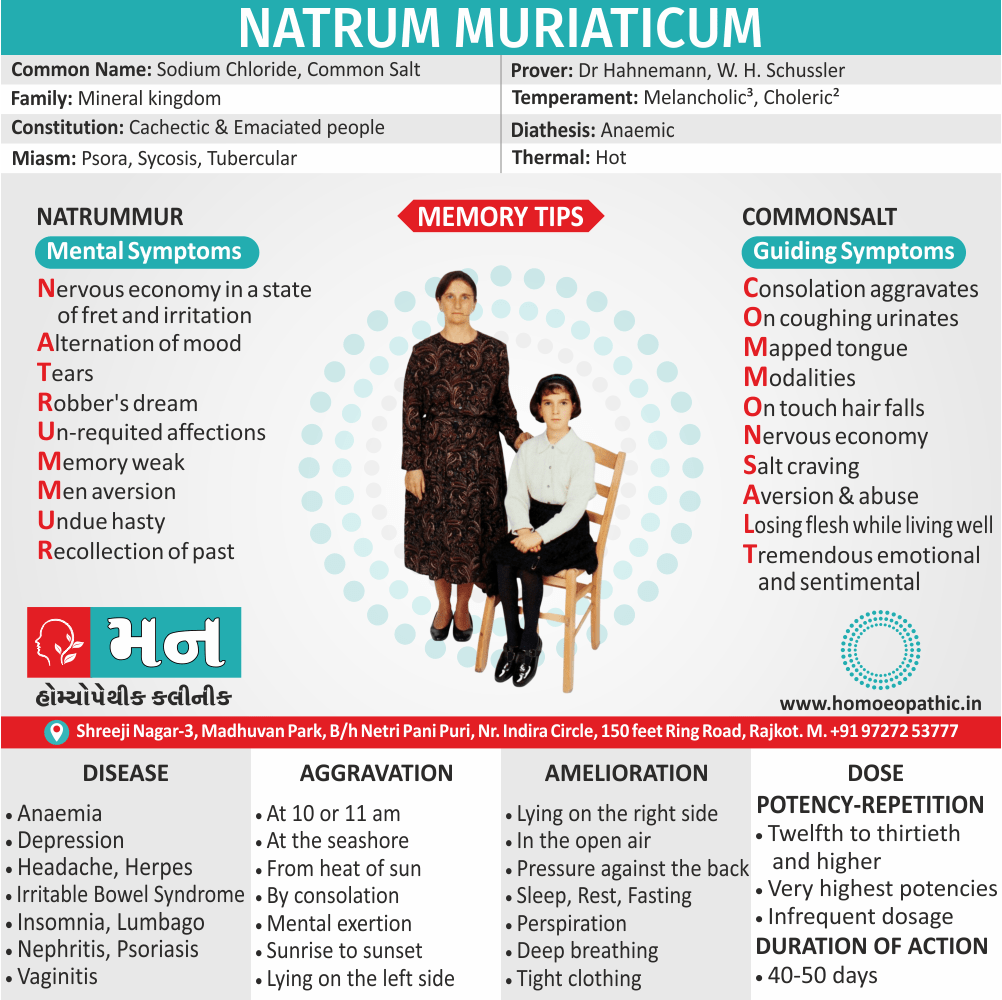
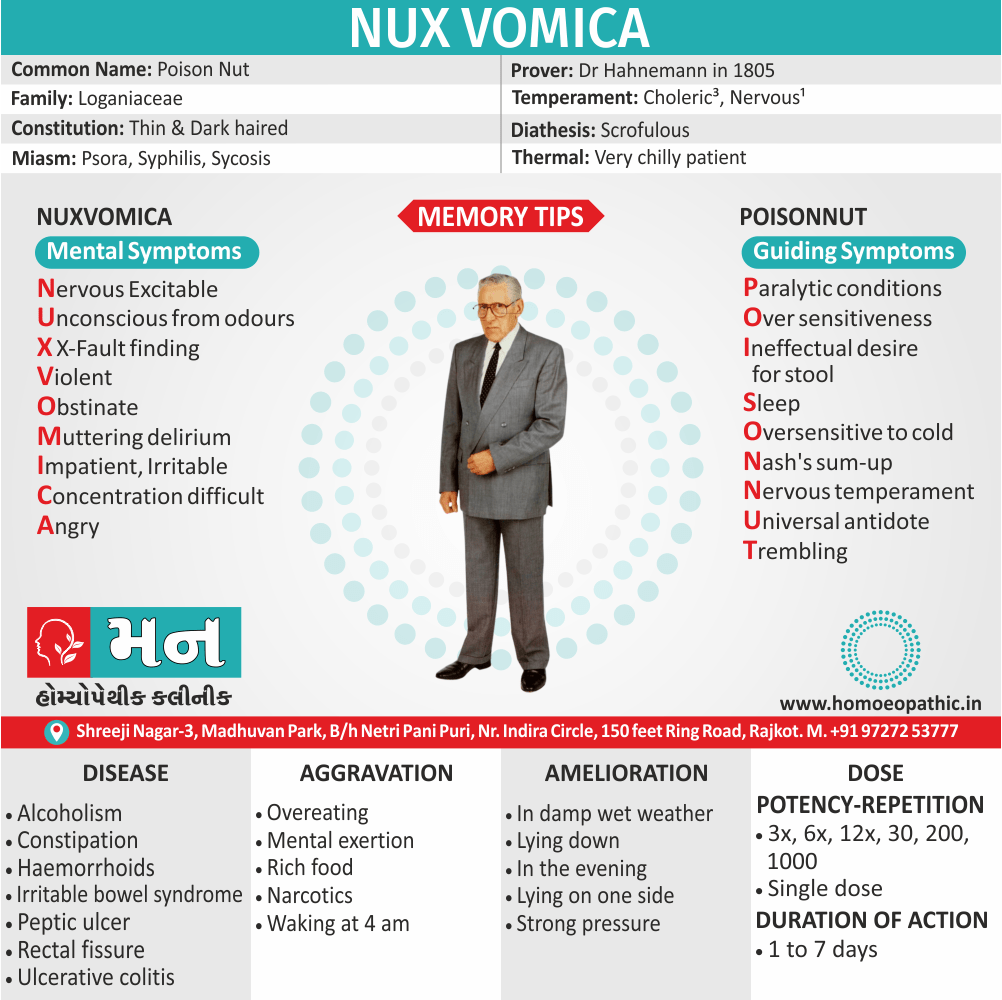
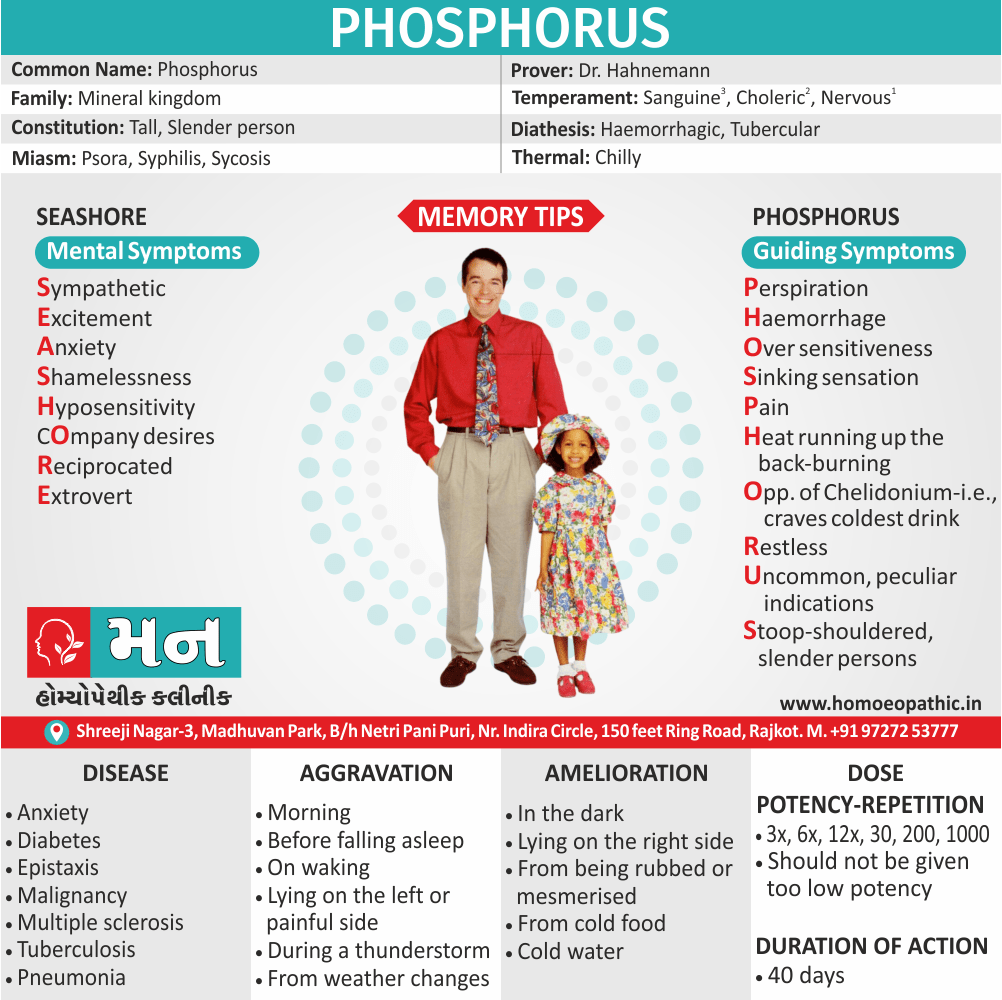
Homeopathic Medicines for Disorders of Sexual Preference
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
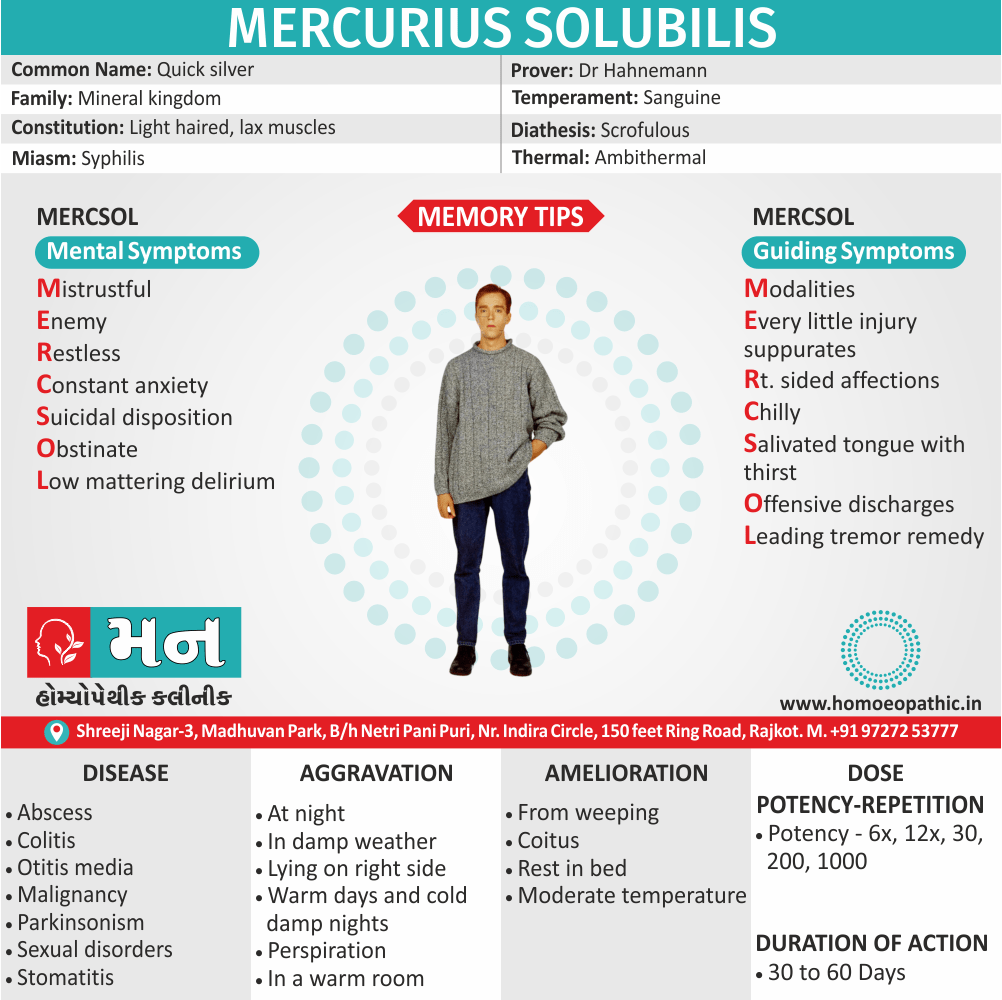
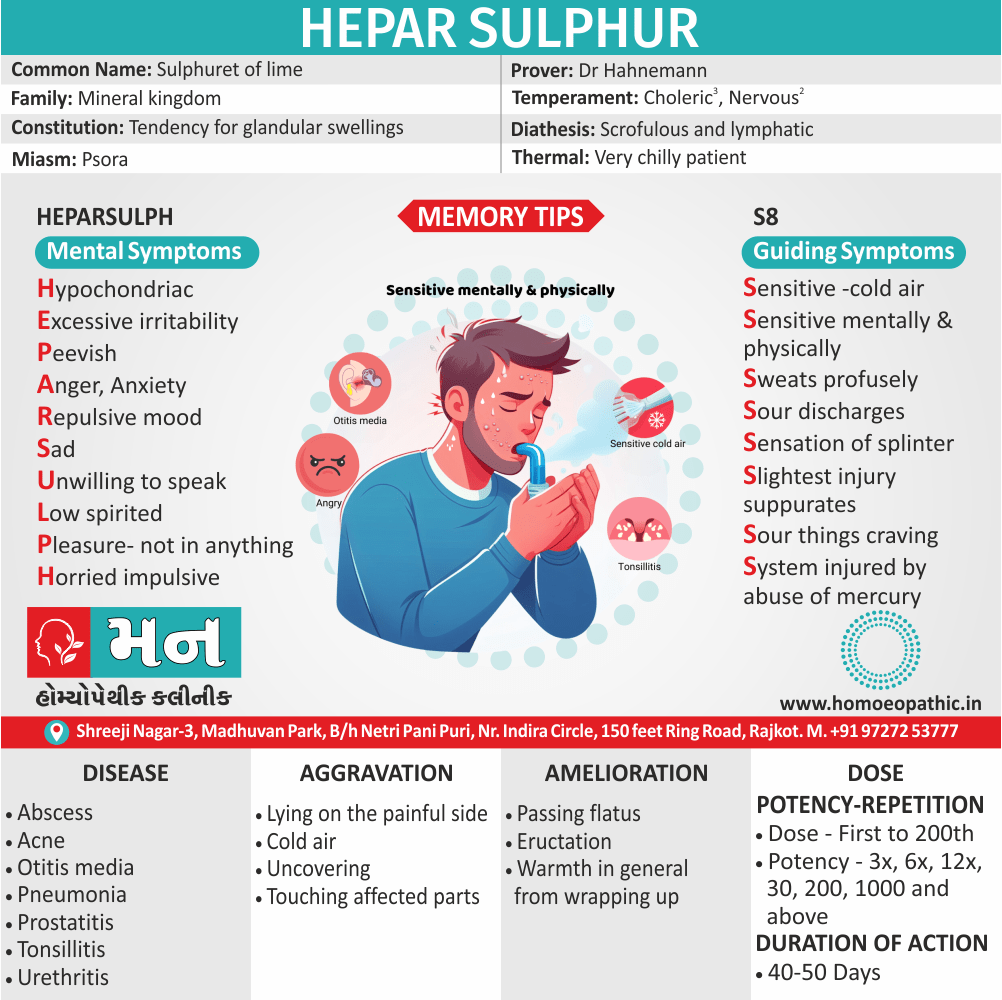
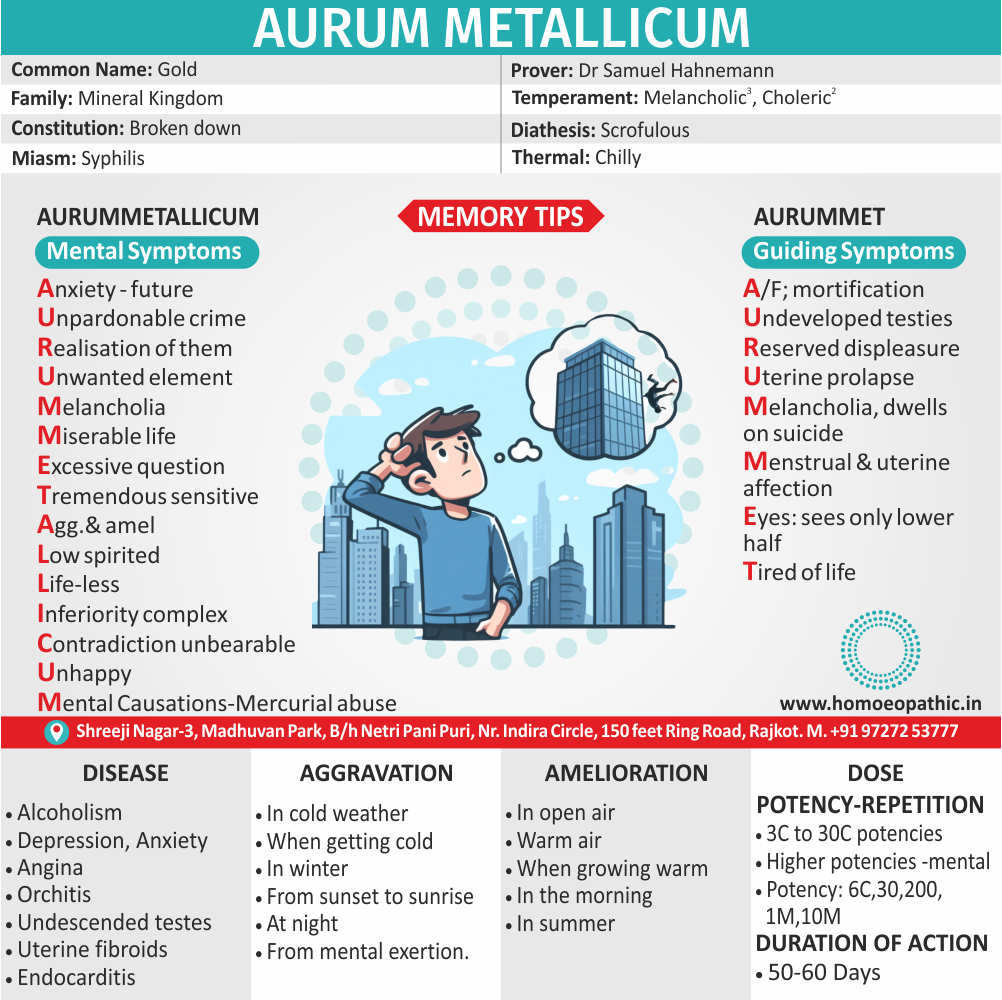
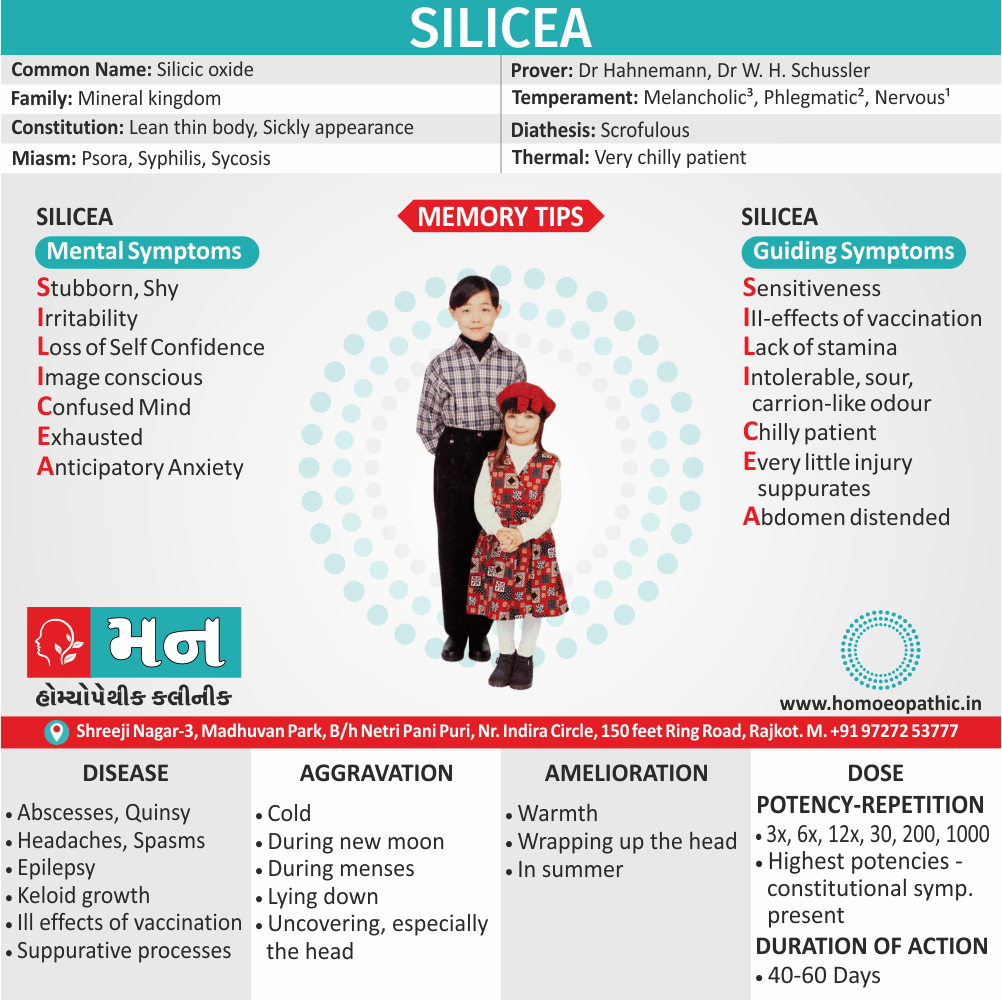
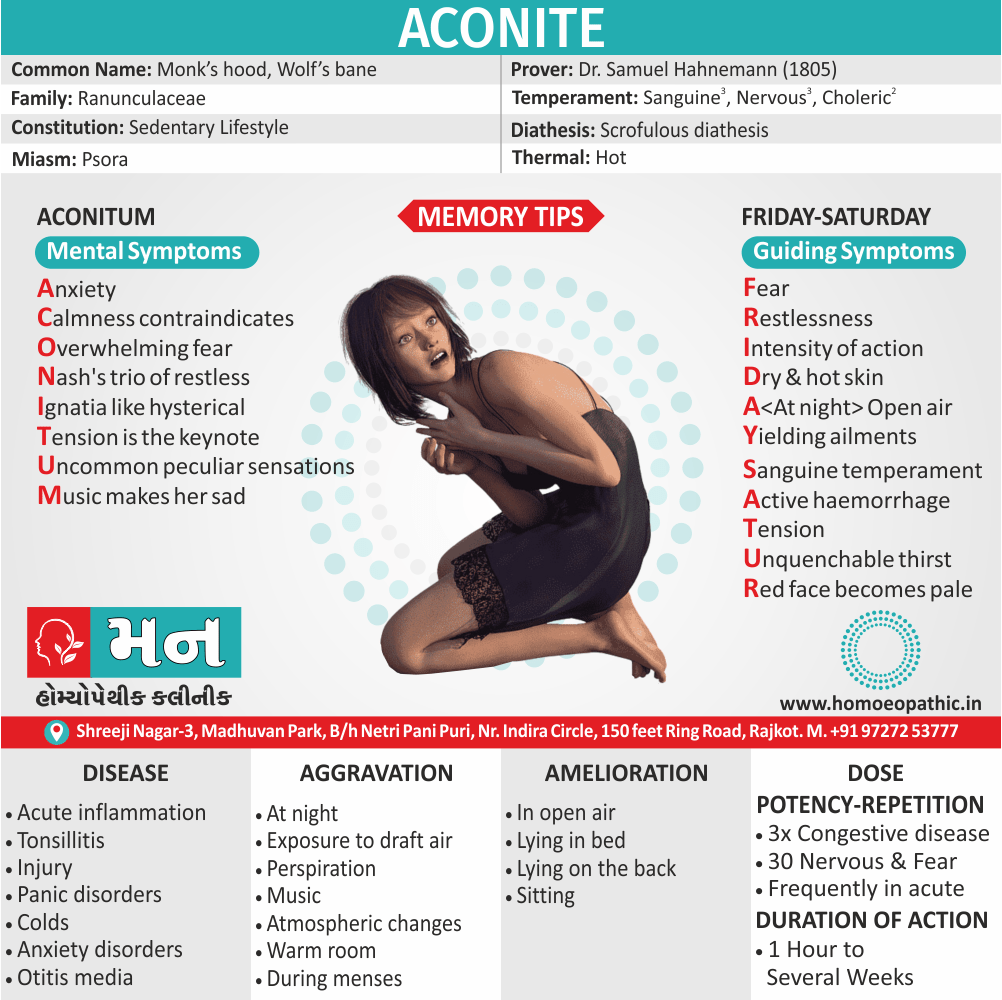
Medicine:
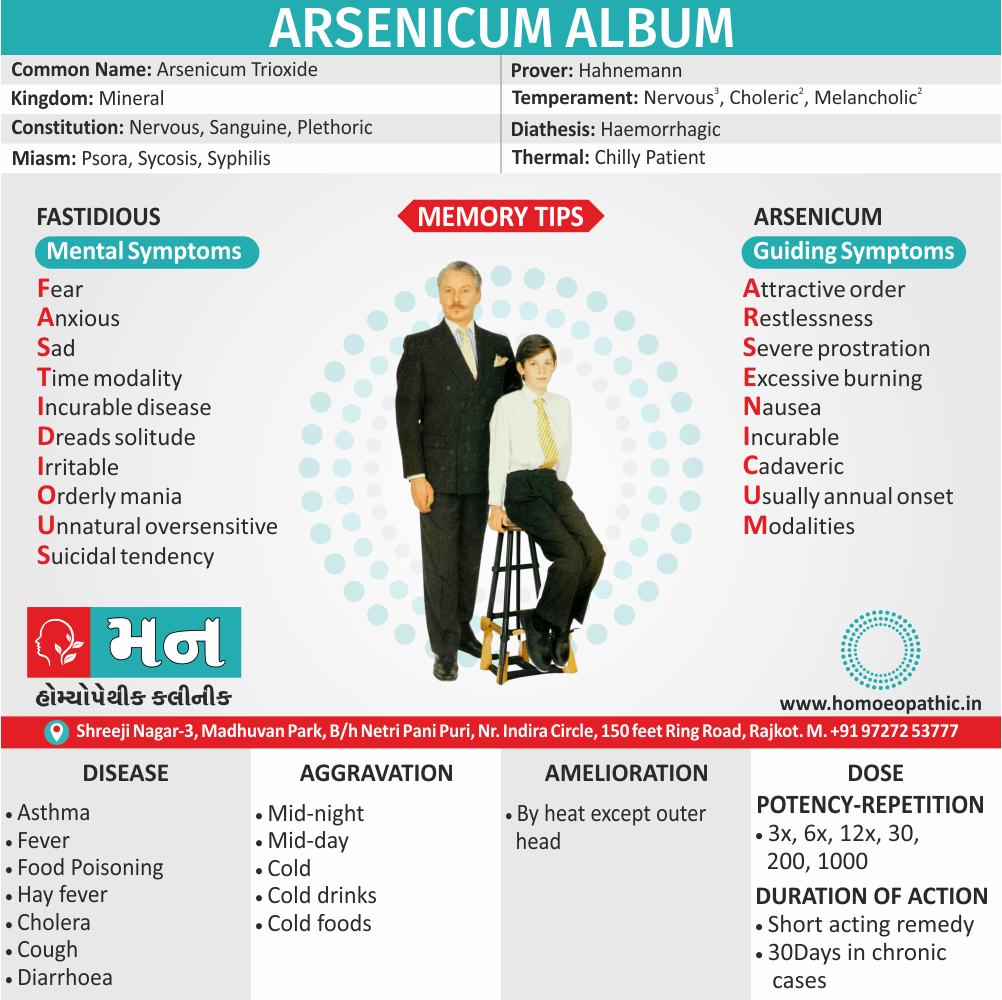
Lachesis:
“Sees” through, is highly sexual and possessive and wants to keep his loved ones under tight control. He puts sex to love; according to him sex is the only way of love.
Emissions always ameliorate him and he can’t control his sexual instinct also suffers from suppression of sex.
He is romantic, joyous, also passionate, and ecstatic and the female lachesis is mannish and often takes a lead in sexual activity.
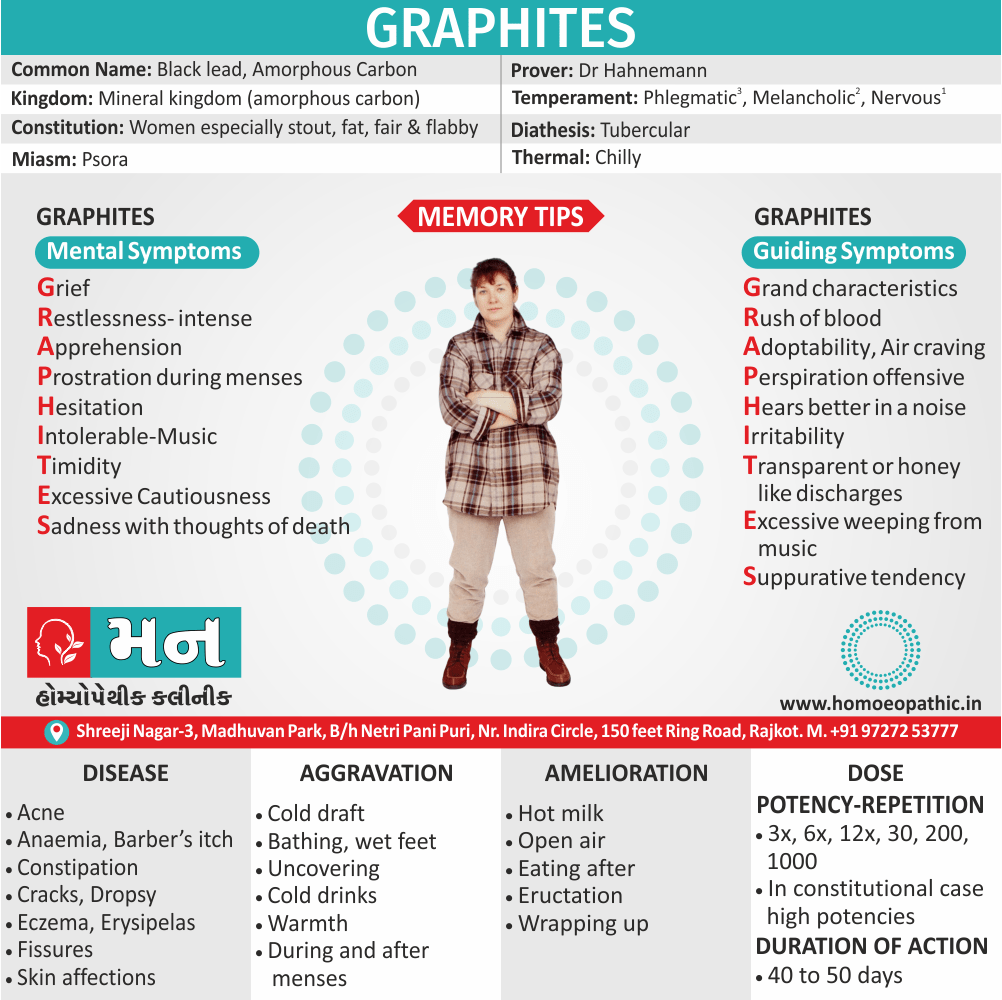
Conium:
Represents imbalance of energy between upper also lower parts of the body.
He is no longer able to draw up energy from the lower parts to upper parts. Additionally, The energy finds its way soon in emission on the slightest provocation.
Besides this, Forced abstinence causes sexual impotence or/and excessive desire (e.g. satyriasis, nymphomania).
The suppressed sexual energy goes deeper to cause aberrant immune response, to cause cancer.
Fluoric-Acid:
It is materialistic, libertinistic and hedonist.
He has irresponsible gaiety, an easy going complacency he is interested in only physical pleasure without any emotional involvement.
Lastly, He goes from one sexual partner to another and suffers from STDs.
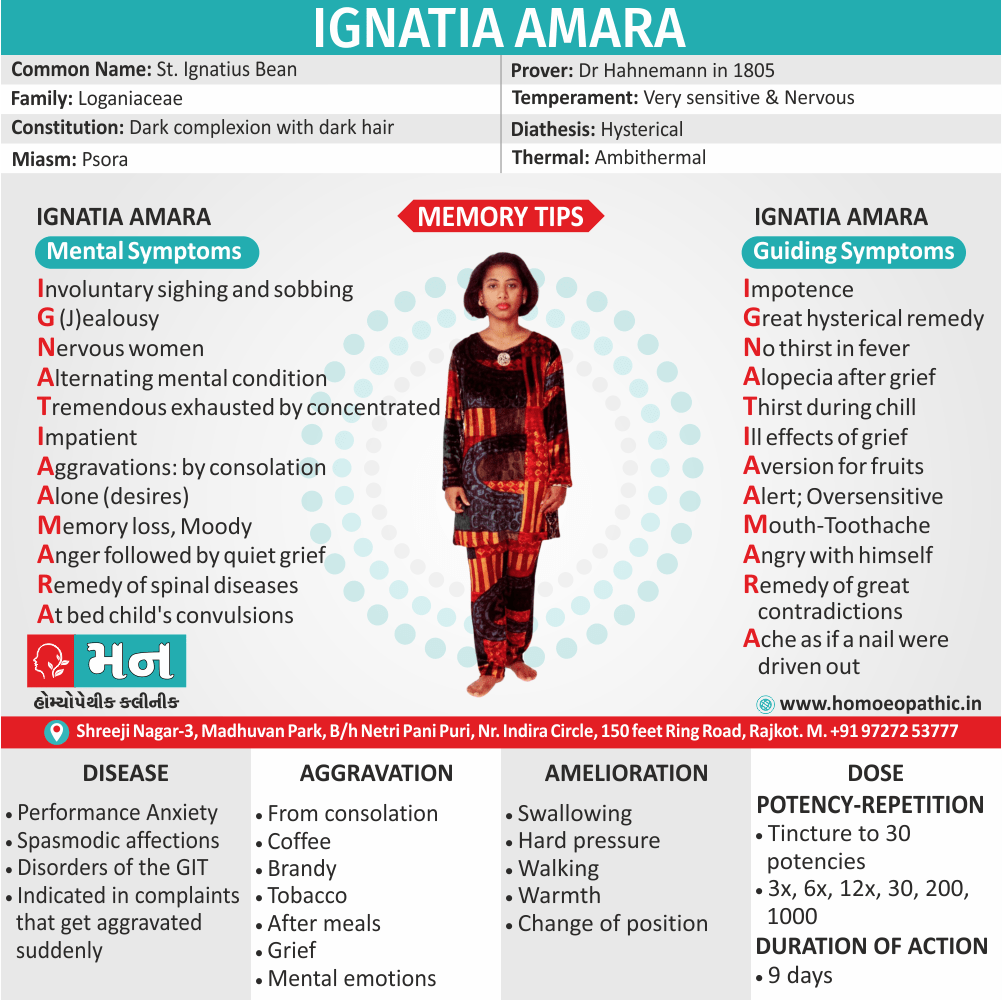
Staphysagria:
Represents a range of action from shyness of opposite sex to excessive indulgence in sex.
It has unsatisfied sexual urge; in widows.
Sex is for the sake of honour and ‘no’ to sex by other partner is viewed by staph as indignation.
He can then show the violent outburst of passion. Moreover, Sex then can be harassing for the partner who has to tolerate the wrath of staph.
Haughtiness, libertinism also wounded honour characterize staph.
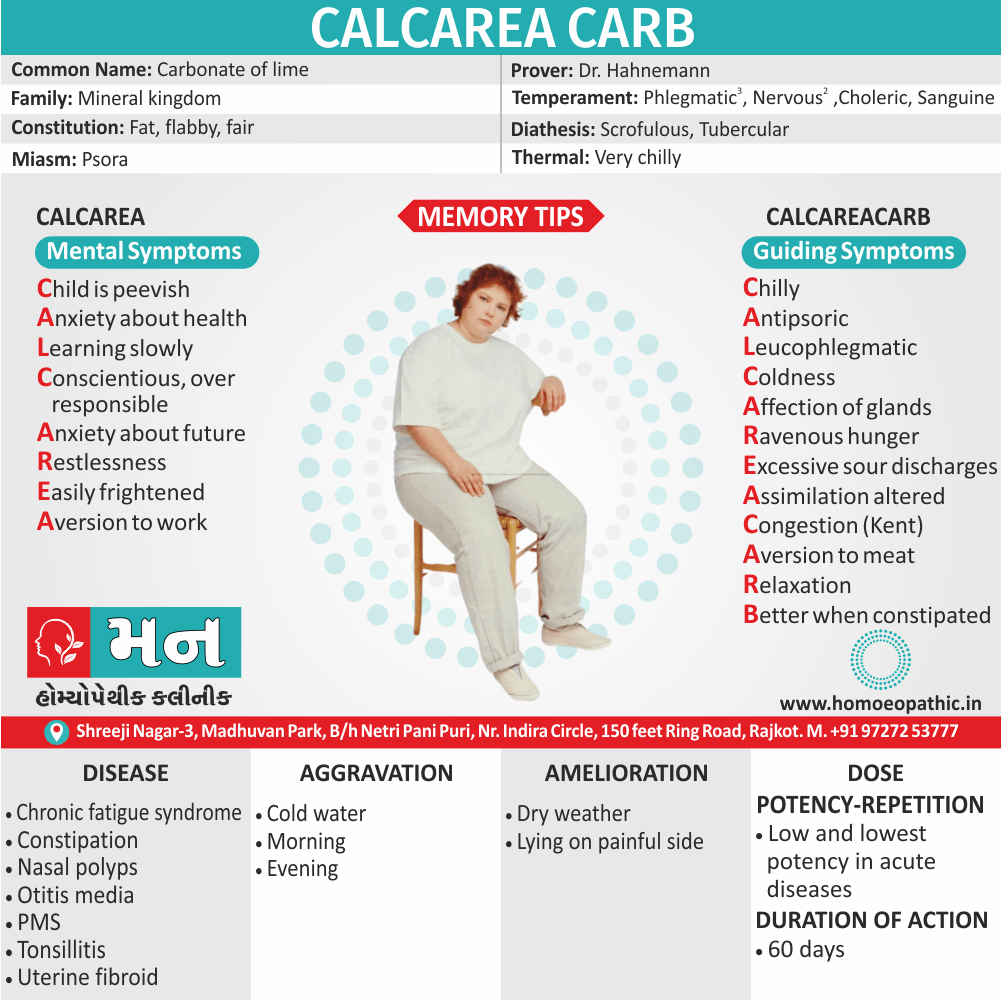
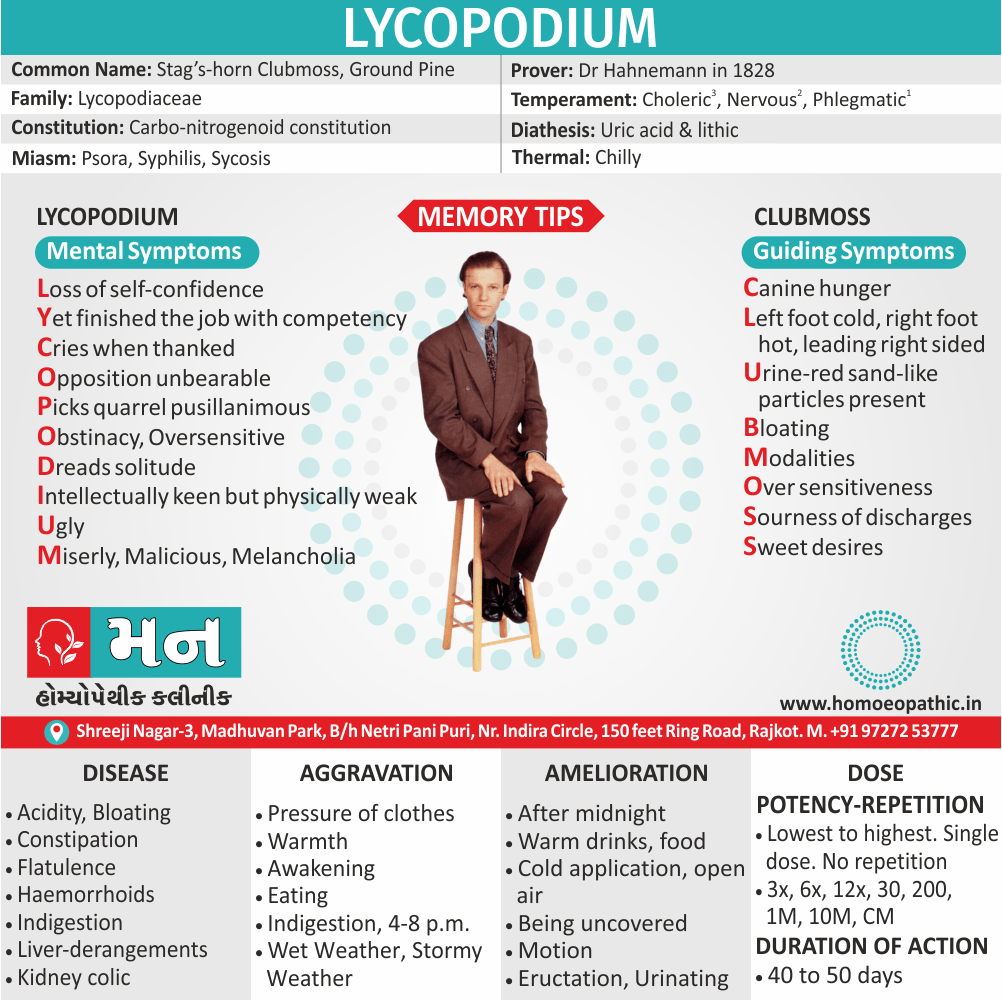
Lycopodium:
Generally, Represents the right side, the masculinity and this is reflected in sexual relations.
In detail, The inner weakness, anticipation, also anxiety of performance fall upon the organ that is unable to show its worth.
Repeated bad experiences makes Lyco refrain from sex as he wants to keep his honour.
Lyco has both loss of sexual desire and too strong sexual desire.
Lyco is deceptive, a liar, also an opportunistic.
The sense of impotency inside is reflected to act as bravado ‘I-am-potent.’ [3]
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Paraphilias?
Paraphilias are disorders of sexual preference in which sexual arousal occurs persistently also significantly in response to objects which are not a part of normal sexual arousal.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Paraphilias?
- Lachesis
- Conium
- Fluoric-Acid
- Staphysagria
- Lycopodium
What are the 8 Paraphilic Disorders?
- Sexual fetishism
- Transvestism
- Paedophilia
- Exhibitionism
- Voyeurism
- Sexual sadism
- Sexual masochism
What are the examples of Paraphilias?
- Fetishism
- Fetishistic Transvestism
- Paedophilia
Reference
- Psychiatry, Fourth Edition- Oxford Medical Publications – SRG- by Geddes, Jonathan Price, Rebecca McKnight / Ch 30.
- A Short Textbook of PSYCHIATRY 7th edition by Niraj Ahuja / Ch 10.
- Homeopathy in treatment of Psychological Disorders by Shilpa Harwani / Ch 16.
- Sexual Disorder: What It Is, Types, Categories, Symptoms And More – PsychoTreat
- Disorders of Sex Development – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- diagnosis of Disorders of Sexual Preference – Search (bing.com)
- Differences (Disorders) of Sex Development (DSDs) Differential Diagnoses (medscape.com)