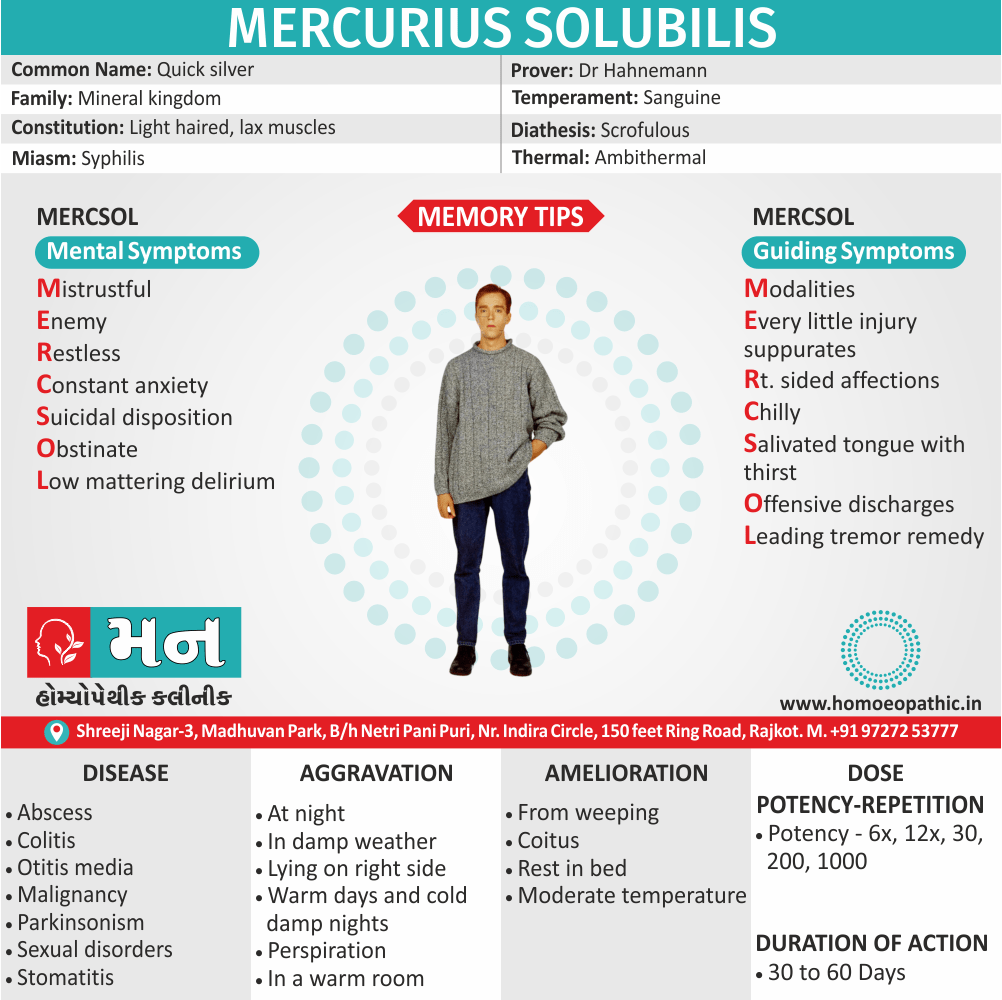
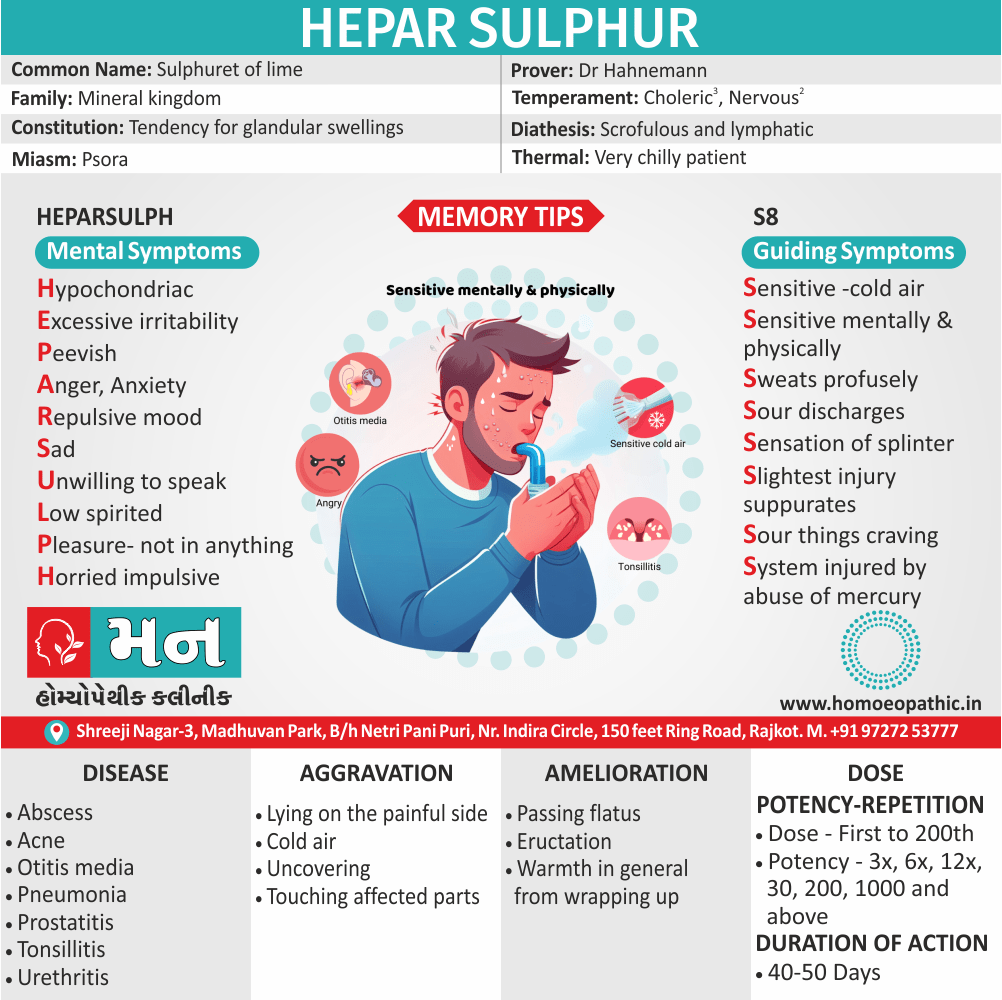
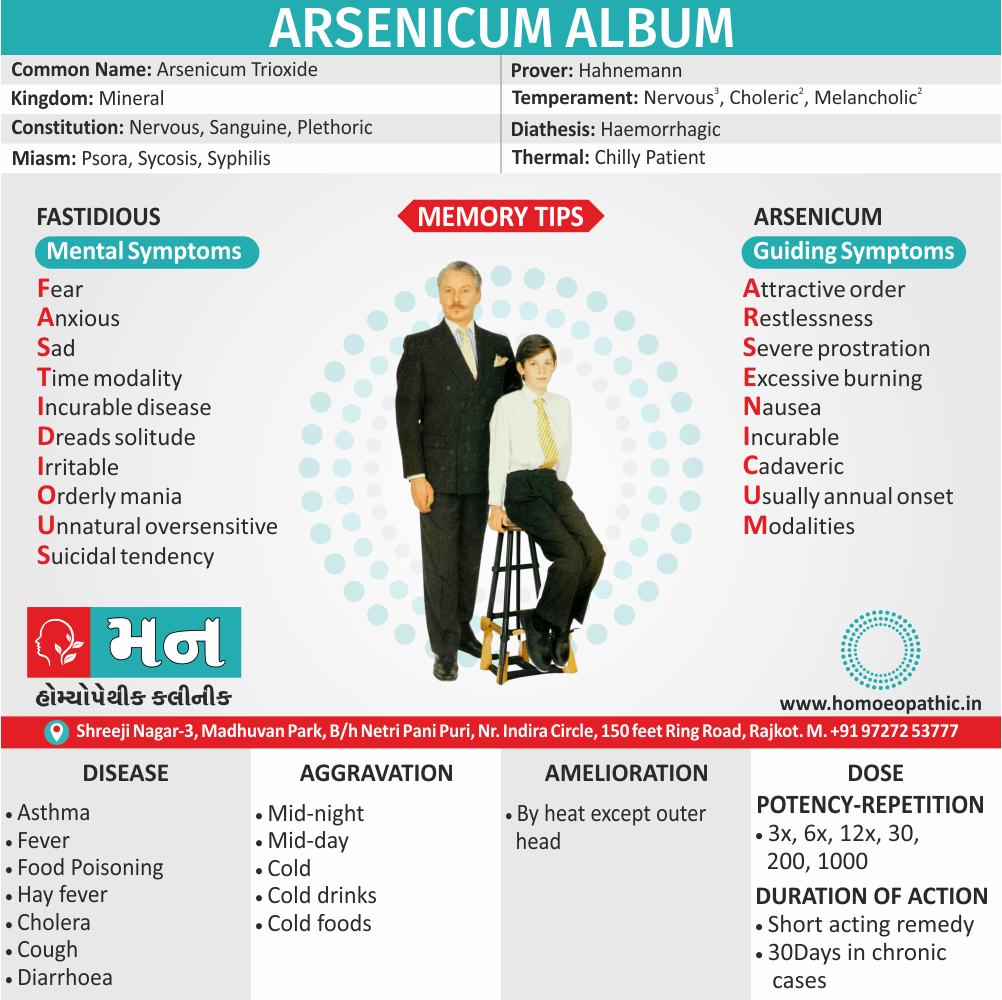
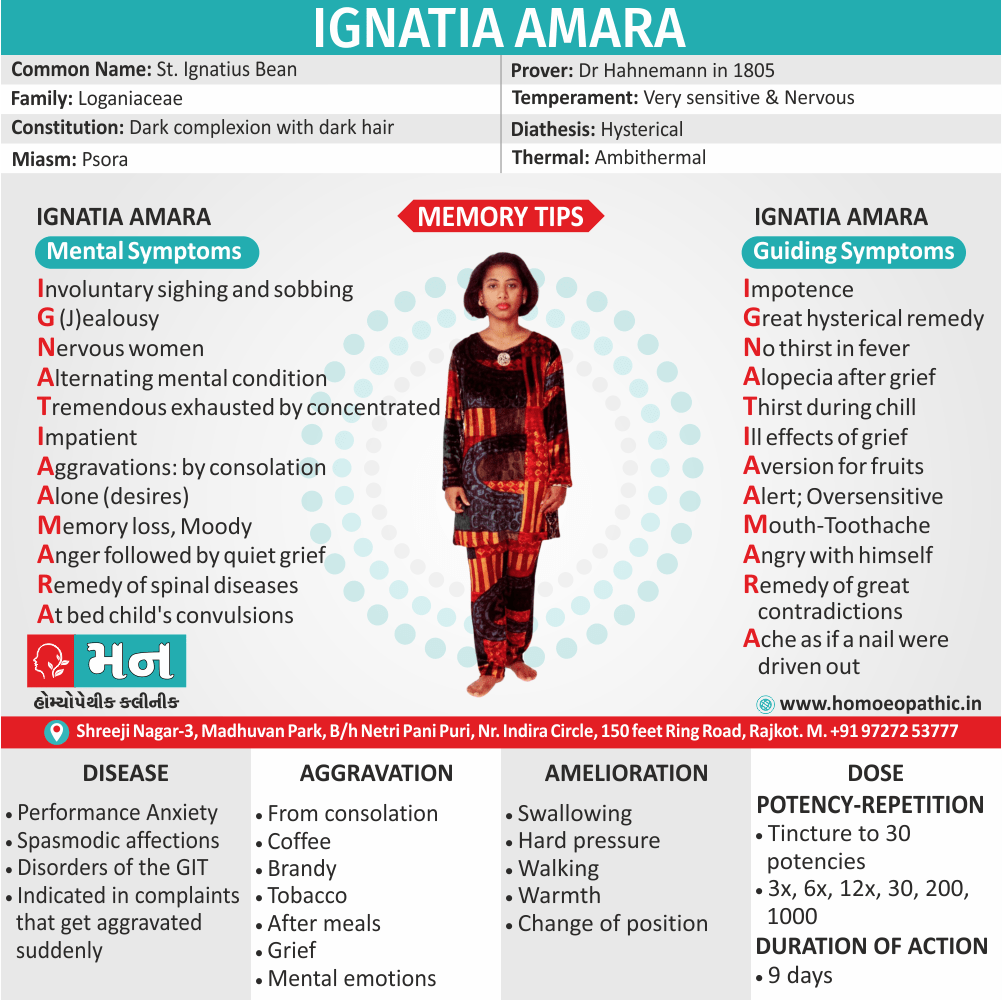
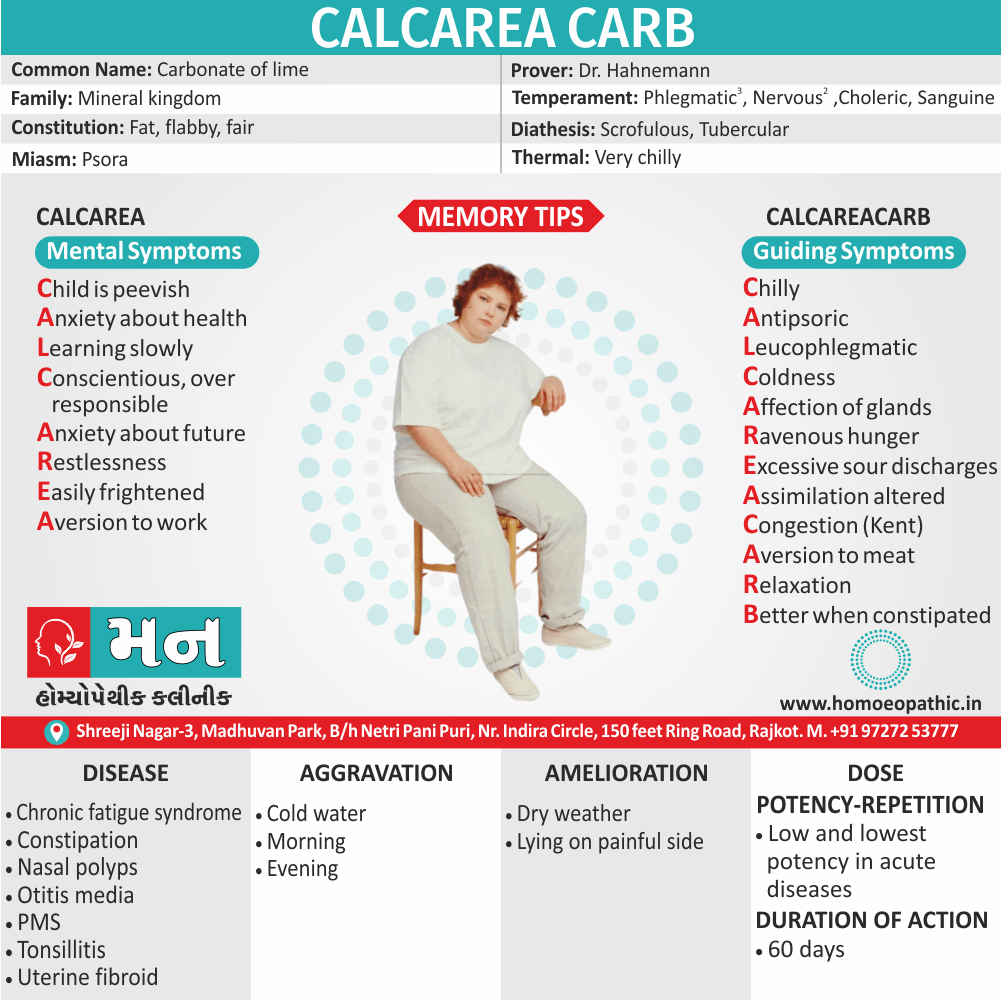
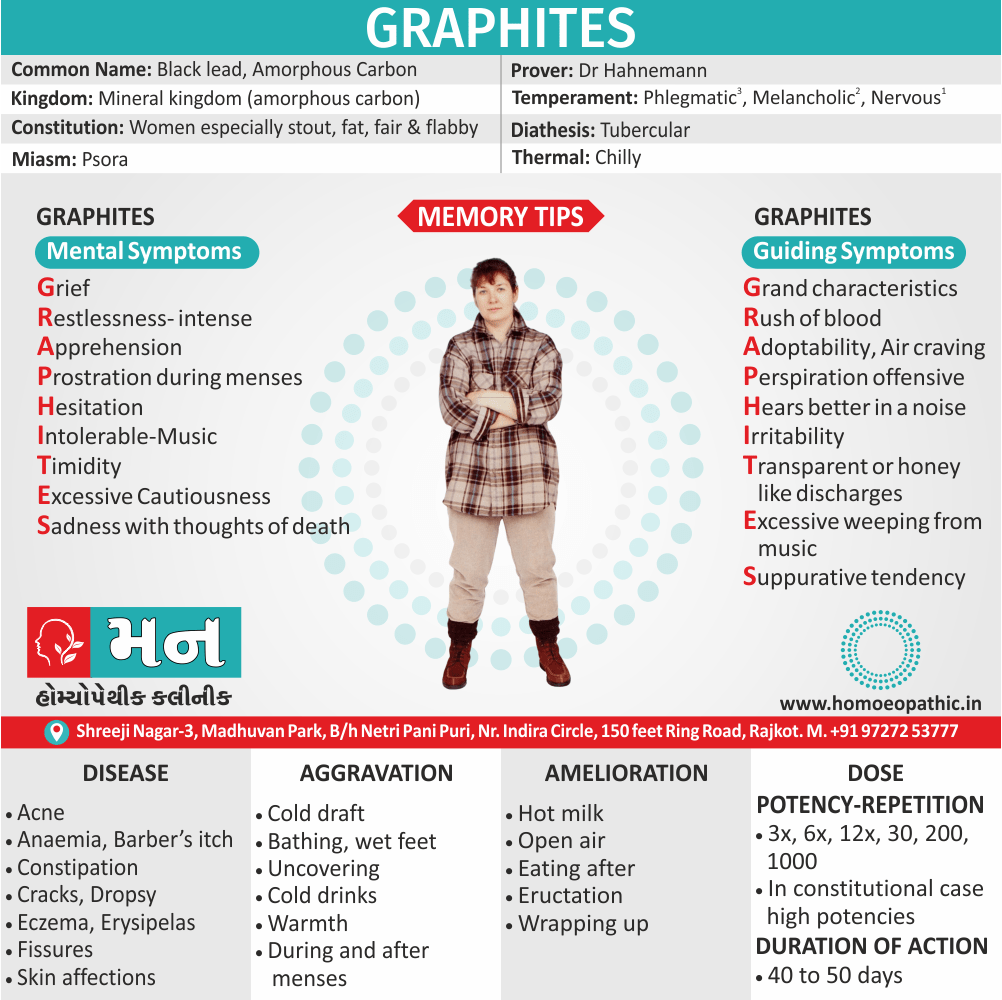
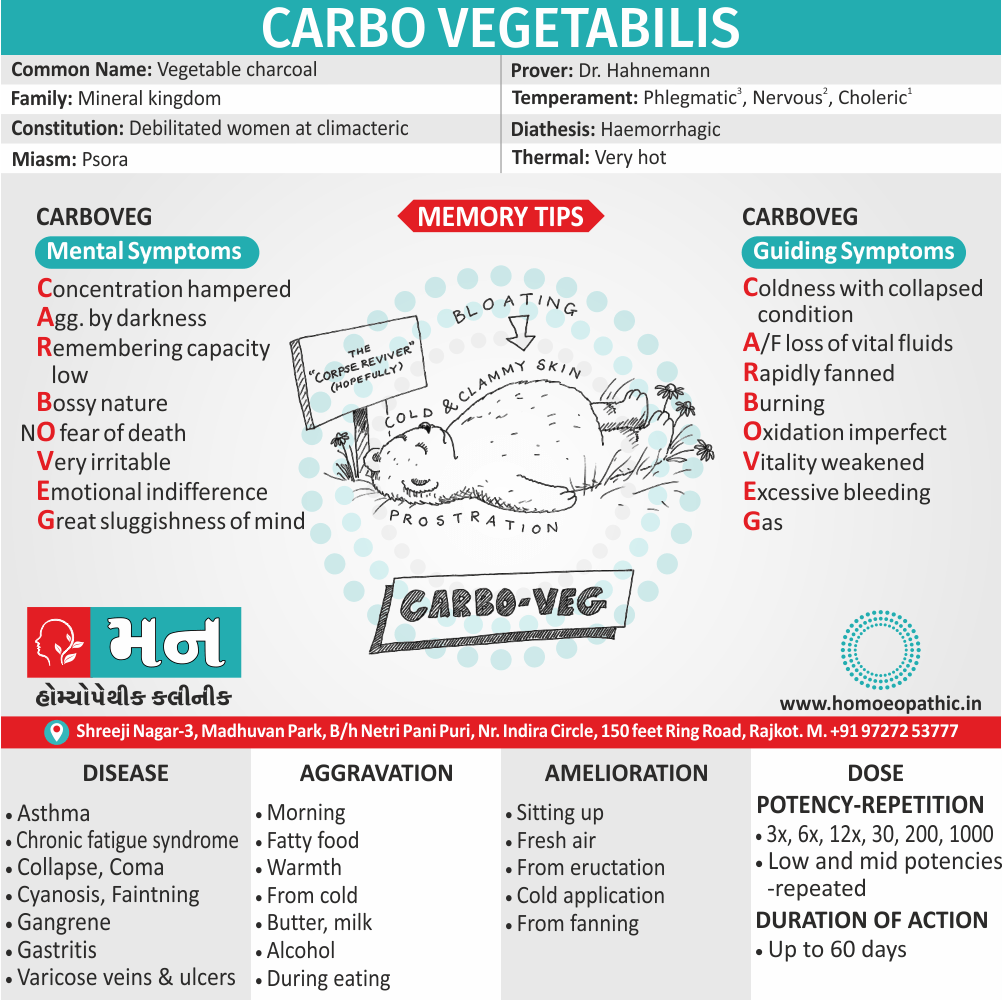
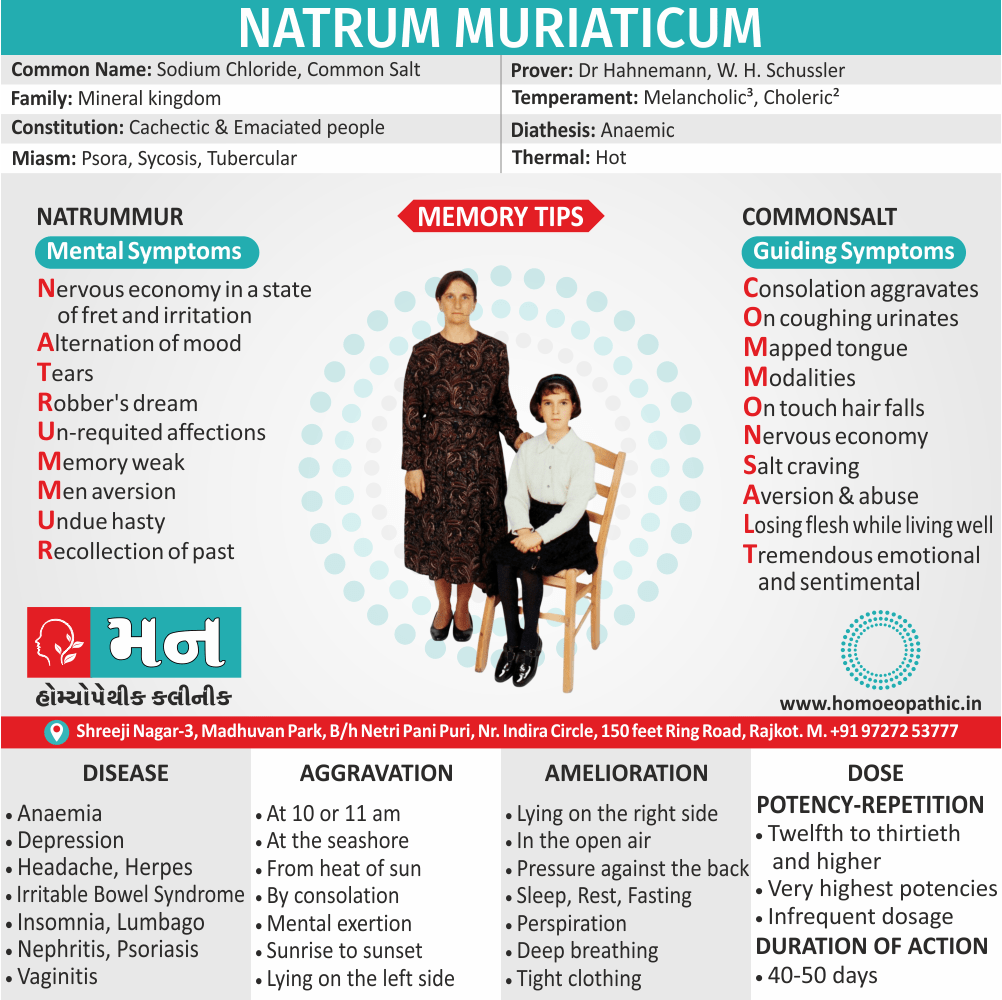
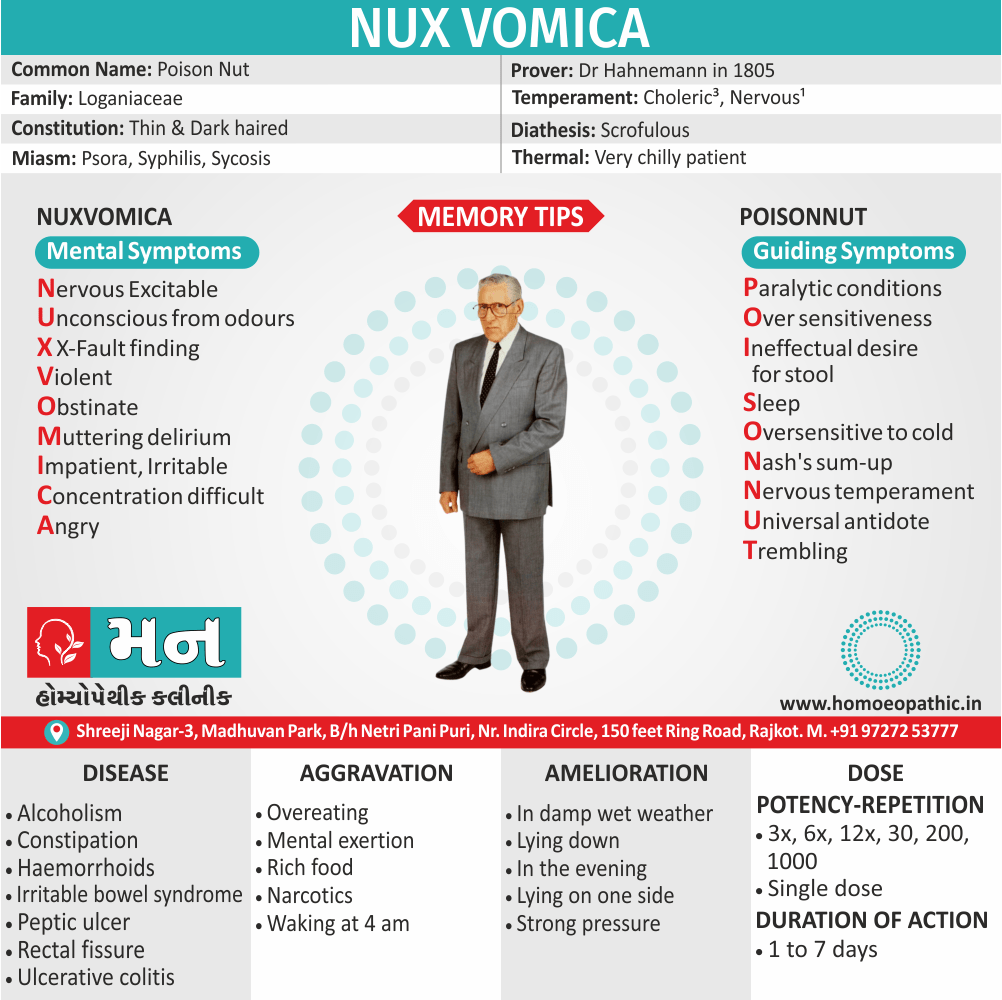
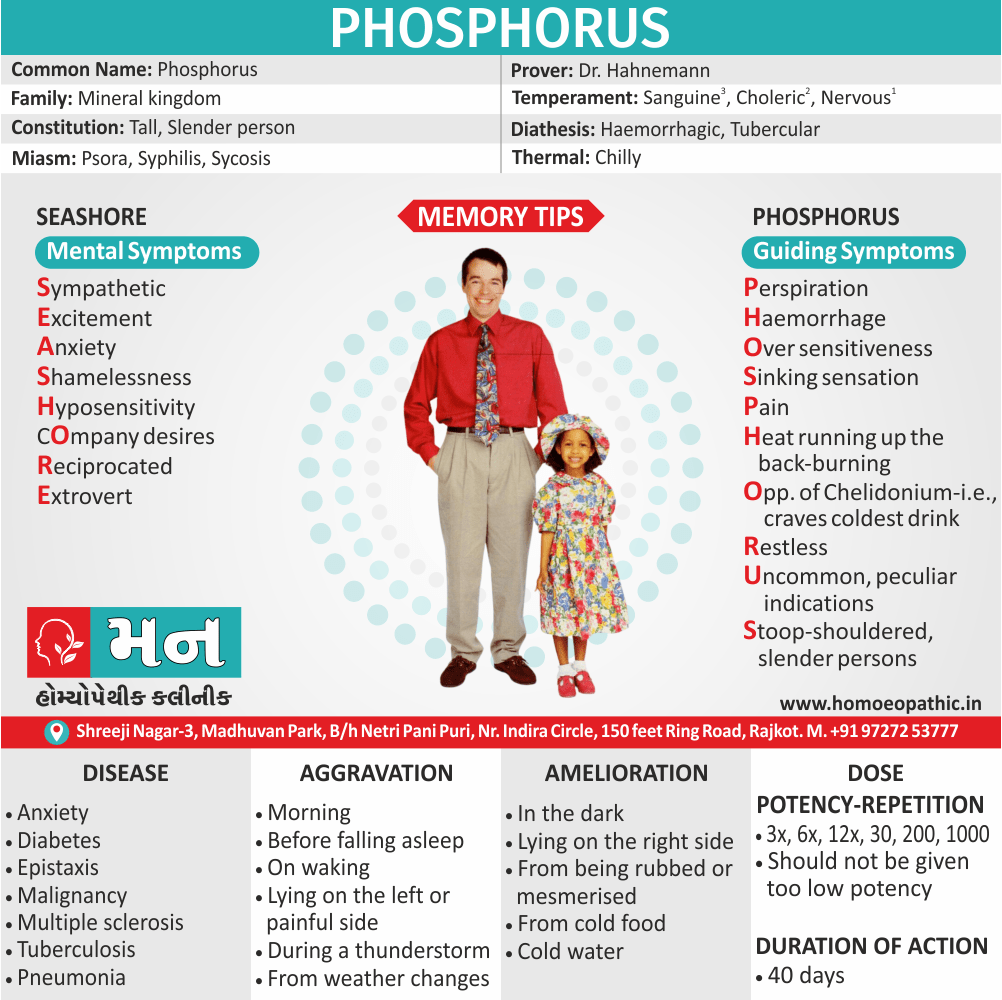
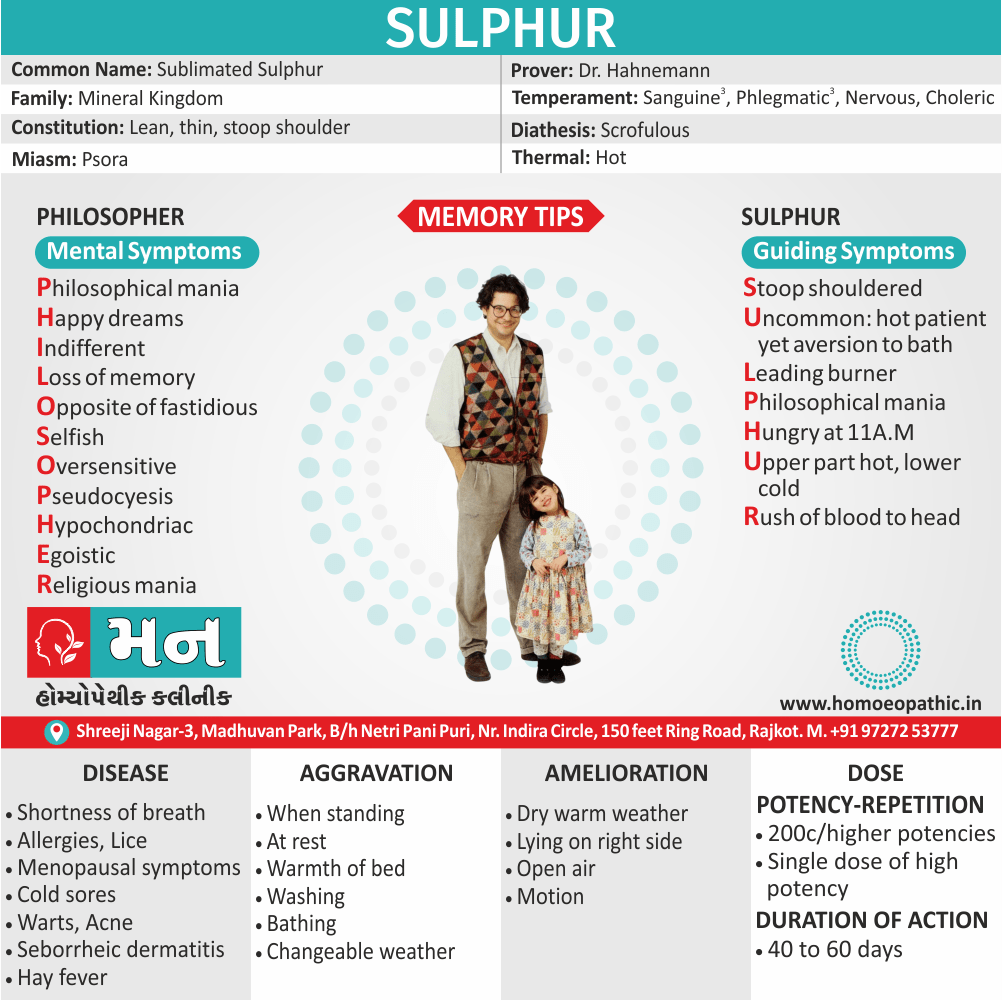
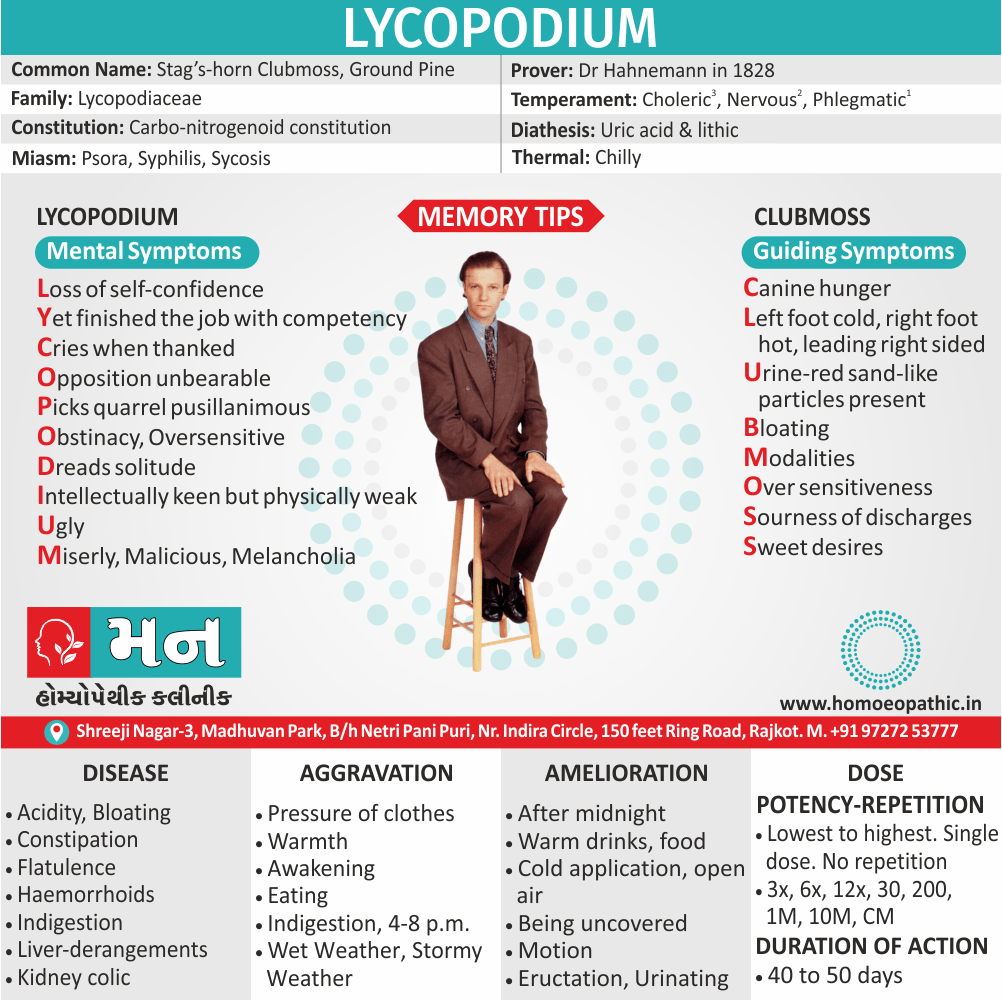
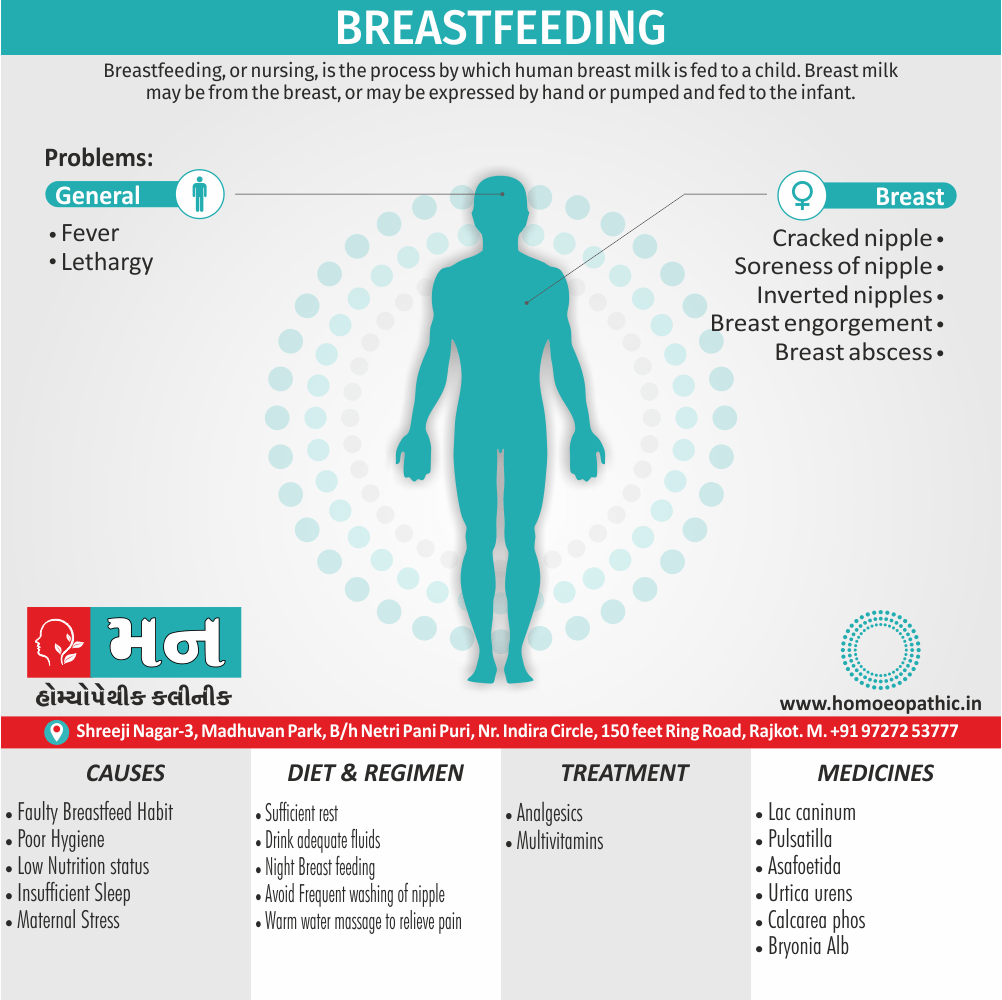
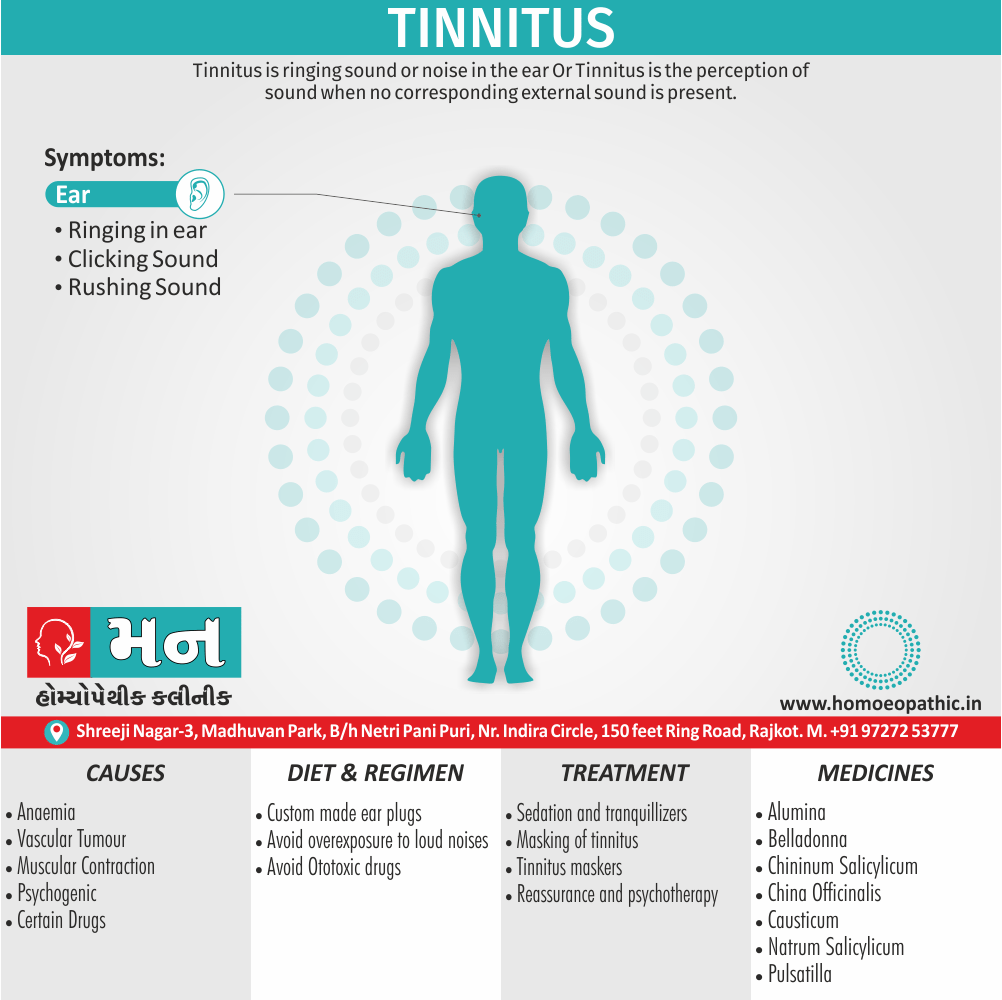
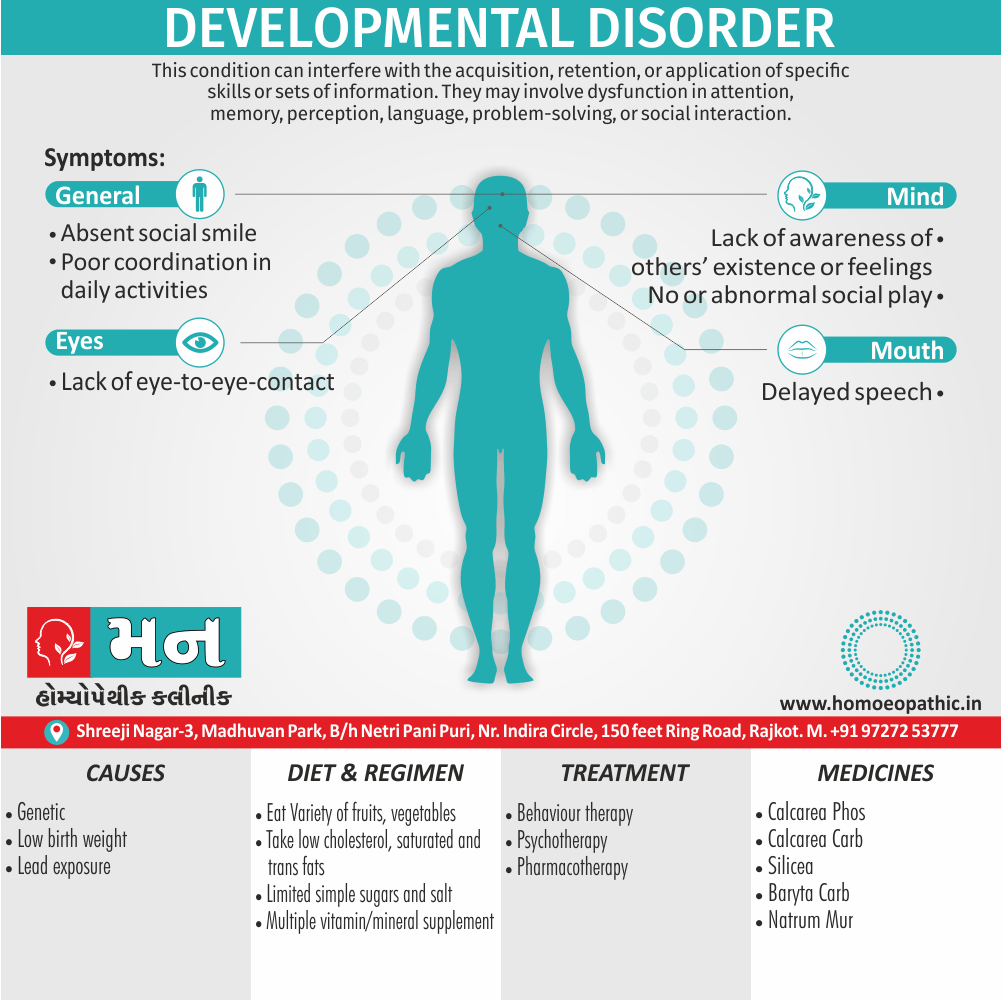
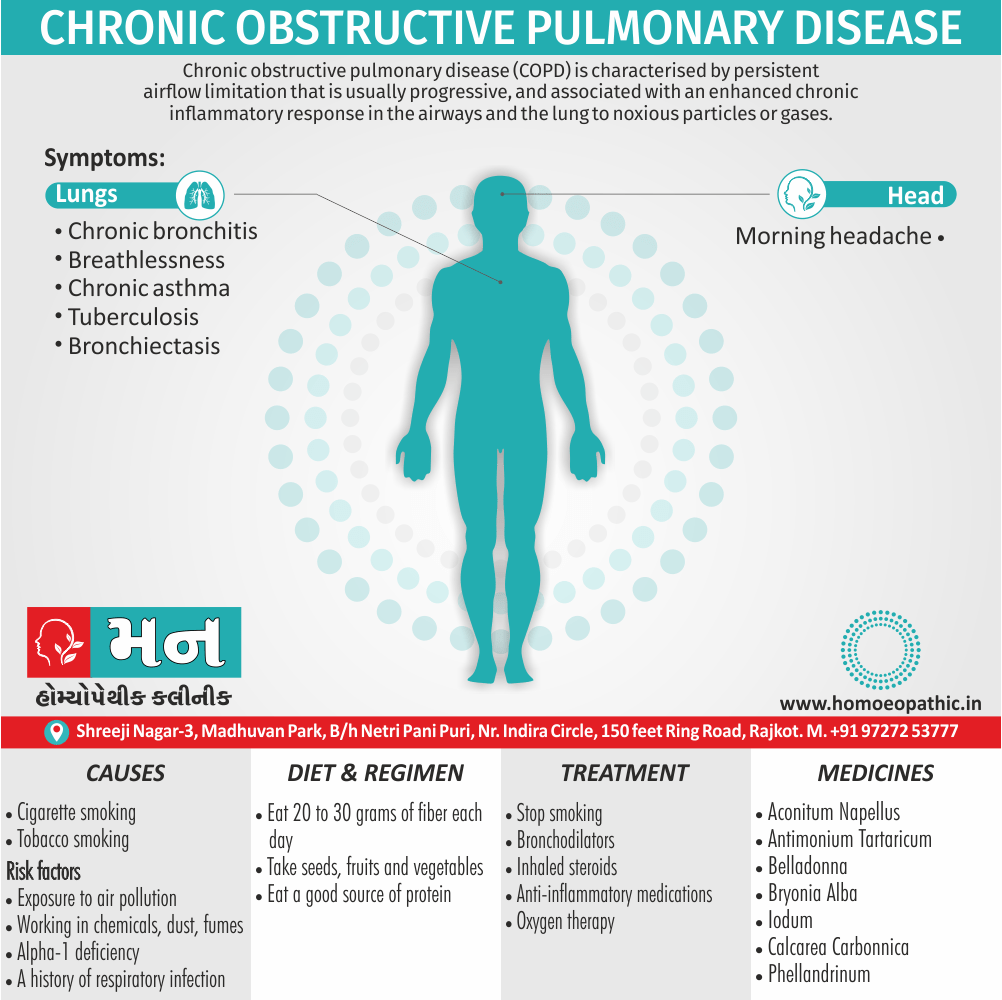
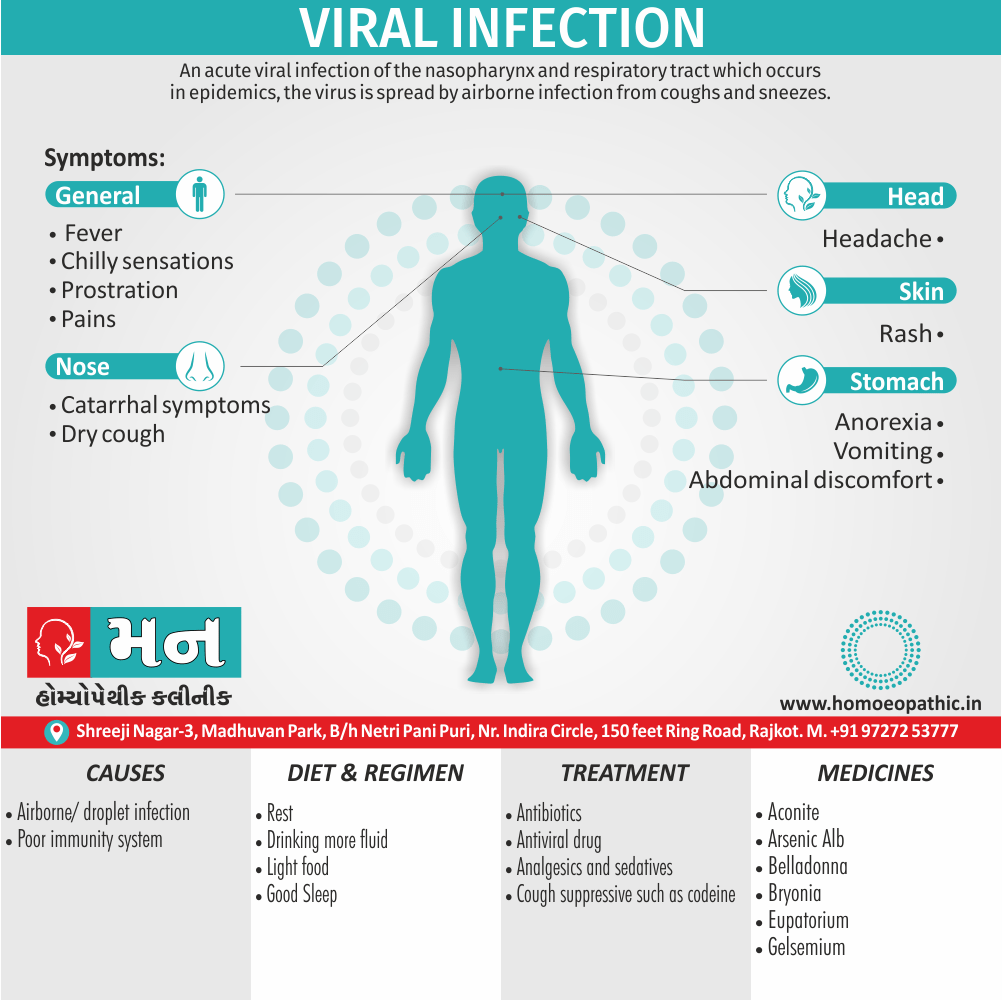
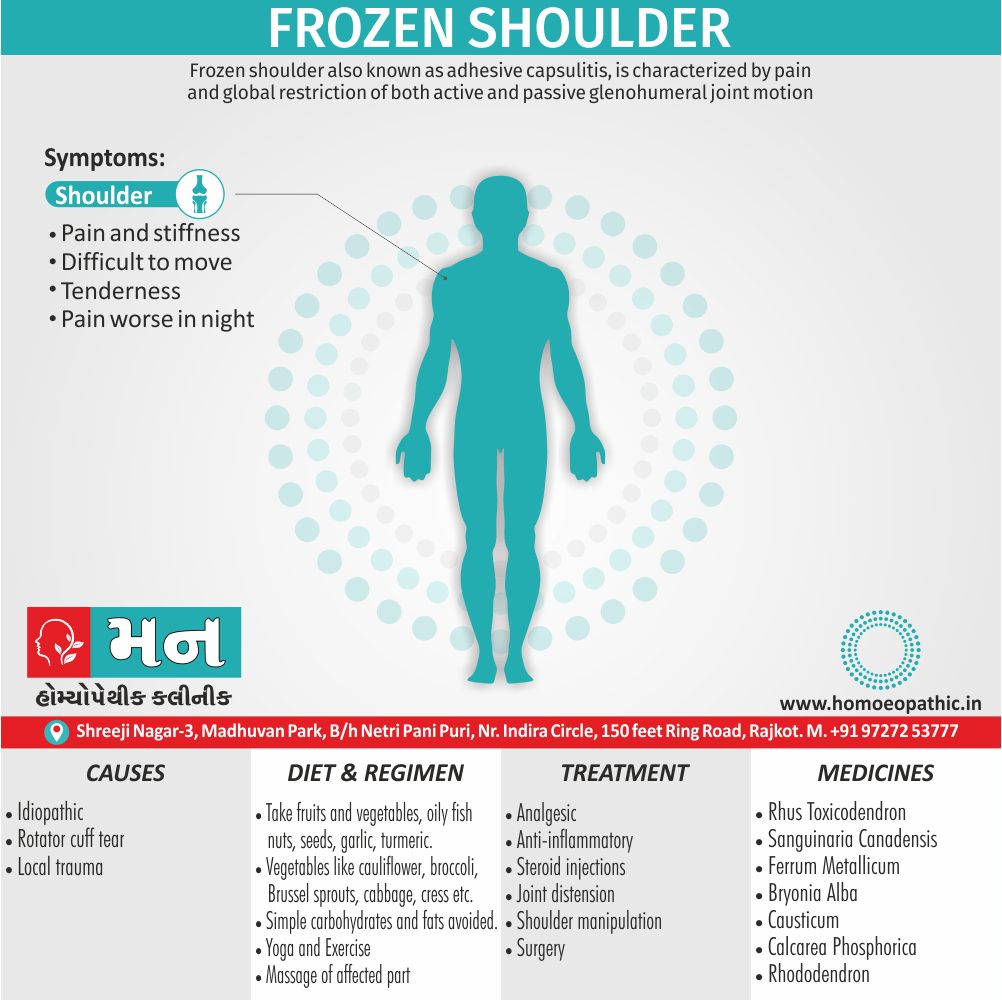
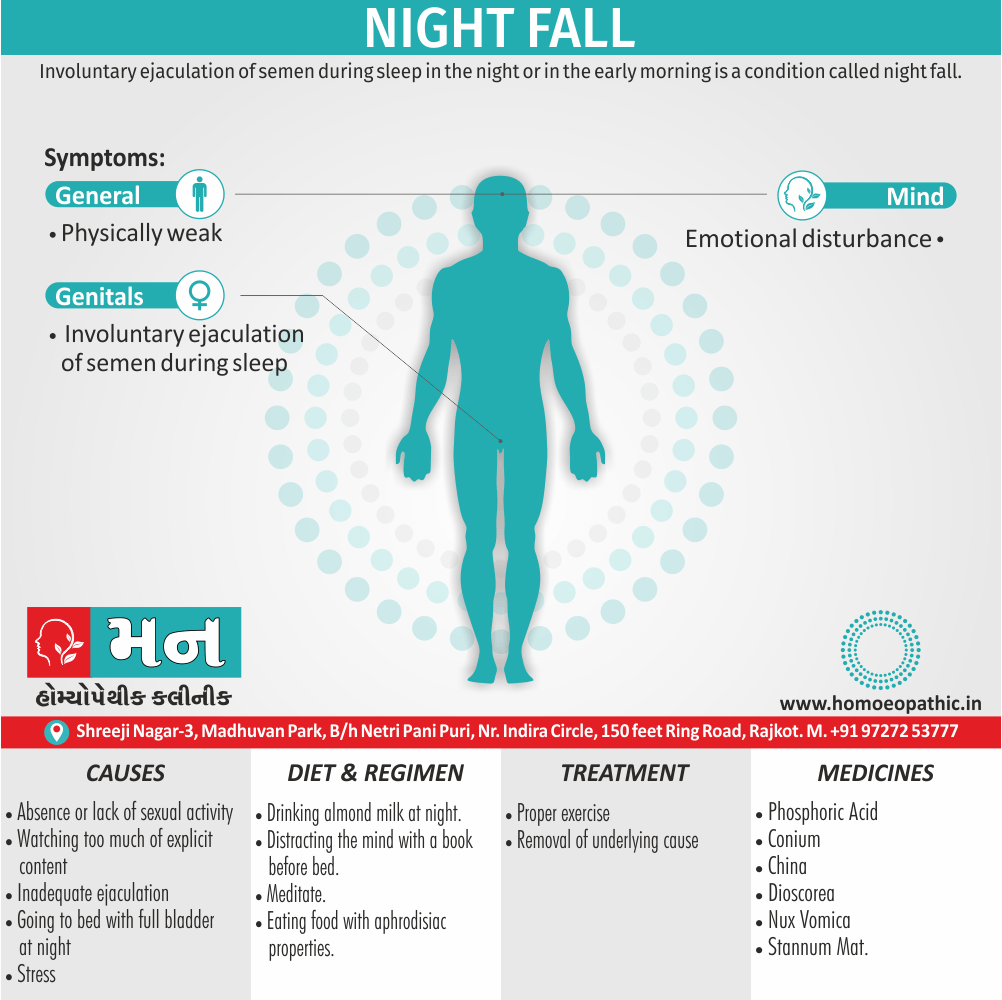
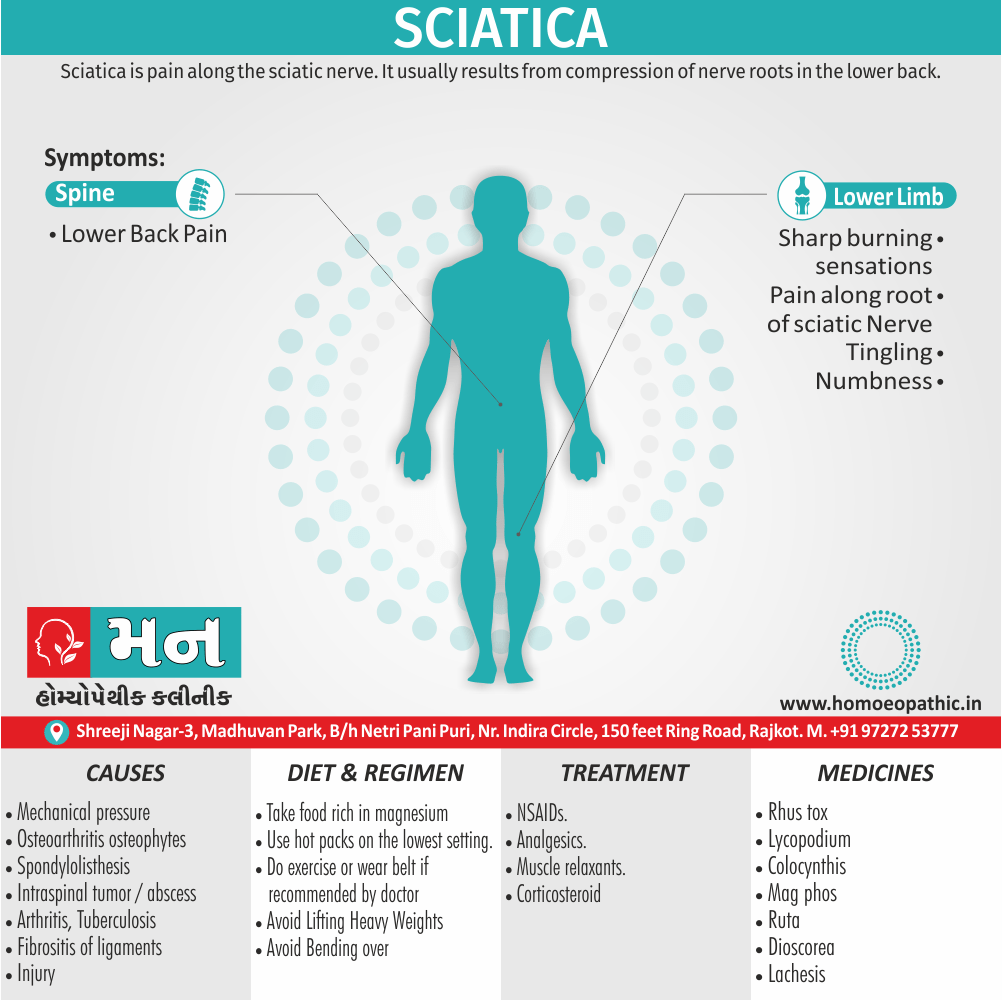
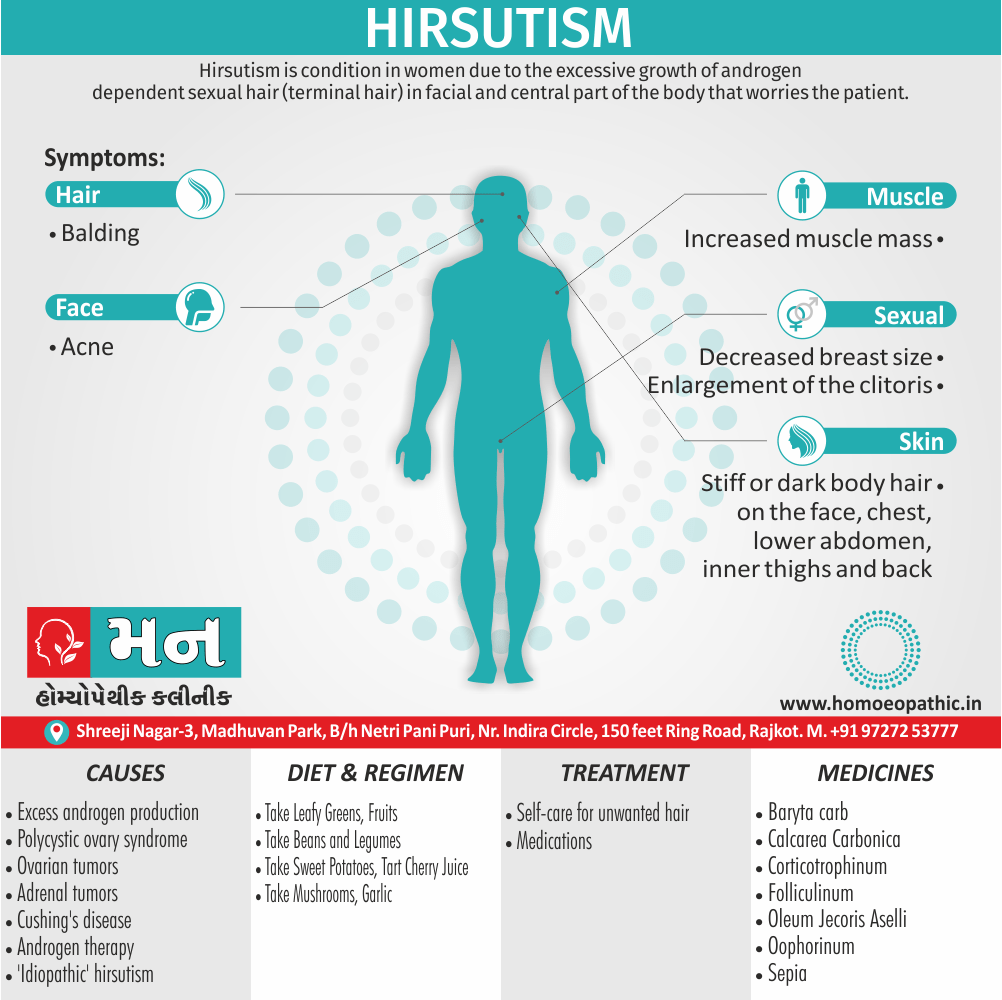
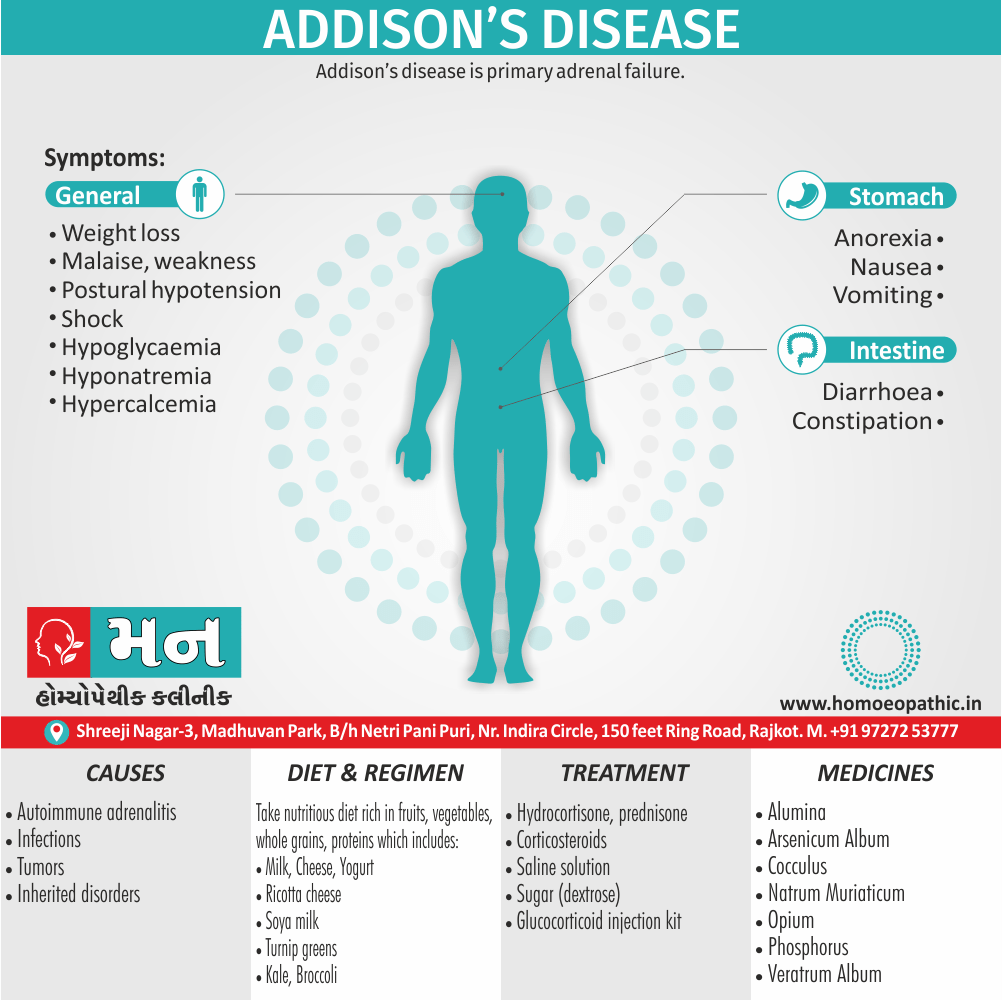
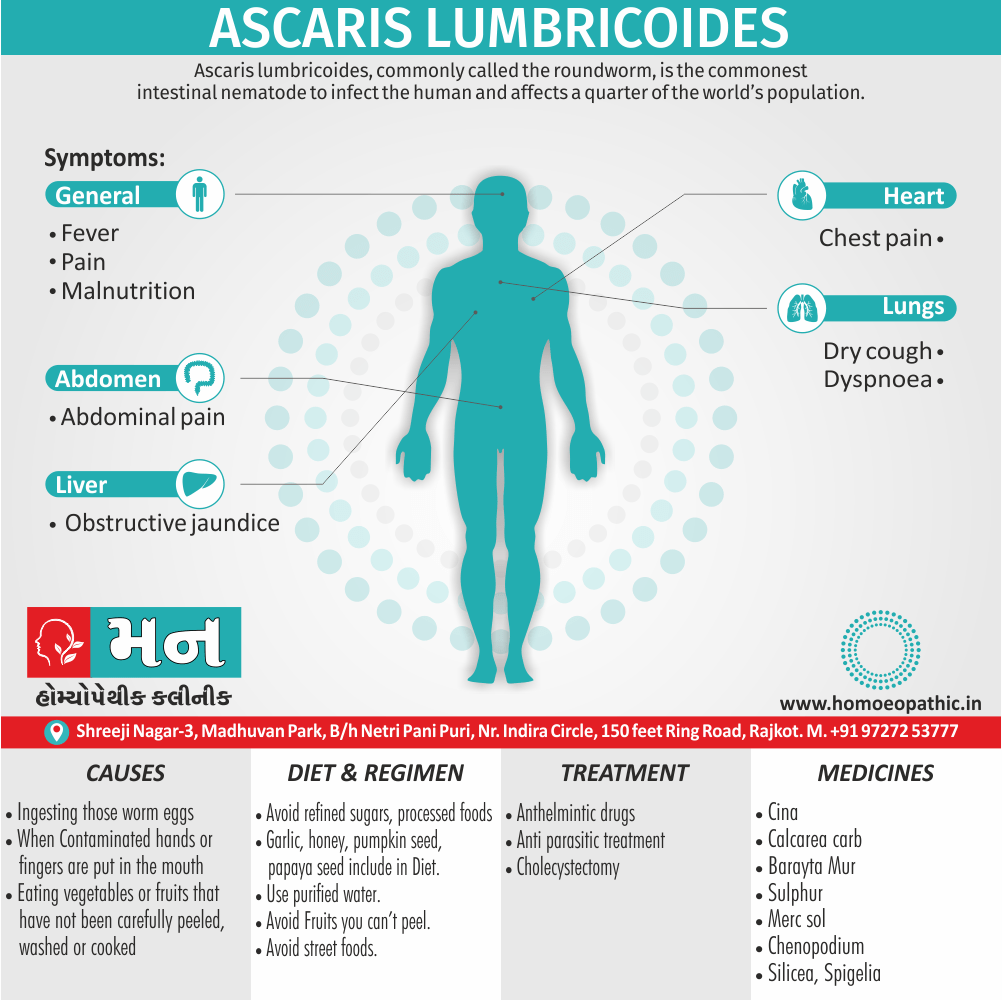
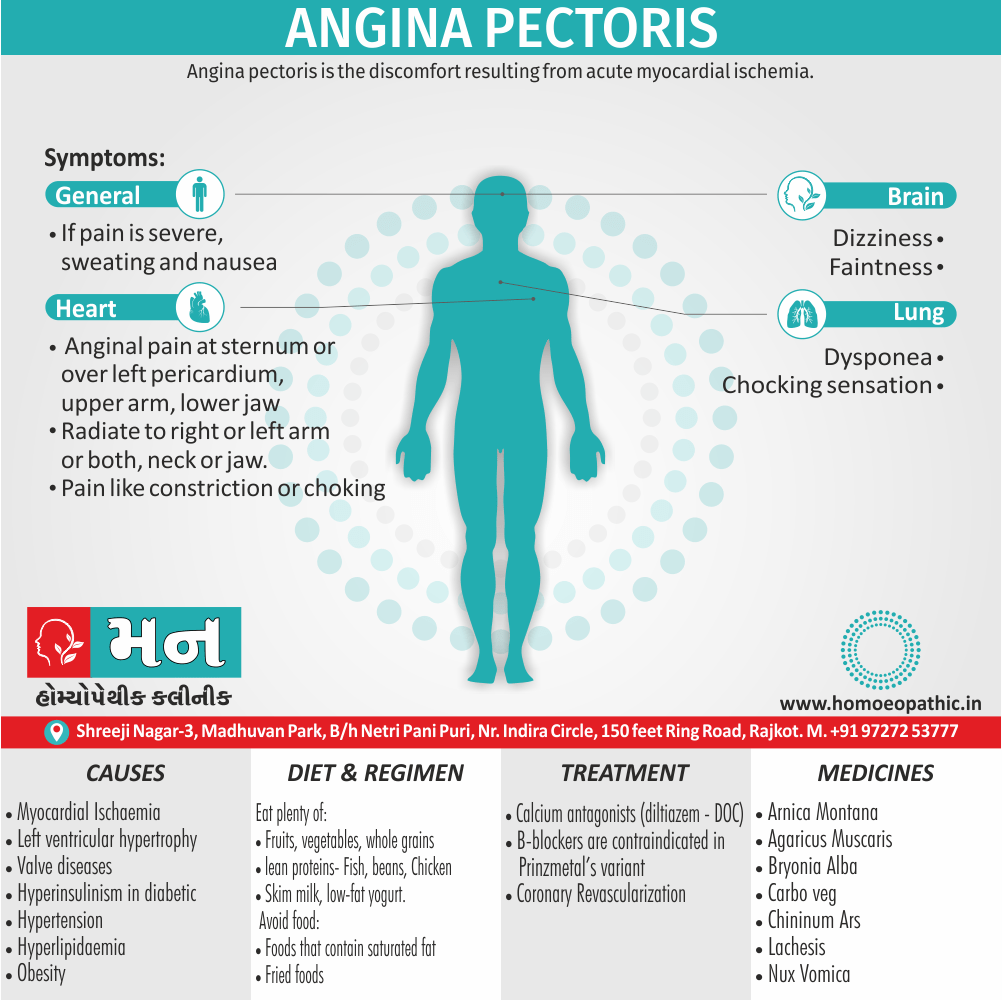
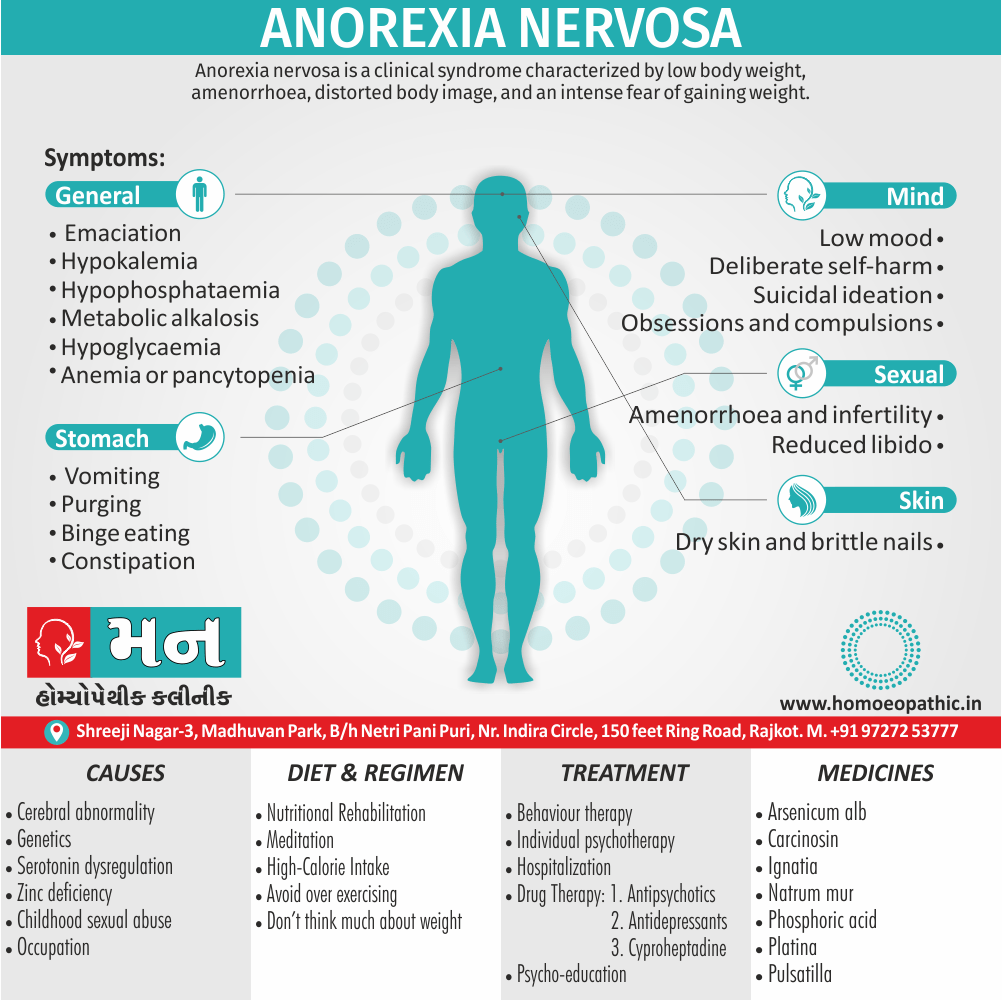
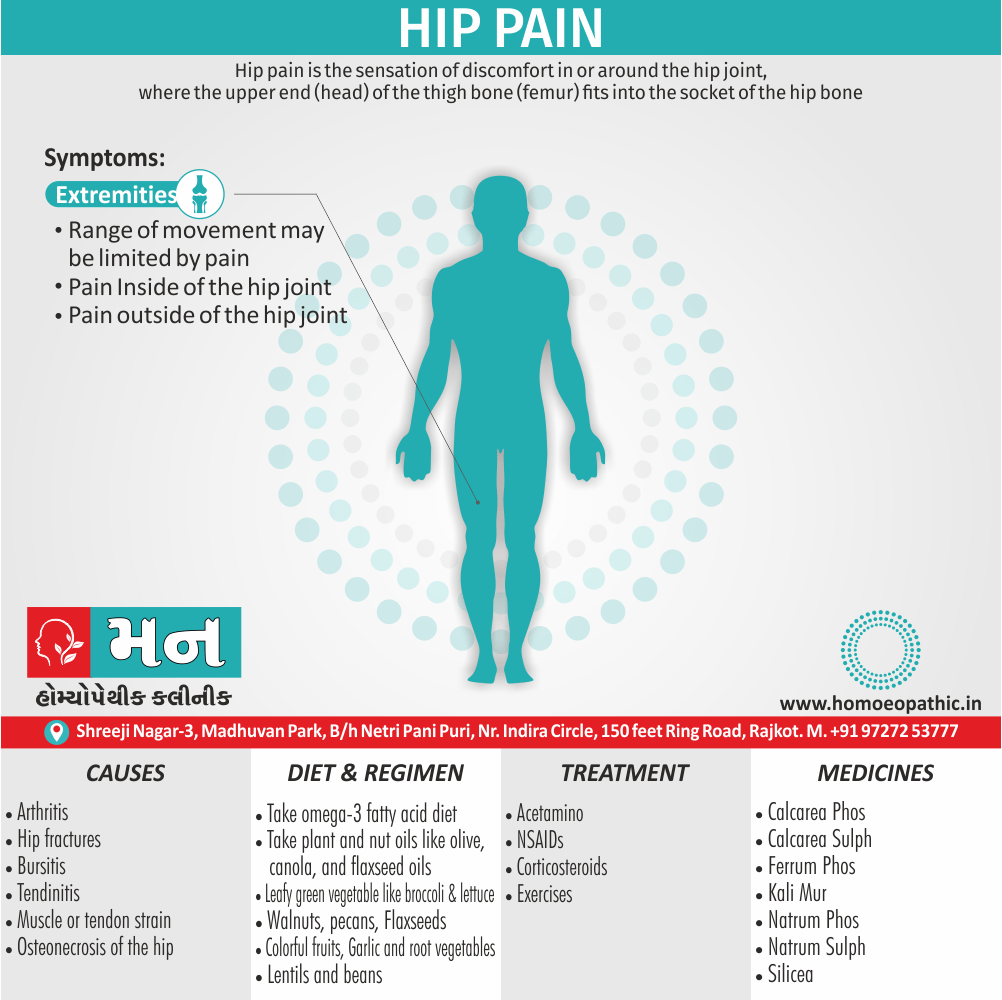
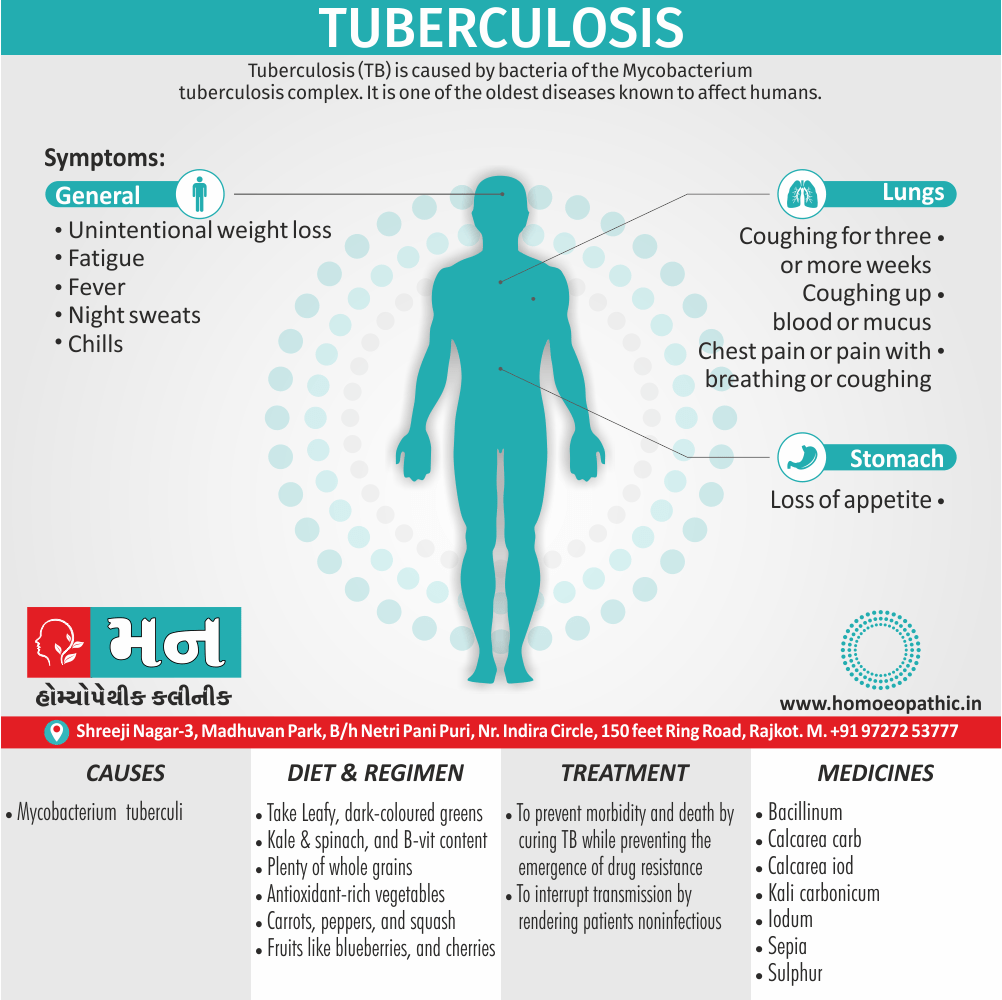
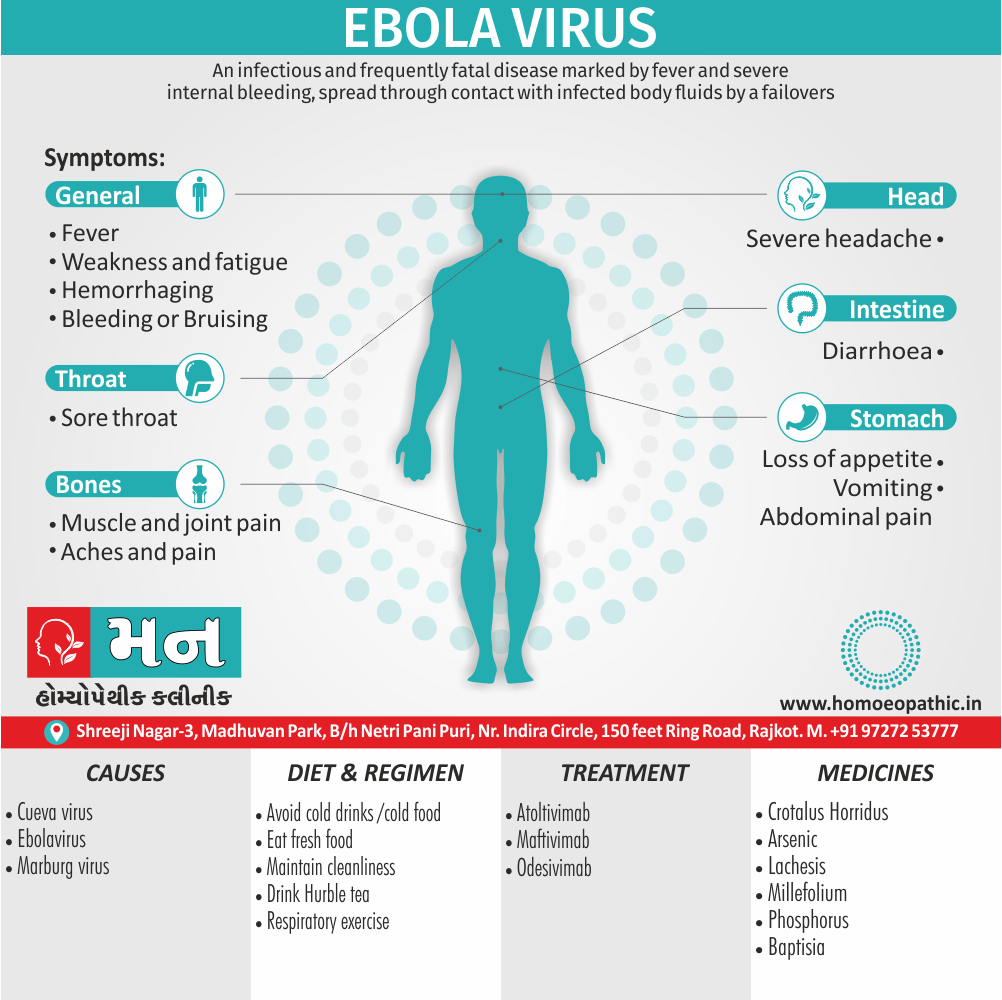
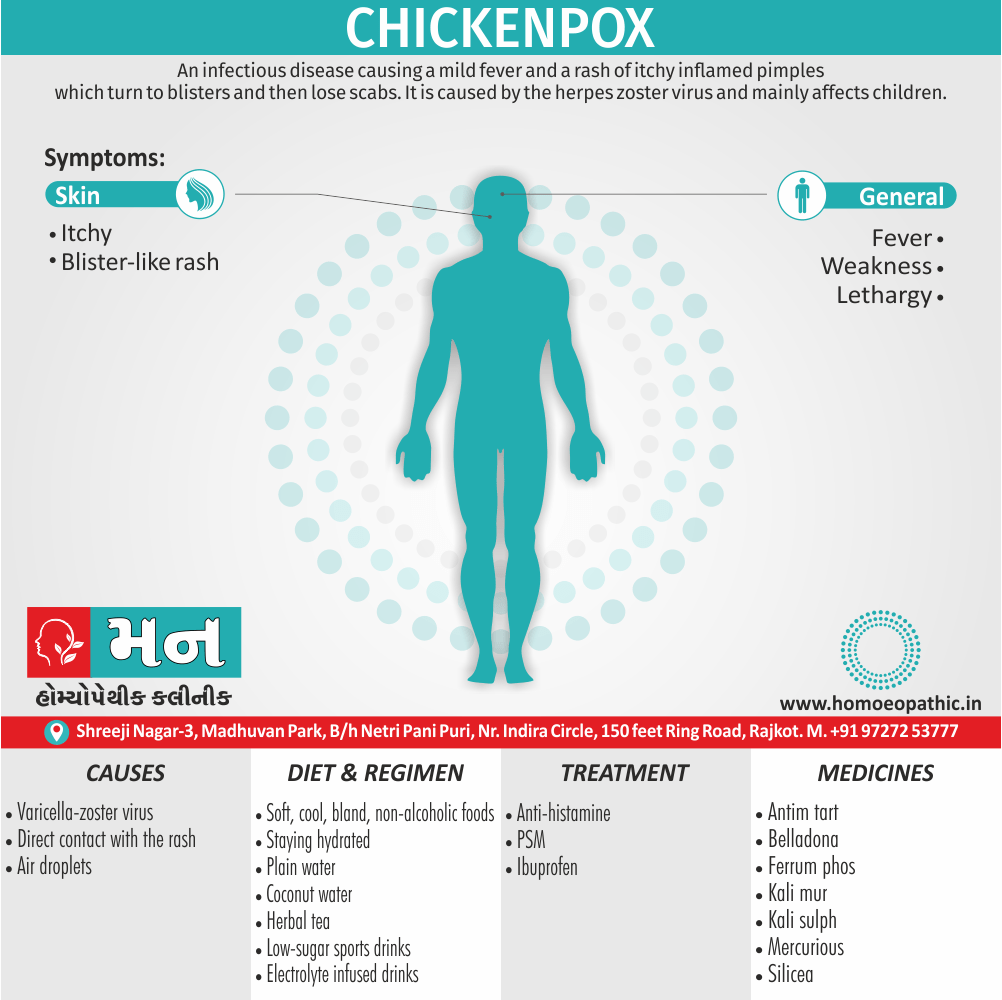
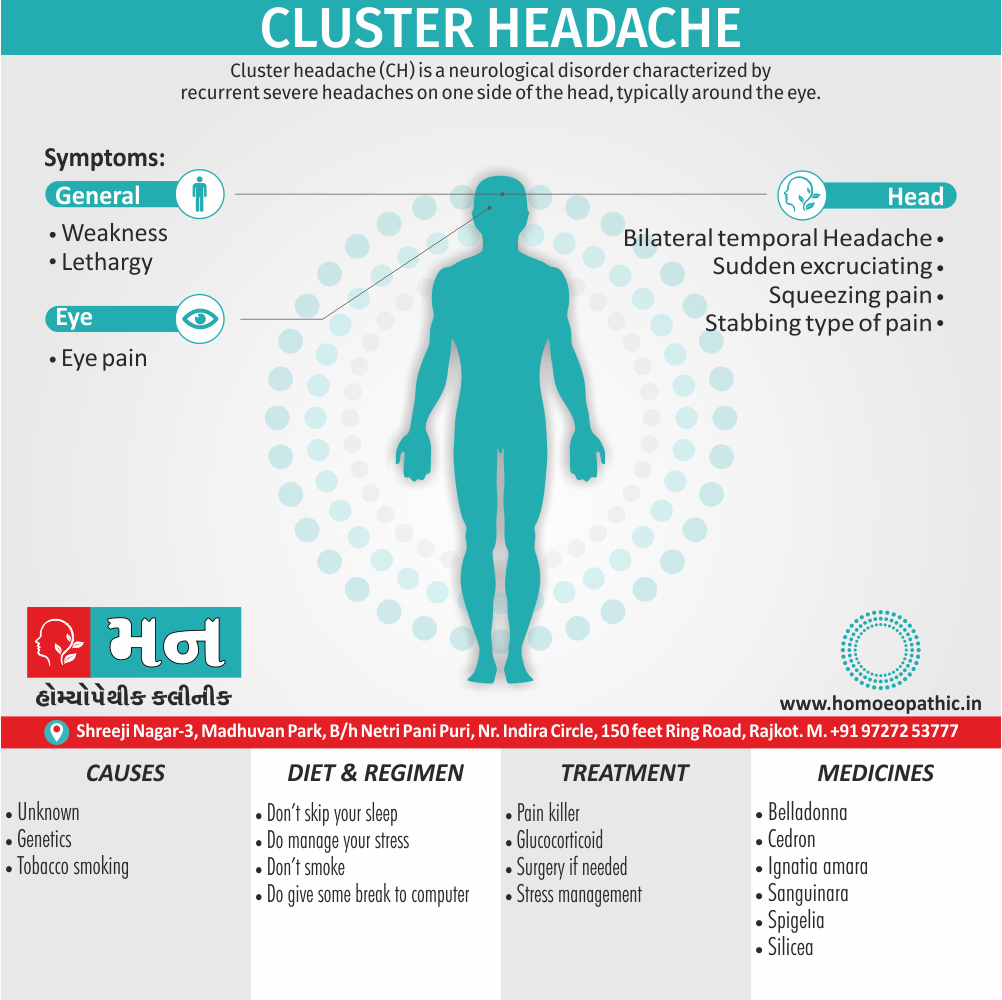
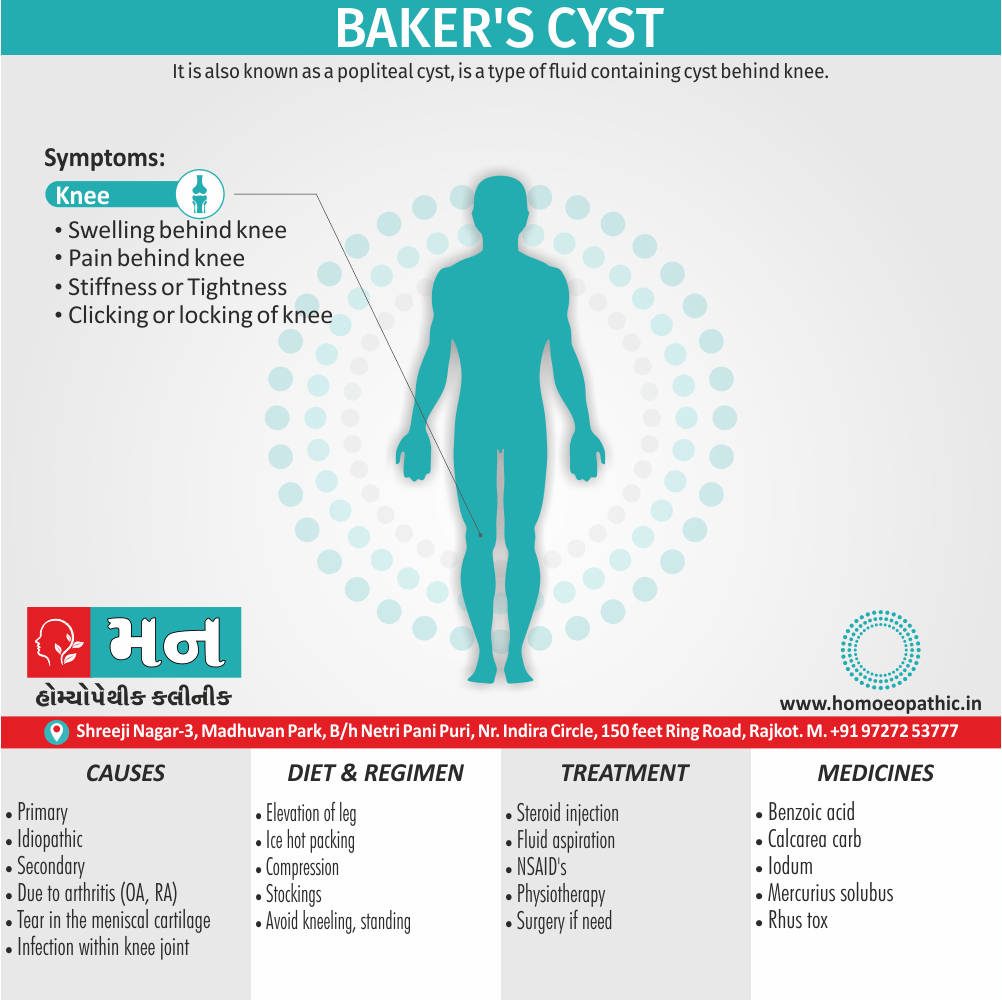
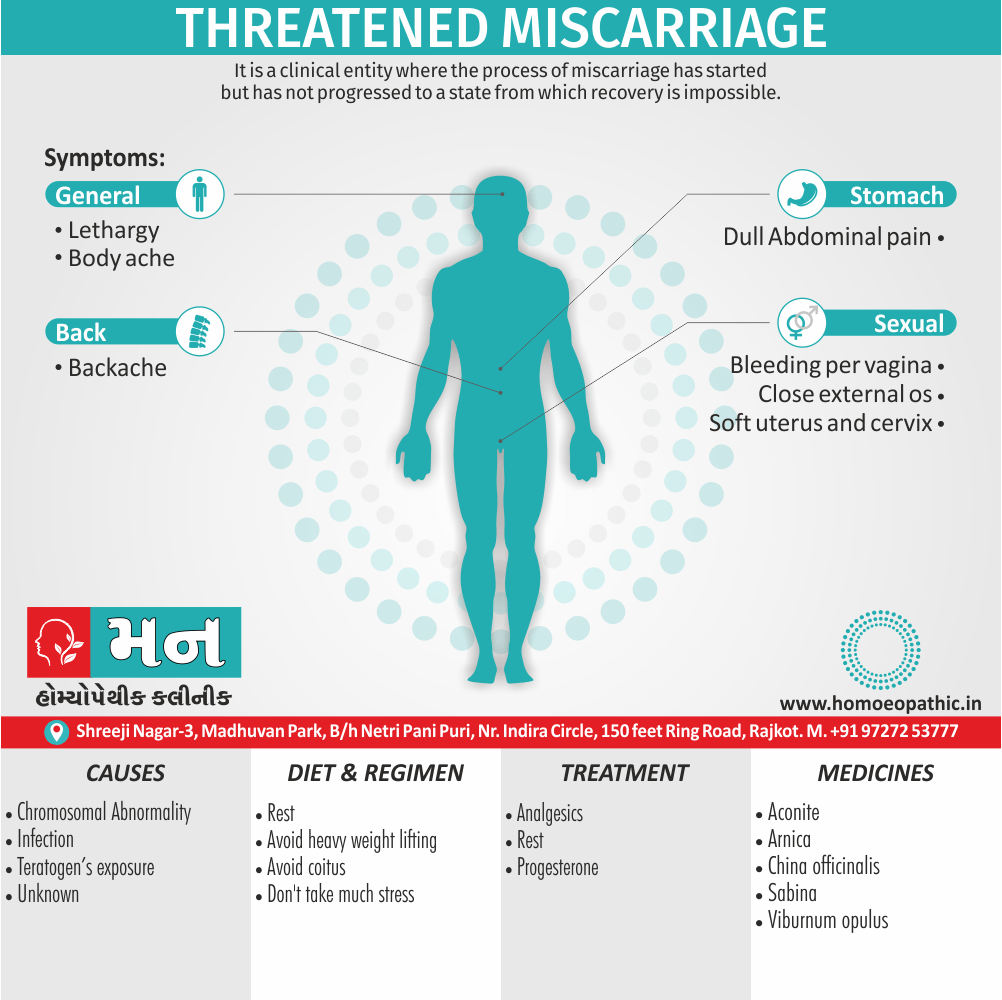
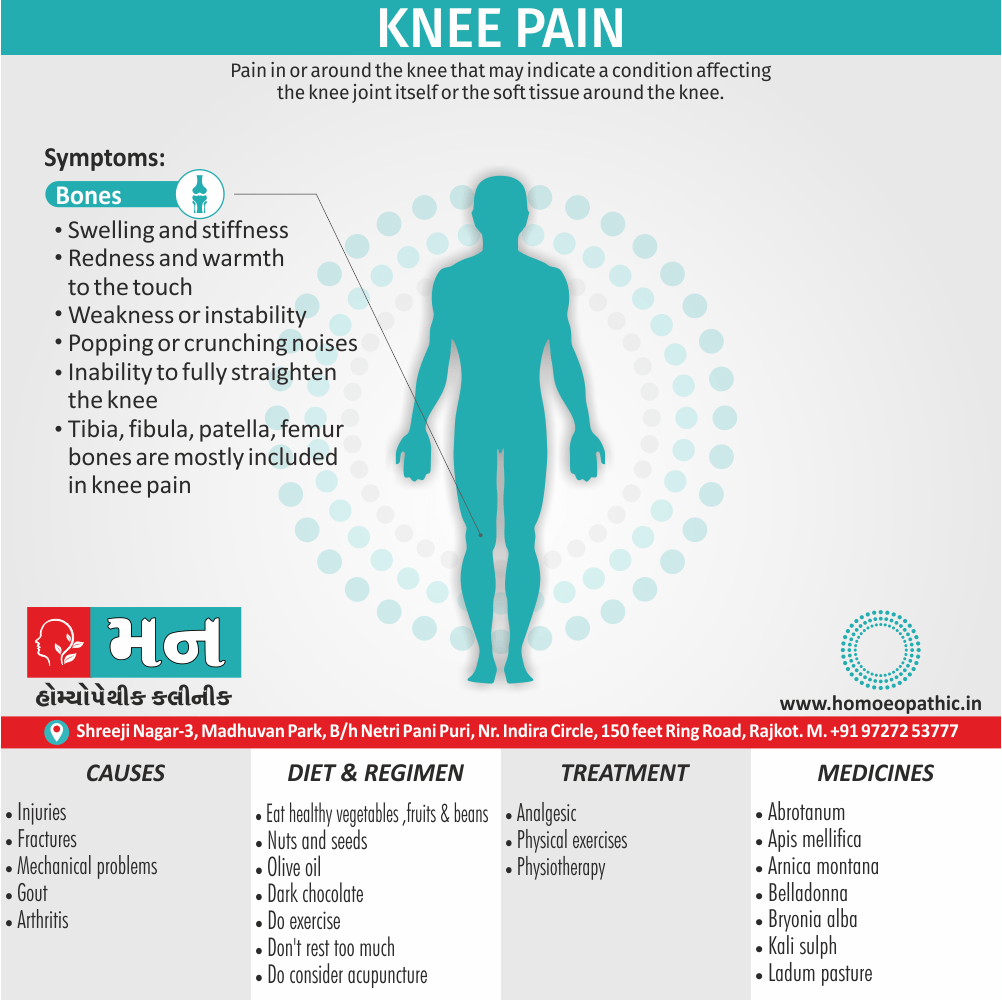
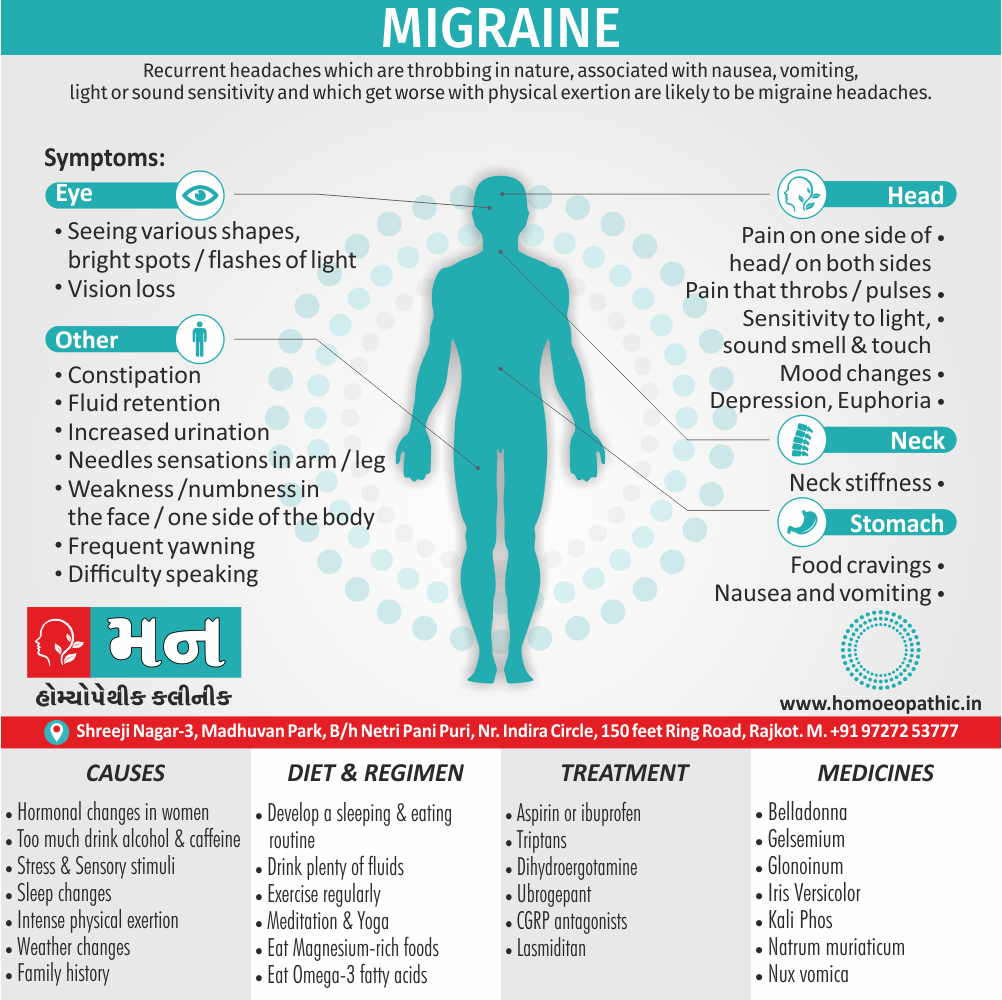
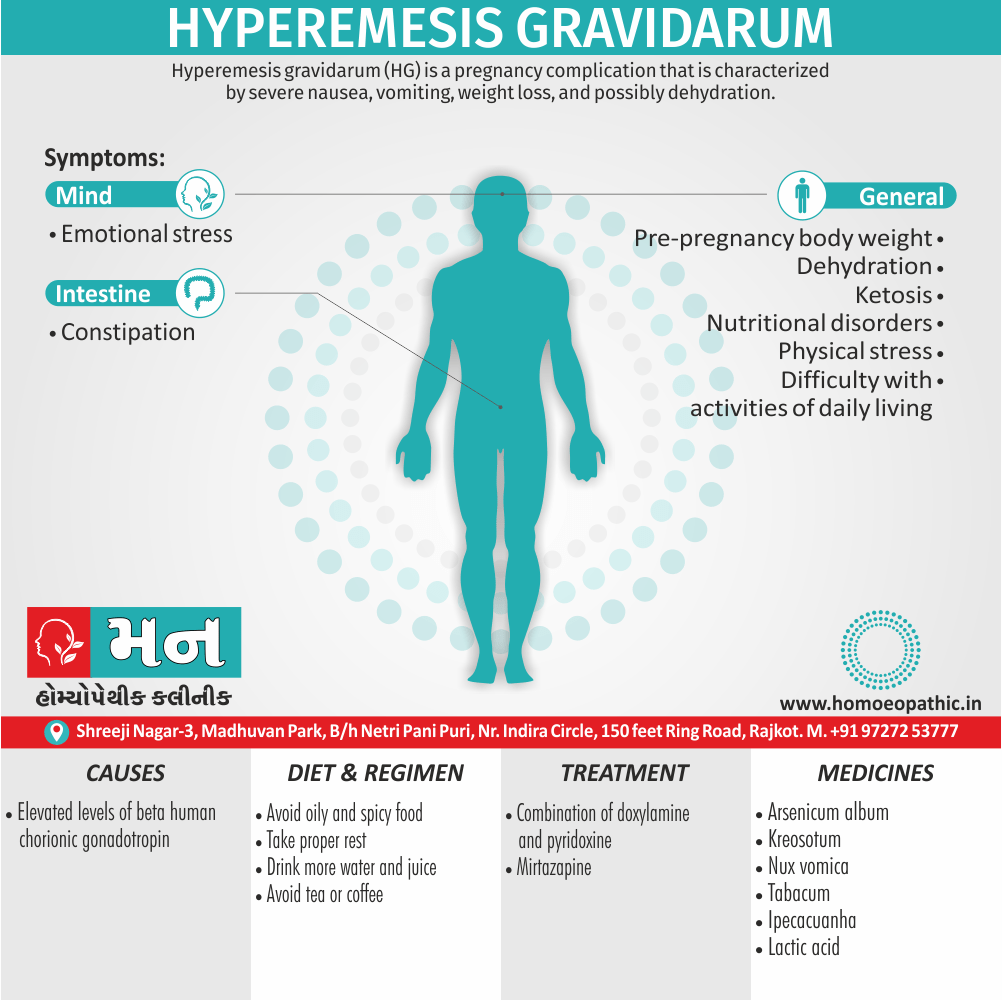
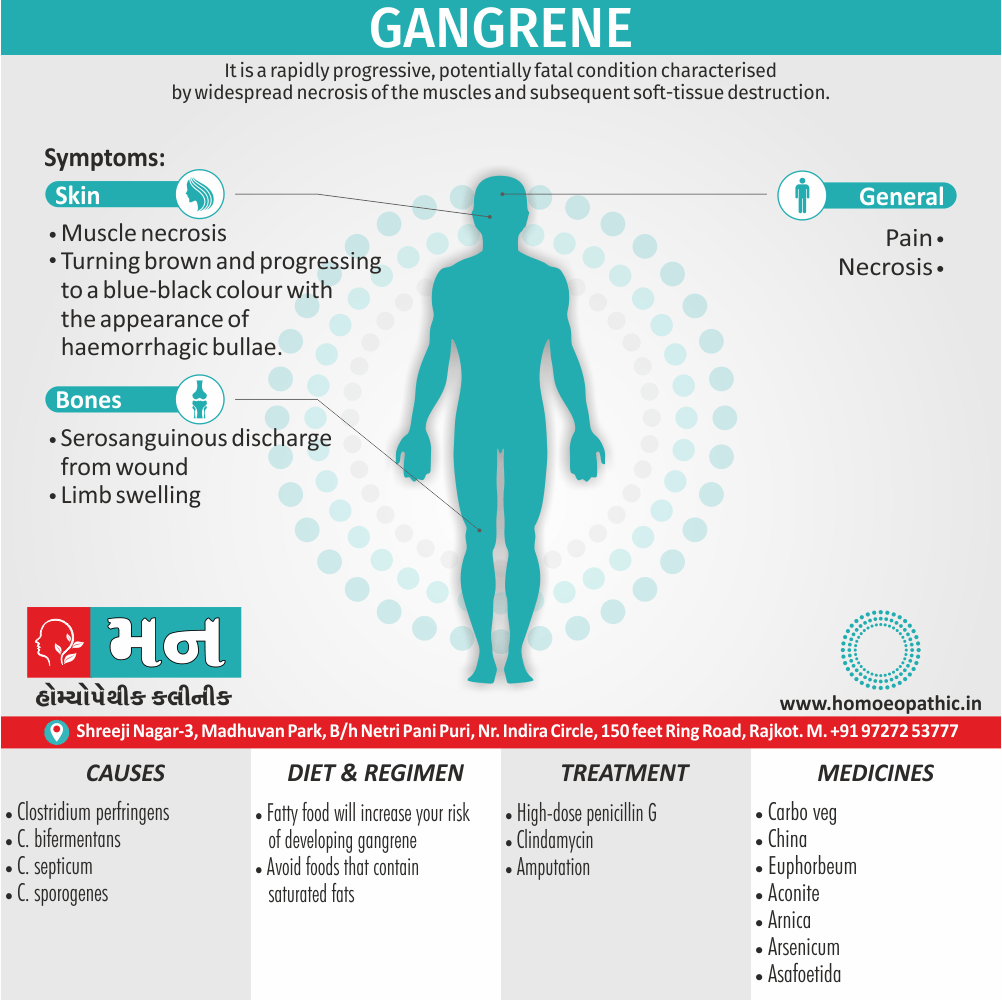
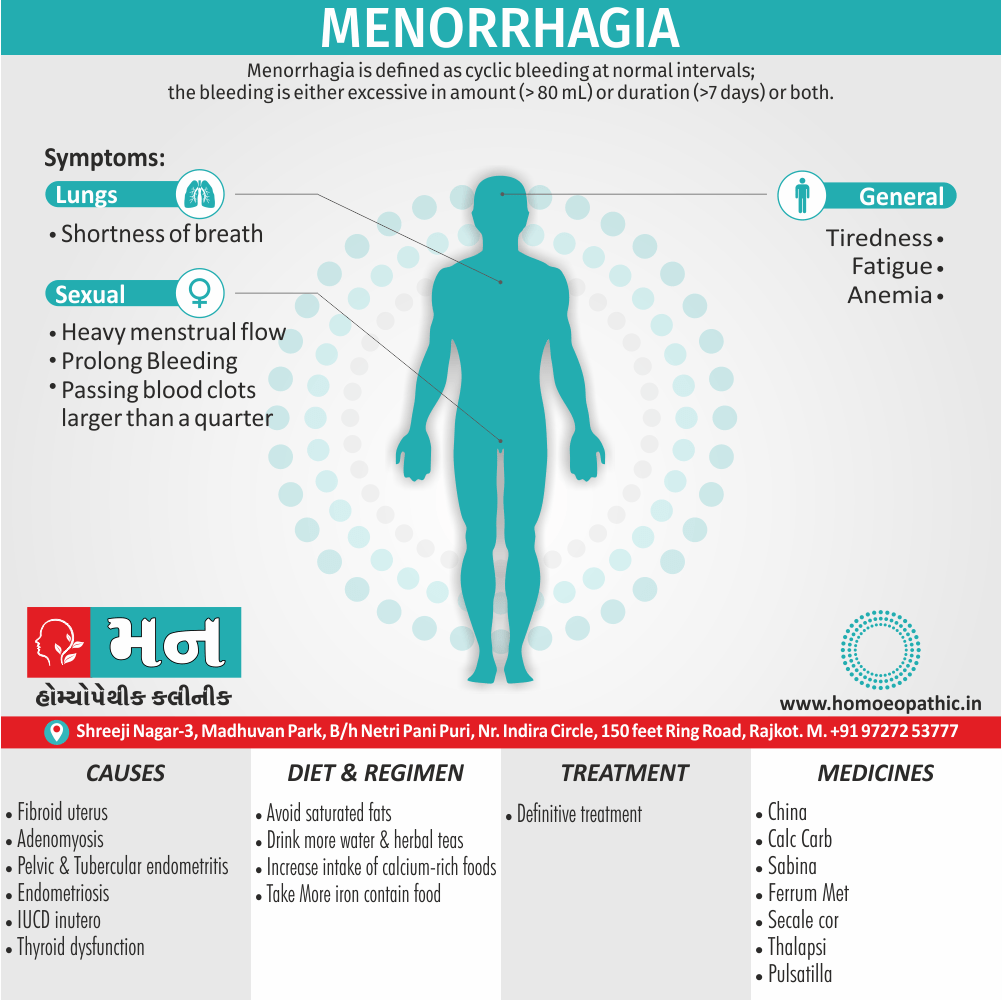
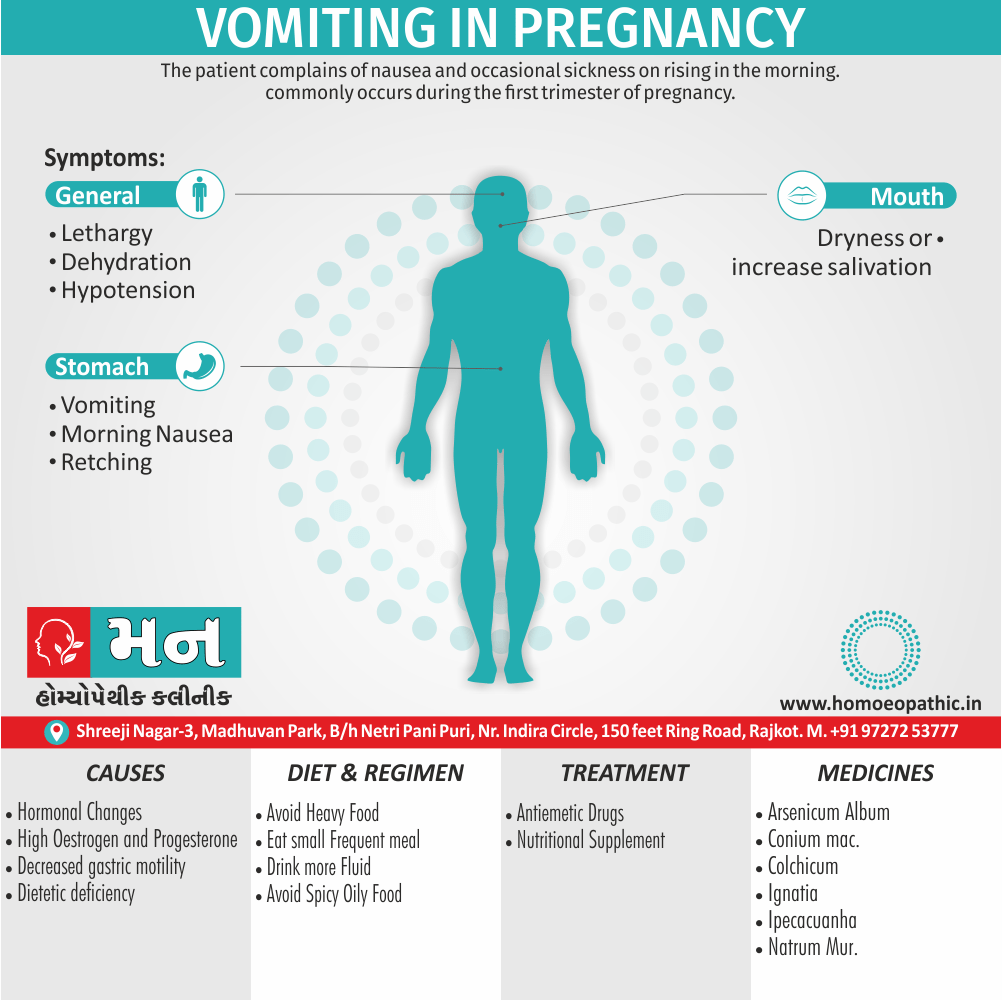
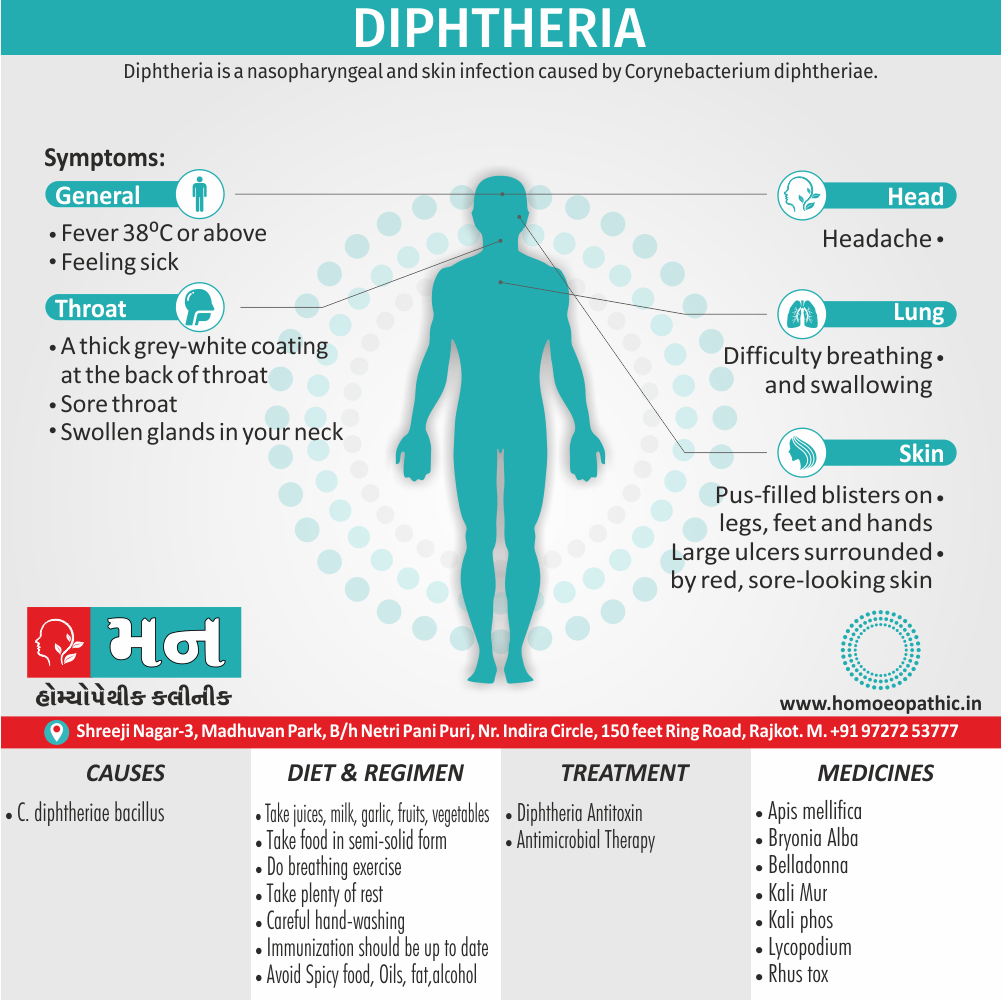
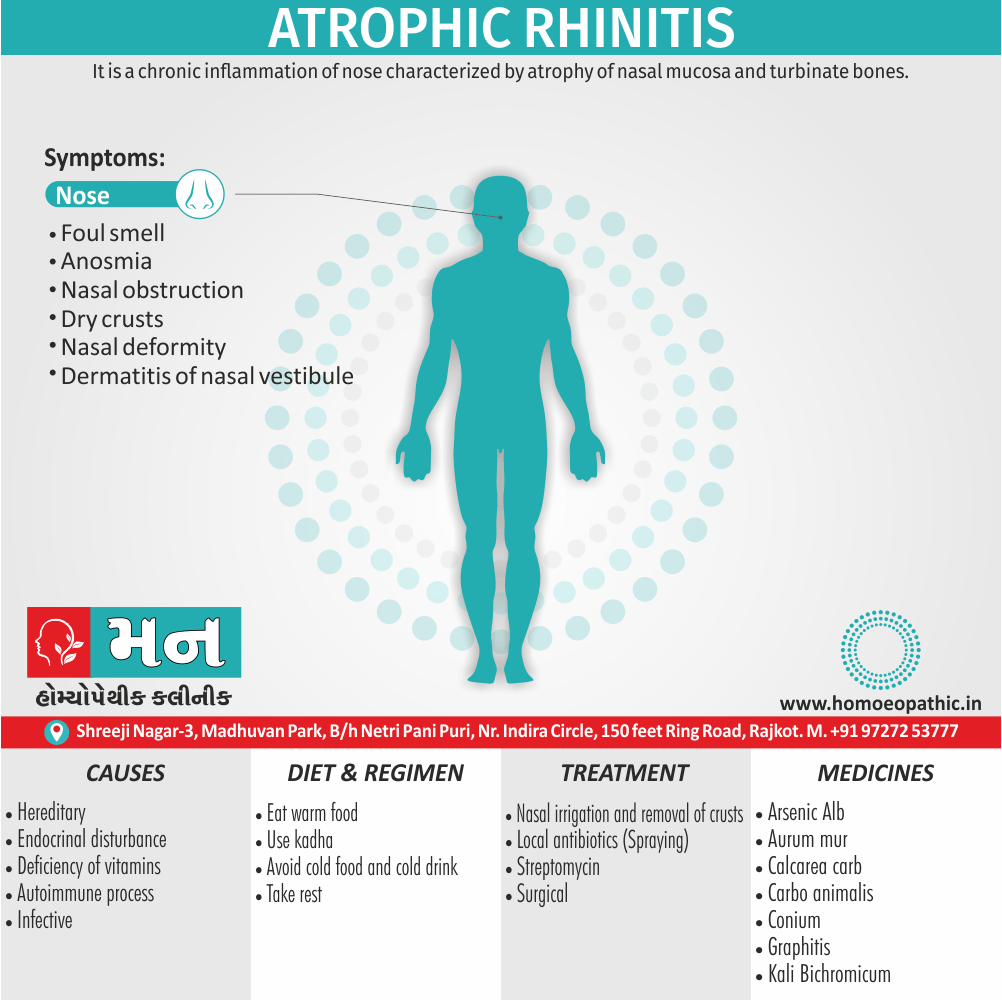
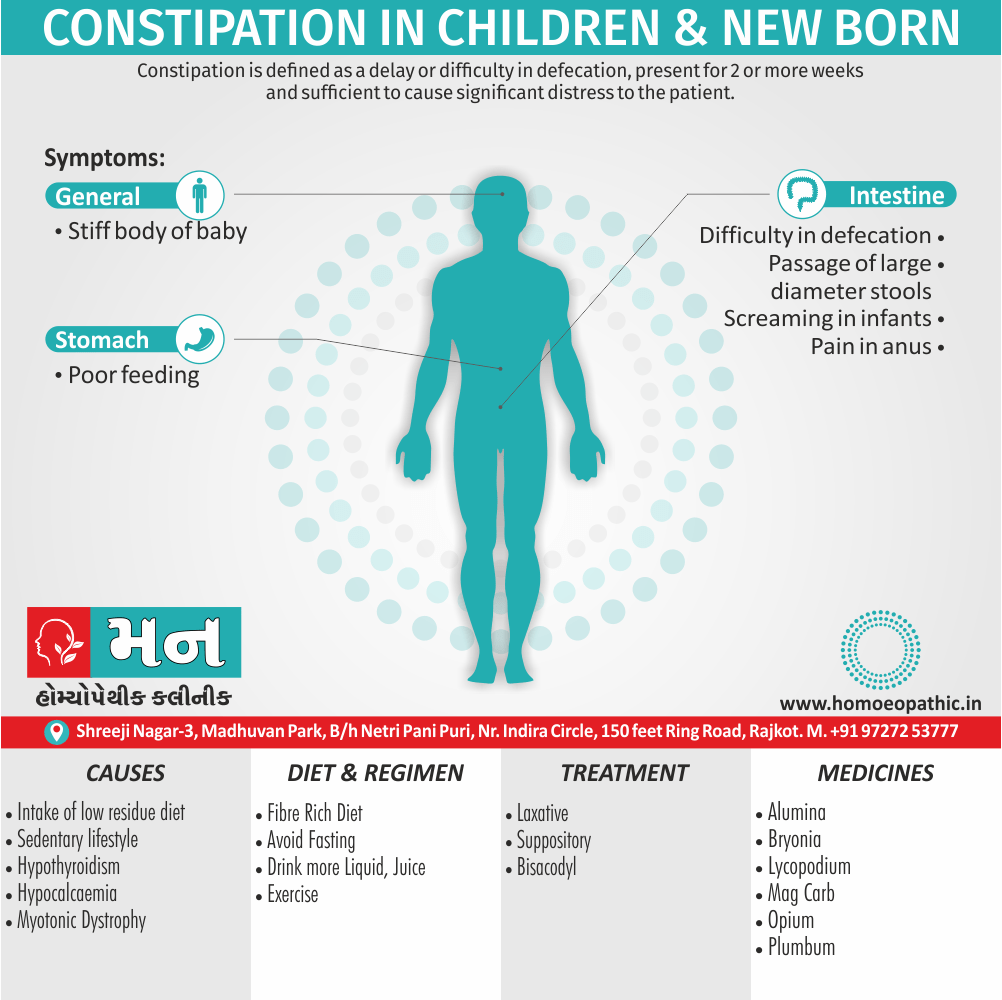
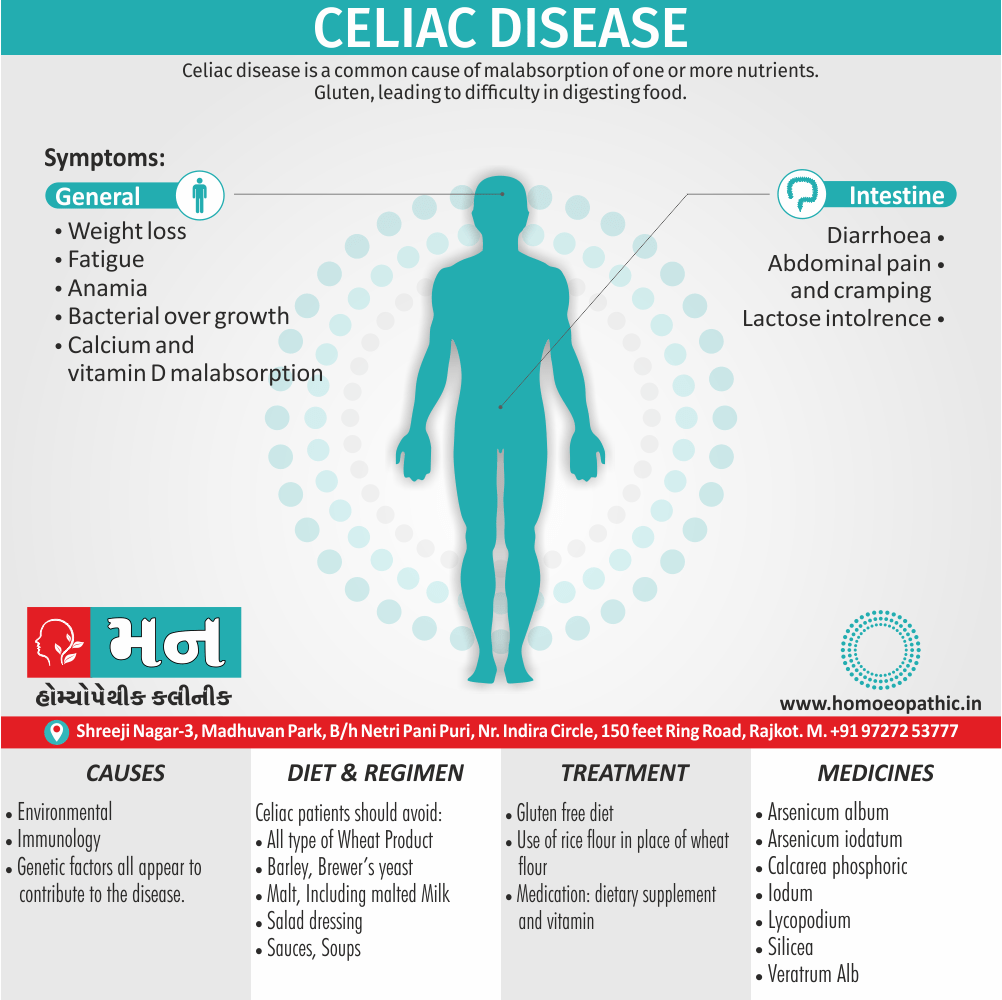
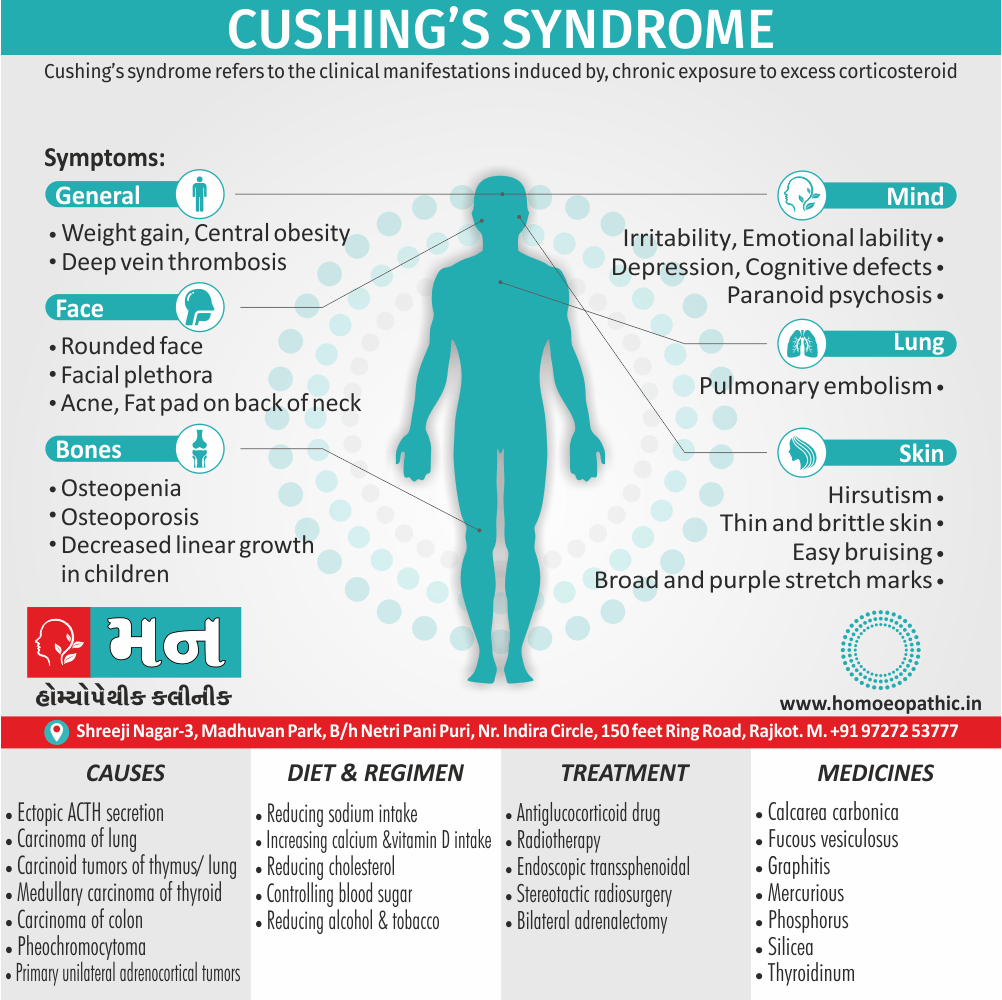
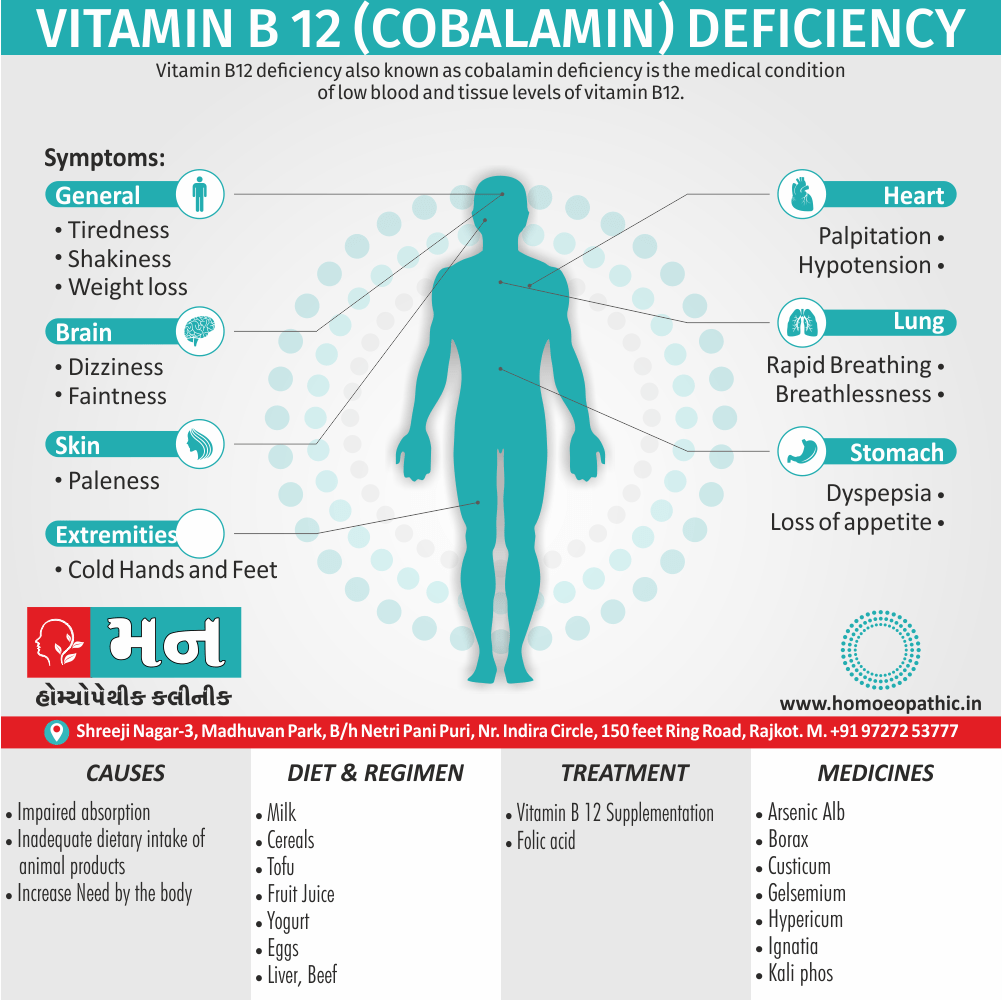
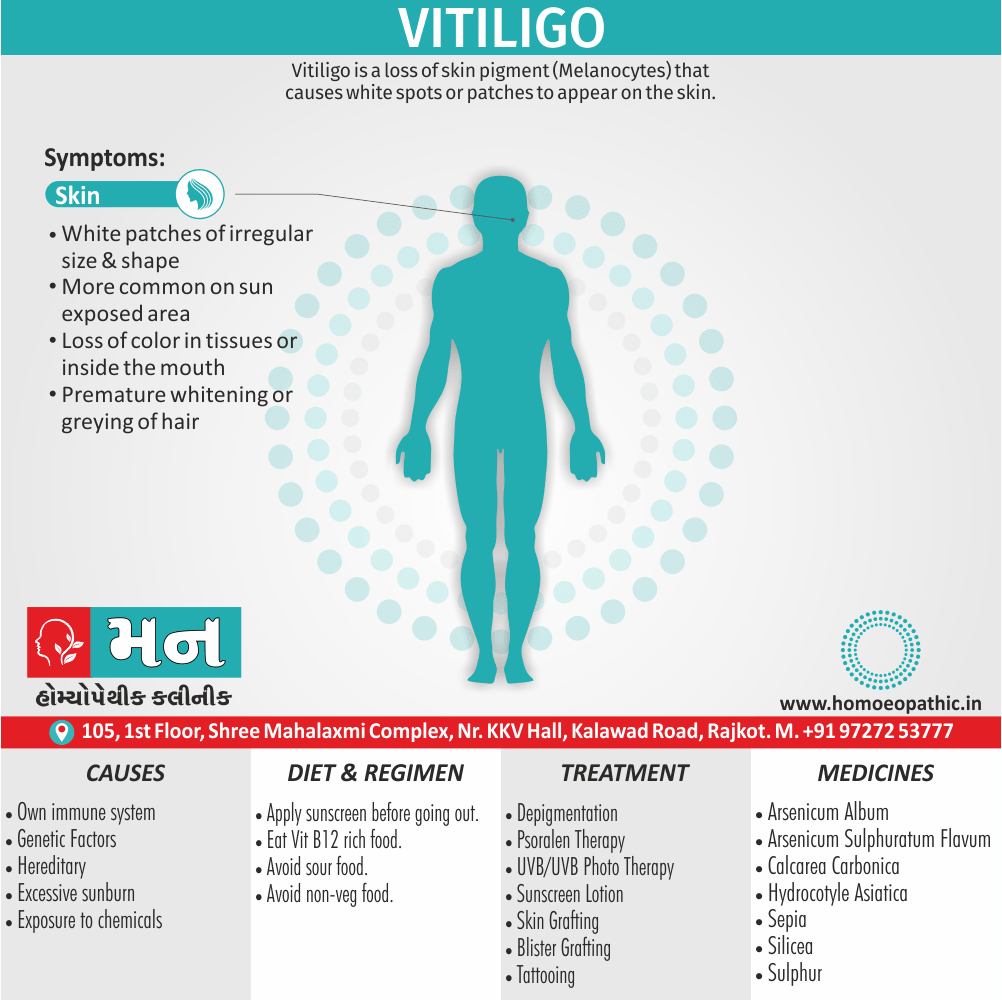
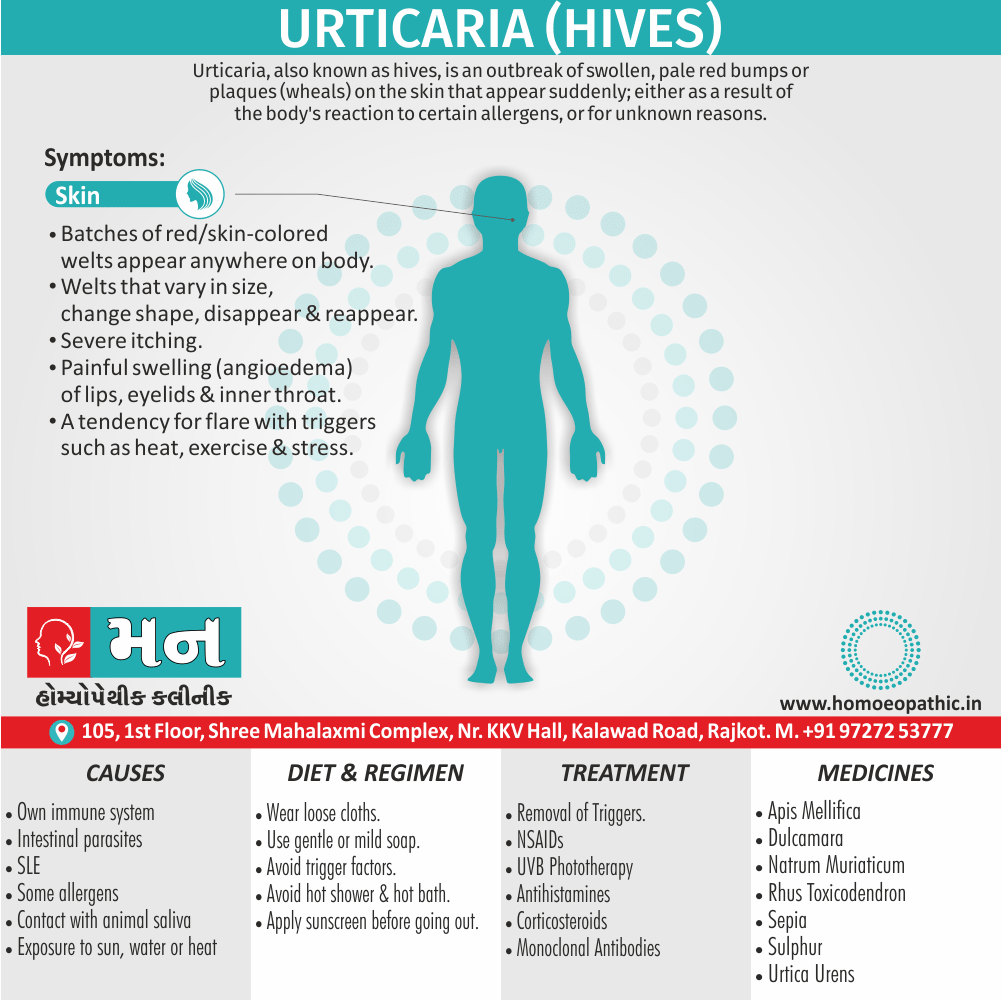
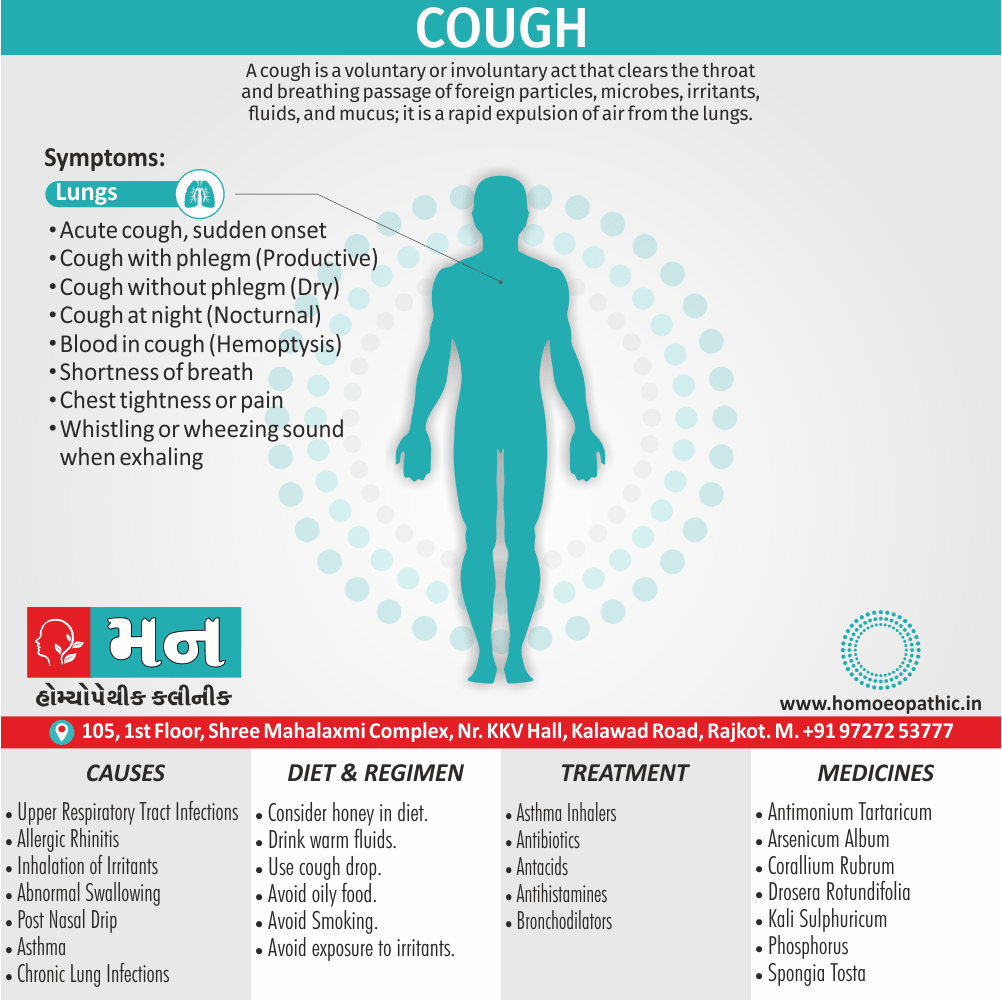
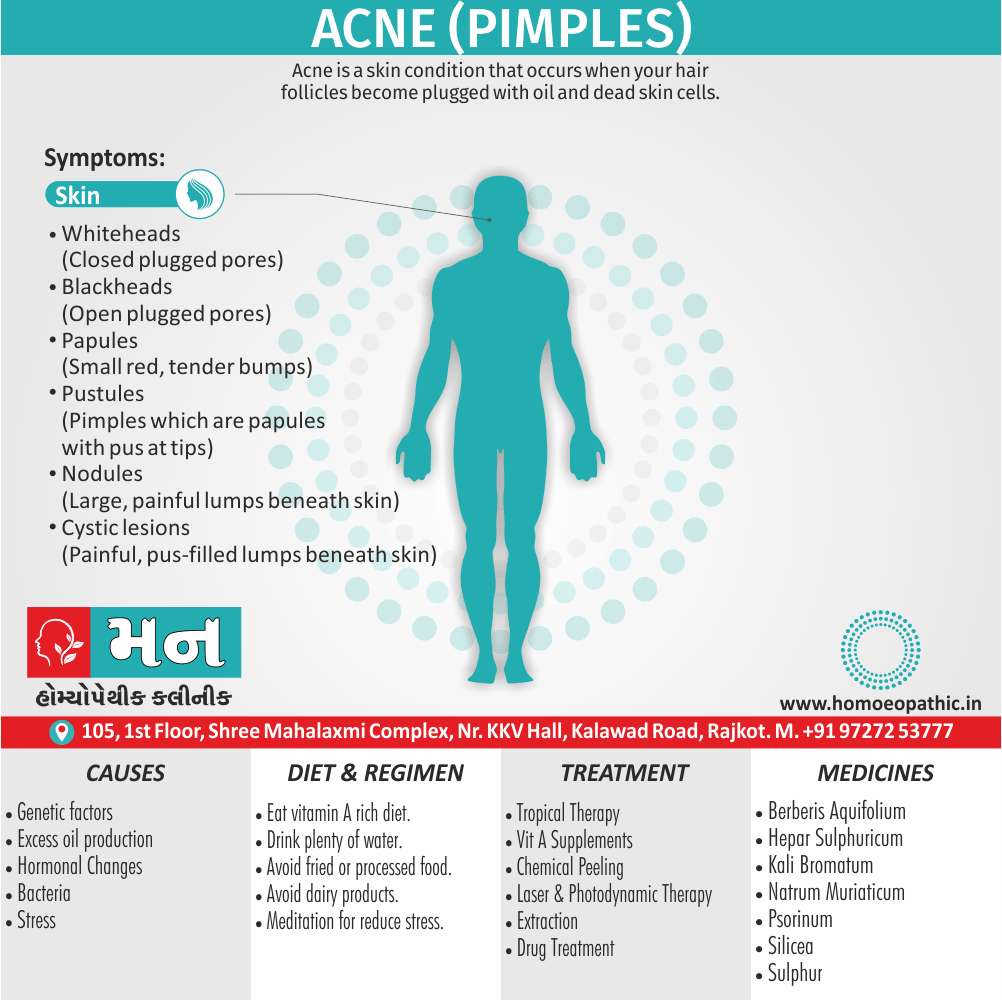
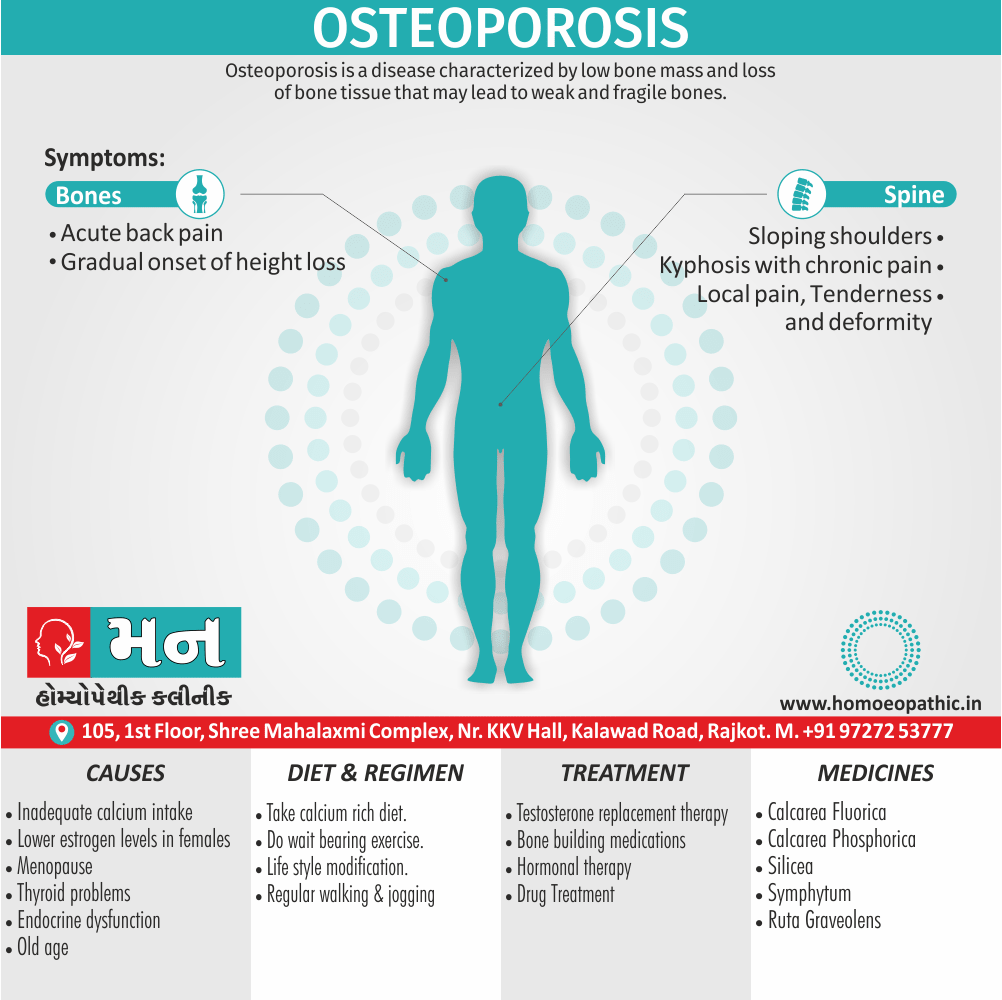
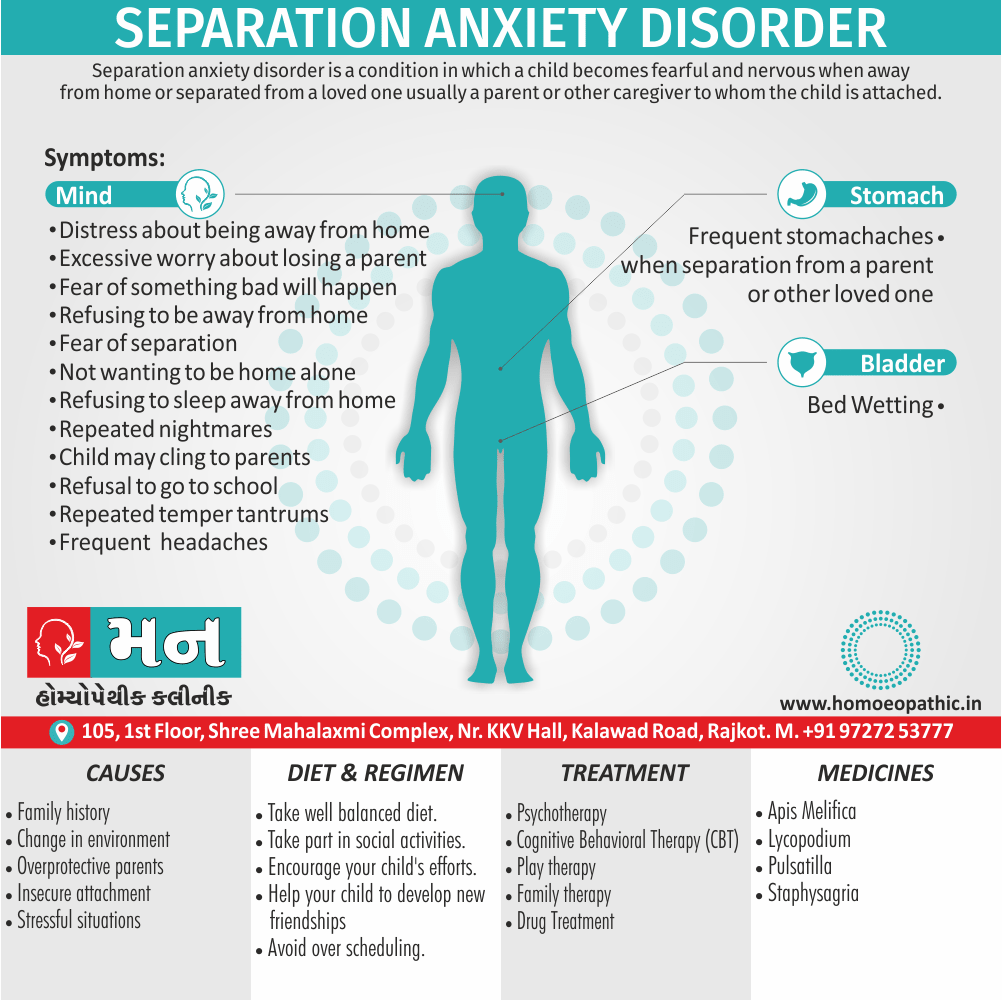
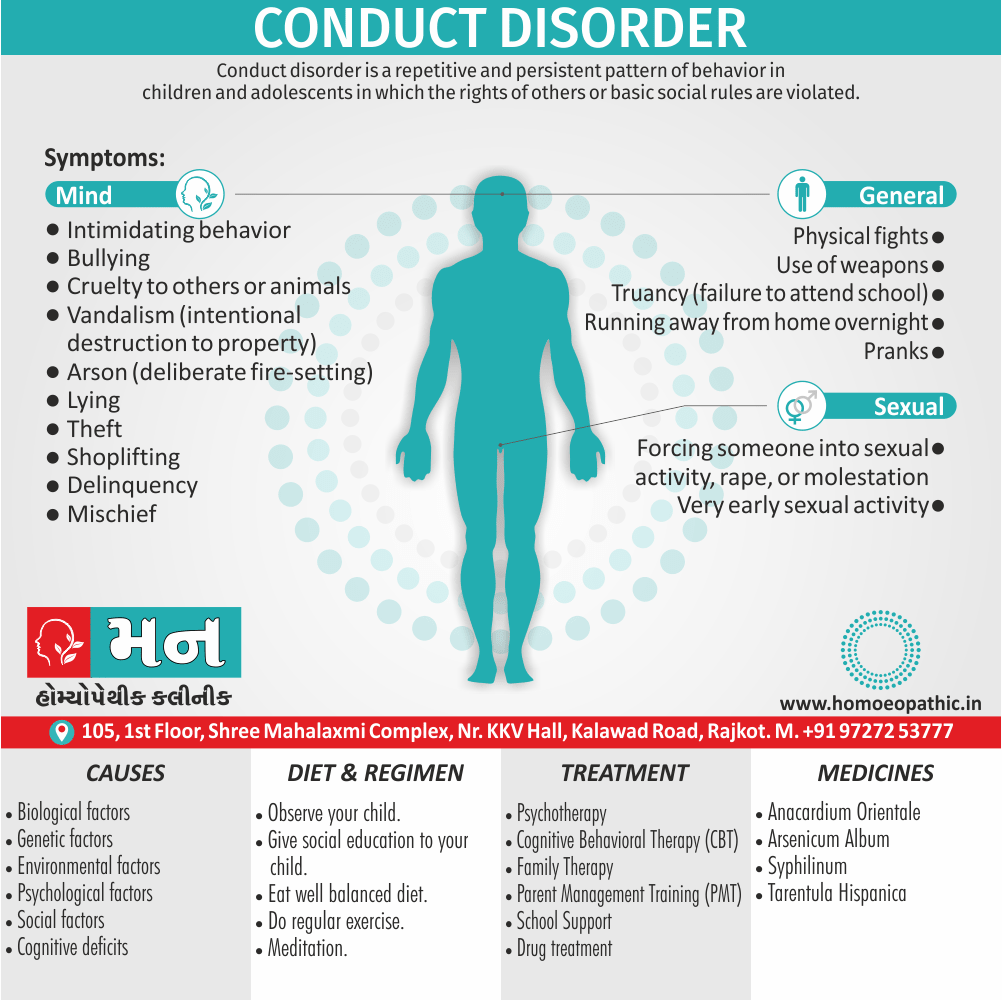
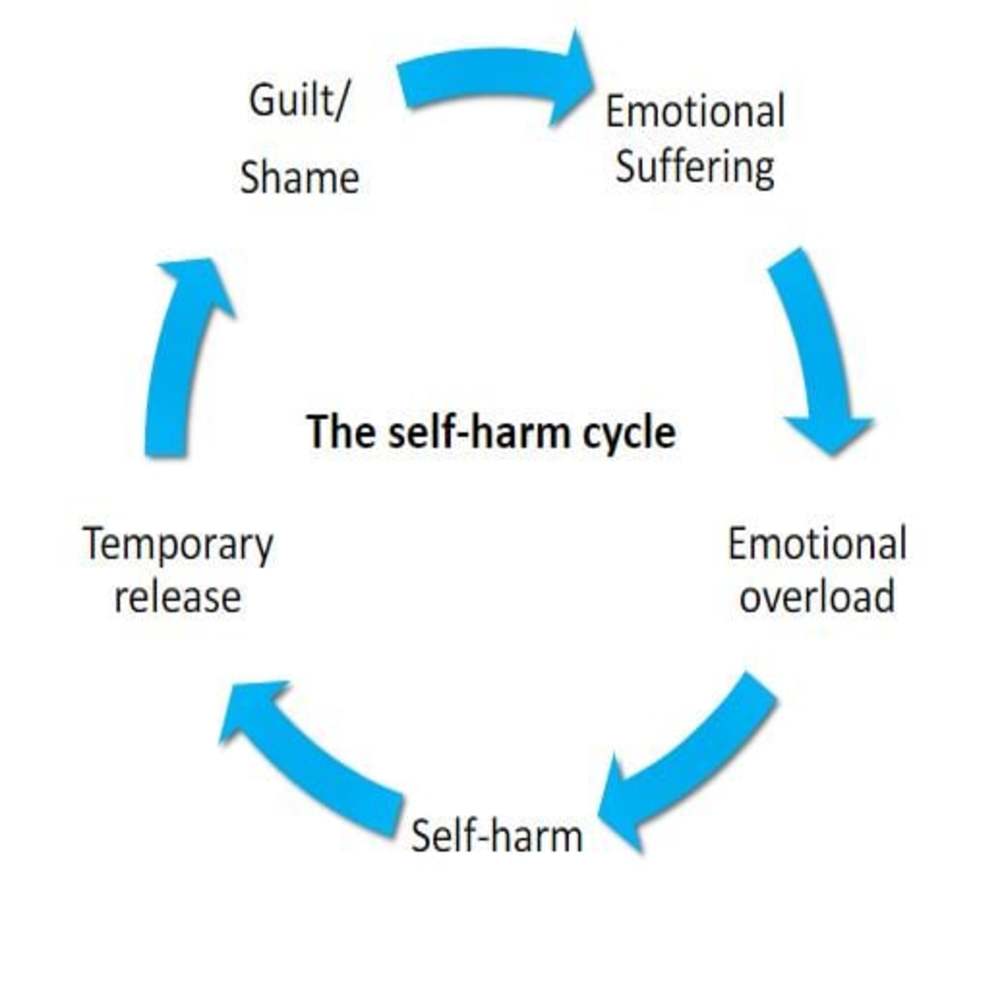
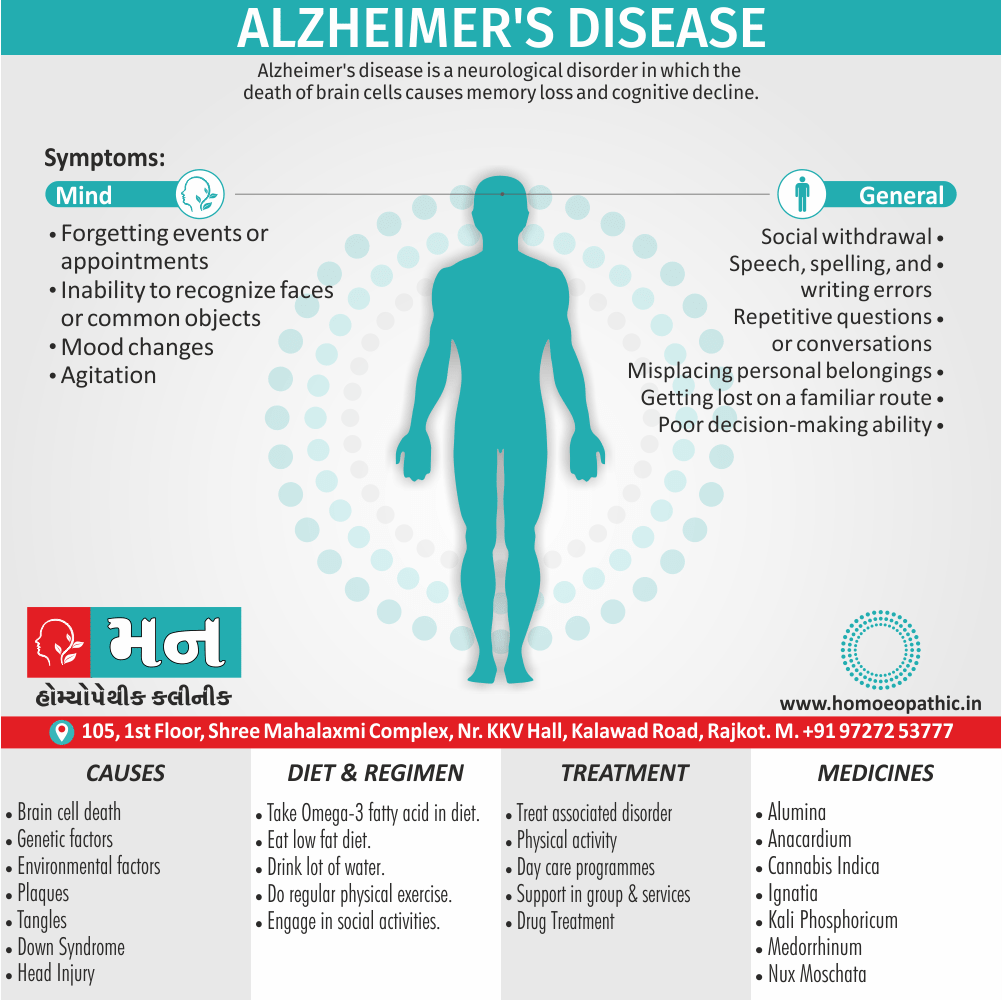
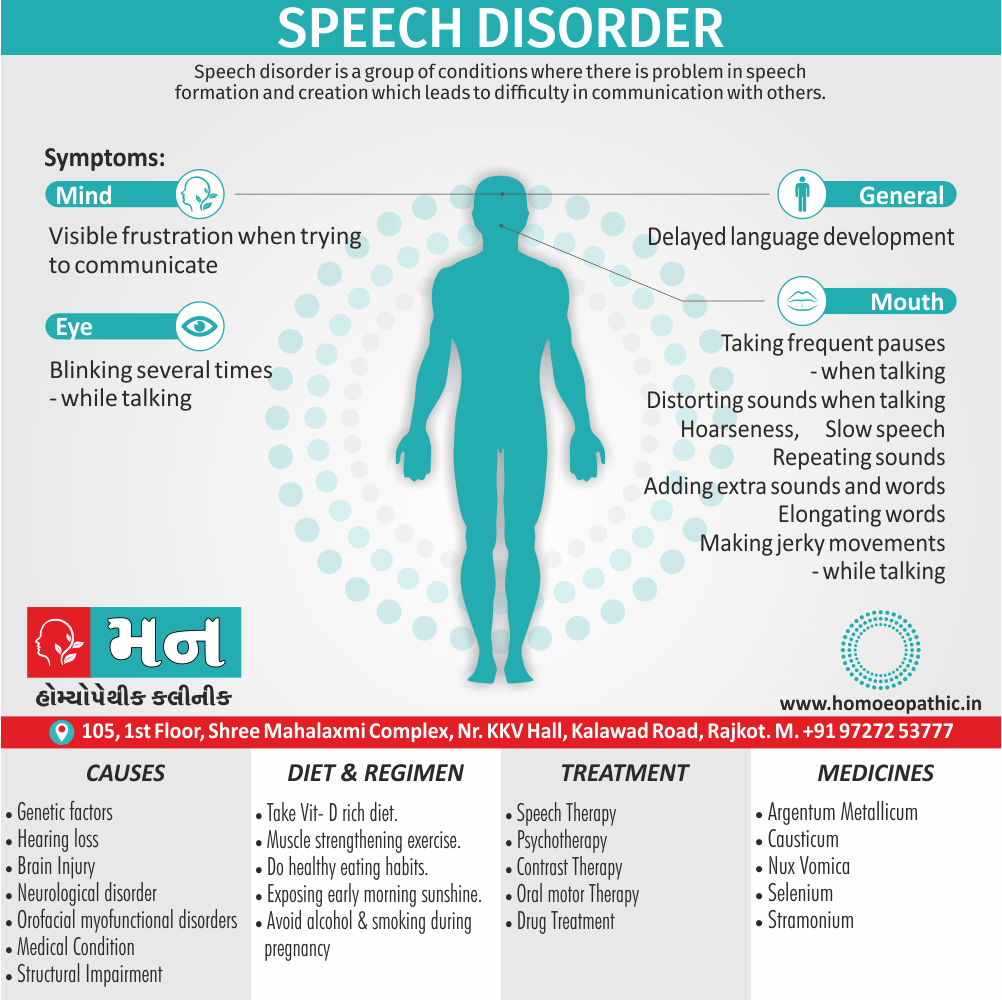
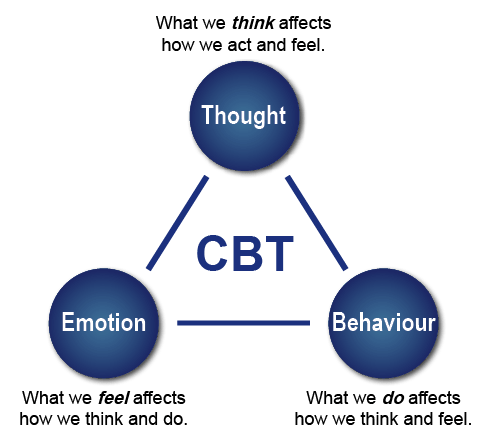
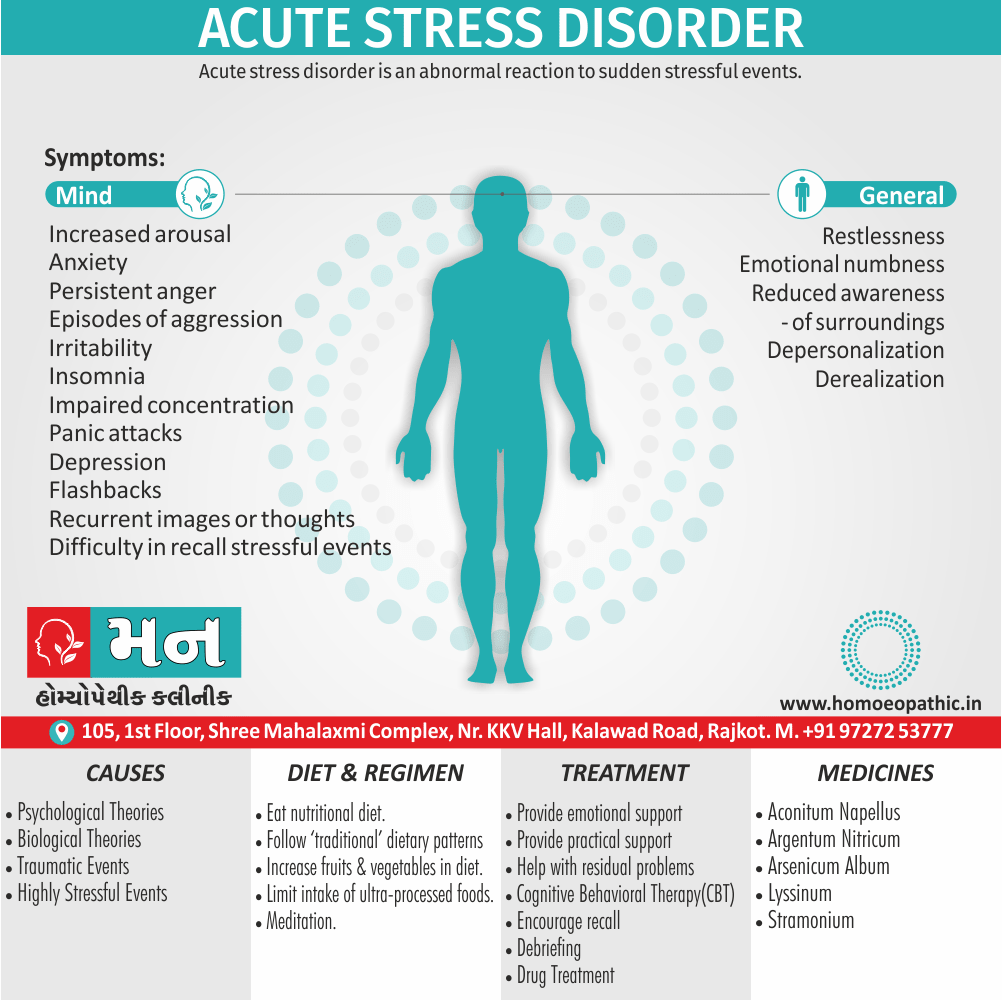
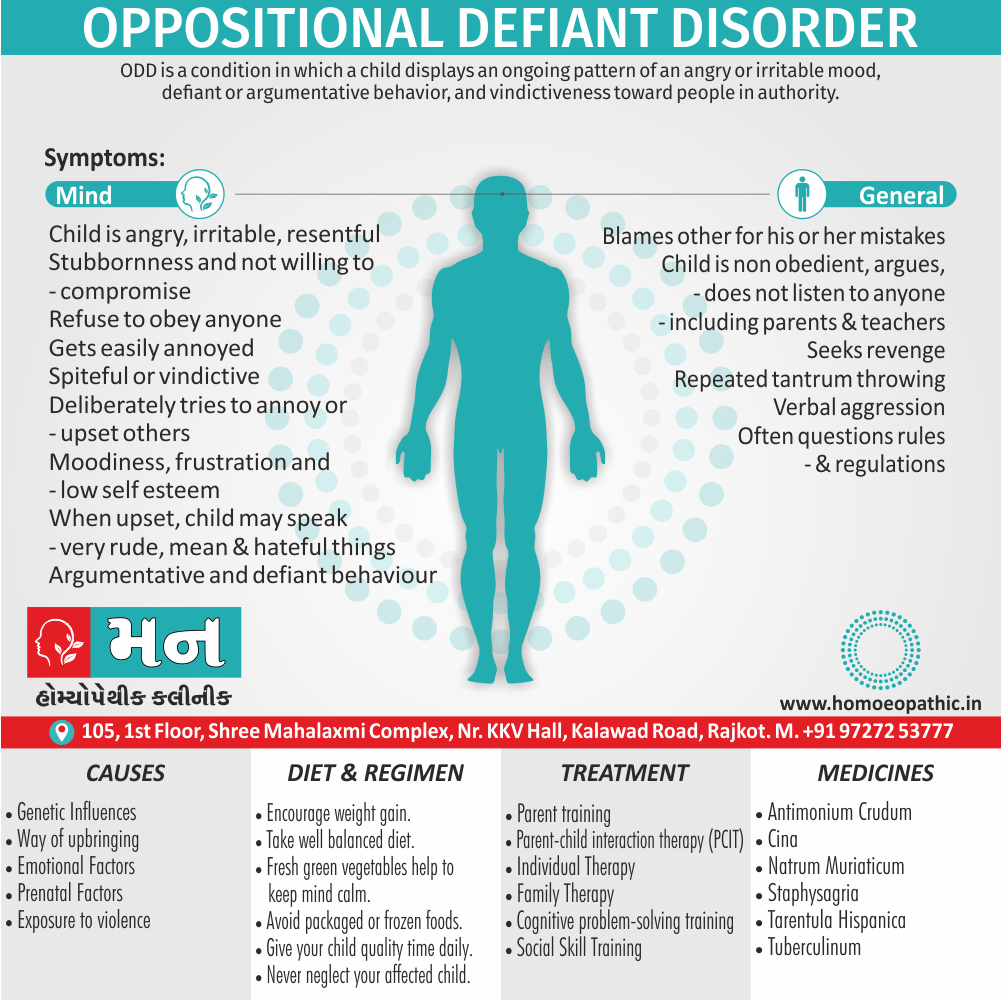
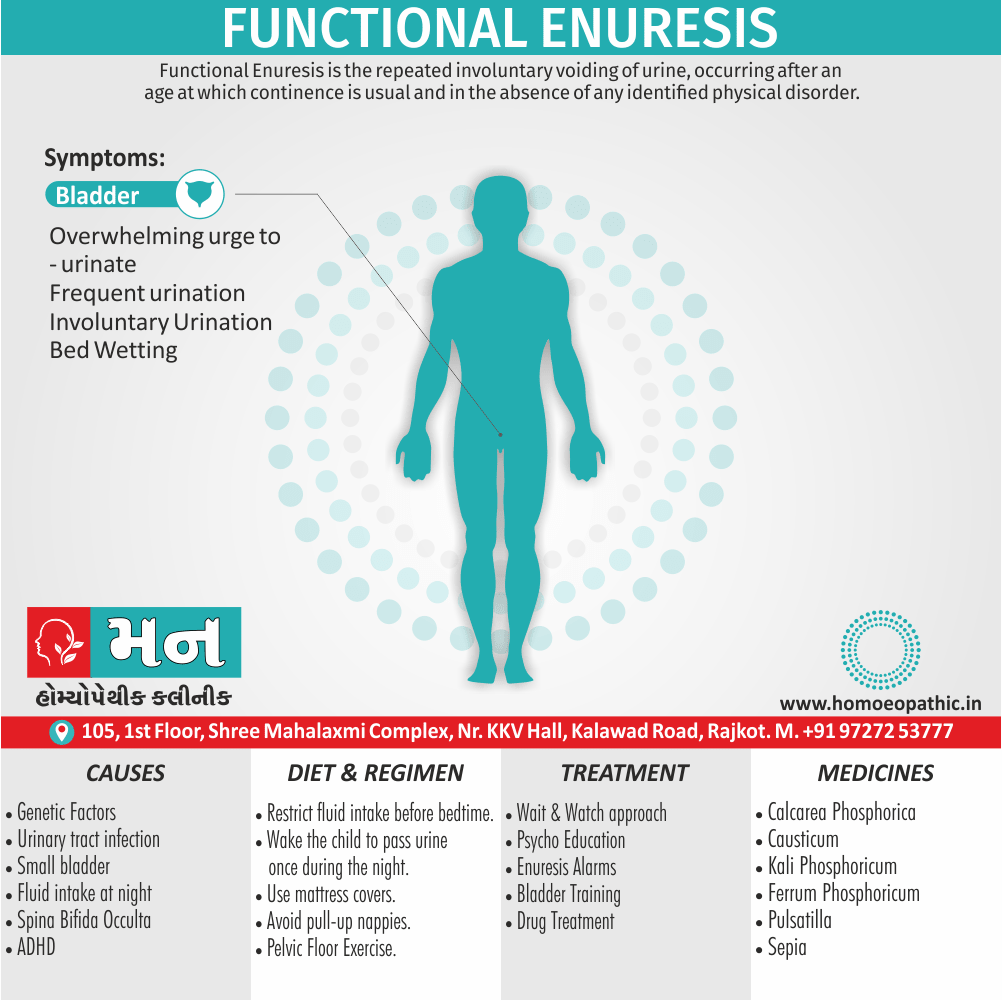
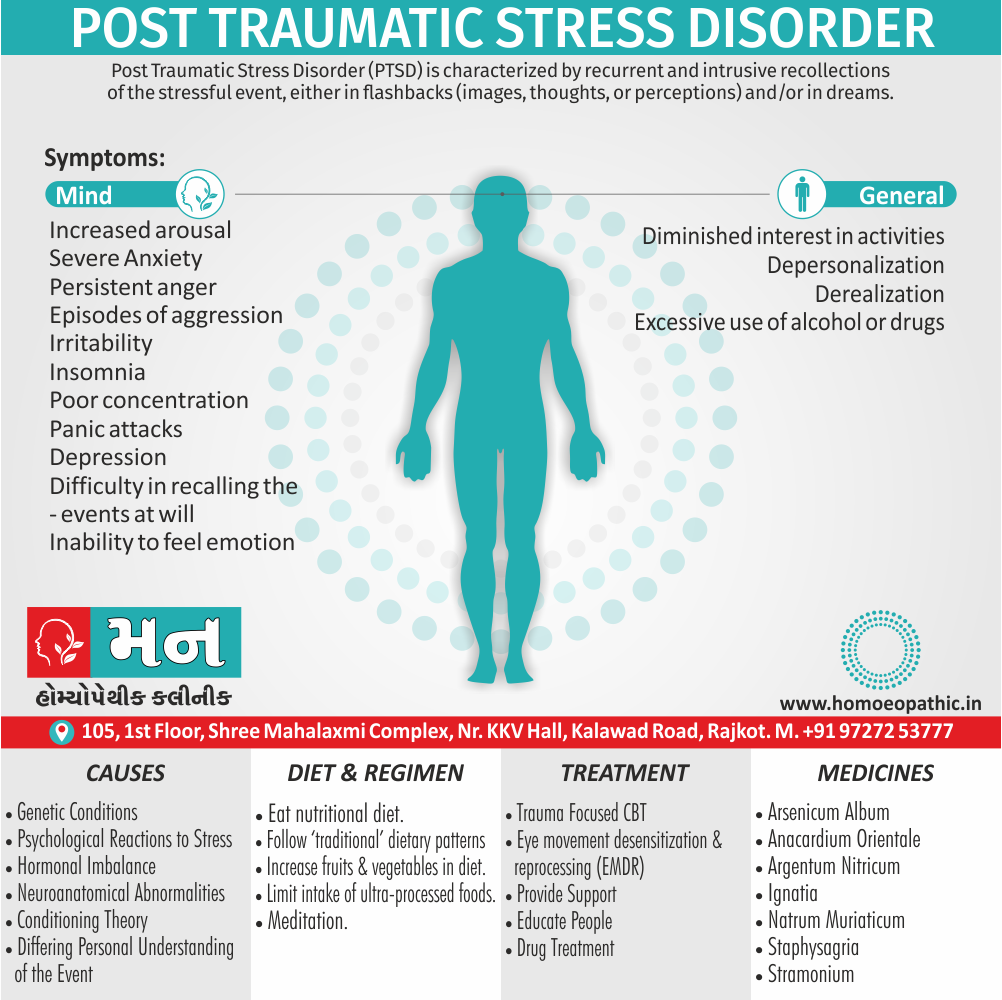
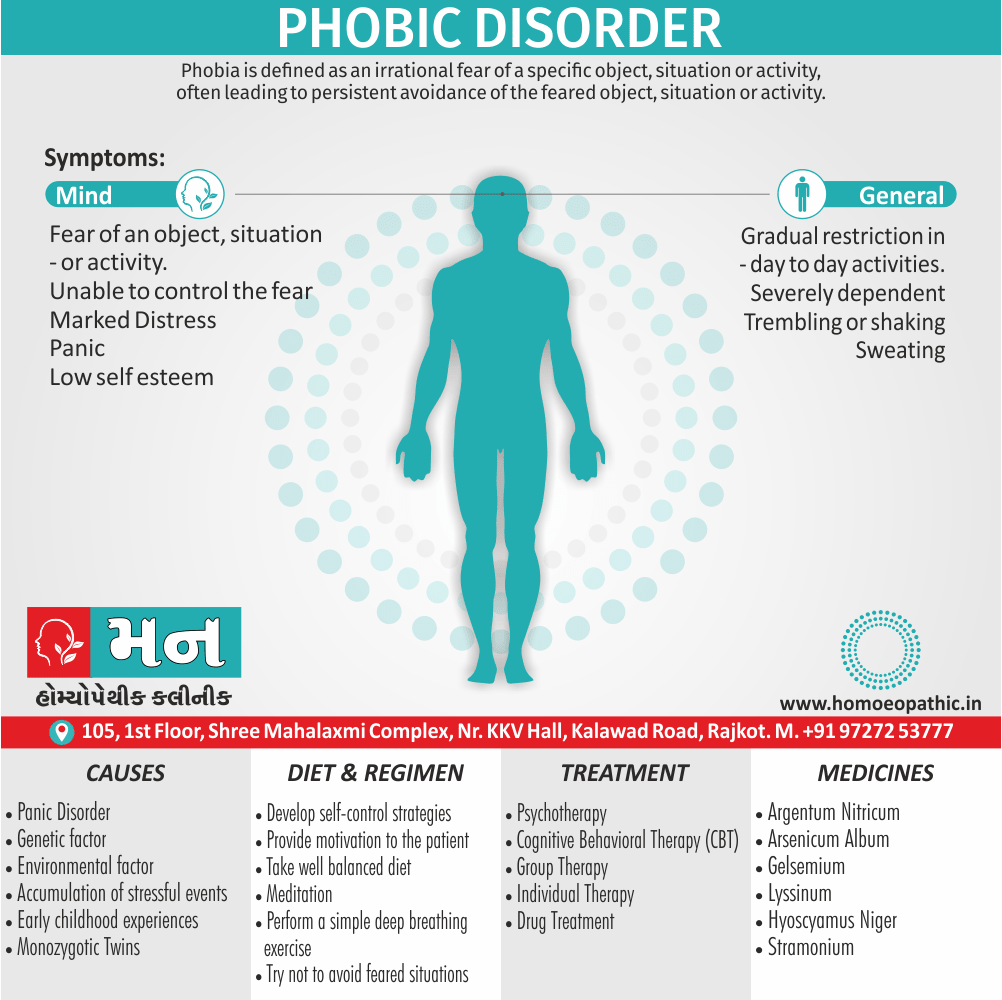
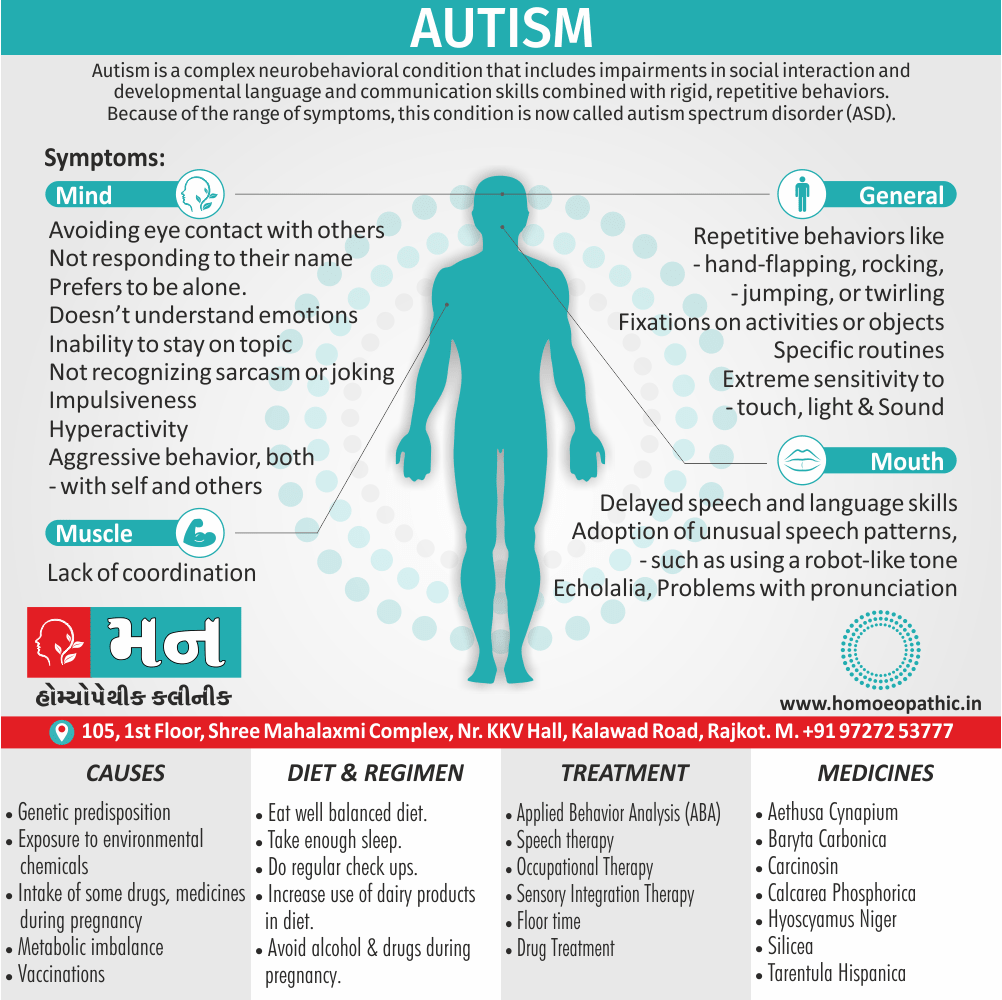
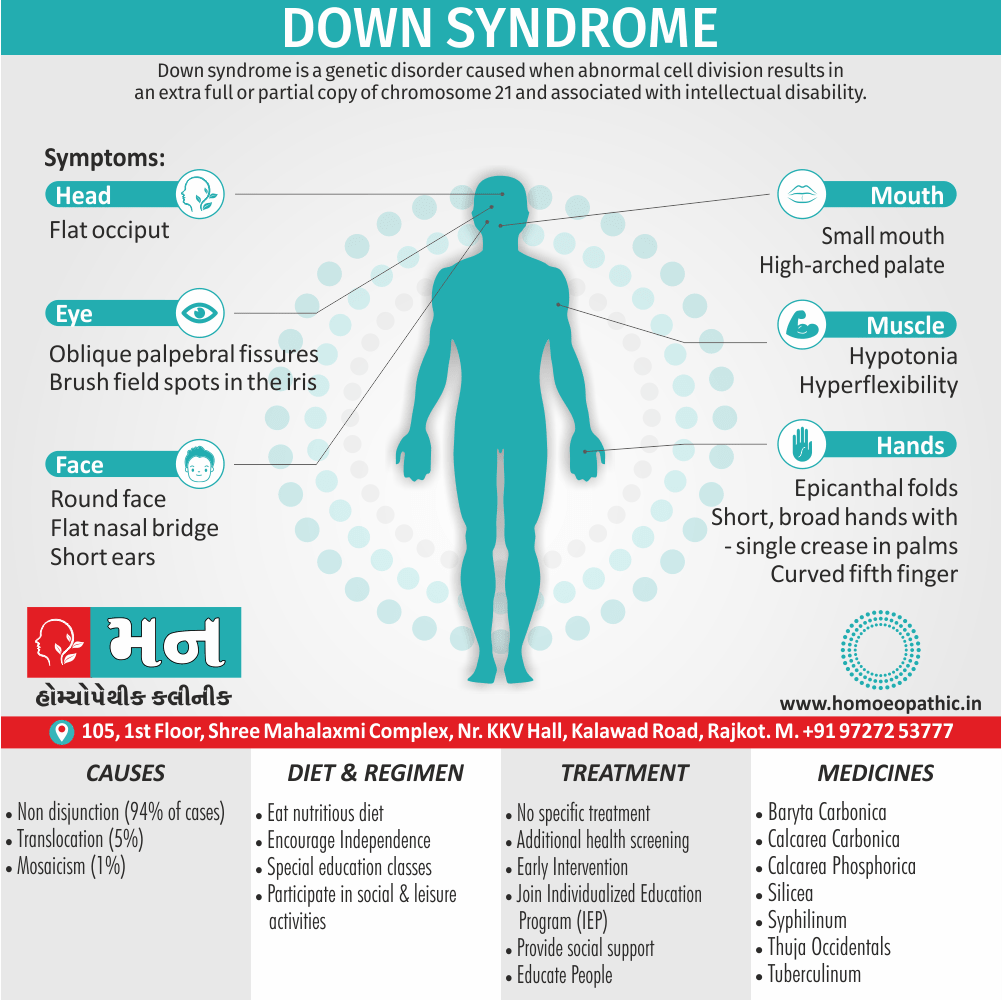
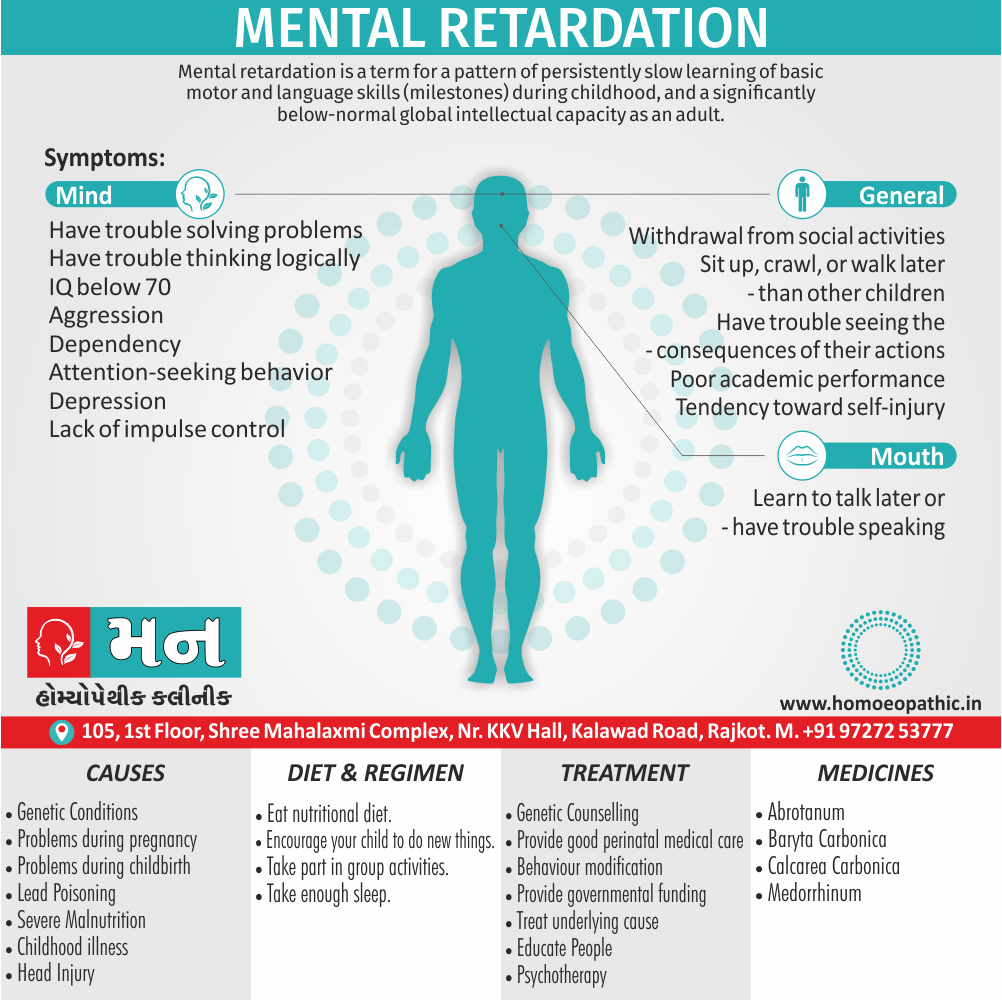
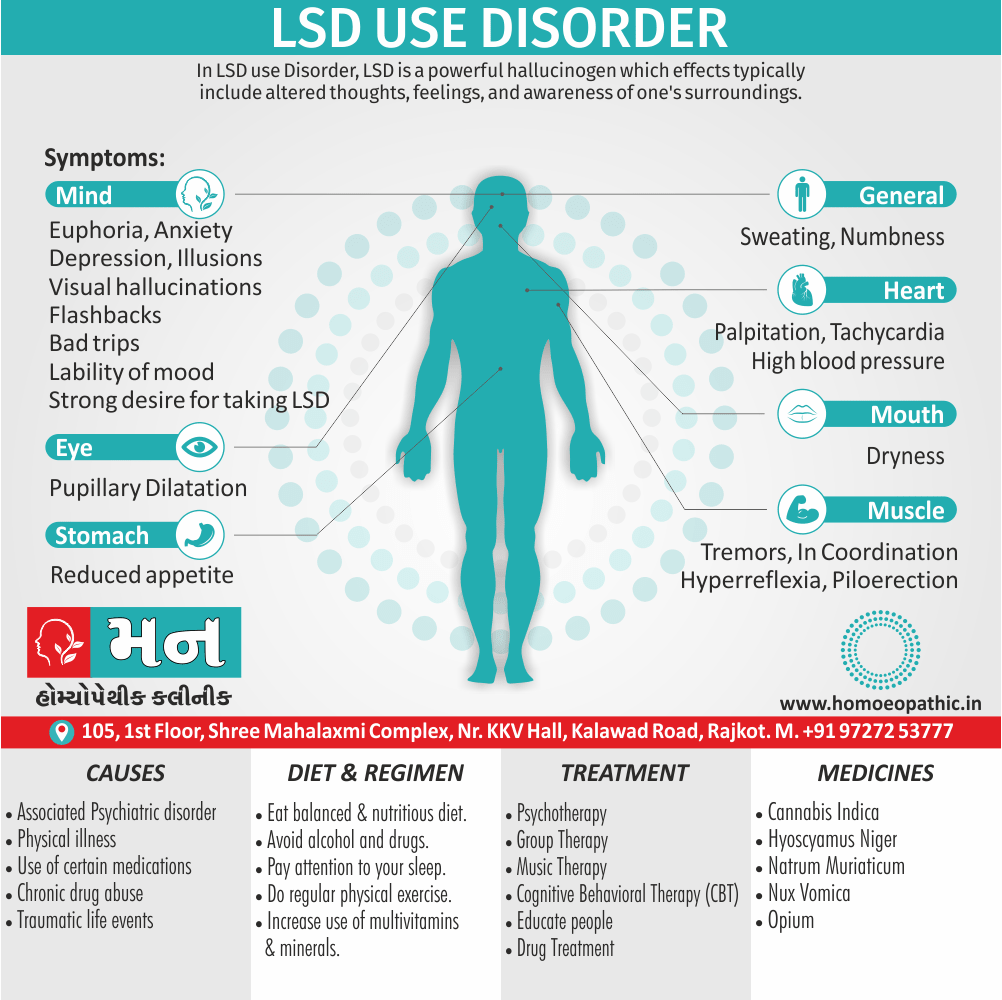
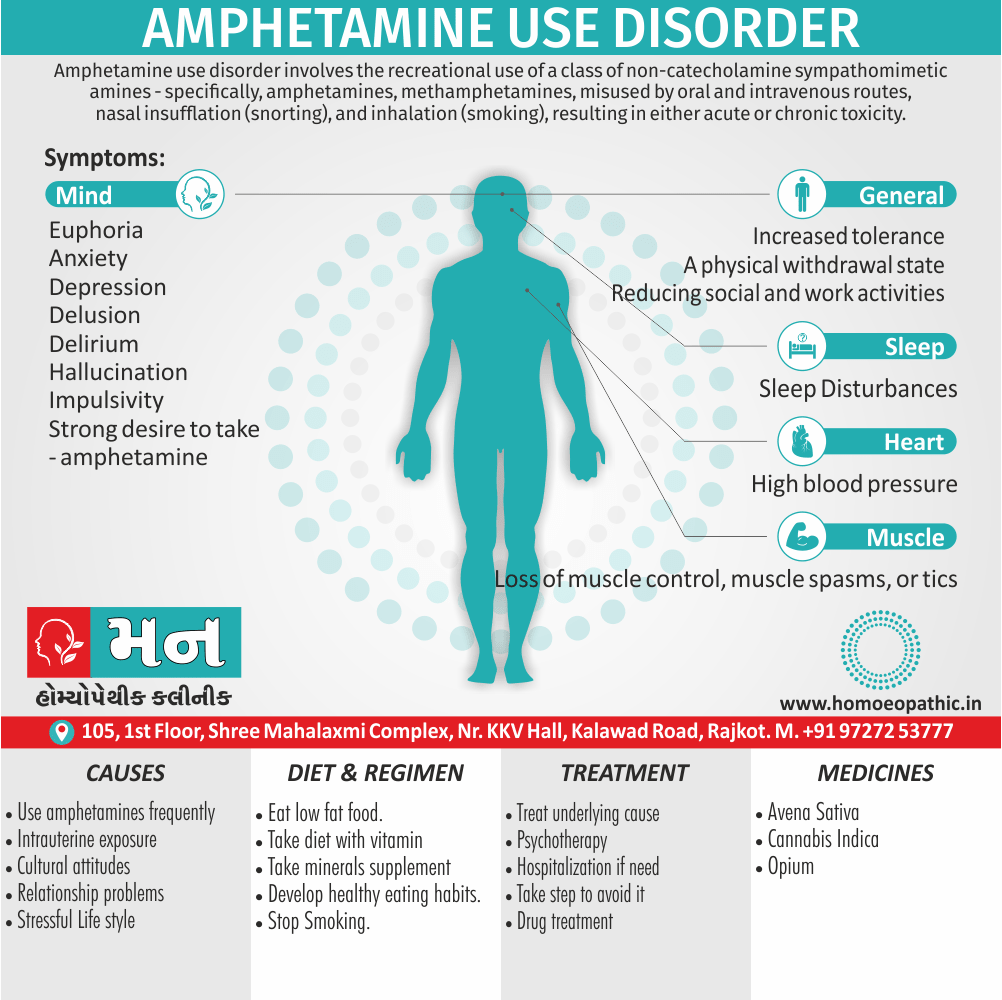
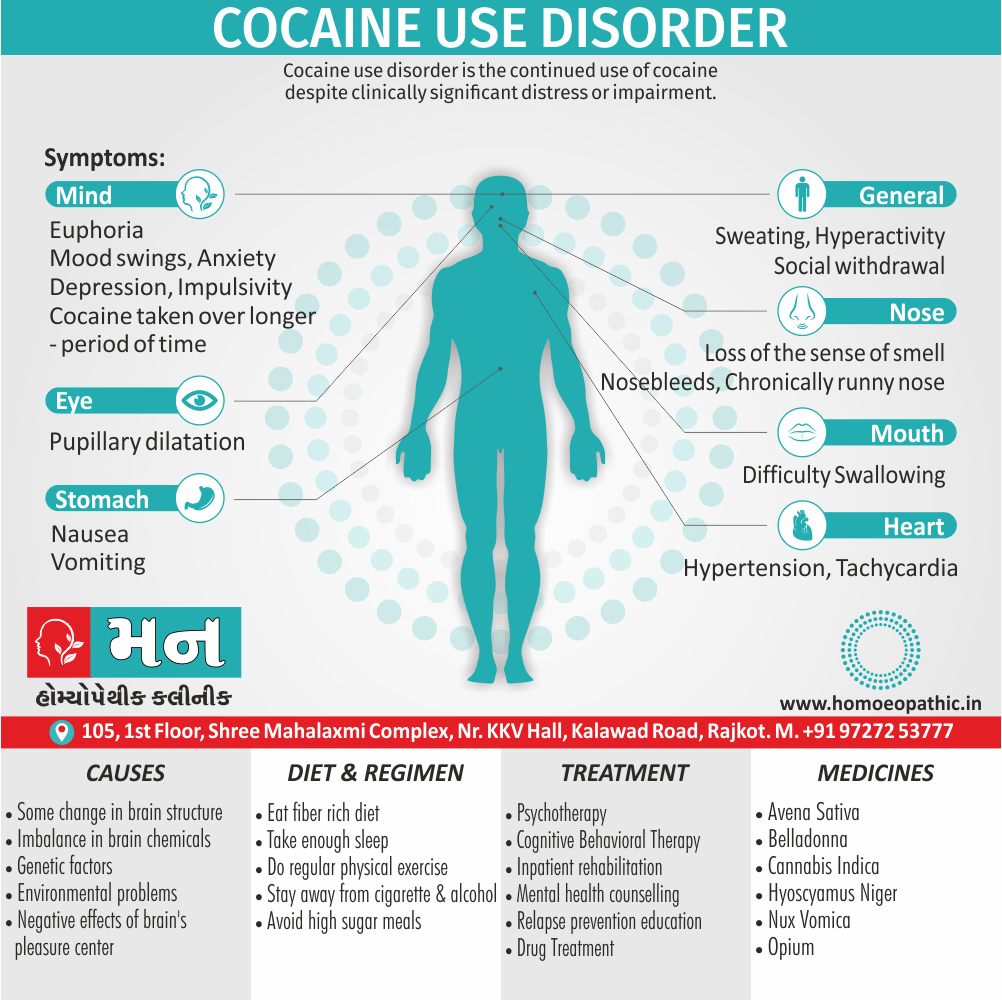
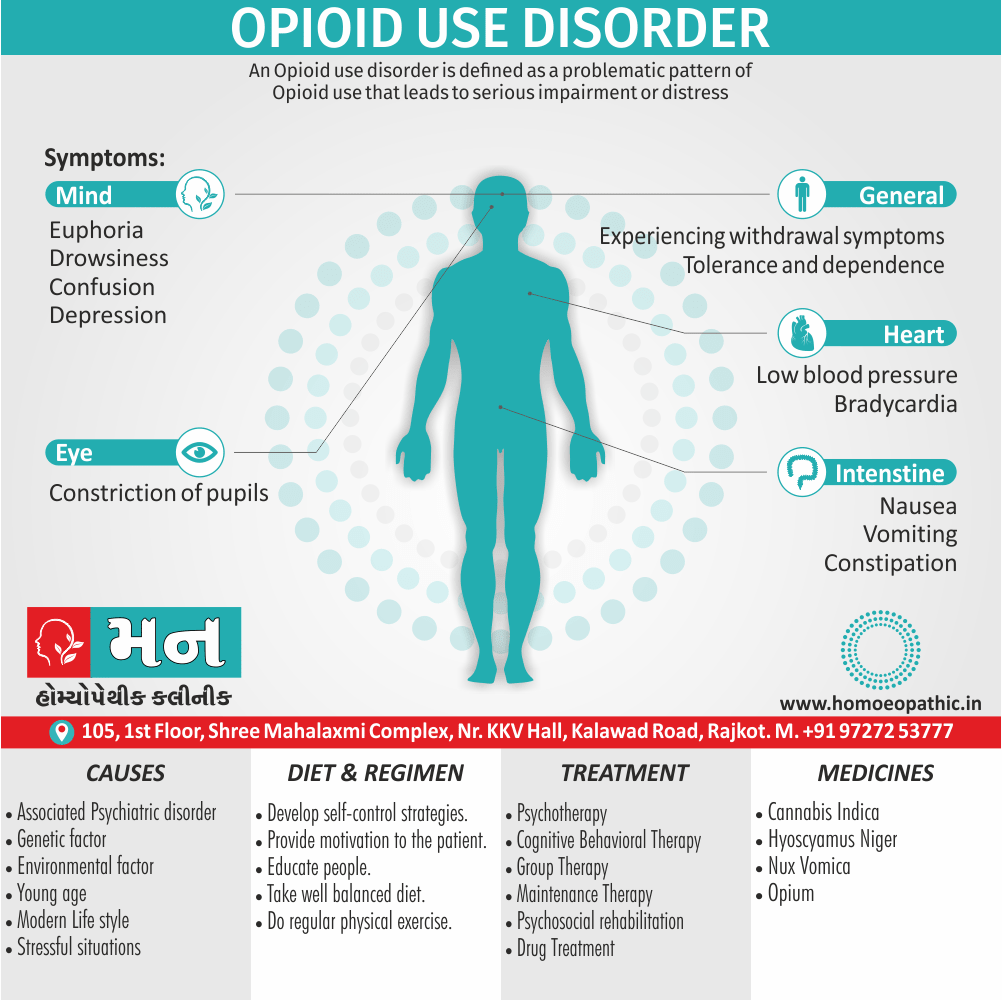
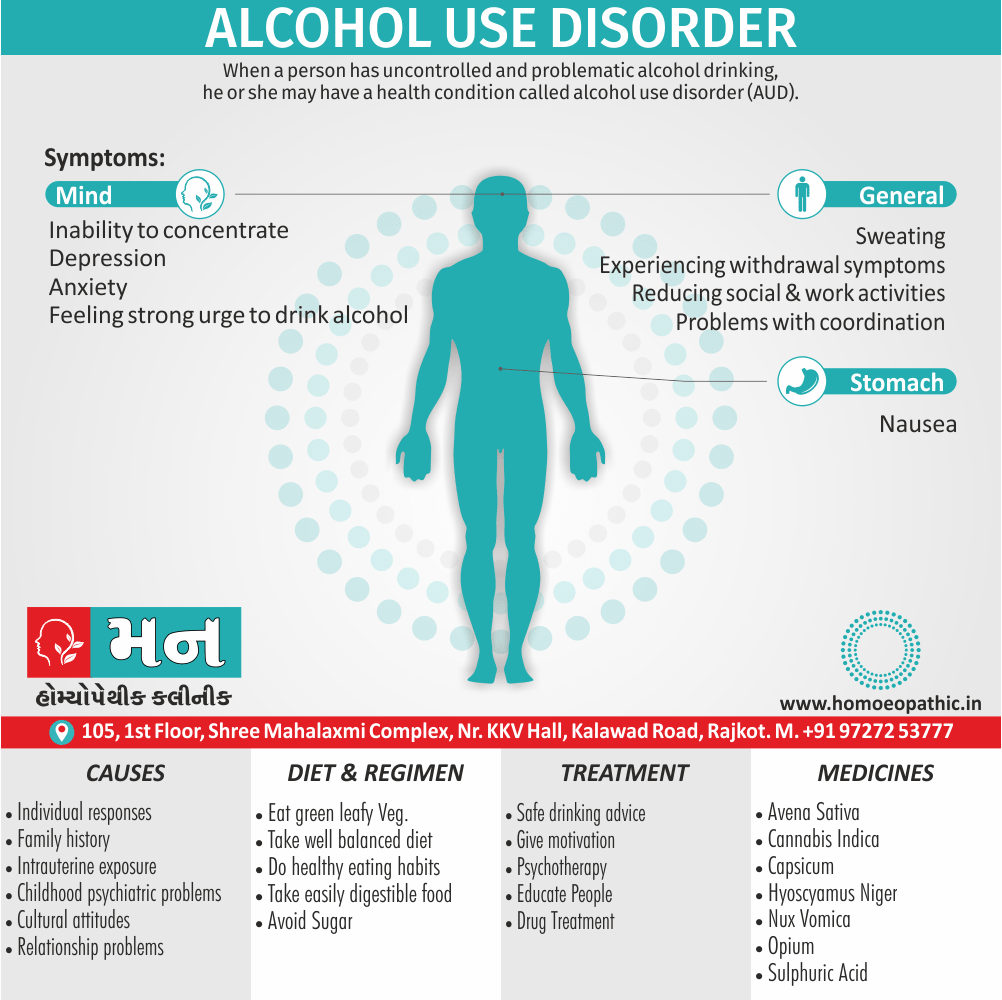
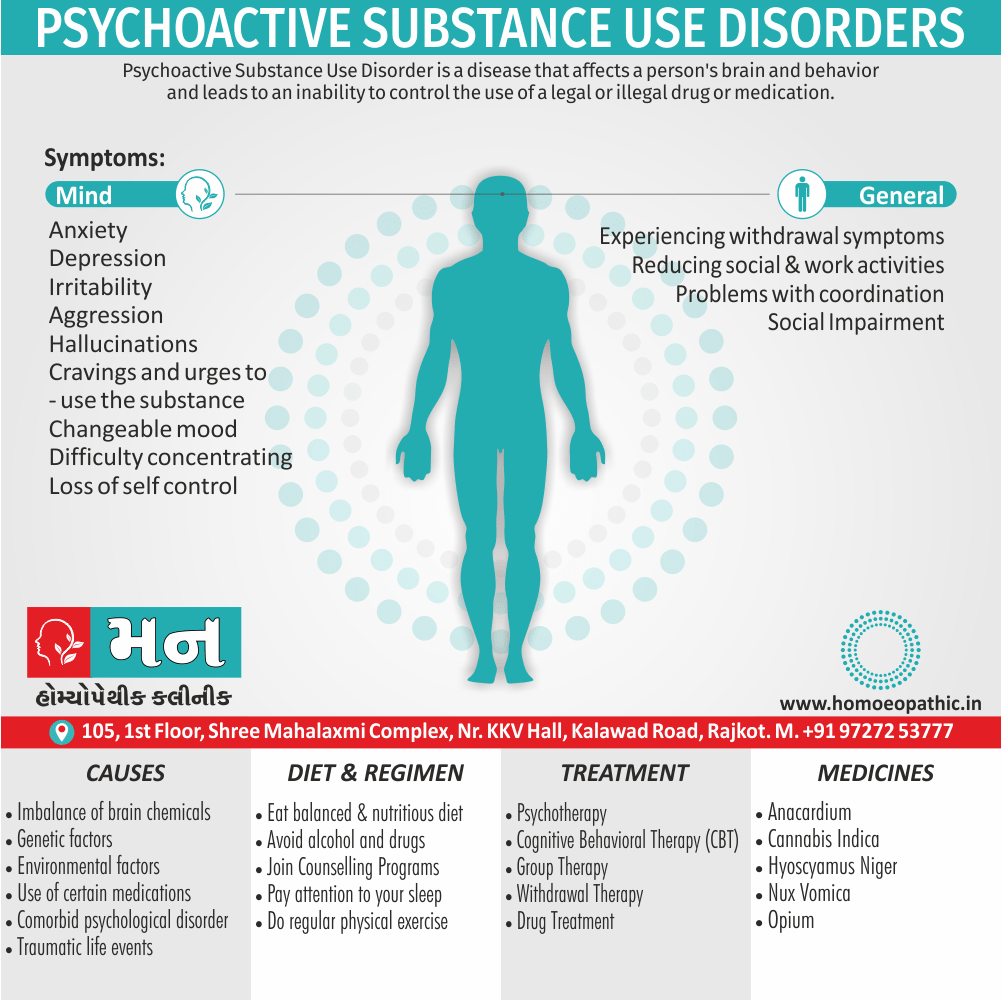
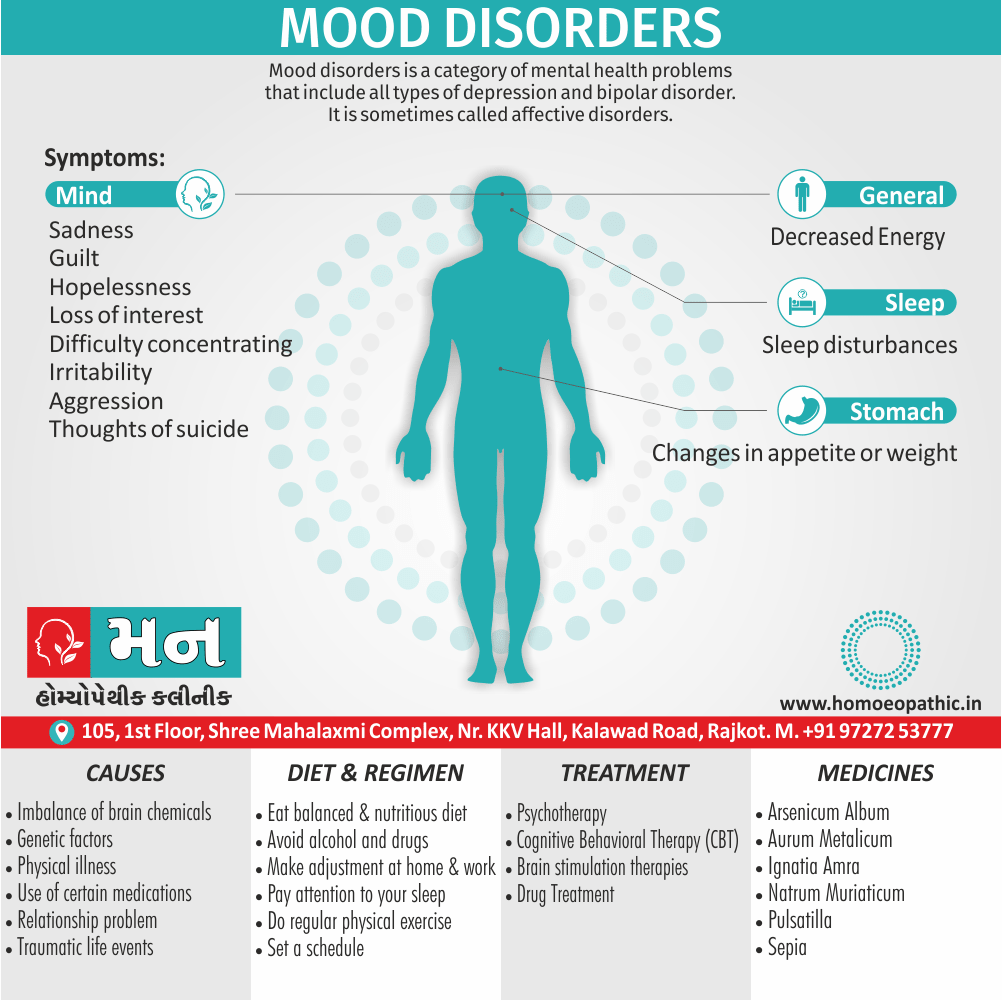
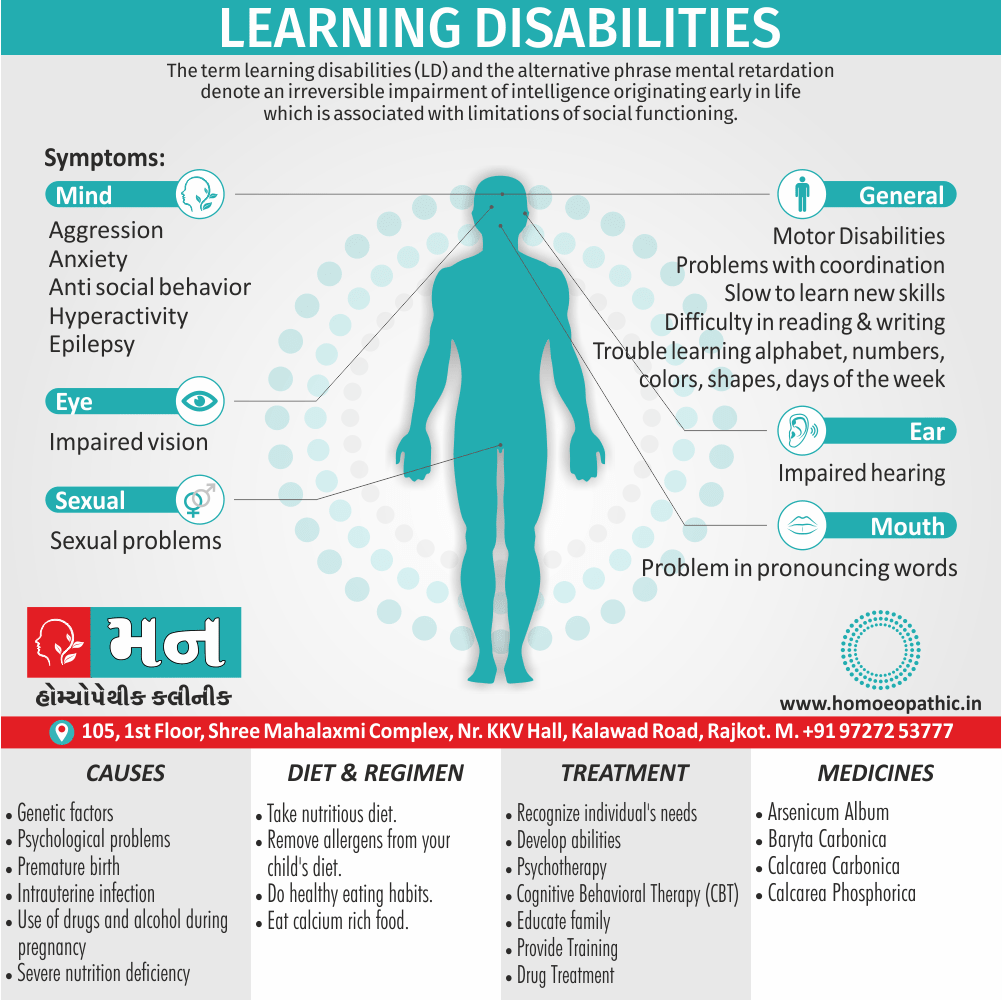
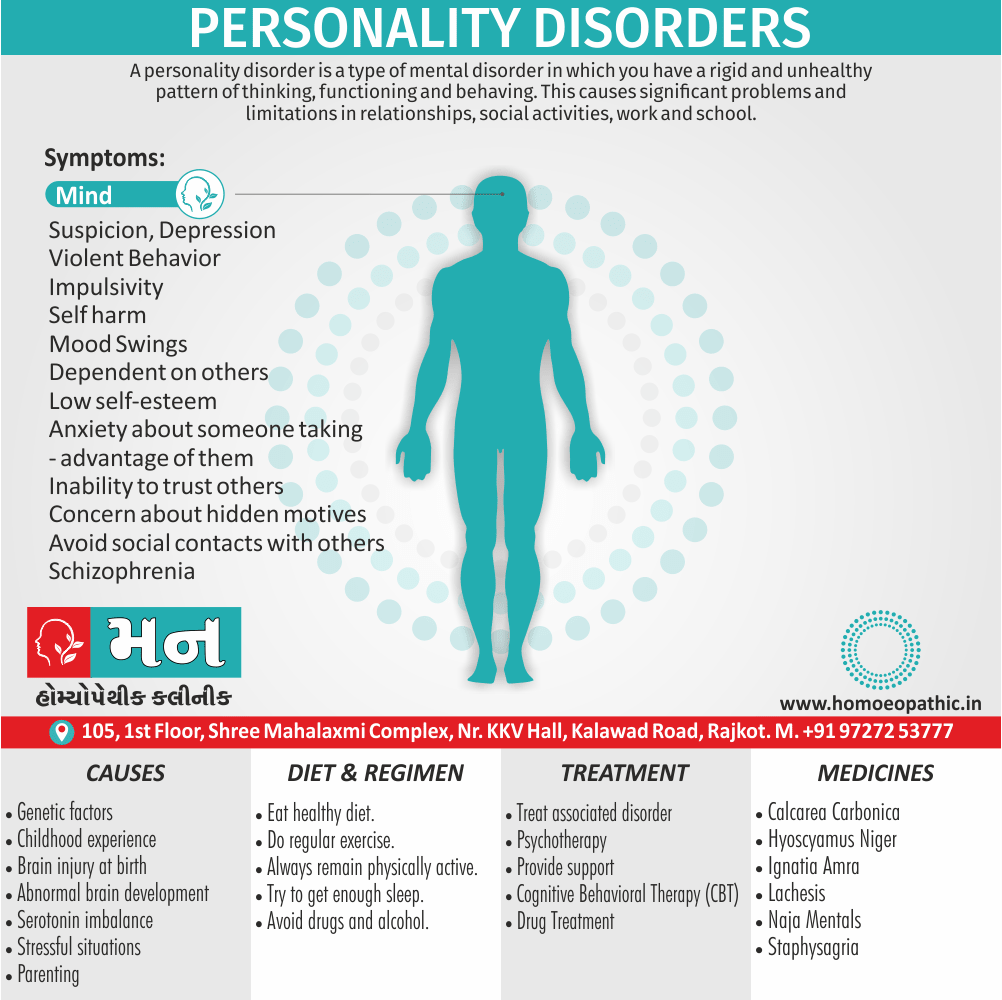
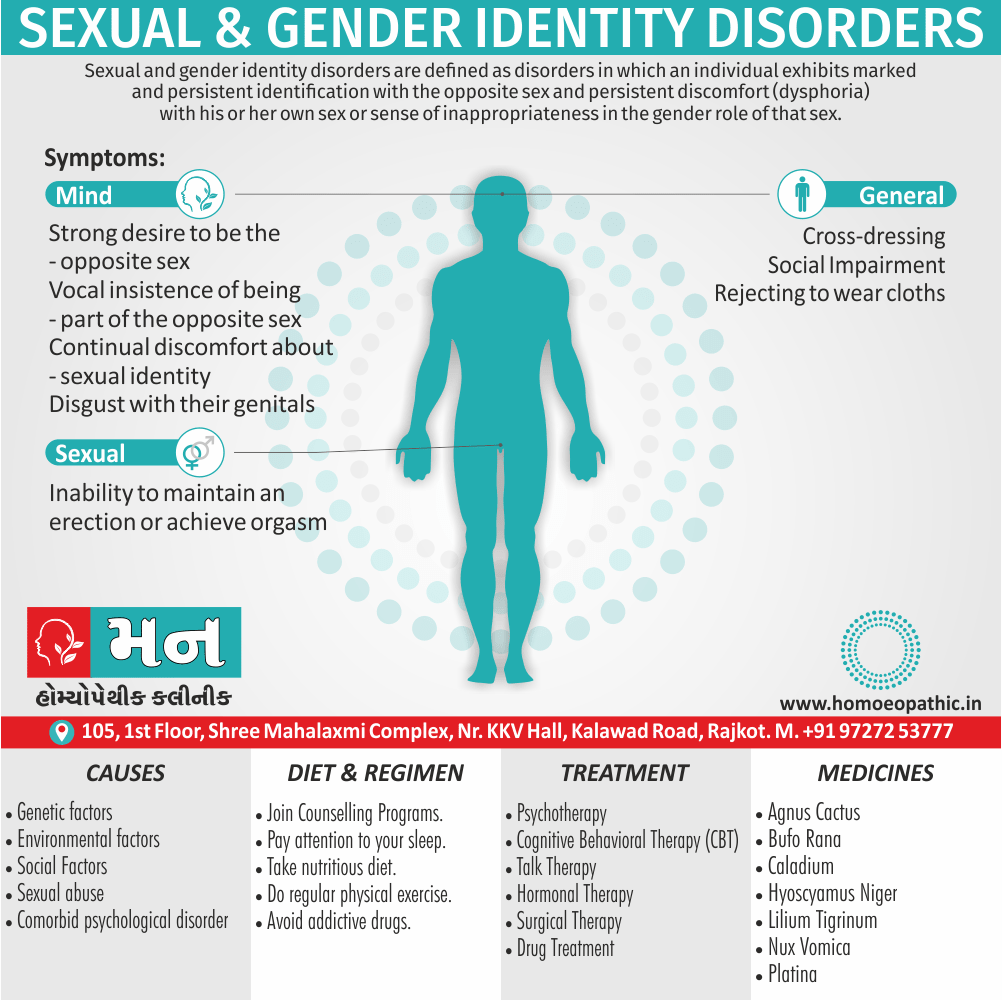
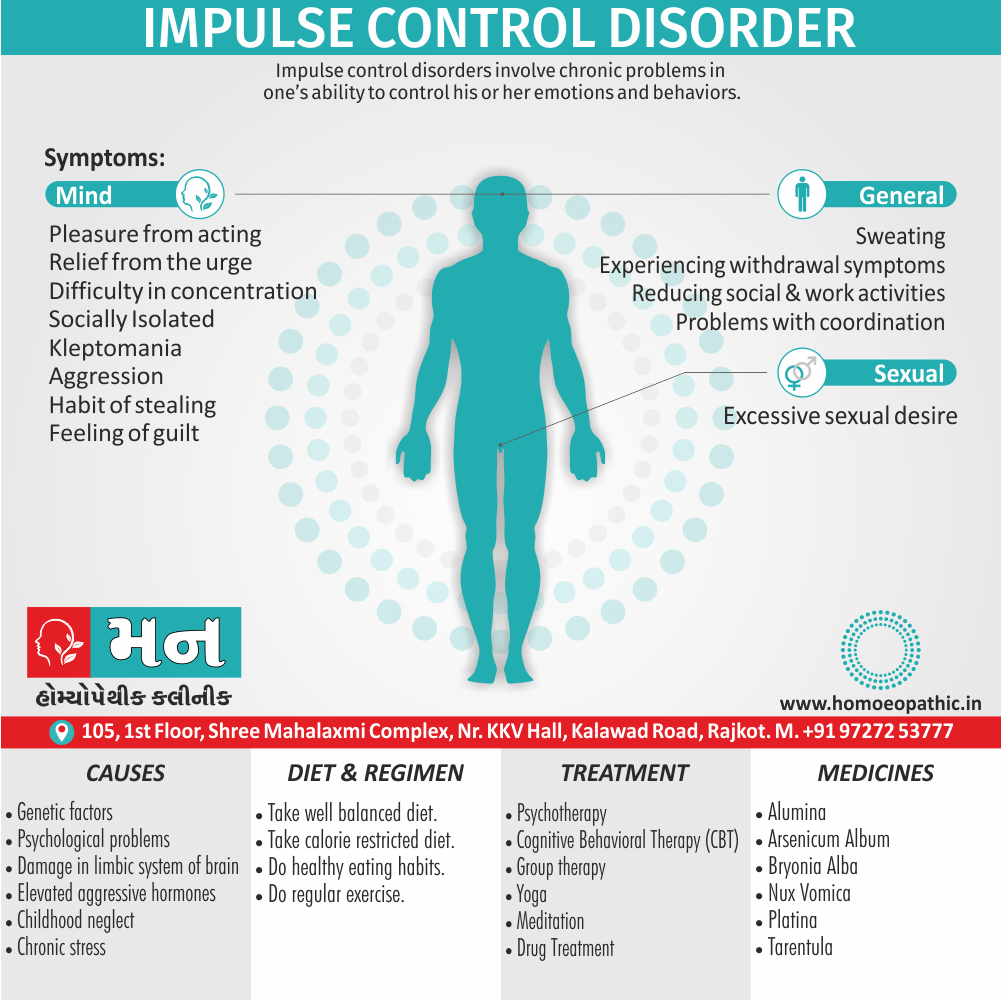
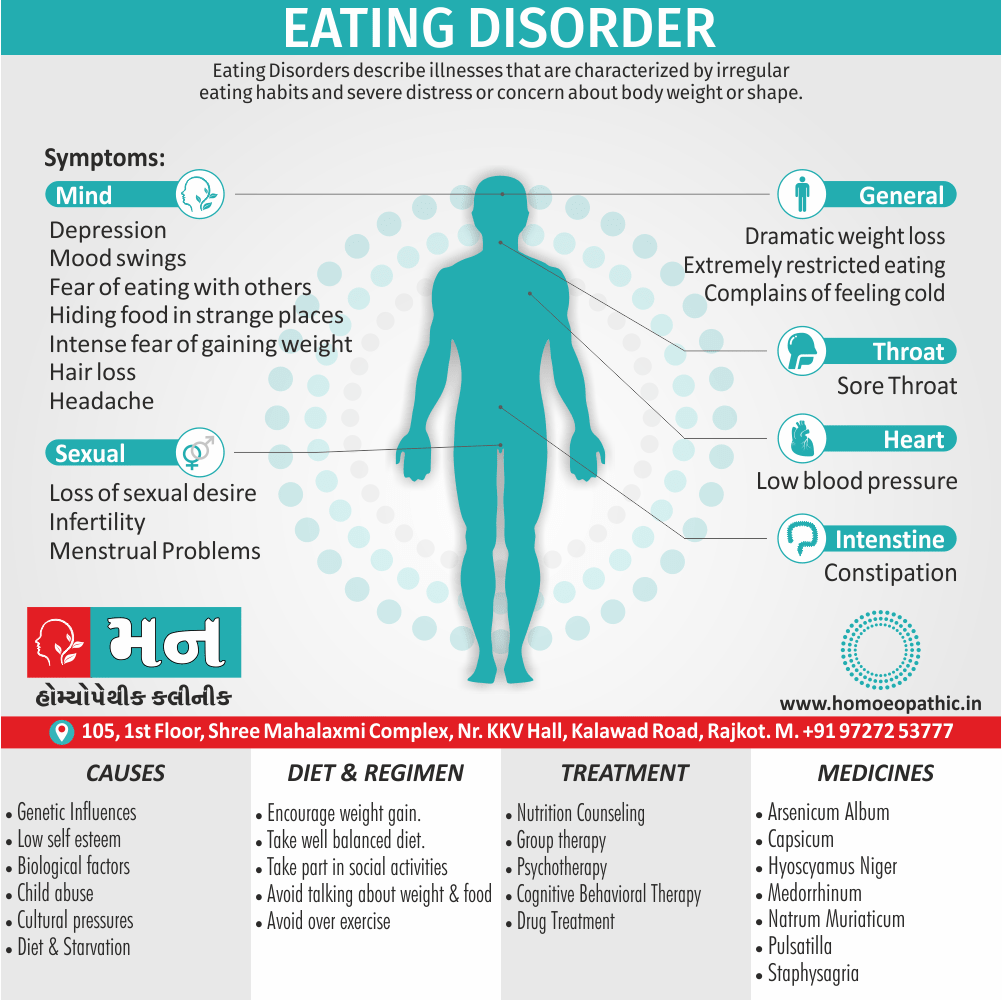
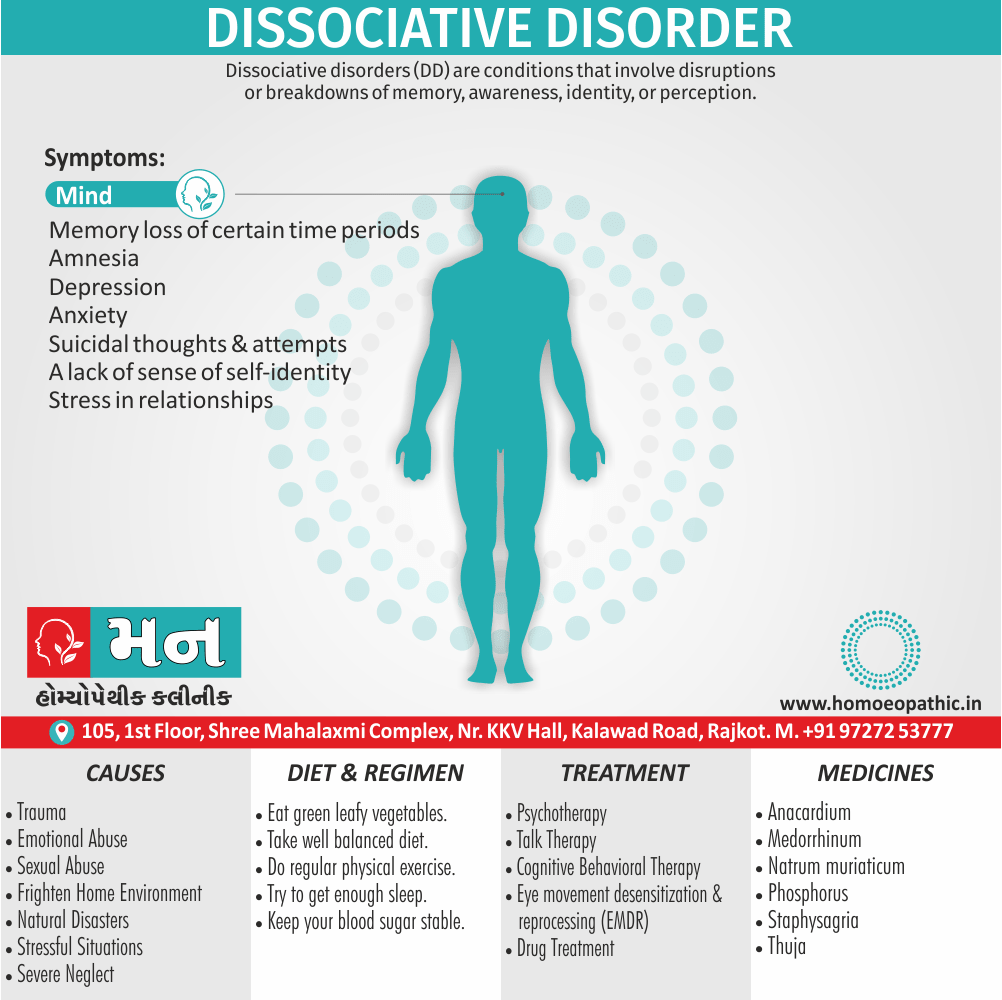
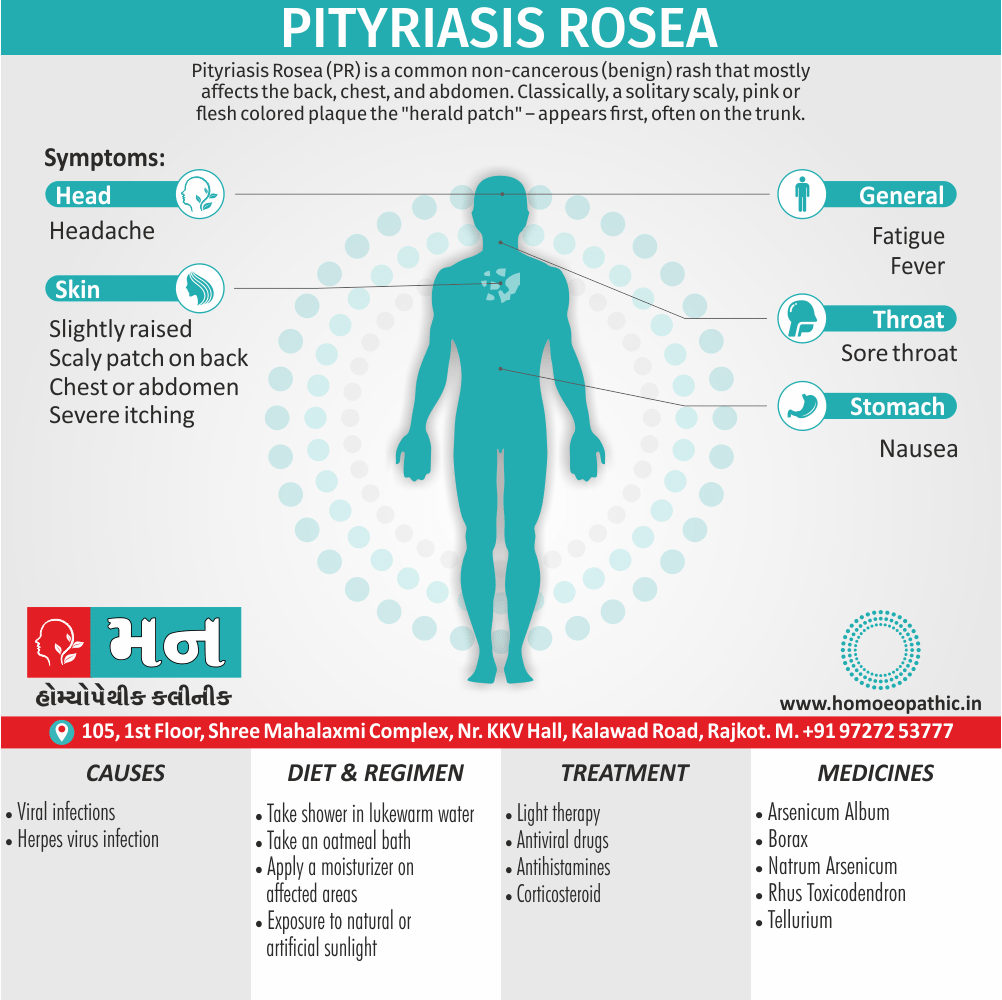
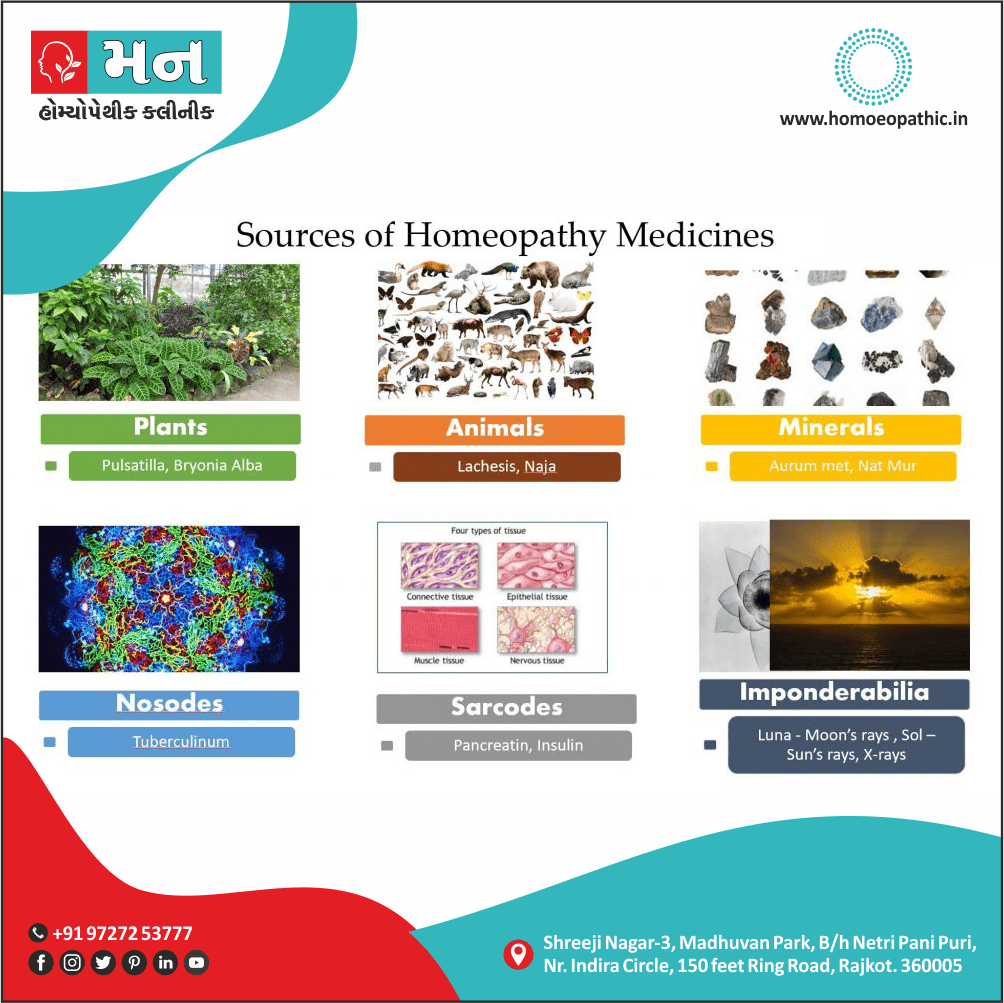
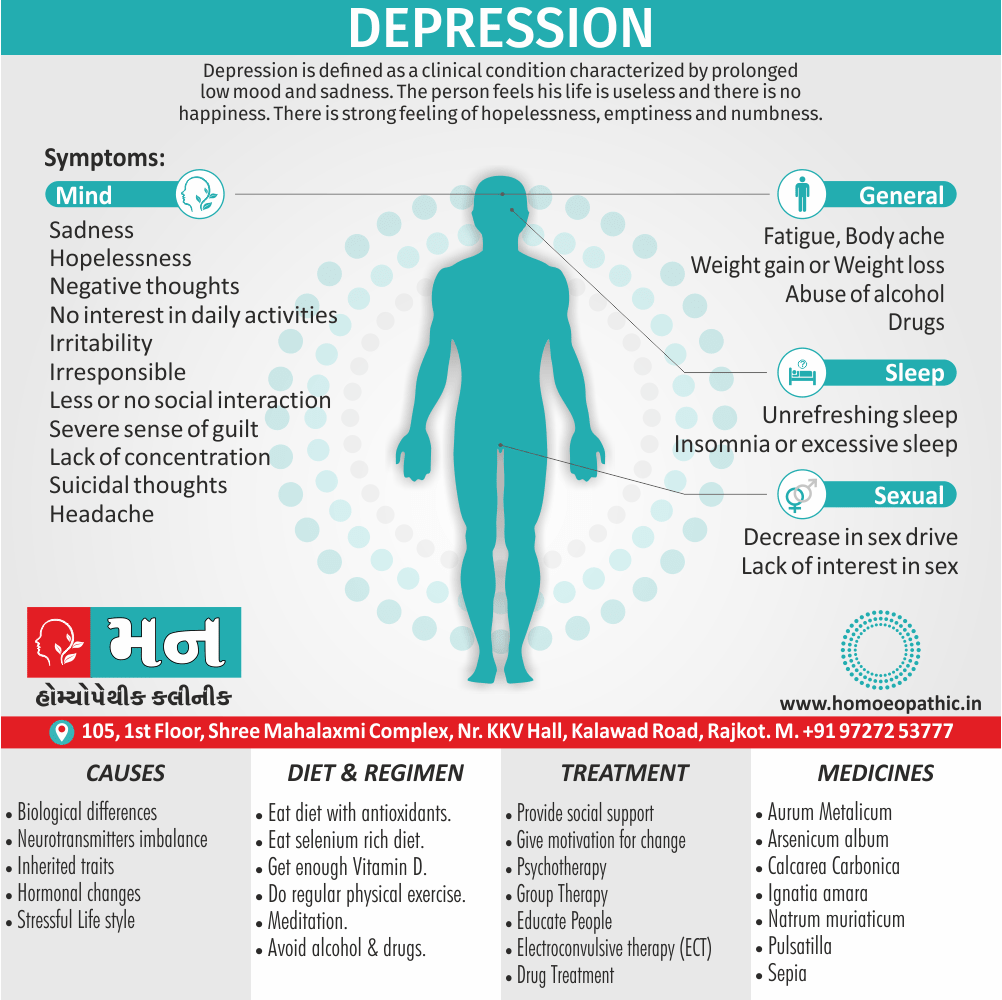
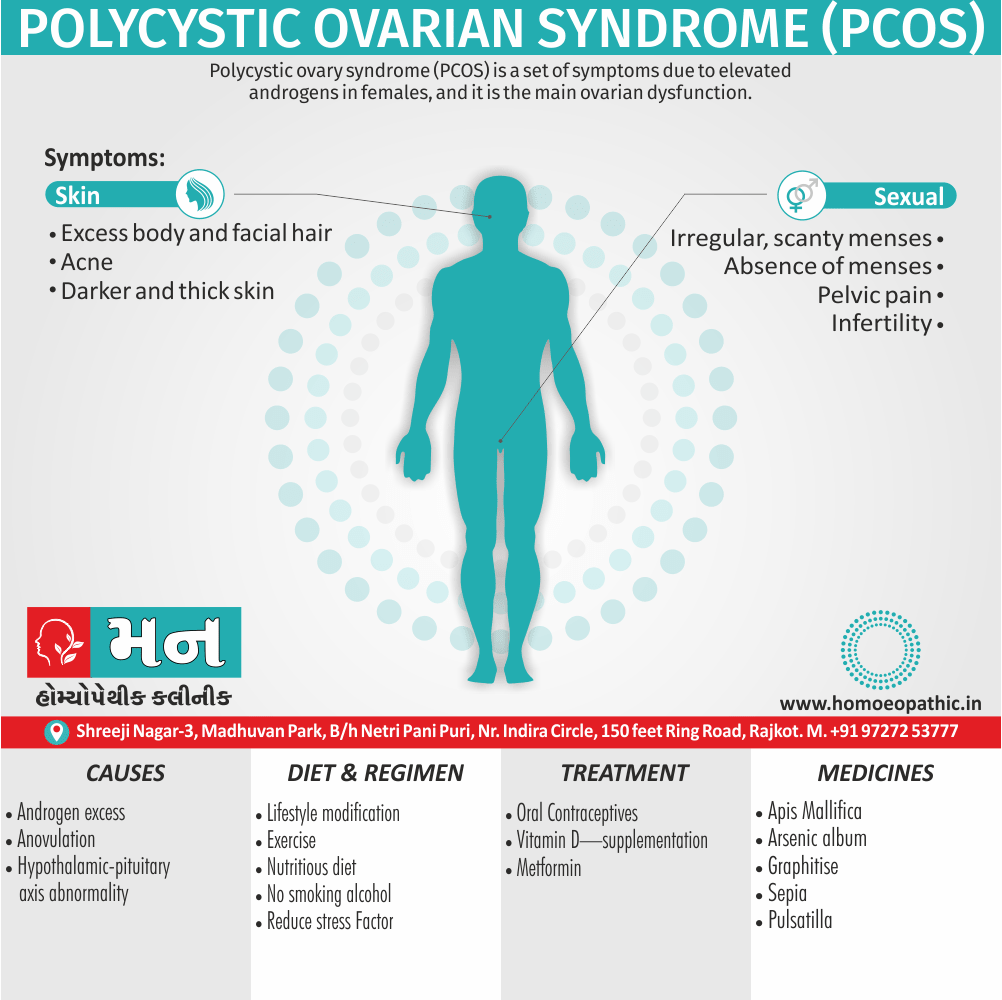
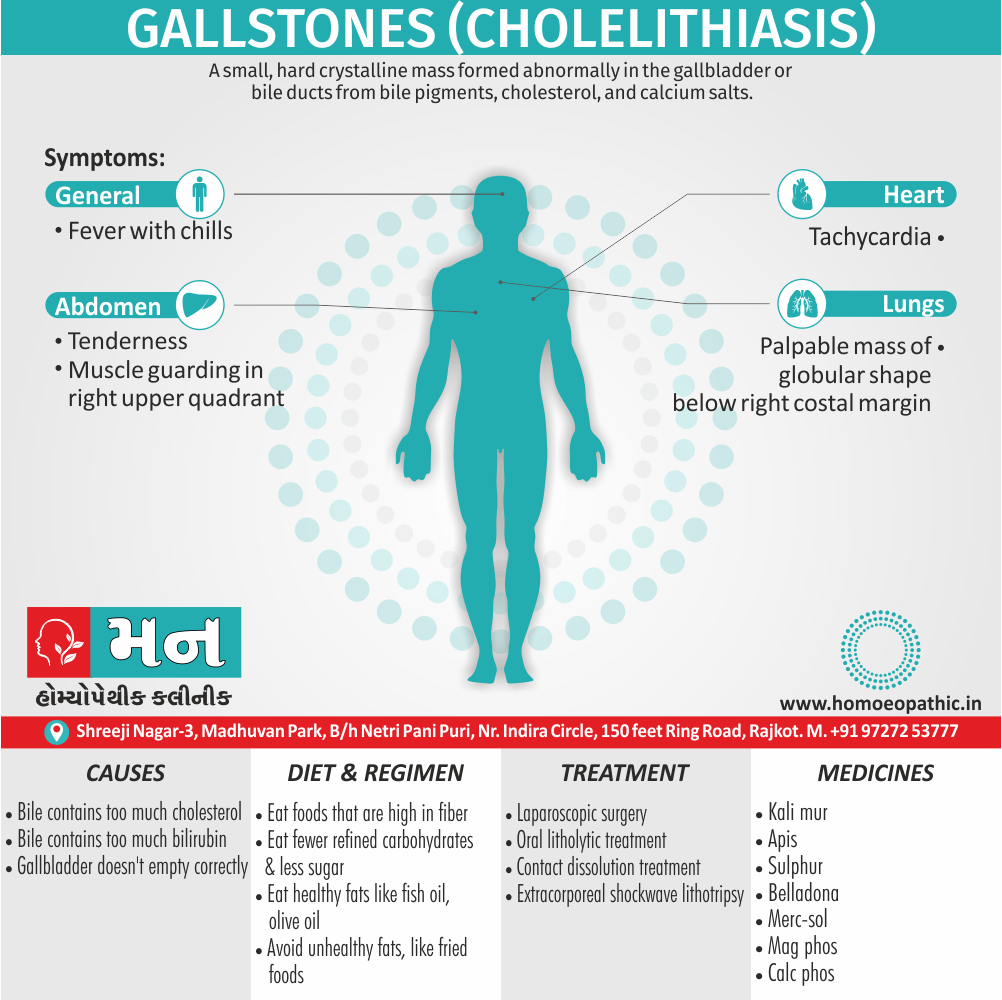
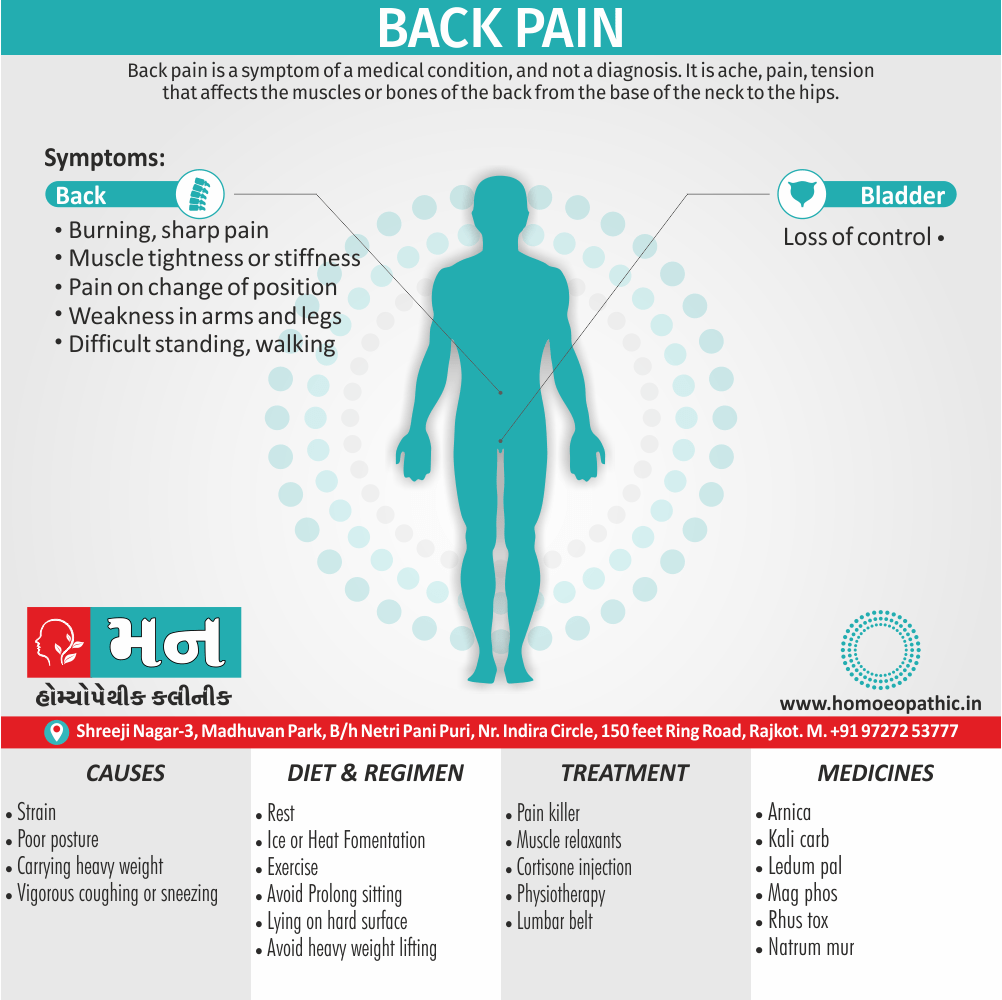
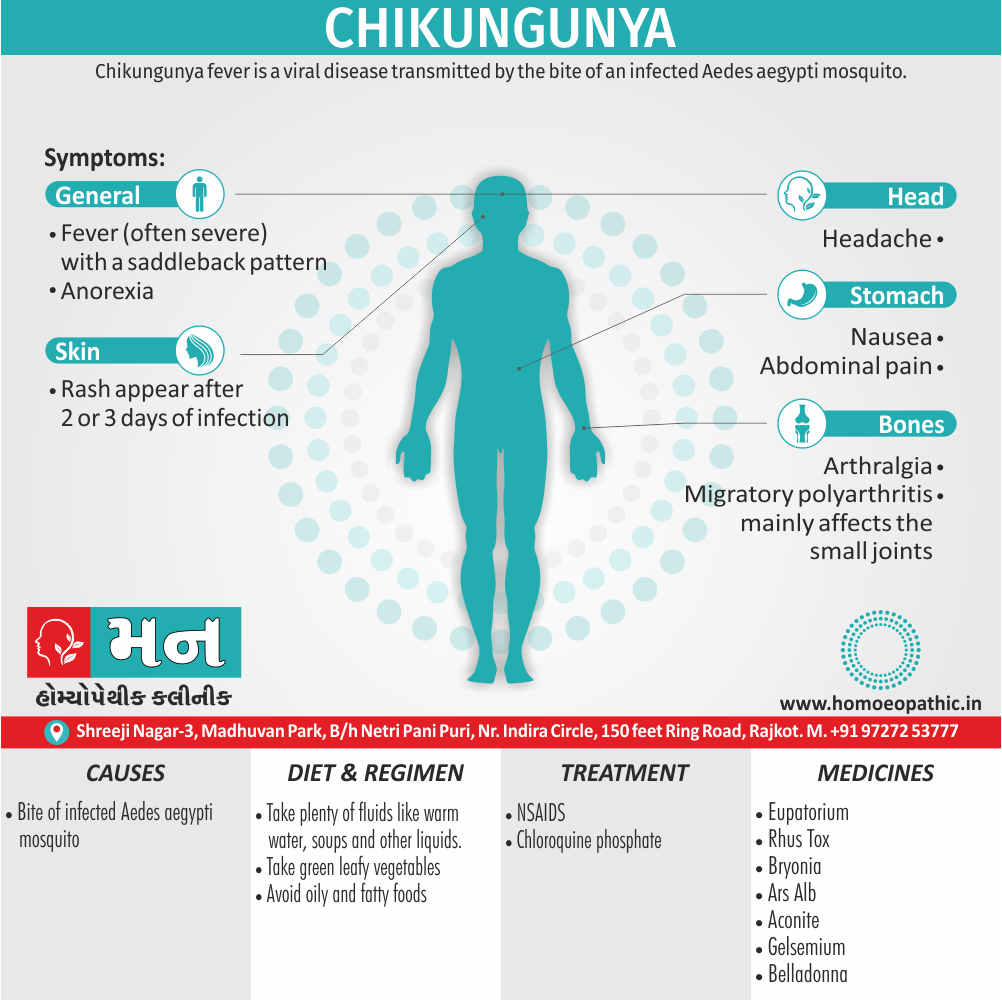
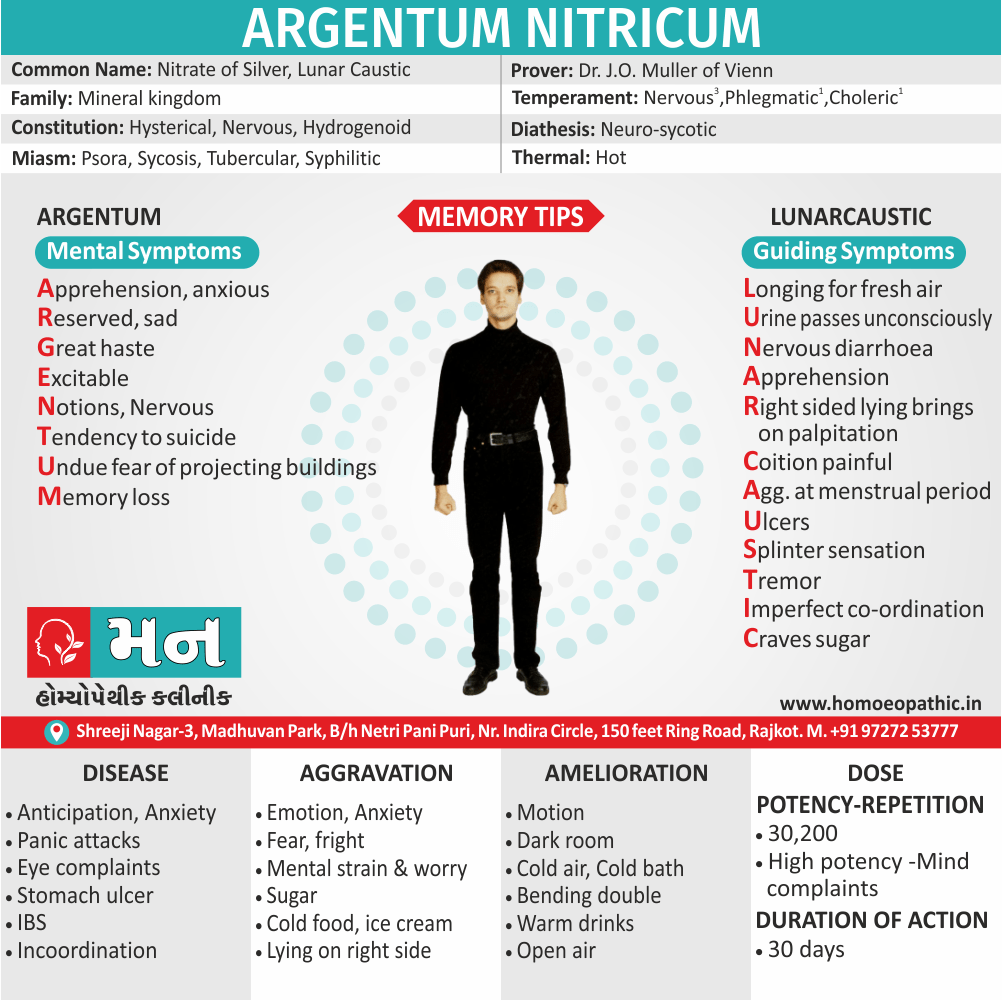
Memory Tips for Guiding Symptoms
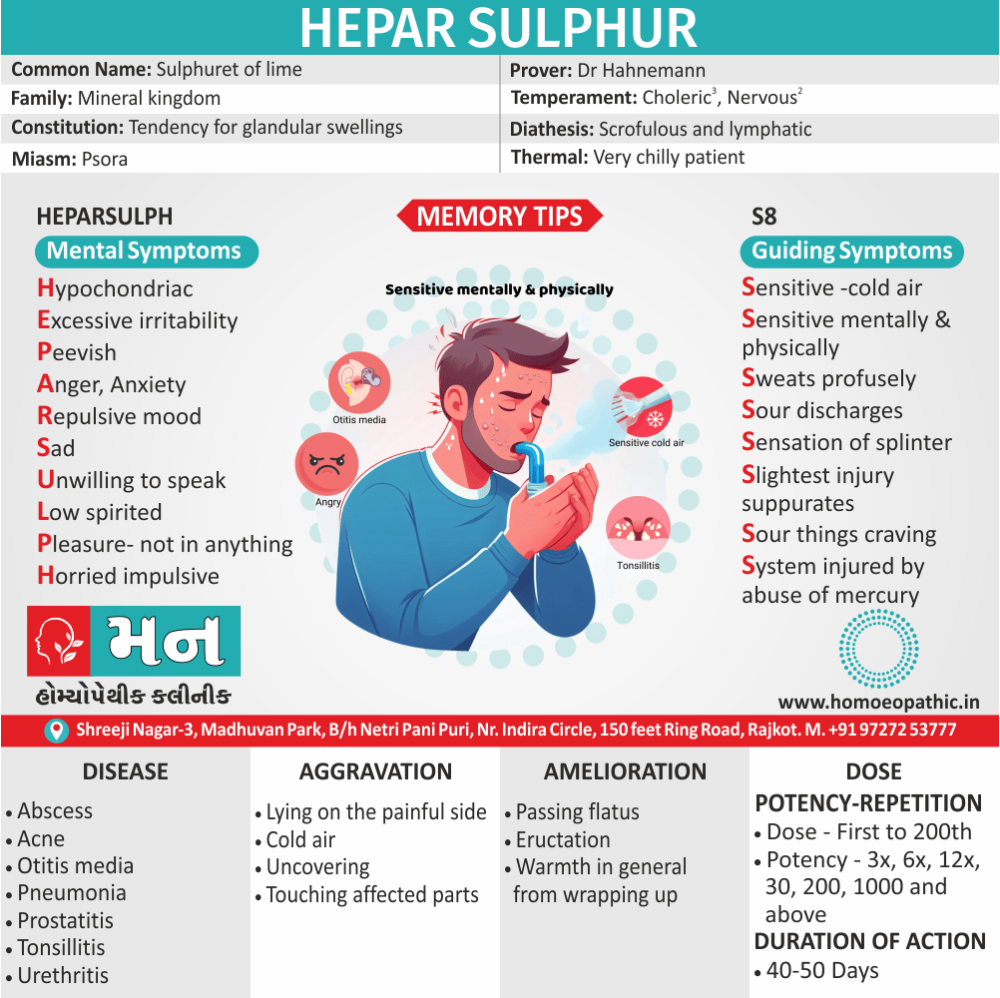
Hi Friends As Dr. E. B. Nash said that the strongest characteristic of our Hepar pt. is hyper-sensitiveness (both mentally and physically) hence let me impress you Hepar Sulph, through the word ‘S-stands for sensitiveness. So remember Hepar Sulph, through the word ‘S’.
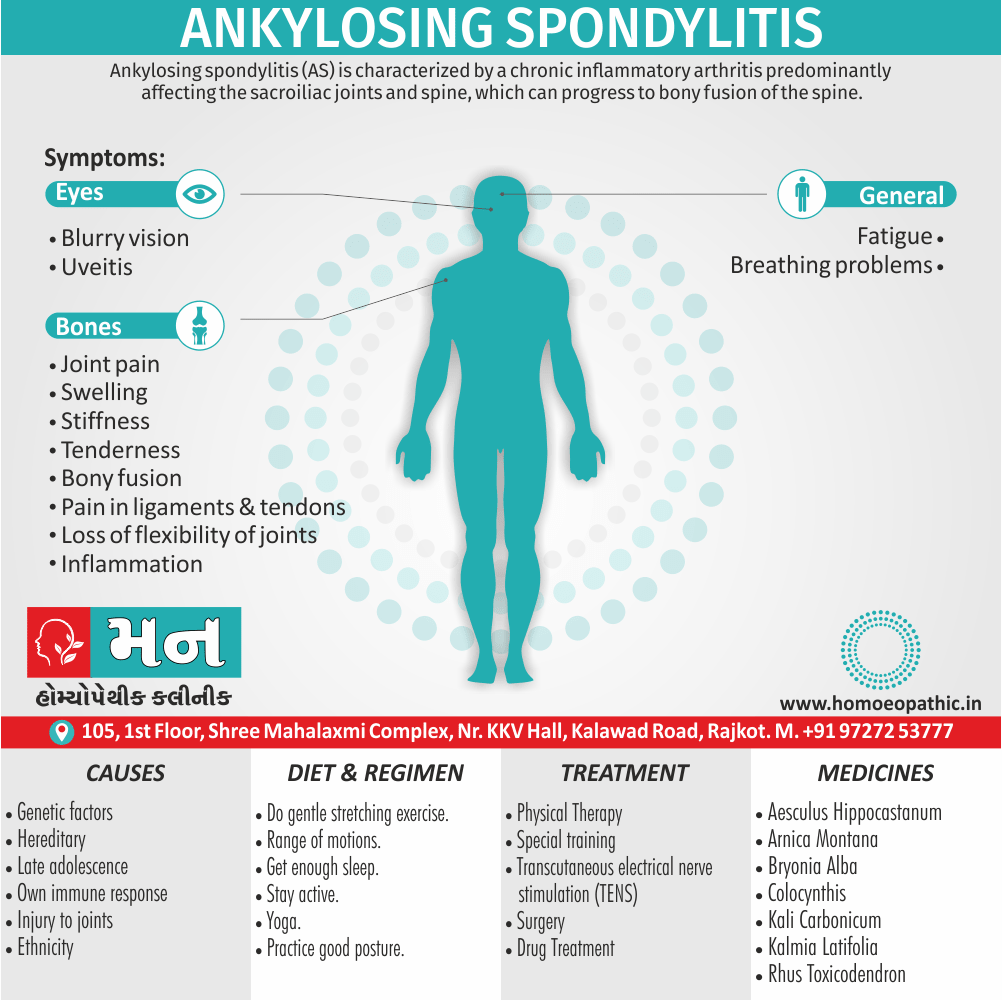
Sensitivity to cold air
- Our Hepar pt. is extremely sensitive to cold air (+++), imagines he can feel the air, if a door is opened in the next room, must be wrapped up from head to foot, even in hot weather (Psor.): cannot bear to be uncovered (Nux Vom.–can’t bear to covered. Camph., Sec. Cor. (always chilly even when taking active exertion, Sil, Led., Sop.). (-Chilliest medicines of our Materia Medica, Hepar Sulph, Nux. Vom. Sil.. Psor.).
- Takes cold from slightest exposure (Tuber). (-Master Kent graded Hepar in first degree under the sub- rubric, tendency to take cold easily. Acon. 1, Baryta.1, Bry.1, Chamo.1, Dulc.1, Hep.1, Lyco.1, Merc.1, Nat. Mur.1, Nit. Ac.1, N.V.1, Psor.1, Rumex.1, Sep.¹, Sil.’, Tuber.) (Dr. Nash said, remedies esp. < in cold air, Ars. Alb., Calc, Carb., Nux. Vom., Psor., Sil., Tuber.).
Sensitive both mentally and physically
- a) Mental hypersensitivity: Slightest cause irritates him, hyper-Impulsive.
- b) Physical hypersensitivity: Characterized by hyperaesthesia – oversensitive to touch, to pain. Dr. Nash said. This super-sensitiveness to pain runs all through the drug. Sensitiveness to touch even to clothes (Lach).
Sweats profusely
- Master Kent graded it in first grade in his voluminous Repertory- profuse perspiration, Ant. Tart. 1, Ars. 1, Bell. 1, Bry, 1 Calc. 1, Carbo Veg. 1, China. 1, Hep. 1, Kali. Bi. 1, Merc. 1, Nat Mur. 1, Psor. 1, Samb. 1, Sep. 1, Sil. 1, Tuber. 1, Verat. 1
- Profuse perspiration, day and night without relief, Hep., Merc.2, Samb2.
- Hepar has perspiration of cheesy odor Hep.2 (-honey like, Thuja; -sour, Ars. 1, Bry. 1, Colch. 1, Hep. 1, Lyco. 1, Nit. Ac. 1, Psor. 1, Sep. 1, Sil. 1, Sulph. 1, V.A. 1 ; -odor of Sulphur, Phos;
- oily perspiration, Bry. 1, China. 1, Merc. 1, Thuja. 1; -in single parts, Calc. 1, Caust. 1, Ign. 1 ,Mez. 1, Puls. 1, Sep. 1).
Sourness of all the discharges
- All the discharges of Hepar Sulph pt. is sour-sweat, stool etc. Dr. Tyler said smelling like old cheese. Dr. Nash said, the whole child smells sour.
Sensation of splinter
- There is sensation of splinter, fish bone or plug in affected parts, -ulcers, piles, throat etc. (Arg Nit., Dolichos, Nit. ac., Sil) (-sensation of a ball rolling in the bladder. Lach: sensation of band around the head, Carb.Ac.. Nit.Ac.. Sulph.).
Slightest injury suppurates
- Slightest injury tends to suppurate (Graph., Sil, Sulph, Merc, Petro, Psor)
Sour things craving
- Master Kent graded Hepar in first grade in his Repertory -desire for sour, acids etc. (Hep. 1, Verat. 1, Ant.C.2, Ant.Tart2, Apis.2, Arn.2, Ars.2, Bry.2, Calc. 2, C.V. 2, Chamo. 2 Ign 2 ,Nat.Mur. 2, Medo. 2, Phos. 2, Podo. 2, Sulph 2
System injured by abuse of mercury
- The entire system has badly drugged or abused by mercury (Aur. 1, Carbo. Veg. 1, Hep. 1, Lach. 1, Nat S. 1 Nit.Ac. 1, Phyto. 1, Staph. 1, Sulph. 1). Hepar antidotes the bad effects. (8)
Memory Tips for Mental Symptoms
Hi Friends Let’s memorize mental symptoms of Hepar Sulph through name of Medicine ‘Hepar Sulph’.
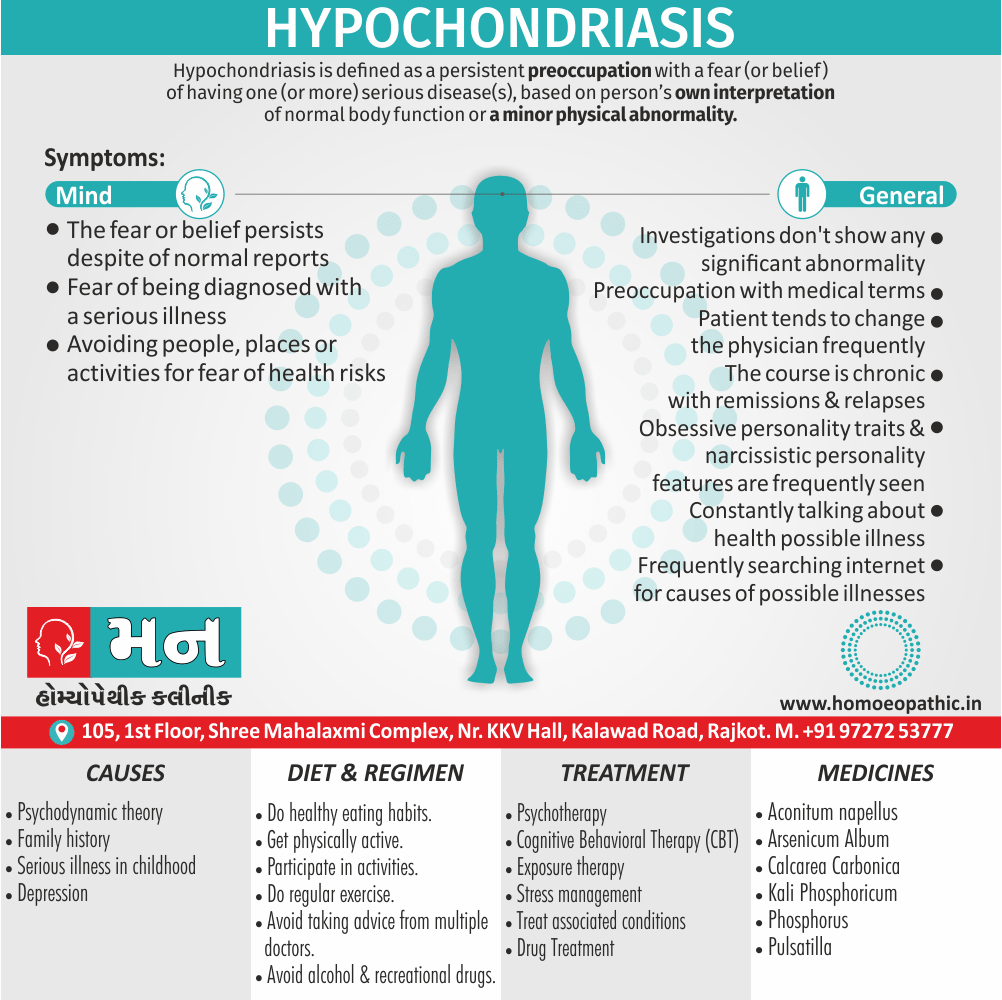
Hypochondriac
- Very hypochondriac in nature. (11)
Excessive irritability
- Excessive irritability.
- Vexation and passion, with hasty speech and excessive weakness of memory. (12)
Peevish
- Extremely peevish and obstinate.
- Vexed about trifles.
- Very peevish; every trifle vexed her.
- The least thing put him into a violent passion, he could have murdered anyone without hesitation.
- Great weakness of memory during his peevishness; he had to think quite a while before he could remember anything. (11)
Anger, Apprehensive, Anxiety
- Anger, would have no hesitation in killing a man who offended him, only he knows better. Visions in the morning, in bed. (12)
- Dejected, sad and apprehensive. Fearful anguish, in the evening, for two hours; he thought he had to perish and was sad even so that he could have die by suicide. (11)
- Great anxiety in the evening. (15)
Repulsive mood
- Great anguish in the evening.
- Repulsive mood. The slightest cause irritates him. (13)
Sad
- Sad and dejected, inclined to shed tears. (13)
- Sad mood for many hours, she has to cry bitterly. (14)
Unwilling to speak
- Ill-humored, in the morning after rising, is unwilling to speak, but cheerful while in bed.
- Contrary mood; he does not like to look at his folks.
- Very discontented and peevish over his pains and discouraged.
- Irritable mood; whatever she started to do, was not satisfactory, she wished to be alone. (11)
Low spirited
- Low spirited even to thoughts of suicide.
- Dementia, with complete stupidity, sits silent in a corner. (13)
Pleasure- not in anything
- No pleasure in anything.
- Dissatisfied with oneself.
- She thinks about everything disagreeable that happened to her in her lifetime. Whatever she thought about was unsatisfactory and did not suit her. (11)
Horried impulsive
- DISSATISFIED, with oneself and others.
- Ferocious; wants to kill who offends him; wants to set things on fire.
- Horrid impulses. (5)
Hepar Sulph Introduction
Hi Friends, Now we describing Drug picture of Hepar Sulph
Common name:
Sulphuret of lime (1)
Synonyms:
Hepar sulphuris calcareum, Liver of sulphur, An impure sulphide of calcium (1)
Family / Group / Class / Order:
Mineral kingdom (1)
Habit and habitat / Description:
- It is a white, porous, friable mass or a white amorphous powder.
- It has the odour and taste of sulphurated hydrogen.
- It is insoluble in water. It is also insoluble in alcohol but soluble in hot HCl with evolution of hydrogen Sulphide.
- It responds to all the reactions which are characteristic of calcium and of sulphides.
- Hepar sulphuris is prepared by mixing Calcarea carbonica and Sulphur.
- It’s symptoms, however, show a wide range of similarity and variations in contrast to Sulphur and Calcarea carbonica. (1)
Formula / Symbols:
CaS (1)
Name of prover:
Dr Hahnemann (1)
Introduction and history:
- It is one of the artificial compounds used in homeopathy.
- In 1794, Hahnemann used this drug internally to remove the bad effects of the intake and topical application of mercury, the use of which was very common.
- Hepar Sulph is a constitutional remedy.
- Hepar Sulph is the surgeon amongst our homeopathic remedies.
- Due to the administration of this remedy in homeopathy the distracted patient escaped and saved himself from mutilation.
- Hepar sulphuris is one of our leading and strongest antipsorics. It is antisyphilitic too. It’s action in old syphilitic cases, when indicated by symptoms is very deep and radical in character.
- Being a chemical combination of Calcarea carbonica(oyster shell) and Sulphur, it has, as one might naturally expect, points of resemblance with Calcarea carbonica and Sulphur. (1)
Preparation:
- Triturations are prepared from the impure sulphide of calcium, from which higher potencies are prepared according to the directions given in the homeopathic pharmacopoeia. (1)
Constitution
Physical make up: It is best adapted to scrofulous, psoric and lymphatic constitutions in which there is a tendency to have eruptions and glandular swellings. Torpid constitutions with lax fibre. (1)
Temperament: Choleric 3, Nervous 2 (2)
Diathesis: Scrofulous and lymphatic (1)
Relation with heat & cold: Very chilly patient (1)
Miasm : Psora (1)
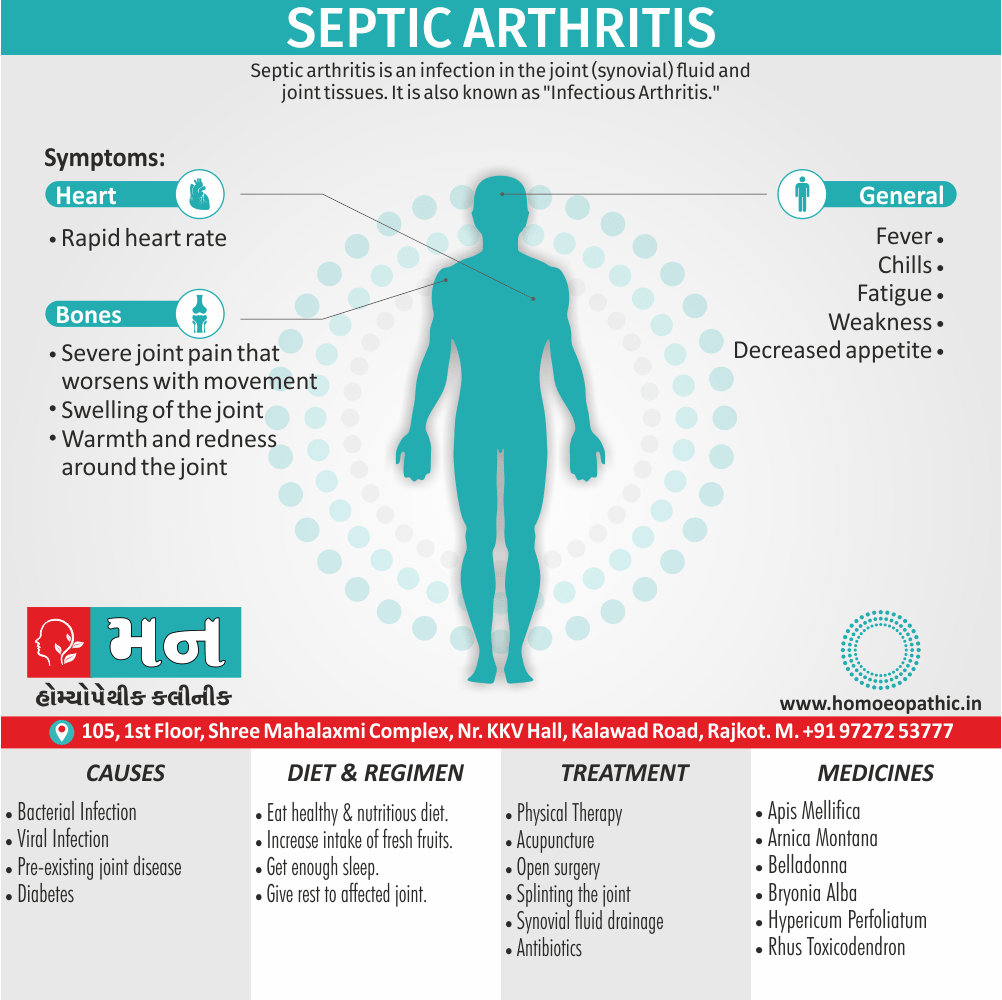
Clinical Features
Clinical conditions
In Homeopathy Hepar Sulph medicine use by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of following Disease Conditions
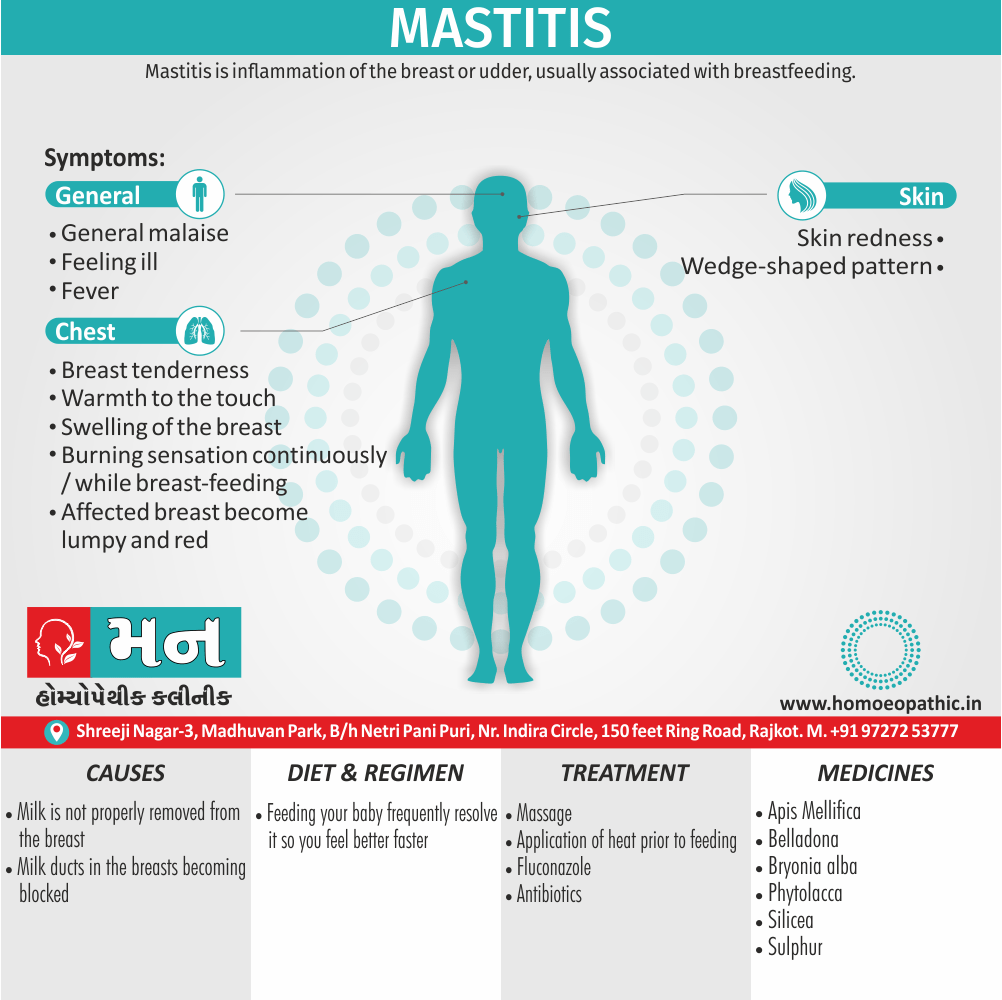
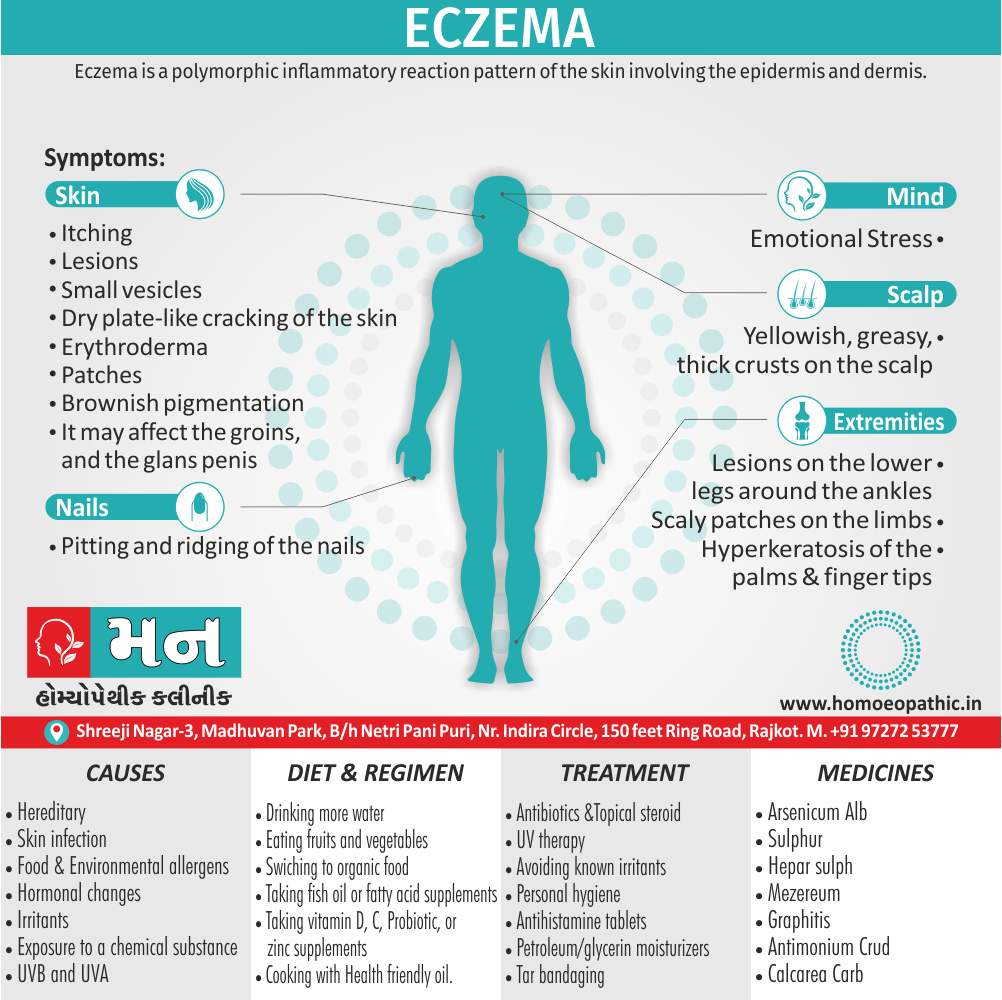
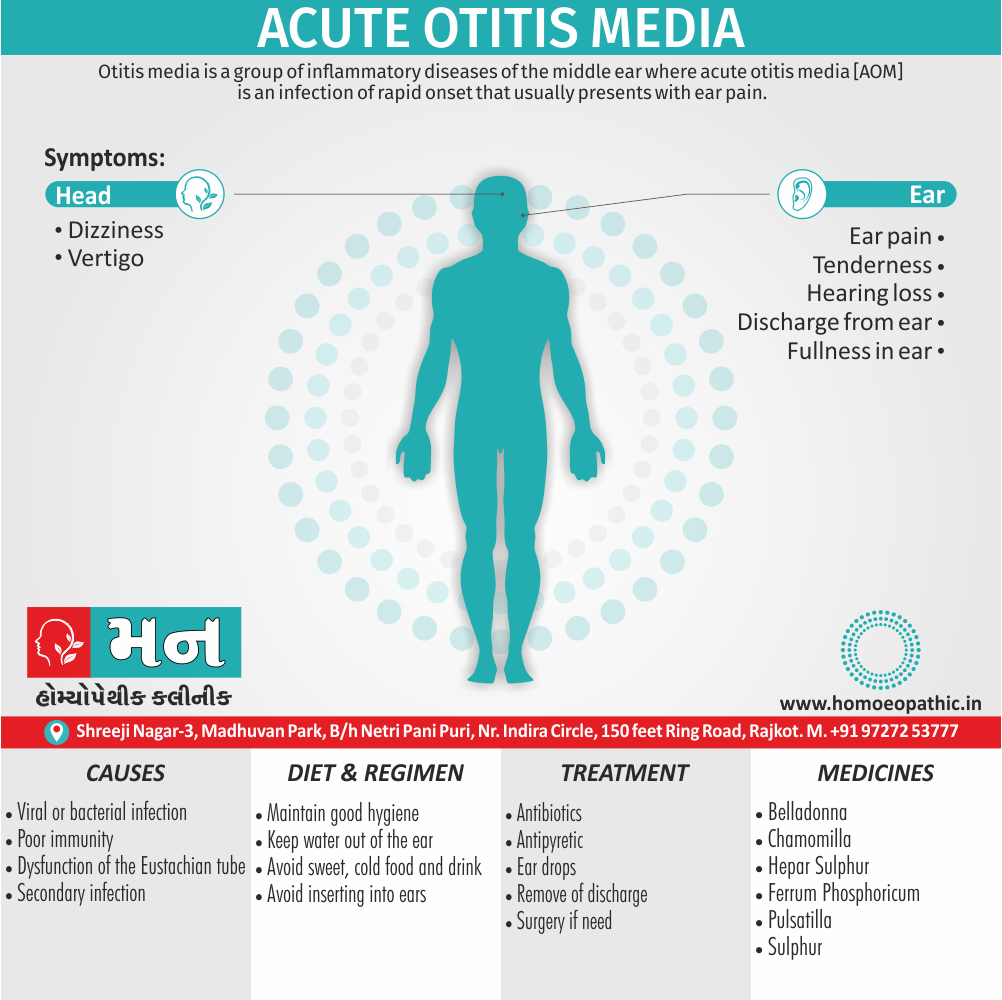
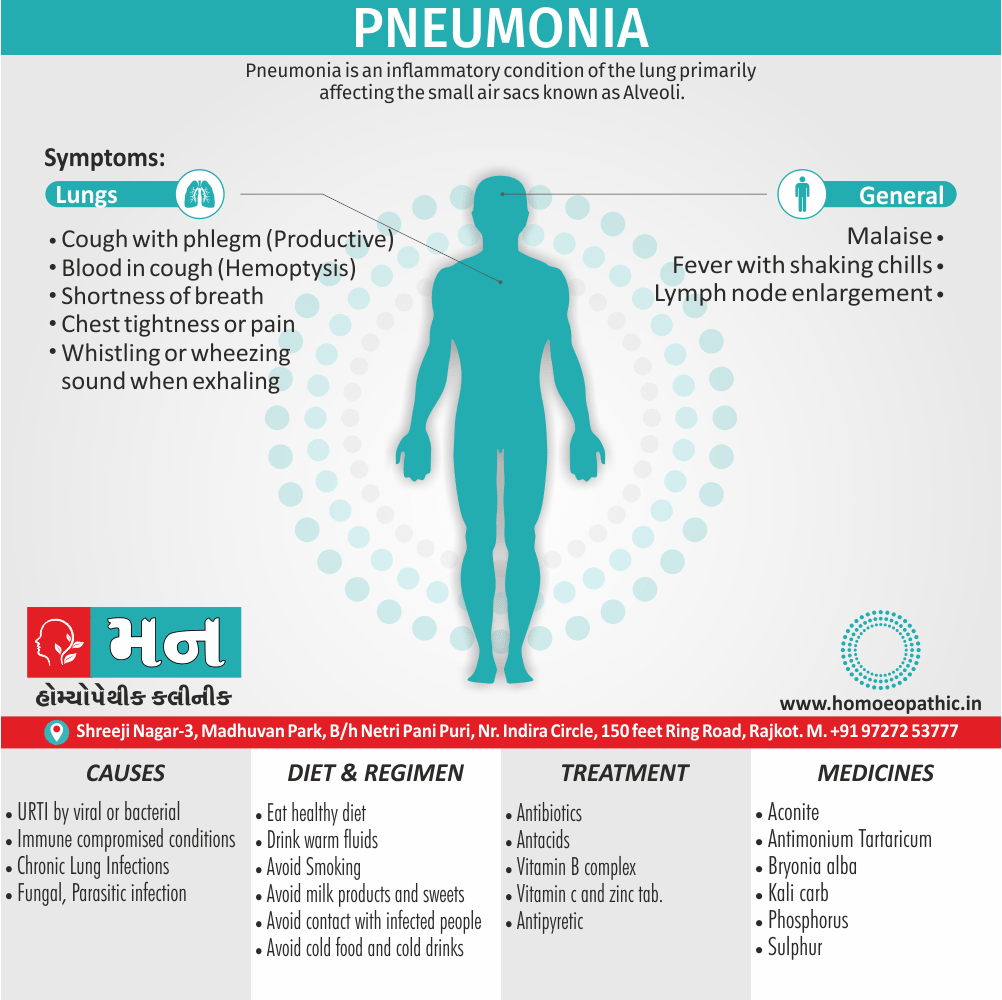
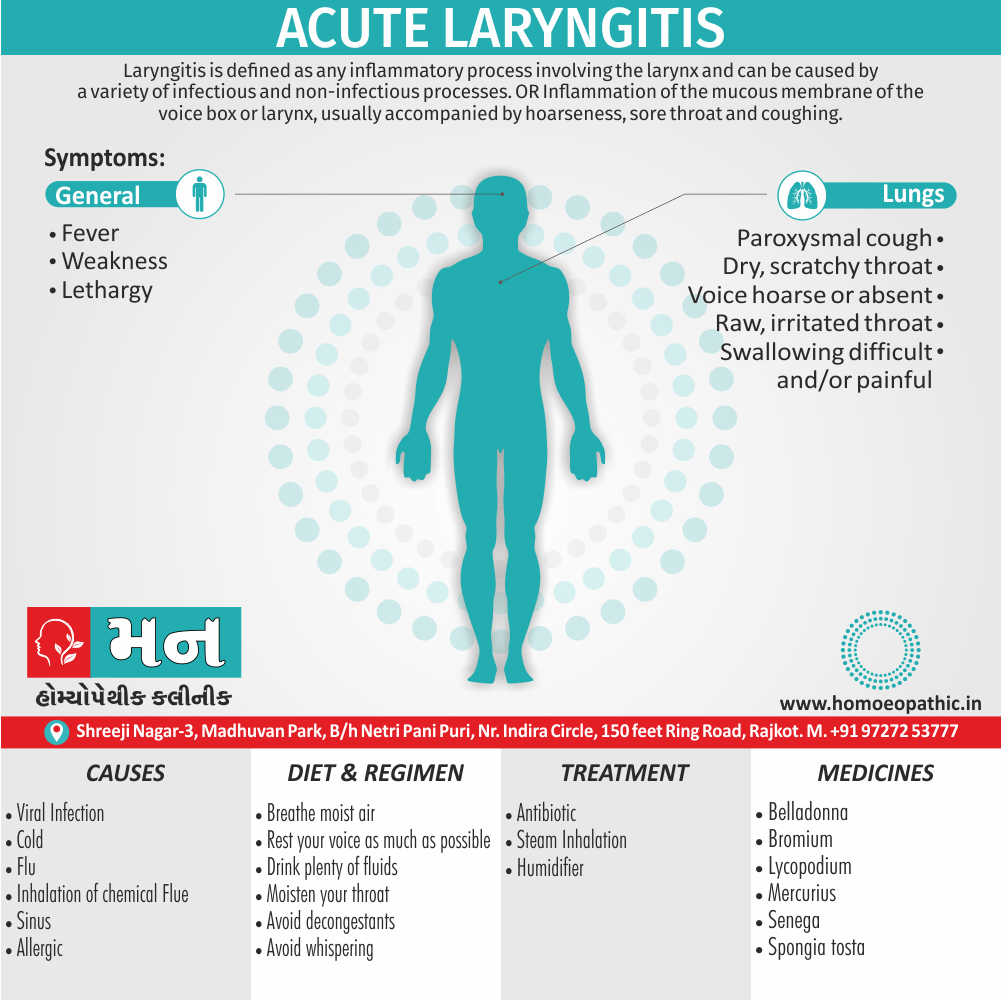
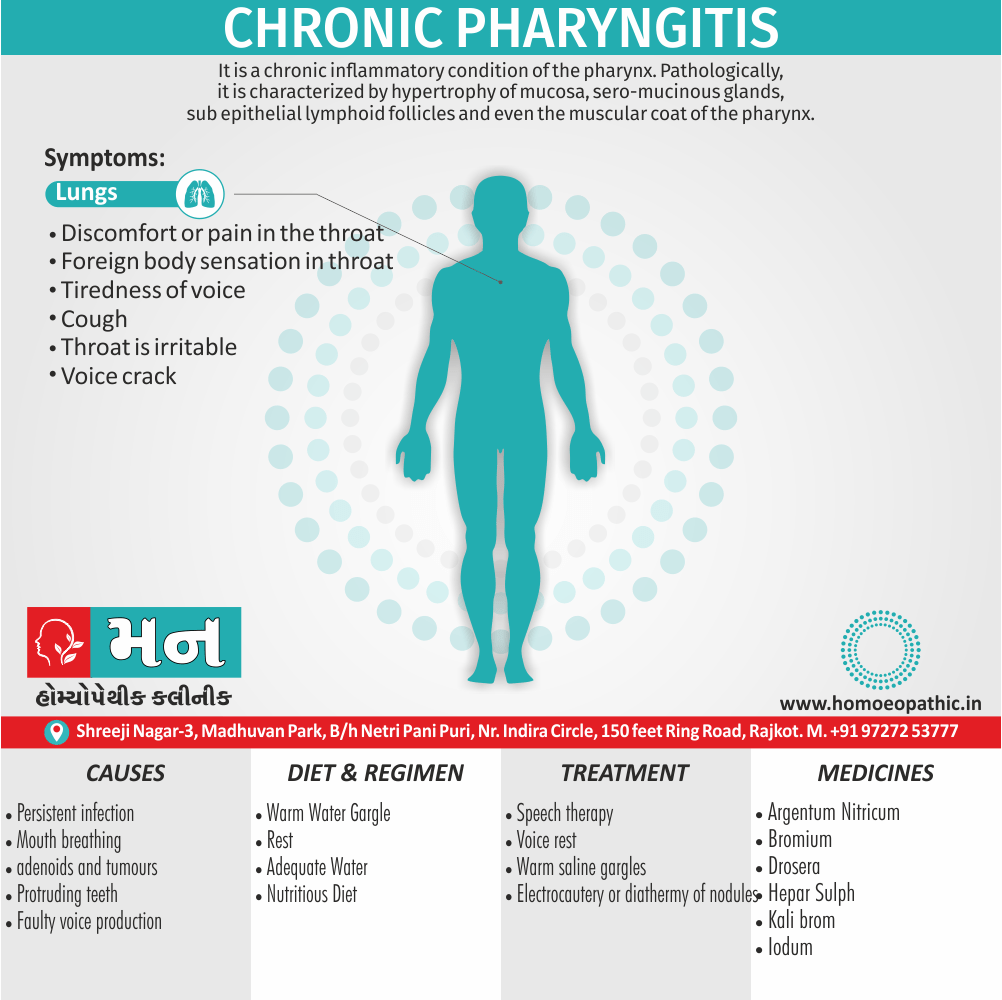
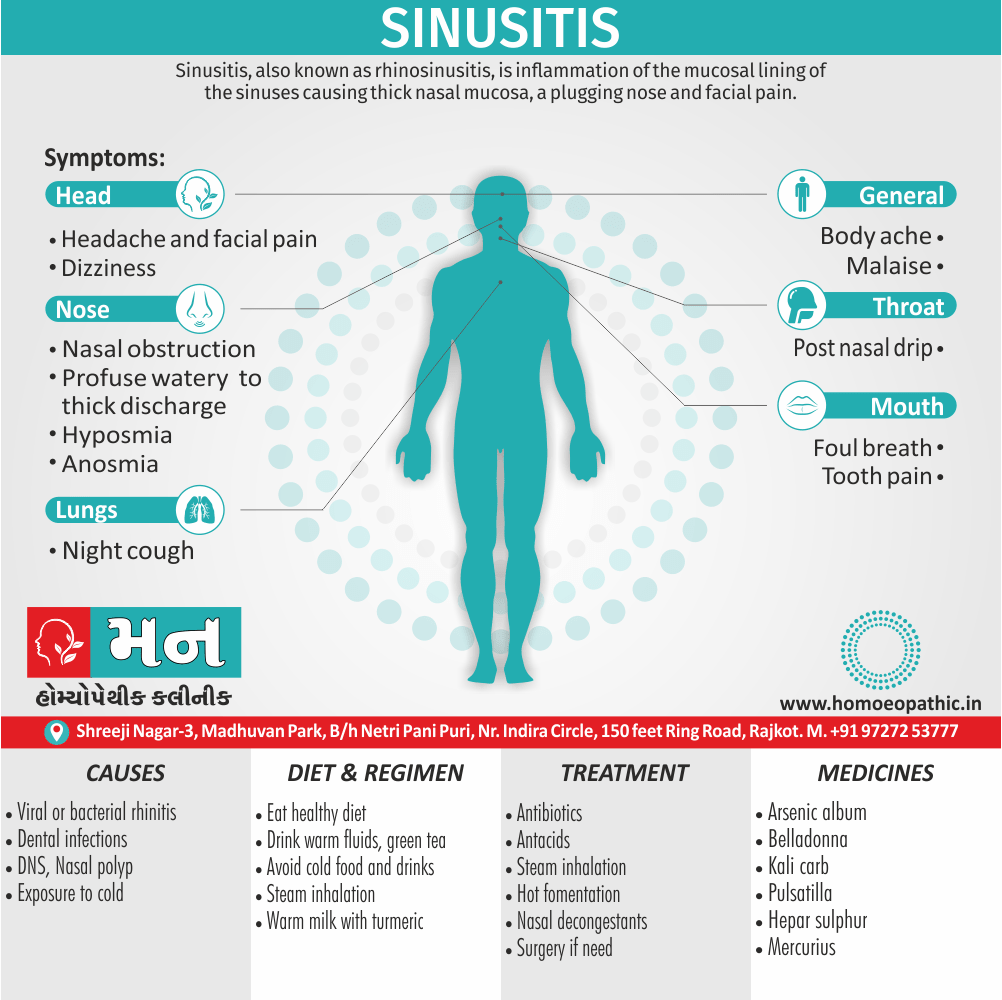
- Abscess, Acne, Adenopathy, Agoraphobia, Asthma, Balanitis, Blepharitis, Bronchitis, Croup, Eczema, Iritis, Laryngitis, Mastitis, Otitis media, Paronychia, Pharyngitis, Pleurisy, Pneumonia, Prostatitis, Rectal abscess, Sinusitis, Tonsillitis, Urethral stricture, Urethritis.
- It has been used for chronic malarial poisoning that has been maltreated with calomel and quinine.
- In otitis media, in the adolescence, give Hepar sulph- Dr. Foubister. (3)
Sites of action / Pharmacodynamics
- Nervous system, skin, kidneys, connective tissues, respiratory system, lymphatic and glandular system, mucous membrane, etc. (1)
Causation (Causes / Ailments from)
- Cold, dry wind, injury, abuse of mercury, suppressed eruptions, suppression of syphilis and gonorrhoea. (1)
Physiological action
- This agent acts upon the glandular system, Producing enlargement with a tendency to suppuration.
- The resistance of the tissues in general to pathogenic bacteria is lowered.
- Given in the lower attenuations, It will hasten suppuration; as a result the skin is rendered unhealthy and there are catarrhal conditions of the mucous membranes.
- There is a binaural hyper sensitiveness established to touch, pain and cold air; this may be mental when the patient is displayed with himself, as well as others. (4)
Patho-physiological changes / Pathogenesis
- It acts upon nerves and causes great oversensitiveness, hypersensitiveness and irritability. Slight pain causes the patient to faint.
- It acts upon the mucous membrane of the respiratory system causing
- excessive secretion and copious catarrhal inflammation.
- It acts on lymphatic glands producing enlargement and suppuration.
- Acts on skin producing ulcers, suppuration, eruptions, unhealthy skin and a condition of non-healing, moist eruptions in the folds of skin.
- It prevents the formation of pus and hastens the pointing of an abscess. Ulcers have a tendency to burrow deep causing necrosis and caries in the bones.
- It acts on the urinary bladder and produces atony of the urinary bladder. (3)
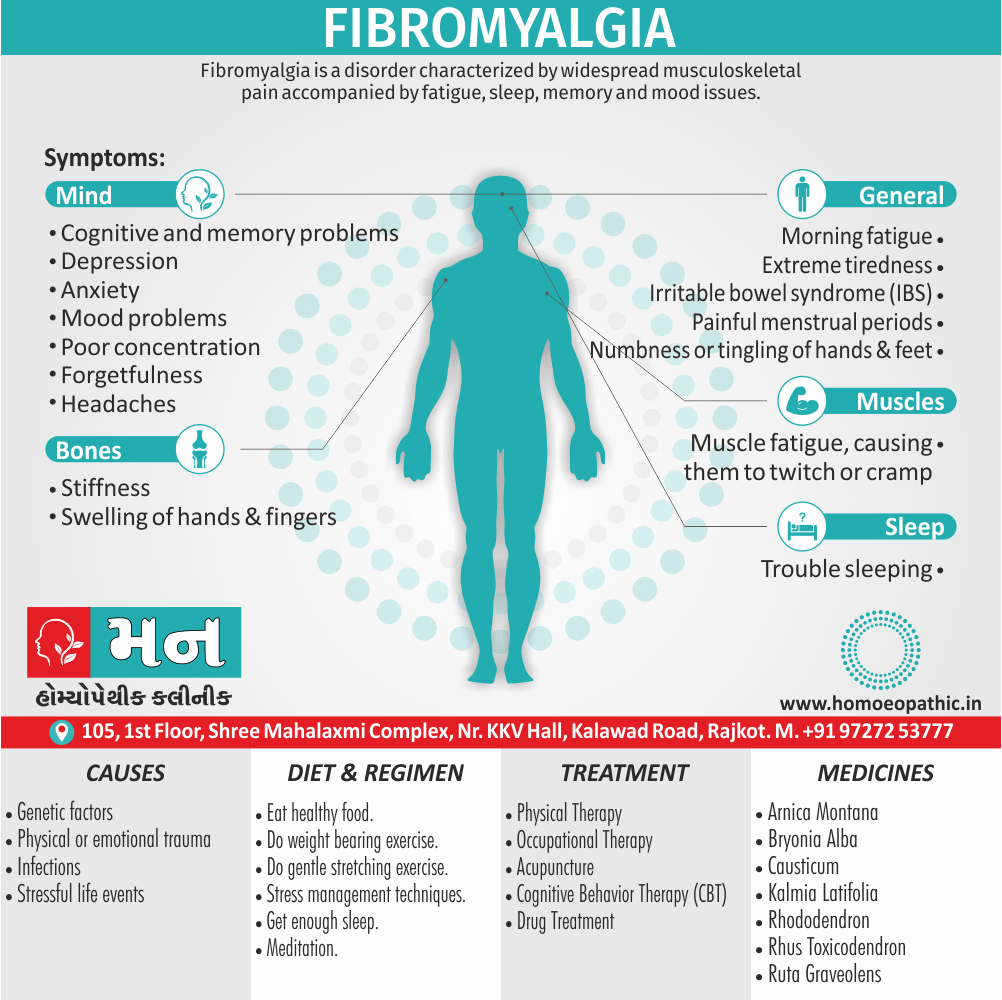
Characteristic mental symptoms (psychology)
- Great weakness of memory, with irritability.
- The patient is very impulsive. Impulse to do violence and to destroy, for example a mother may have the impulse to throw her child from the gallery or throw the child into the fire.
- The patient is very quick in action, very depressed and hypochondriacal.
- Great anxiety in the evening, low spirited, thoughts of suicide.
- The patient is very irritable and oversensitive mentally.
- Patient becomes angry very easily at least trifles and is very peevish.
- Sad mood for hours, very quarrelsome, hard to get pleased.
- Anguishness marked in the evening and at night. The slightest cause irritates him and makes him extremely vehement. (1)
Guiding Symptoms
H-Hastens suppuration.
E-Every little injury suppurates.
P-Physically and mentally oversensitive.
A-Abuse of mercury.
R-Relief from warmth in general: as very chilly patient.
S-Sweats: profusely day and night without relief.
U-Ulcers: surrounded by little pimples: spread by coalsing.
L-Lower lip cracked.
P-Plug sensation in throat: sensation of splinter.
H-Hasty speech, hasty drinking. (10)
Generalities
- An impure sulphate of calcium. It affects the NERVES making the patient OVERSENSITIVE to all impressions; to cold; to pain; touch, noise, odours, to draught of air; slightest pain causes fainting.
- The patient is of sluggish character, and weak muscles, blondes. CONNECTIVE TISSUE is affected producing THE TENDENCY To SUPPURATION; which is very marked.
- It has a special affinity to RESPIRATORY MUCOUS MEMBRANES producing profuse secretions.
- All the discharges are profuse; foul; like old cheese; sour, stools, smell of the body, sweat etc. SWEATS EASILY and profusely, but dares not uncover; sweats without relief. Glands inflamed; swell and suppurate.
- The patient is CHILLY; even wears overcoat in hot weather. As of a wind blowing on part. Takes cold from exposure to damp cold weather.
- Pains are sore, STICKING; like sharp splinters.
- Skin is usually affected in folds; EVERY HURT FESTERS. Abscess, threatening; much thick pus. Establishes suppuration around and removes foreign body. Yellow; expectoration, sclerotic, sweat etc. Mastoiditis.
- The side lying on at night becomes gradually very painful; he must turn. Pellagra. Hard, burning nodes.
- Touchy mentally and physically. Ill effects of injury; suppressed eruptions; mercury. Trembling weakness after tobacco smoking. Pains in bones; caries. Spasms after injury. (5)
Head
- Vertigo worse riding in a carriage or shaking head.
- Boring headache in right temple and at the root of the nose, worse motion; stooping.
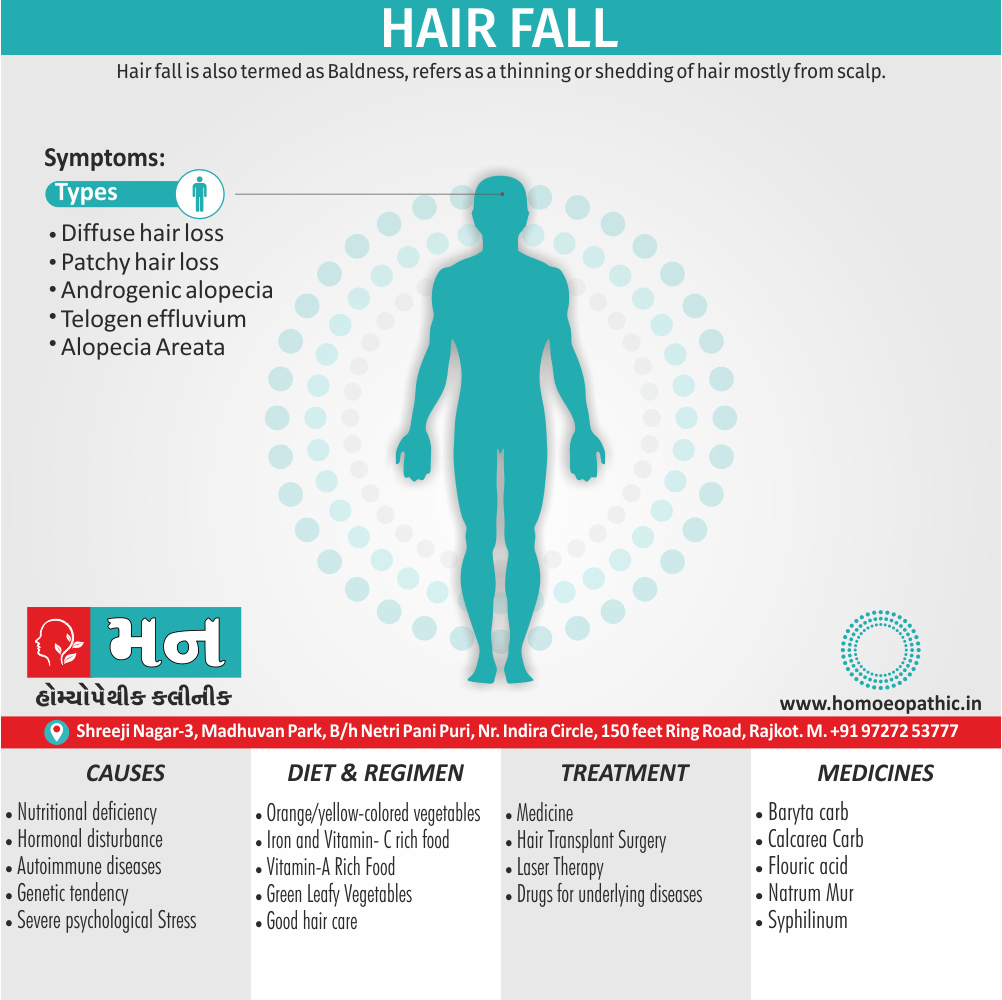
- Hair falls; in spots, after headache.
- Scalp, sore and sensitive.
- Sore nodosity on head.
- Cold sweat on head.
- Constant pressive pain in half of brain, as from a plug. (5)
Eye
- Ulcers on cornea or maculae.
- Hypopion.
- Objects appear red and too large.
- Little pimples surround the inflamed eye.
- Photophobia. Field of vision one half.
- Anaesthesia of retina, from looking at an eclipse. (5)
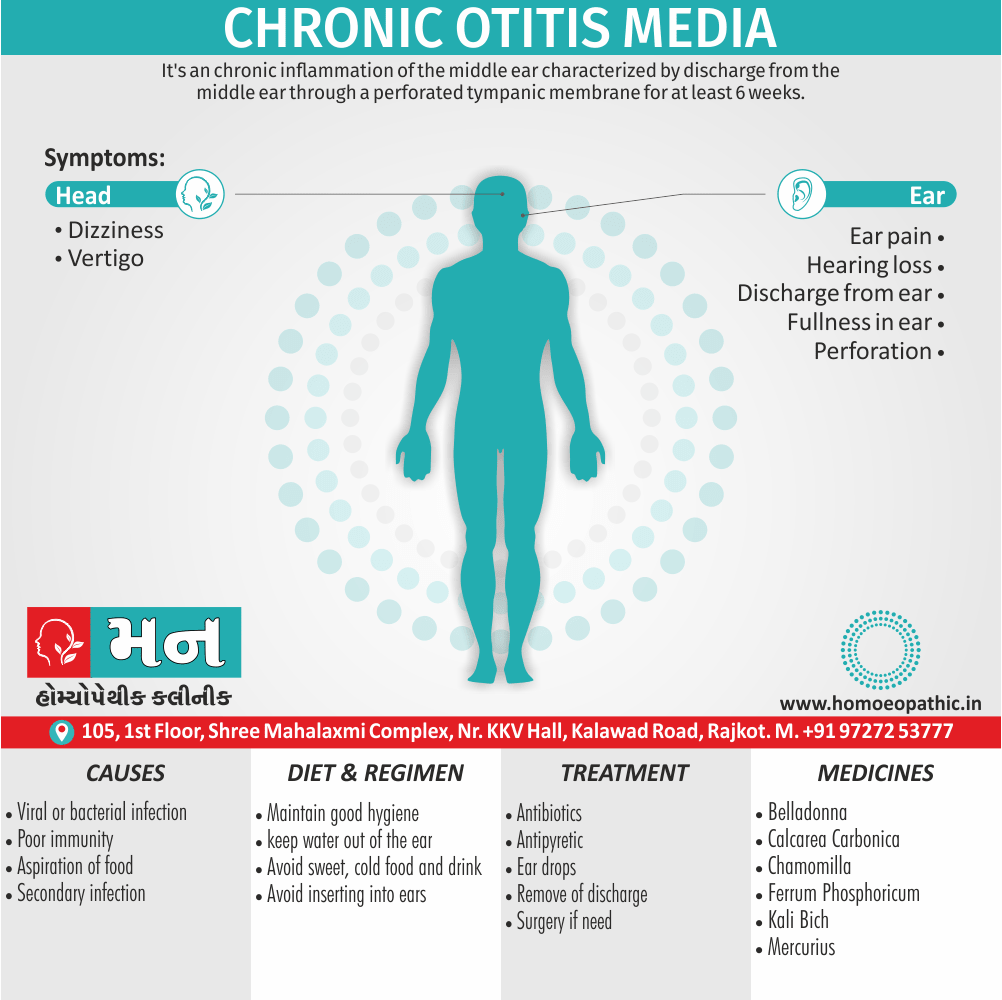
Ears
- Darting pain in the ears.
- Wax increased.
- Perforation of the drum.
- Foetid otorrhoea.
- Mastoiditis.
- Scurf on and behind the ears. (5)
Nose
- Stops up or sneezing and running from the nose every time he goes into cold dry wind. Nosebleed; after singing.
- Sore pain at the root of nose.
- Stuffed painful nose.
- Smell like old cheese.
- Hay fever.
- Ripened colds and old catarrh.
- Sneezes from every cold wind. (5)
Face
- Yellow, with blue rings around the eyes.
- Lower lip cracked in the middle.
- Bones painful to touch.
- Shooting in jaw on opening the mouth.
- Ulcers in the corner of the mouth.
- Upper jaw projects.
- Herpes following the course of the supra-orbital nerve.
- Pimples on forehead which disappear in open air.
- Hard swollen cheek; with a hard growth over it. (5)
Mouth
- Teeth loose.
- Hollow teeth feel too long.
- Gums bleed easily.
- Ulcers of the soft palate that eat away the uvula.
- Offensive breath.
- Aphthous pustules on inside lips and cheeks. (5)
Throat
- Swelling of tonsils and glands of the neck.
- Quinsy.
- Sensation as if a fish bone or splinter sticking in the throat, extending to ears on yawning.
- Sensation of a plug.
- Hawks mucus.
- Goiter (right), pains into the head.
- Stitches extending to ear when swallowing.
- Chronic tonsillitis, with hardness of hearing. (5)
Stomach
- Longing for acids, condiments and stimulants; vinegar.
- Stomach; weak; burning and heaviness in stomach, after slight meal, easily upset.
- Constant acid rising sensation into oesophagus.
- Eating refreshes but causes heaviness.
- Drinks hastily.
- Aversion to fatty food.
- At times desires something but when he gets it does not like it.
- Painful on walking, as if it hangs loose. (5)
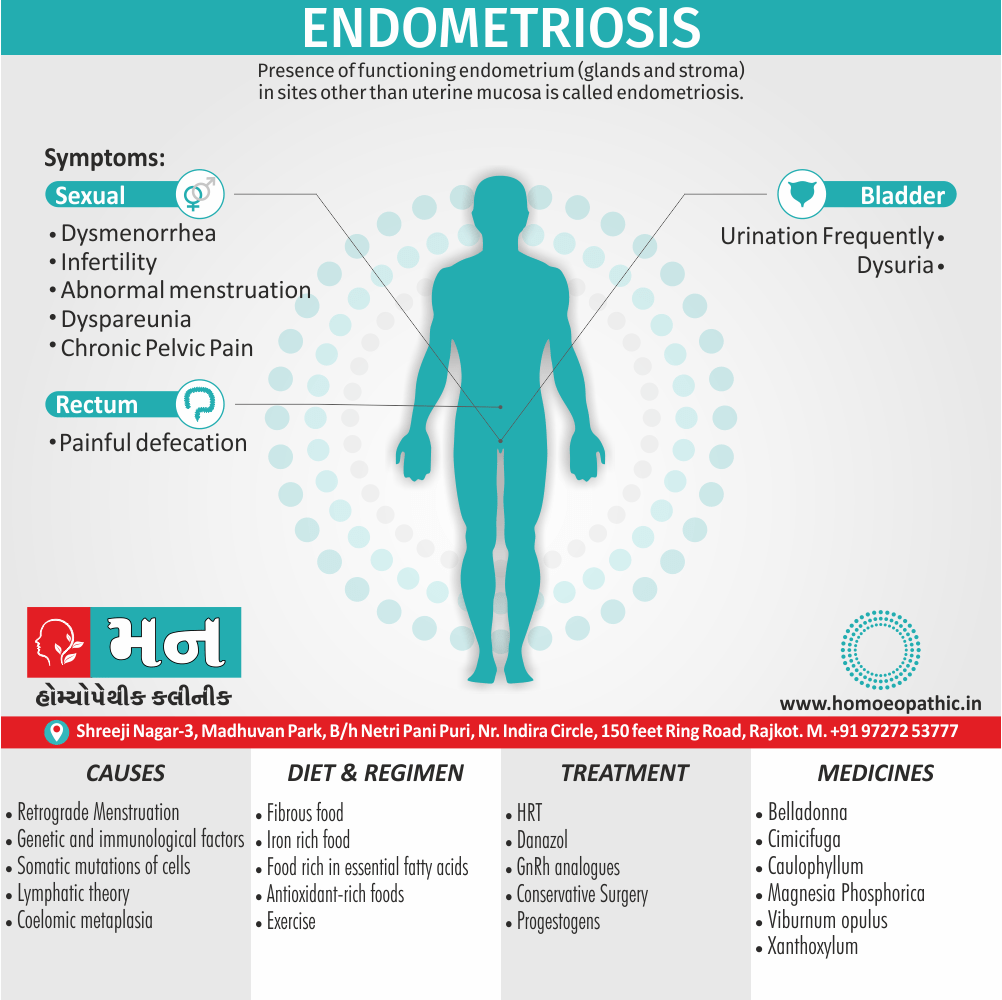
Abdomen
- Stitching in the region of liver worse walking, coughing, breathing or touching it.
- Stools soft but expelled with difficulty.
- Abdomen; distended, tense.
- Foul mucus from anus.
- Bleeding from rectum with soft stool.
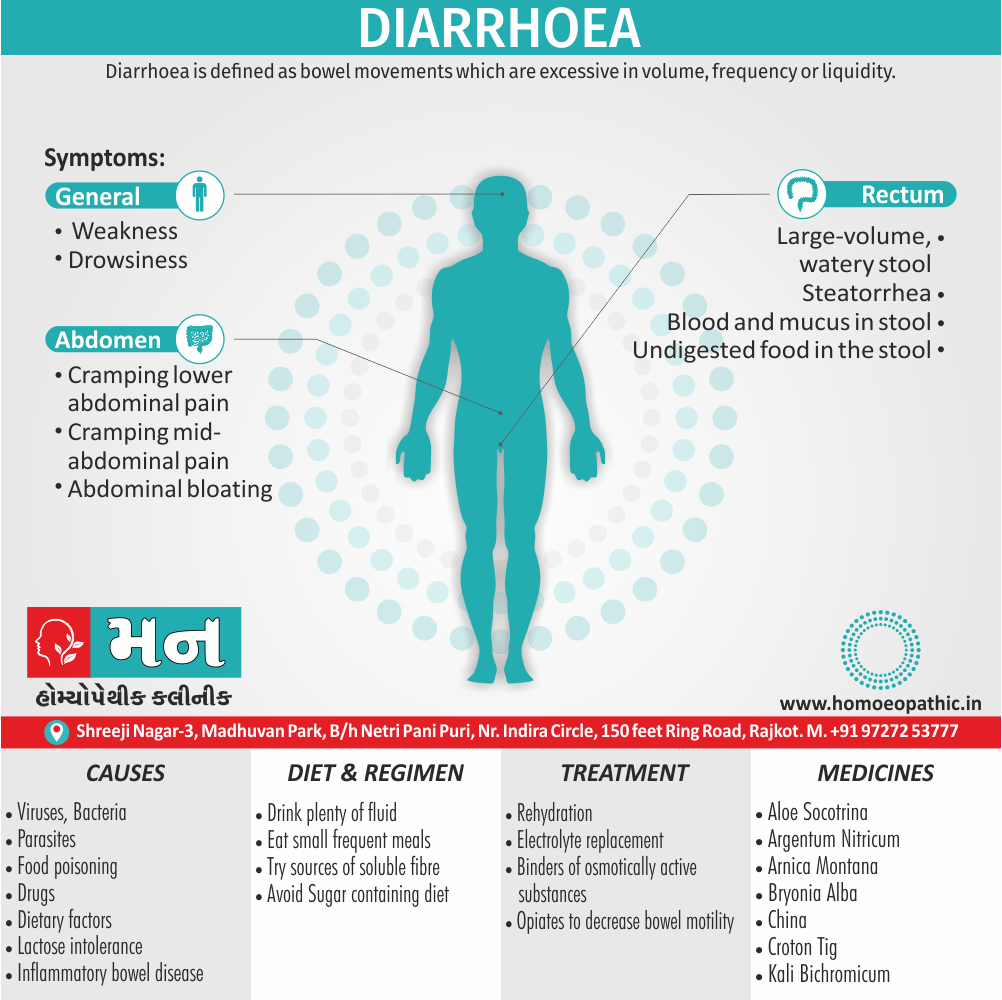
- Diarrhoea after drinking cold water.
- Hepatitis. Hepatic abscess. Stools; sour, white.
- Piles. (5)
Rectum & Anus
Loss of power to expel even a soft stool. (6)
Stool
Clay-colored and soft. SOUR, white, undigested, FETID. (6)
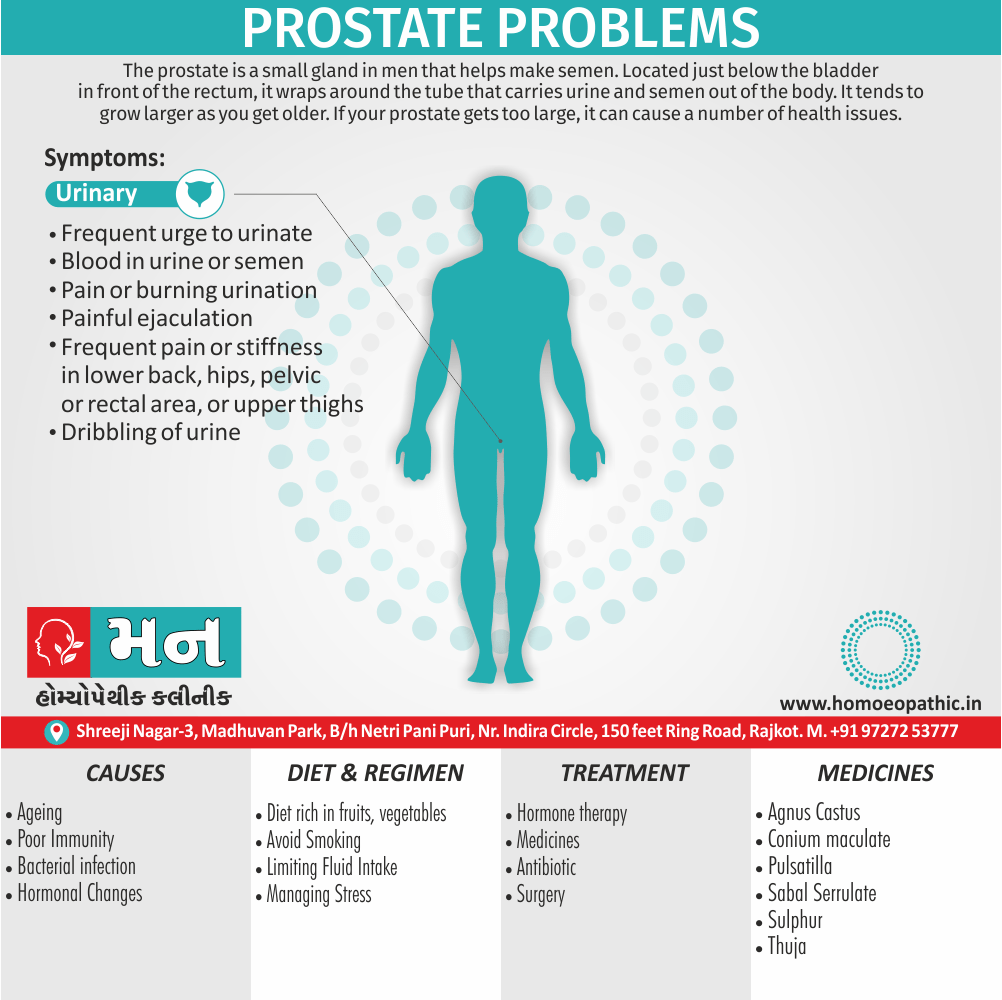
Urinary Organ
- Urine is passed slowly; with difficulty; drops out perpendicularly.
- Must wait to urinate.
- Passing of blood or pus after urination.
- Nephritis, after exanthemata.
- It seems that some urine always remains in the bladder; after urination. (5)
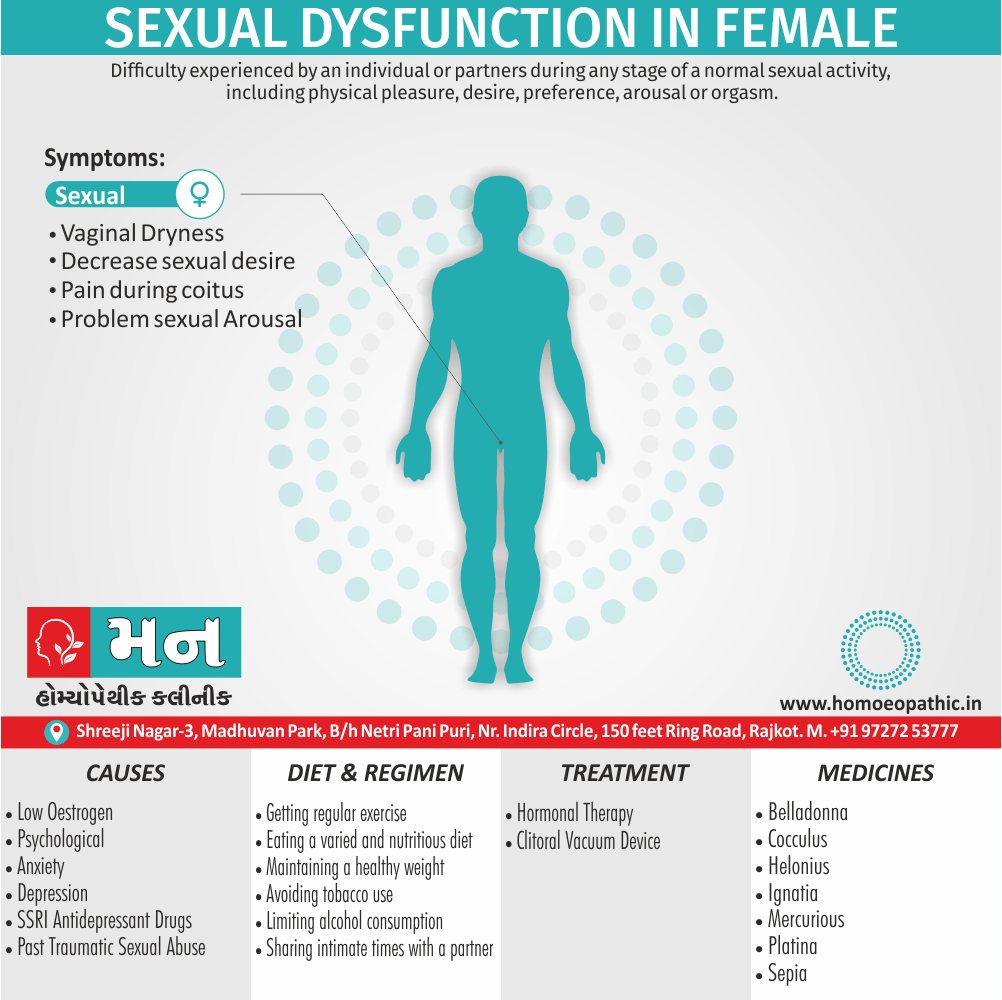
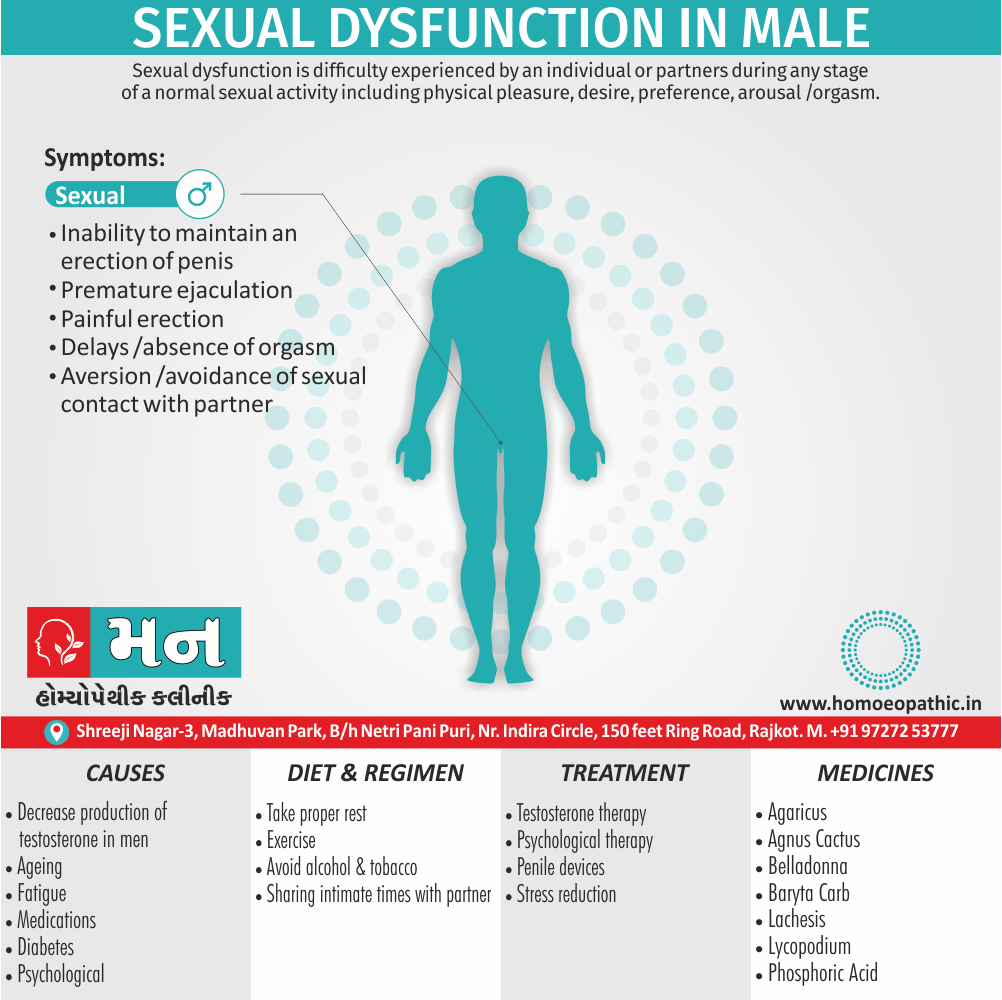
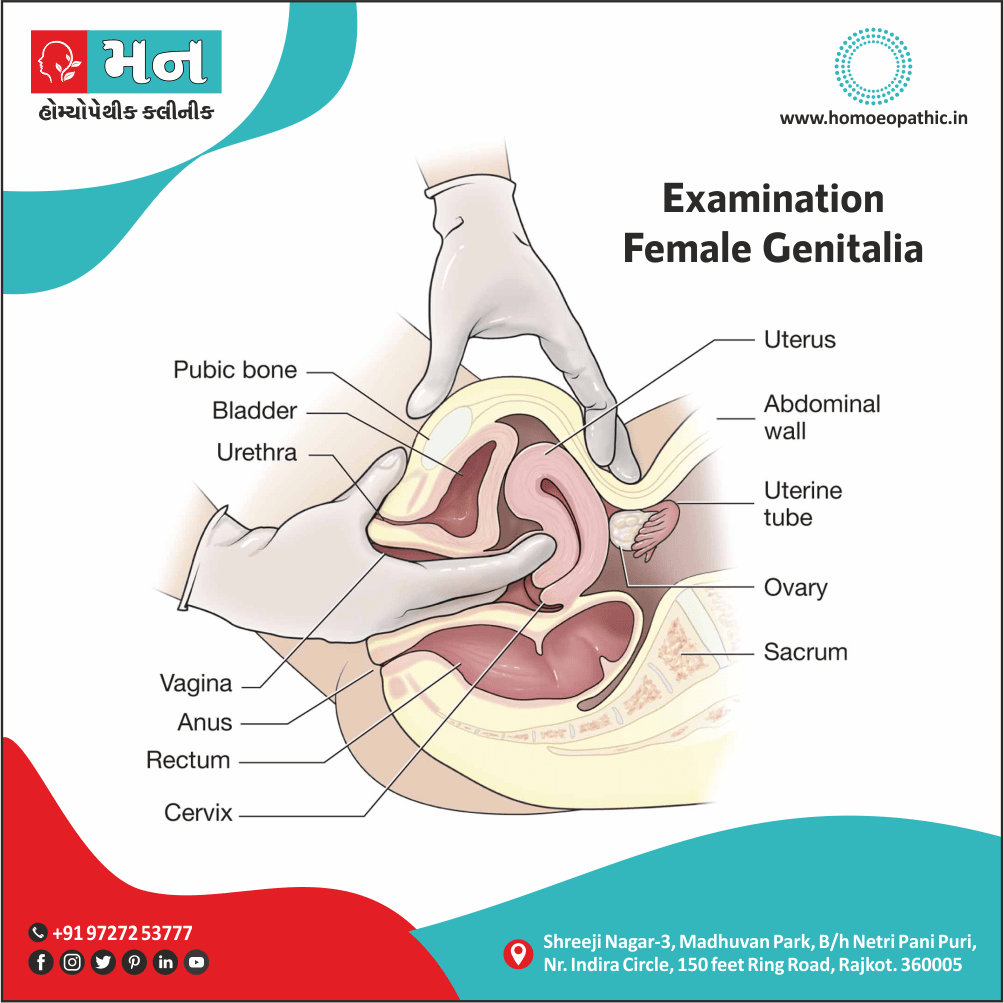
Sexual Organ
MALE
- Chancre-like ulcers on prepuce.
- Flow of prostatic fluid after urination, during stool.
- Condylomata, foul.
- Obstinate gonorrhoea.
- Skin of folds between scrotum and thighs becomes moist and sore.
- Glands in groins suppurate.
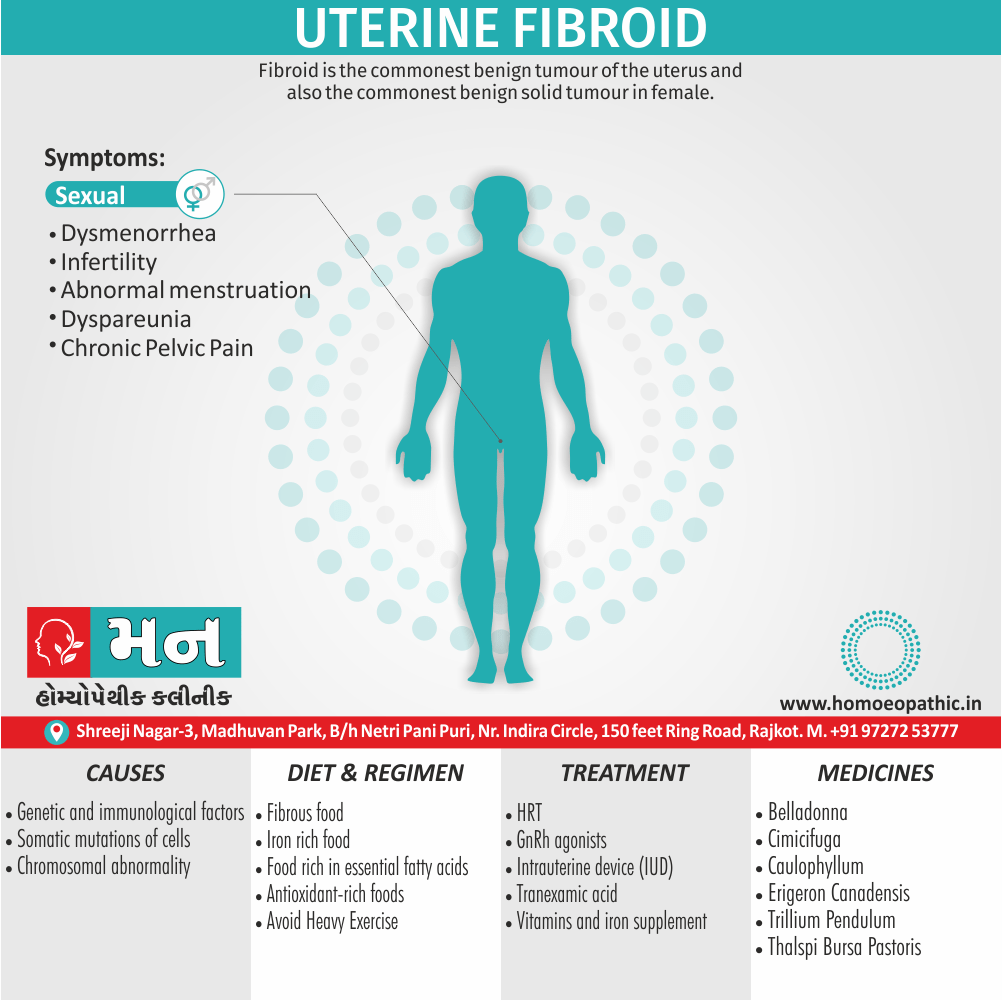
FEMALE
- Discharge of blood from the uterus during or after stools.
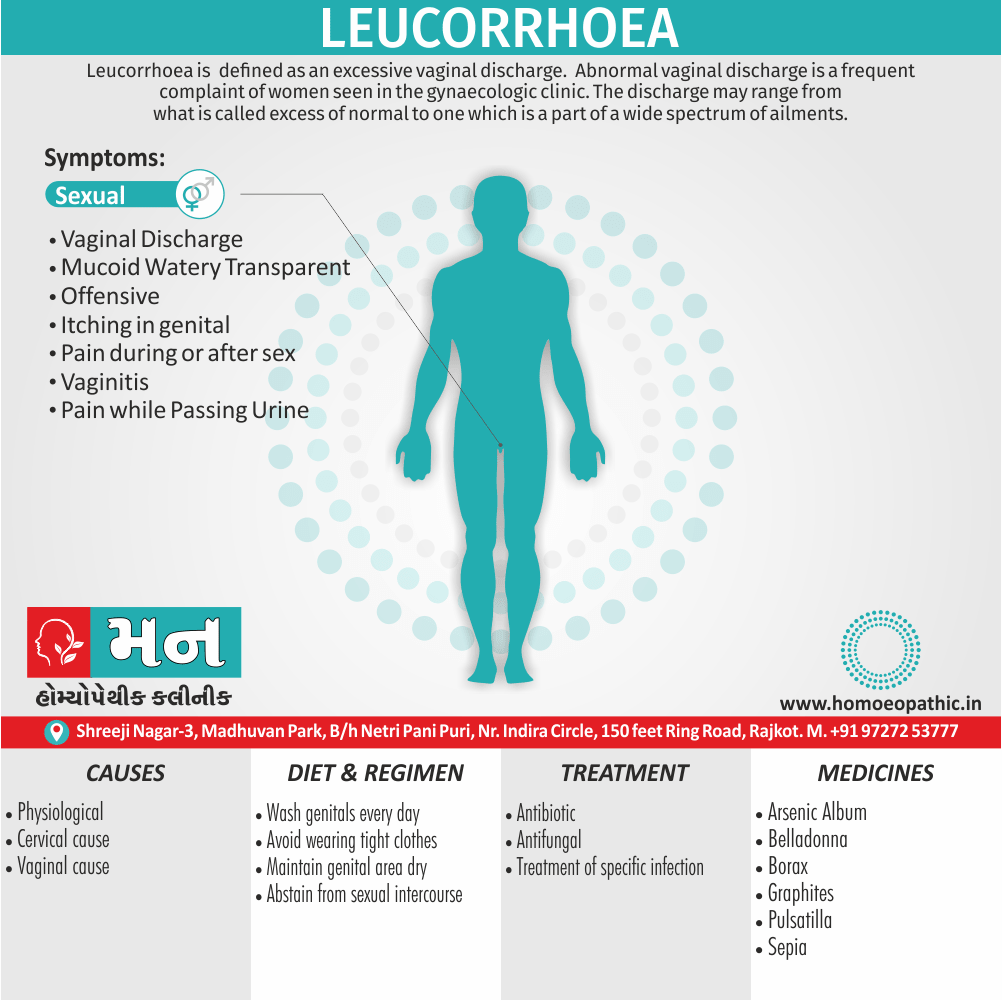
- Very foul, hot, membranous, leucorrhoea; smells like old cheese.
- Abscess of labia with great sensitiveness.
- Itching of nipples and pudenda worse menses.
- Cancer, with ulceration.
- Coitus very painful from enlarged and anteverted uterus, with congestion of ovaries. (5)
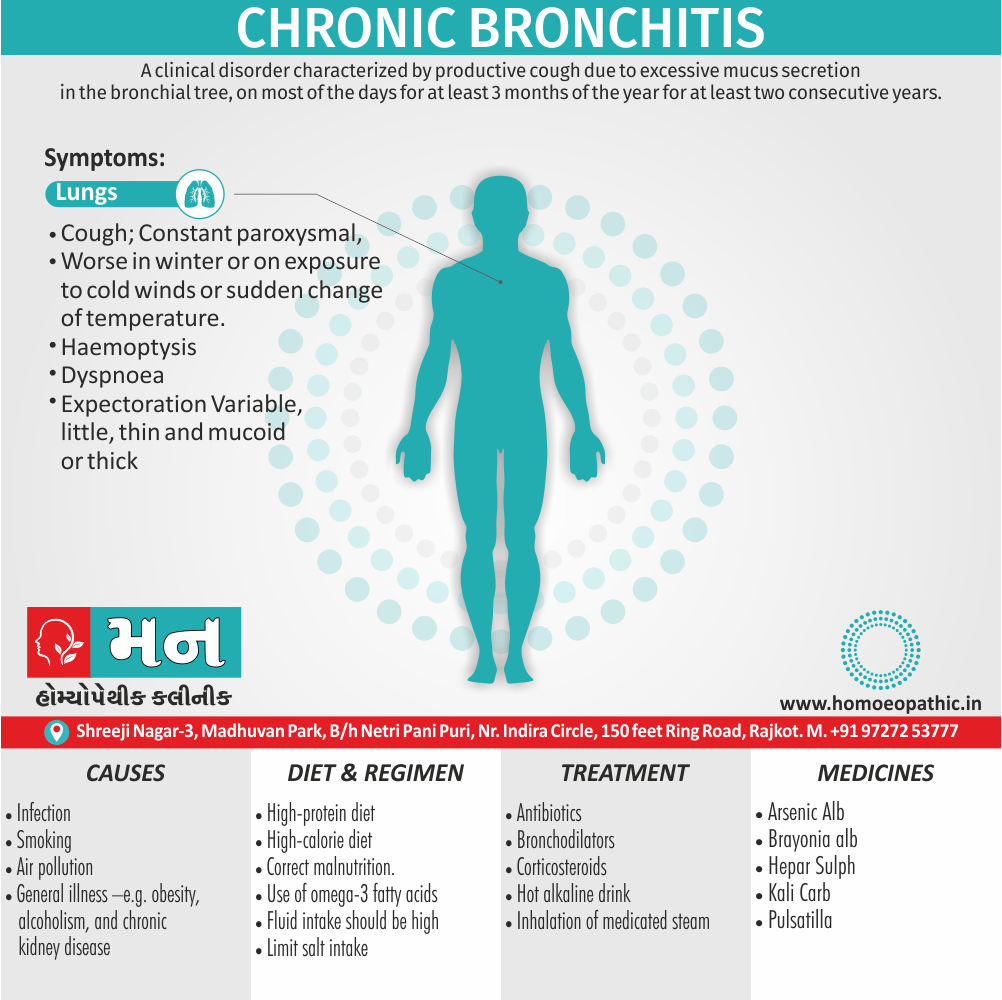
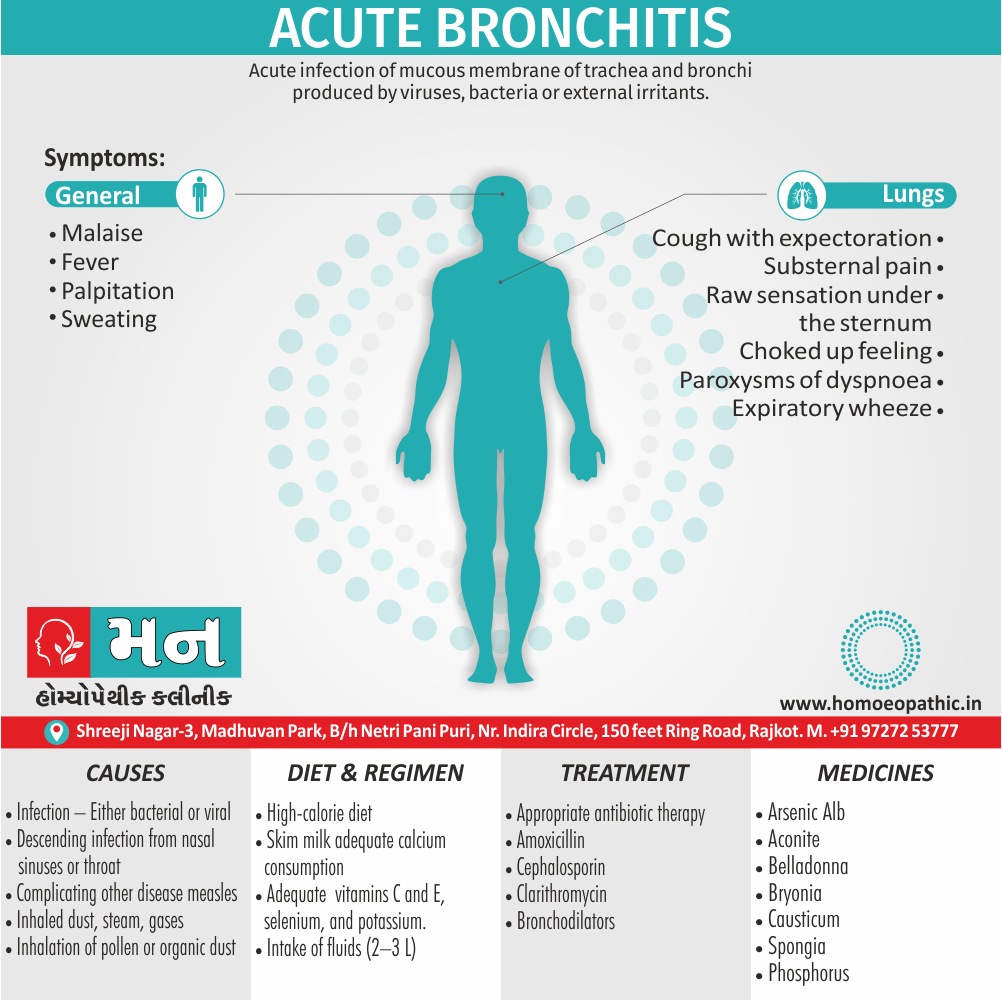
Respiratory System
- Larynx; sensitive to cold air; painful.
- Loss of voice, and cough when exposed to dry cold wind.
- Cough from least uncovering.
- Hoarseness; chronic; of singers.
- Whistling, choking; breathing, must bend head back.
- Cough choking, barking worse cold drinks or in a.m.; hacking; as from feather.
- WEAKNESS AND MUCH rattling in chest; expectoration LOOSE; but cannot expectorate; tightens up in cold air. Much, thick, yellow expectoration.
- Recurrent bronchitis, from every cold.
- Sensation as of drops of hot water in chest.
- Asthma; after suppressions. Cries before cough. Aphonia.
- Cough worse evening till midnight. (5)
Heart & Pulse
Palpitation, with stitches. (5)
Neck & Back
Crawling in right scapula. (5)
Extremities
- Encysted tumour at the point of elbow.
- Whitlow.
- Nail of great toe painful on slight pressure.
- Easy dislocation of finger joints.
- Laming pain in hip joint worse walking.
- Swelling of knee, ankle and foot.
- Drawing pains in limbs.
- Abscess in axilla.
- Swelling of feet around ankles, with difficult breathing. (5)
Skin
- Sensitive to cool air.
- Foul moist eruptions in folds.
- Torpid pulsating ulcers, encircled by smaller ones or by pimples or boils.
- Skin; chapped, deep cracks on hands and feet.
- Very sensitive cold sores.
- Chronic and recurring urticaria.
- Angioneurotic oedema.
- Body exhales a foul odour.
- Impetigo.
- Poor granulation. (5)
Sleep
- Sleeplessness; anxious dreams of fire.
- Unrefreshing.
- Wakes at night, with erection and desire to urinate. (5)
Fever
- Low fevers; hectic.
- Profuse sweat; with least exertion; day and night; sour, sticky, offensive.
- Night sweats. (5)
Important characteristic features
Keynotes / Redline
- Sensitiveness to cold air, pain, touch, etc.
- Sensation of splinter and splinter-like pains.
- Tendency towards suppuration, which is rapid.
- Easy sweating with relief.
- Sourness of all discharges.
- Discharges smell like spoiled cheese.
- Faints from pain. (3)
Guiding
- Intense sensitivity to pain.
- Suppuration-tendency for all inflammations to terminate in suppuration. Suppuration sudden and rapid. Here, connective tissue is affected (Graph, Merc, Sil).
- Chilliness. Extreme sensitiveness to cold air. Takes cold from slightest exposure to fresh air. Can feel air if door is opened in next room (Tub).
- Pains-sore, sticking, like sharp splinters (sensation of splinter in parts).
- Discharges-profuse, foul, sour, like spoiled cheese, offensive.
- Periodicity- everyday, every 4 weeks (paralysis), every 4 months, winter, spring, autumn.
- Craving for sour, strong things, acids, wine, vinegar, pickles, spicy, pungent.
- Aversion to fat food.
- Eructations and flatus smelling like bad eggs.
- Ulcers very sensitive to contact, burning, stinging, easily bleeding.
- Can’t bear to be uncovered (even one part of the body), wants to be wrapped up warmly.
- Chronic and recurring urticaria. Urticaria preceding or also with chill, disappears as heat begins. (3)
PQRS
- Extremely sensitive to cold air, imagines he can feel the air if a door is open in the next room. Though the patient is chilly but all symp. > by damp, wet weather.
- Must be wrapped up to the face even in hot weather (Psor.), cannot bear to be uncovered (Nux V. – cannot bear to be covered, Camph., Sec.).
- Cough when any part of body is uncovered.
- Skin extremely sensitive to touch. The pain often cause fainting.
- Takes cold from slightest exposure to fresh air (Tub). (7)
Confirmatory
- Chilliness.
- Sensation of splinter.
- Warmth.
- Easy sweating with relief.
- Great sensitiveness to all impressions.
- Tendency to suppuration. (3)
Nucleus symptoms
- Adapted to the psoric, scrofulous diathesis. Persons extremely sensitive, susceptible to cold.
- Oversensitive to external impression, pain may cause fainting.
- Tendency to suppuration with (old cheesy) sour discharges.
- Easy sweating. (3)
Therapeutic value
Abscesses, Asthma, Boils, Breast affections, Burns, Carbuncles, Chilblains, Chlorosis, Cold, Cough, Diarrhoea, Ear affections, Eczema, Eye affections, Headache, Hoarseness, Jaundice, Liver affections, Marasmus, Menstrual disorders, Pneumonia, Rheumatism, Skin affections, Suppuration, Tuberculosis, Whooping cough. (1)
Modality
Aggravation:
- Lying on the painful side, cold air, uncovering, touching affected parts, night waking, while swallowing, while urinating, in dry weather, from slightest draught, eating and drinking cold things.
Amelioration:
- Passing flatus, eructation, warmth in general, damp wet weather, after eating, from wrapping up. (1)
Remedy Relationship
Complimentary
Calen (1)
Follows Well
Bell, Bry, Nit-ac, Sep, Sil, Spong. (1)
Antidoted By
Merc, Iod, cod liver oil. (1)
It Antidotes
Ars, Bell, Cham. (1)
Comparison
Silicea, Calcarea Sulph, Spongia Tosta (4)
Posology (Dose)
Potency:
Potency:
-
- 3x, 6x, 12x, 30, 200, 1000 and above/
Dose:
- First to 200th. The higher potencies may abort suppuration, the lower promote it. If it is necessary to hasten it, give 2x. (6)
Duration of action
- 40-50 Days. (3)
Frequently Asked Questions
Qu. 1. State the preventive aspect of Hepar Sulph.?
Ans. Renders patient less susceptible to atmospheric change and cold air.
Qu. 2. State the effects of cold in Hepar Sulph.?
Ans. a) Extremely sensitive to cold air
i) Imagines he can feel the air if a door is opened in the next room.
ii) Must be wrapped up to the face even in hot weather.
iii) Cannot bear to be uncovered.
iv) Takes cold from slightest exposure to fresh air.
b) Cough:
i)When any part of the body is uncovered.
ii) From exposure to dry west wind, land wind.
c) Croup:
i) After exposure to dry cold wind.
ii) Aggravation from cold air, cold drinks.
d) General modality:
i) Aggravation from cold air, uncovering, eating or drinking cold things.
ii) Amelioration from warmth in general, wrapping up warmly, especially the head.
Qu. 3. Mention five medicines where slightest injury suppurates.
Ans.
i) Hepar Sulph.
ii) Graphites.
iii) Merc Sol.
iv) Sulphur.
v) Silicea.
Qu. 4. State the eye symptoms of Hepar Sulph.
Ans.
i) Eyeballs: sore to touch.
ii) Pain, as if they would be pulled back into head.
Qu. 6. State the Respiratory symptoms of Hepar Sulph.
Ans. Introduction: Dr. Tyler refers, it is one of the nursery medicines for cold, cough and croup.
Cough:
a) Causation
i)From cold air.
ii) When any part of the body is uncovered etc.
iii) After exposure to dry west wind, the land wind.
b) Character of cough
i) Cough may be dry, rough, deep and braking.
ii) Croupy with choking, gagging and strangling.
iii) Great soreness of the chest.
iv) Suffocative cough.
v) Breathing: It is rattling in character with hoarseness.
c) Modalities
Agg.
i) When any part of the body is exposed.
ii) In the morning, before midnight and towards
evening. Dr. Hering says at night from 11 p.m. to 12 midnight there is violent cough.
iii) In cold air from dry west wind.
iv) After cold drinks.
Amel
i) From warmth in general.
ii) In damp wet weather.
d) Concomitant and accompanying features:
i) Cough along with profuse sweating, which neither aggravate nor ameliorates.
ii) Weeps with or before the cough (Ref. Dr. Tyler).
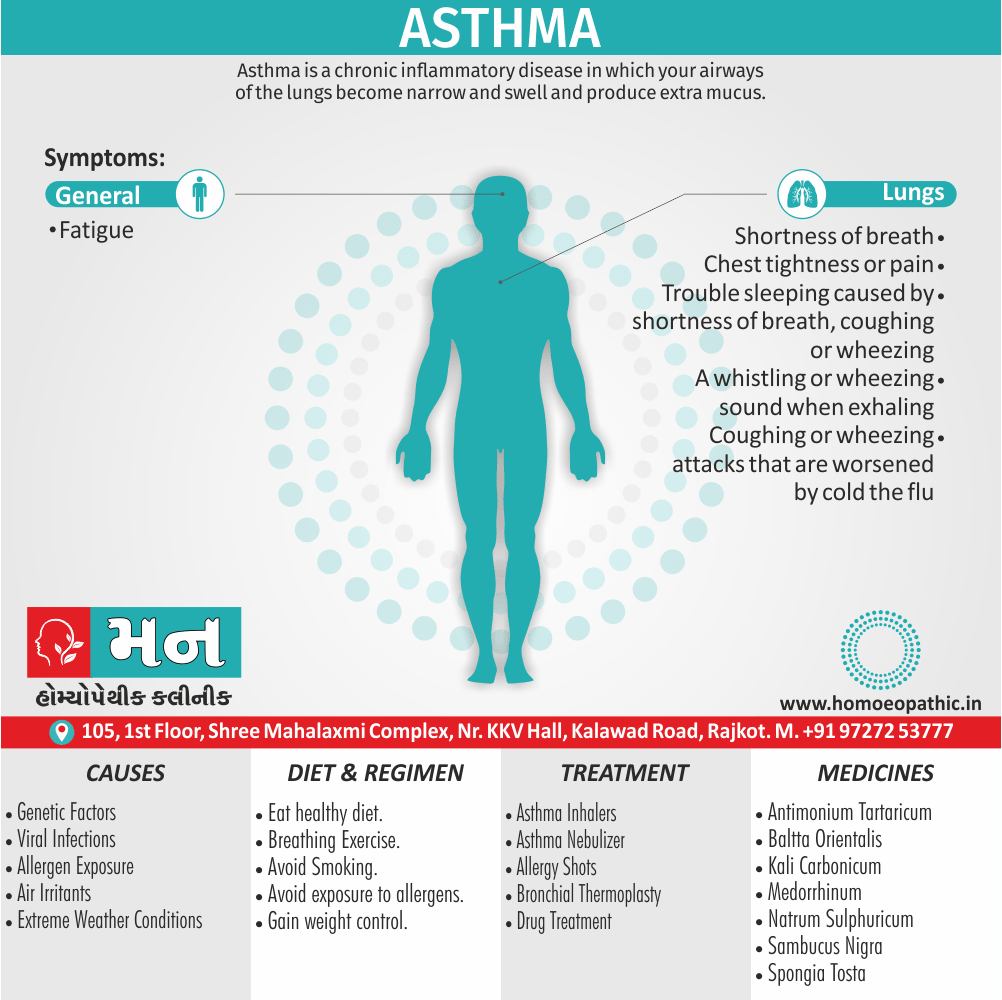
Asthma
a) Causation
i) After suppression of skin diseases.
ii) After abuse of mercury.
b) Character
i) Breathing:-Deep breathing, with wheezing, rattling of mucous.
ii) Suffocation :-Threatened suffocation, takes deep breath must bend head backwards while sitting.
c) Modalities
Amel.
i) From bending head backwards while sitting.
ii) In damp wet weather.
iii) From covering the body warmly, and from warmth in general.
Croup:
Introduction – It is one of the members of Boennighausen’s trio of croup powder, others are Aconite and Spongia: all in 200th potency.
a) Causation :
After exposure to dry, cold wind.
b) Character:
i) Deep, rough, barking cough.
ii) With hoarseness and rattling of mucus.
c) Modalities
Agg.
i) From cold air.
ii) Cold drinks.
iii) Before midnight.
iv) Towards evening.
Hoarseness
Hoarseness with aphonia, agg. in the morning.
Qu. 7. State the urinary symptoms of Hepar Sulph.
Ans.
a) Character of the urine
i) Urine is dark, red, hot and sometimes bloody.
ii) Corrodes the prepuce.
iii) Urine passes involuntarily, without any force.
iv) Flow of urine is impeded, voided slowly drop by drop, intermittent, due to weakness of the bladder.
b) Before urination:
i) is obliged to wait a long time before passing the urine.
c) During urination
i) Bladder is weak, unable to finish.
d) After urination
i) Unable to finish, seems as if some urine always remains in the bladder.
e) Concomitants
i) Very chilly patient.
ii) Prepuce is very sensitive to touch.
iii) Oversensitive, both mentally and physically.
Qu. 8 State the skin symptoms of Hepar Sulph.
Ans.
1) Causative Ailments
i) Mercurialization (abuse of mercury),
ii) Suppressed eruptions,
iii) Gonorrhoea,
iv) Syphilis,
v) Injuries (Ref. Clarke)
2) Clinical
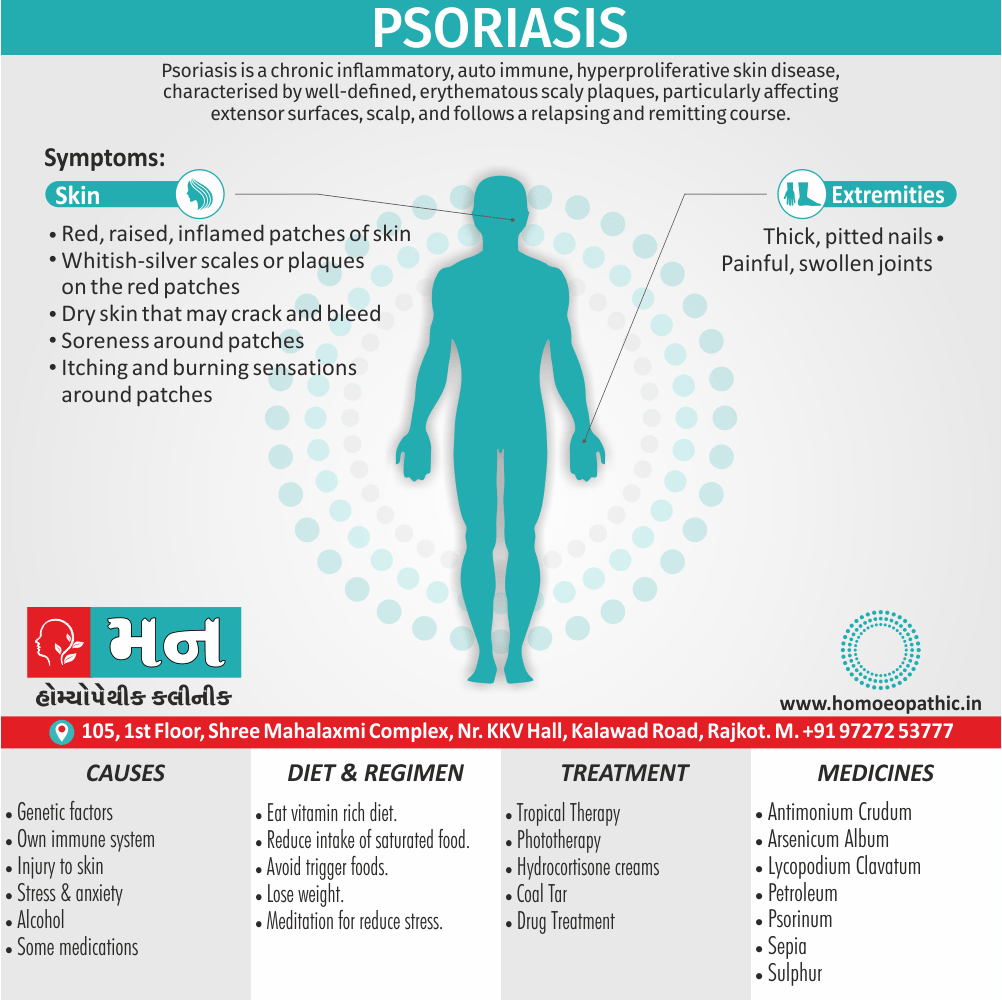
Erysipelatous inflammation: Carbuncle; Nettle rash; Cancerous ulcers; Eczema; Itch; Herpes: Chilblains; Psoriasis; Urticaria; Acne; Boils; Abscess; Rash eruptions, Grocers itch and Psoriasis palmaris (Ref. Dr. Huge), Wool workers’ Itch (Ref. Dr. J. H. Clarke)
3) Location
Dr. Guernsey recommends that flexors of the elbow and knee are the especial seat of those eruptions.
4) Symptomatology regarding Skin
i) Unhealthy suppurating skin, every little injury suppurates (Sulph. Graph, Peter, Sil, Merc. Sol.) boils, abscess and papules are prone to suppuration.
ii) The skin is very much sensitive to touch (+++) which Dr. E, B. Nash calls it the strongest characteristic.
The skin eruptions are so sensitive that the patient can’t endure the touch of cloth even (Lach).
Dr. Guernsey opens his discussion with emphasizing upon this sensitiveness. The great sensitiveness of this remedy is not to be overlooked, (Ref. Dr. Guernsey) Eczema spreads by means of new pimples appear.
iii) ring just above the old one.
iv) Ulcers are very sensitive to contact, easily bleeding, burning and stinging pain. Patient is oversensitive to pain. Dr. E. B. Nash says. patient is so sensitive to pain that she faints away, even when, it is slight. Ulcers surrounded by little pimples and pustules and spread by coalescing.
v) Putrid ulcers, smelling like old rotten cheese and easily bleeding, looking like a lump of lard with hole in it. (Ref. Dr. Guernsey)
vi) The nail suppurates and loosens, comes off. Sensation of slinter (++) under the mails (Ref. Kent). The nails become hard and brittle. Warts crack and opens, bleeds, stinging and burning with suppuration (Ref. Kent). Splinter sensation in the affected part (++) (Tyler says higher than Sil.).
vii) Middle of the lower lip cracked. (Ammon Carb., Nat, Mur).
5) Look-up of the skin
Unhealthy: yellowish colour of the skin esp. on the face (reports Dr. Clarke). Moist skin. (dry skin. Sulph.).
6) Discharges
i) Master Kent says discharges smell like decom. posed (rotten) cheese and this character runs through the remedy.
ii) Body smells like old cheese.
iii) Kent also refers to sour smelling discharge: Kent reports that babies are always scur inspite of much washing.
iv) Kent says perspiration is sour smelling.
v) The discharges from the ulcers are also sour
vi) Pus-Rich, thick and creamy. (Ref. Dr. N. Chowdhury)
7) Sweat
Profuse sweat, day and night without any relief, Sweats easily on every mental or physical exertion.
8) Glandular affections Swelling, inflammation and suppuration of all the glands of the body and Dr. Tyler reports it is sudden and rapid.
9) Modality
Agg. from cold air, uncovering, touching affected parts, from lying on painful side (Bell), in clear fine weather, from getting the skin rubbed off., in the night.
Amel. from warmth in general in damp wet weather (Medo, Nux. Vom.; Caust).
10) Mental generals
Oversensitive both mentally and physically. Very much impulsive, impulse to do violence.
11) Physical constitution
Master Kent says suited to scrawny persons with a tendency to enlargement of glands. Highly chilly patient, with sluggish-tropid, lymphatic constitution, suppurative and scrofulous diathesis.
Qu. 9. State the characteristic symptoms of Hepar sulph.
Ans.
i) Chilliness:-
Extremely chilly patient, imagines he can feel the air if a door is opened in the next room, must be wrapped up to the face even in hot weather; cannot bear to be uncovered.
ii) Oversensitiveness
a) Oversensitiveness both physically and mentally.
b) Mental hypersensitivity :- Slightest cause irritates him, hyper impulsive.
c) Physical hypersensitiveness
i) Hyperaesthesia :- Oversensitive to touch, to pain, even to clothes.
ii) Oversensitive to cold; takes cold from slightest exposure to fresh air.
iii) Sensations :-Sensation of a splinter in the throat, in the affected part viz. in ulcers, piles etc.
iv) Sweat-Profuse sweat: day and night, but sweat does not ameliorates. Hepar has perspiration of cheesy odour.
v) Sourness of all discharges All the discharges are sour smelling. sweat, stool etc. Dr. Tyler says, smells like old cheese. Dr. Nash refers, whole child smells sour.
vi) Suppurative diathesis – Slightest in- jury tends to suppurate is a notable feature of Hepar Sulph.
vii) Sour cravings: – Patient has craving for sour, acids etc., as Dr. Kent in his Repertory has classed it in first grade. (9)
References
- Materia Medica by Dr. J. D. Patil, chap >Hepar Sulph
- Tempraz MM By Dr. Parinaz Humaranwala, chap > Hepar Sulph
- Zomeo lane, Materia Medica, Keynotes, chap > Hepar Sulph
- A Manual Of Materia Medica, Therapeutics And Pharmacology By Blackwood, Alexander Leslie
- Concise Materia Medica Of Hom. Remedies By S.R. Phatak, chap> Hepar Sulph
- Materia Medica By Boericke W., chap> Hepar Sulph
- Synoptic Memorizer of materia medica by Dr. Subrata Banerjea Vol.1, Chap. 3> Hepar. Sulph
- Synoptic Memorizer of materia medica by Dr. Subrata Banerjea Vol.1, Chap. 2> Hepar. Sulph
- Synoptic Memorizer of materia medica by Dr. Subrata Banerjea Vol.2, Part 1 > Hepar. Sulph
- Synoptic Memorizer of materia medica by Dr. Subrata Banerjea Vol.2, Part 2> Hepar. Sulph
- Chronic Diseases, Theory And Practice, Vol.1 By S.Hahnemann
- Dictionary Of Practical Materia Medica (All 3 Vol.) By Clarke J. H.
- A Materia Medica Of Differential Potency By B. F. Underwood
- Characteristics Of The Homoeopathic Materia Medica By Douglass M.E.
- Condensed Materia Medica By Hering C.