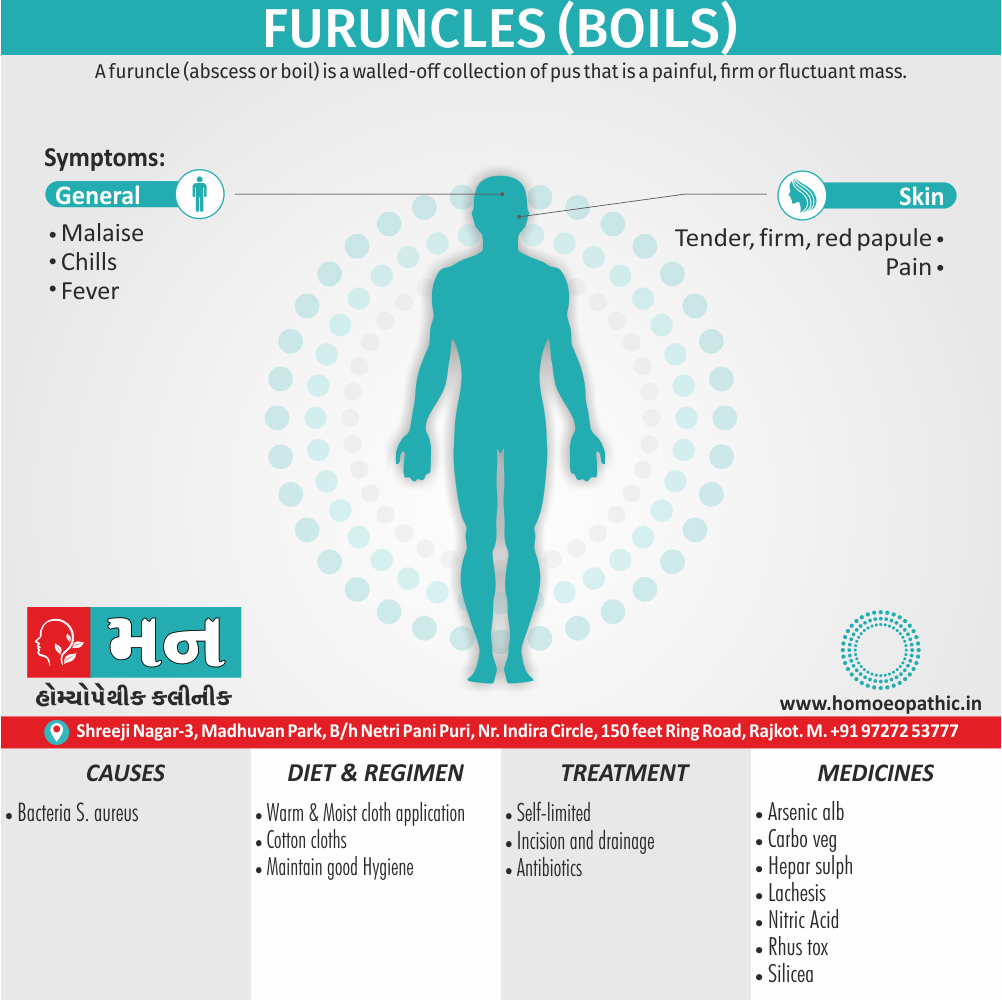
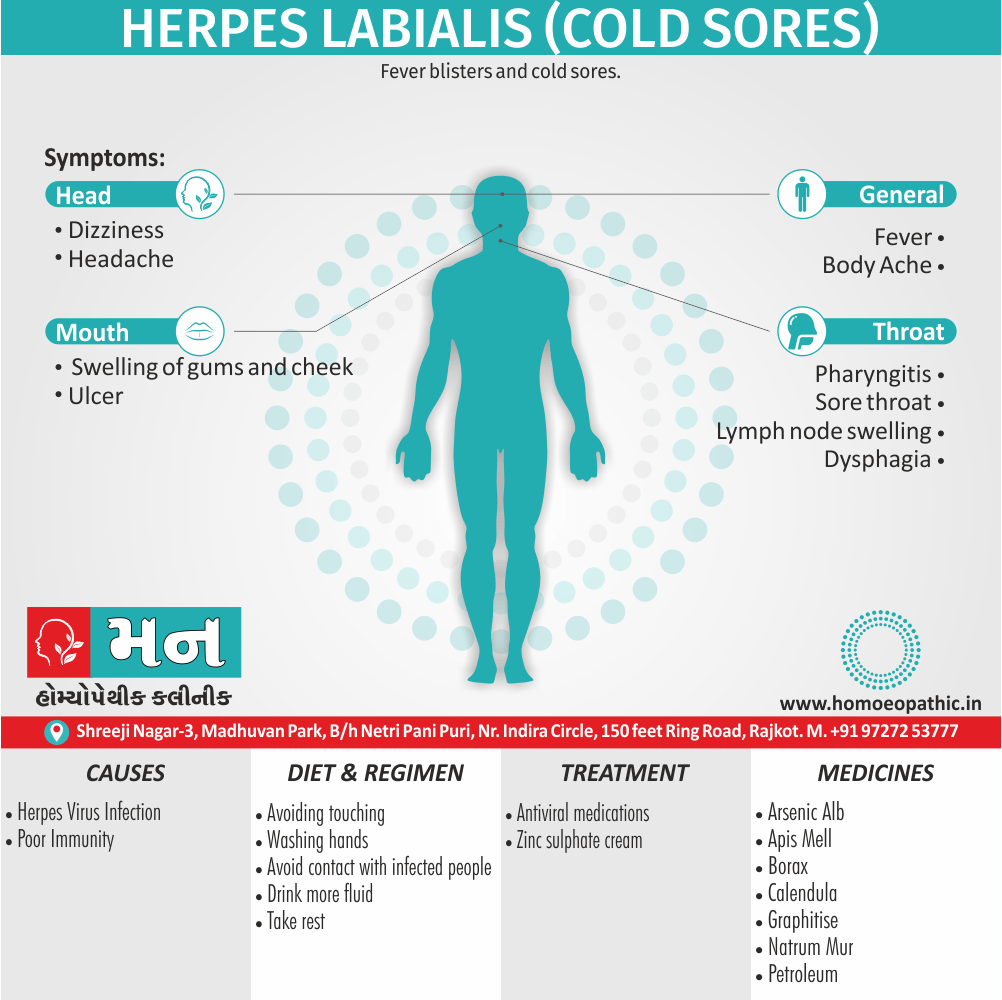
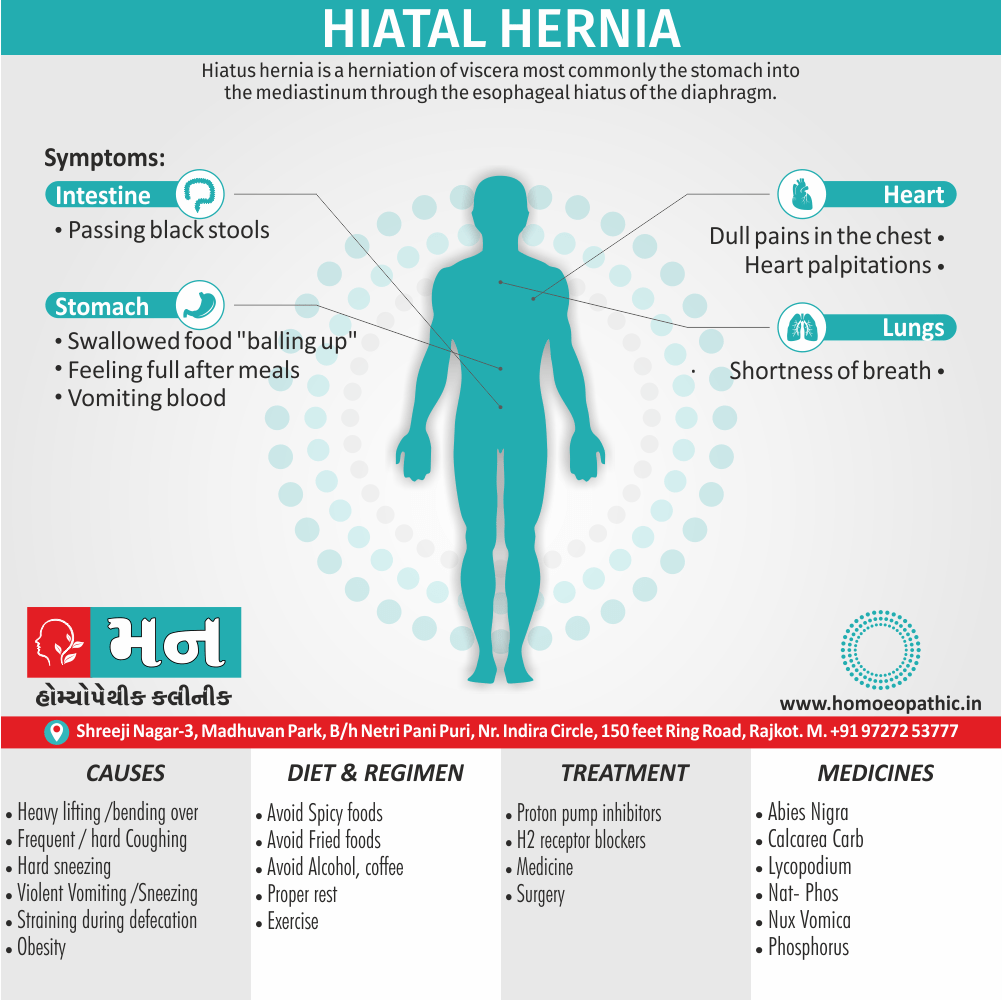
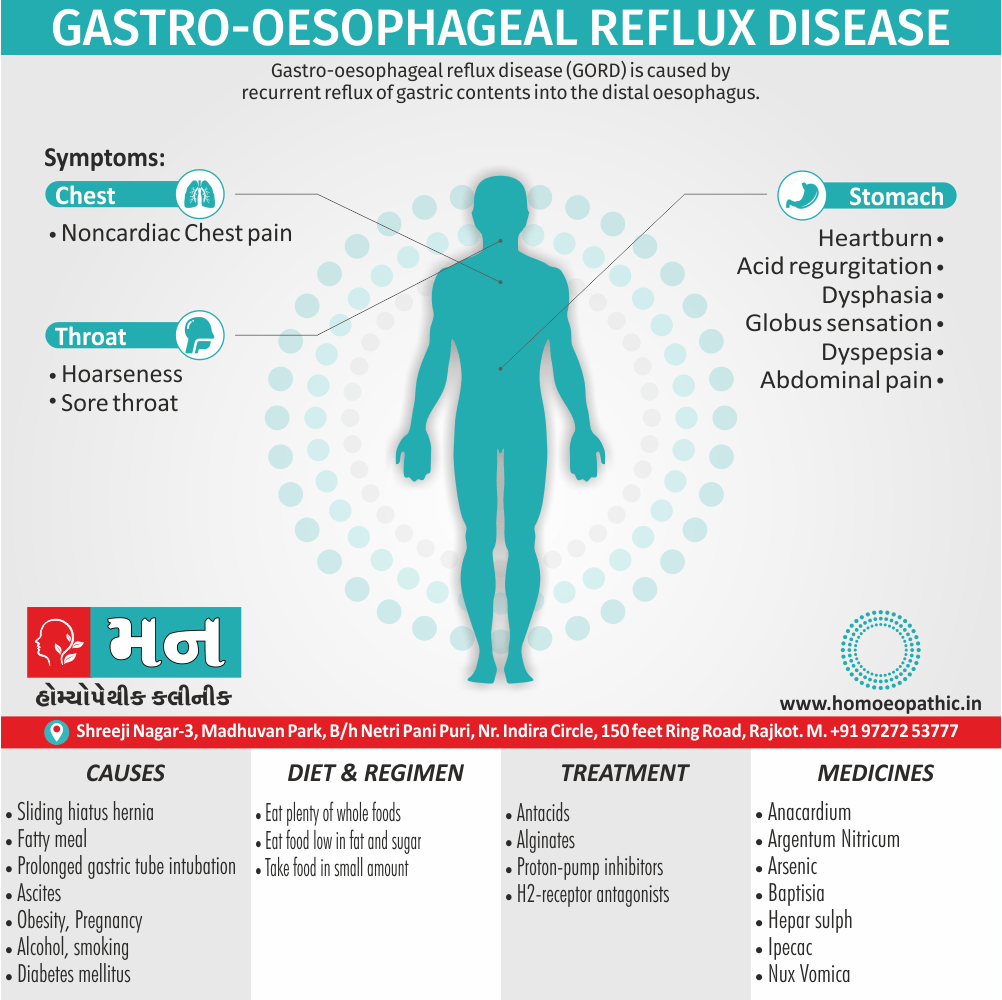
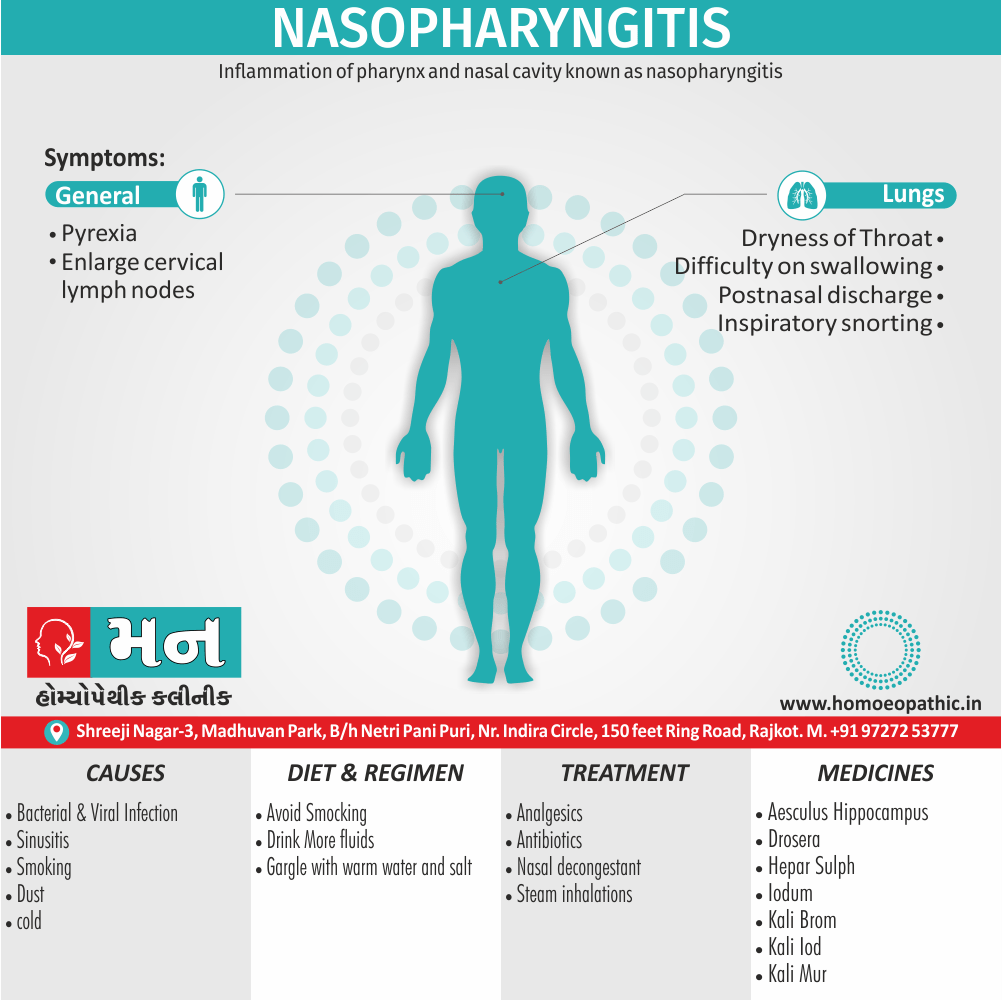
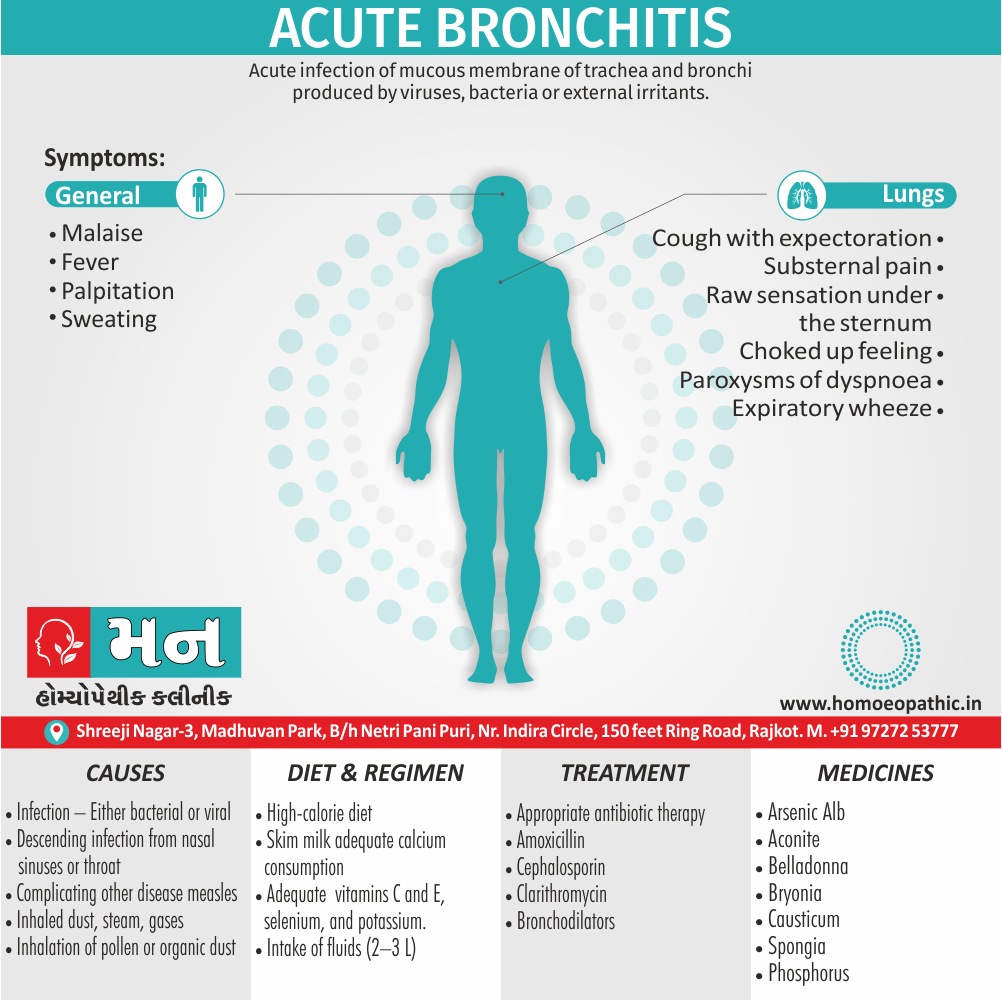
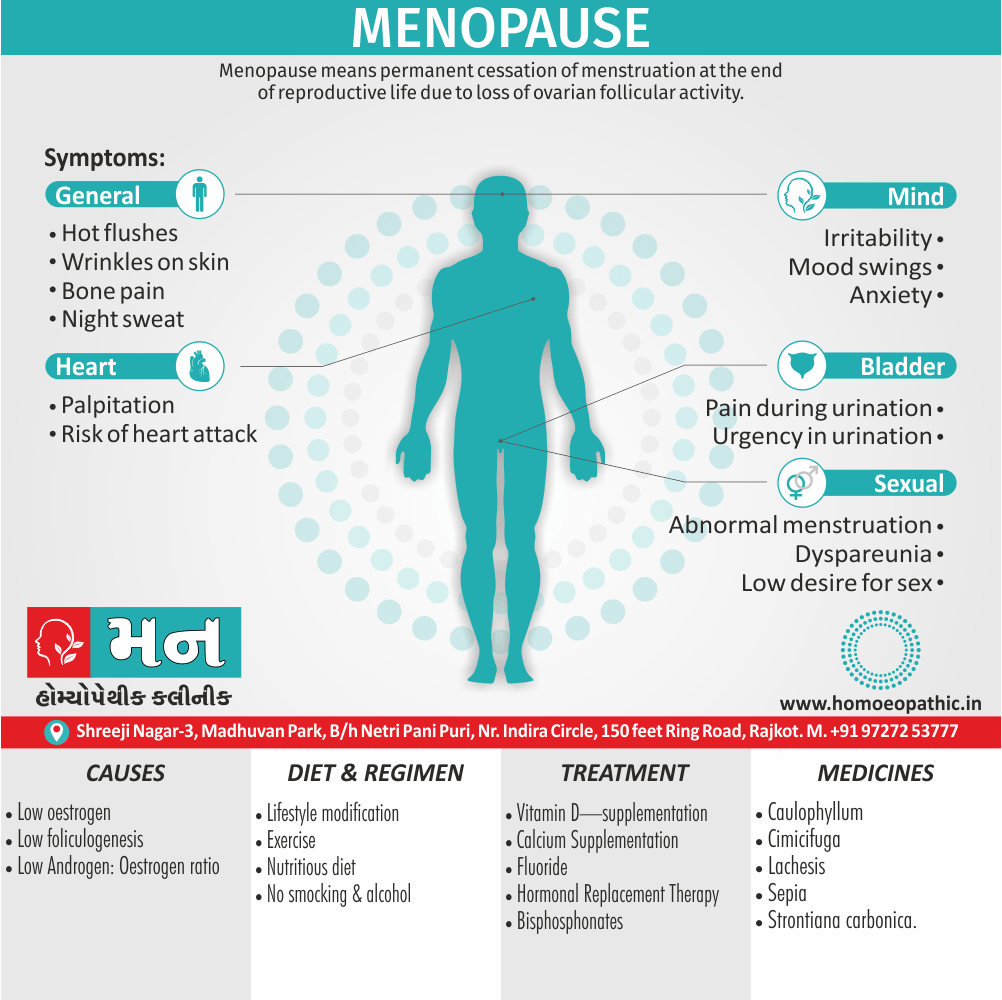
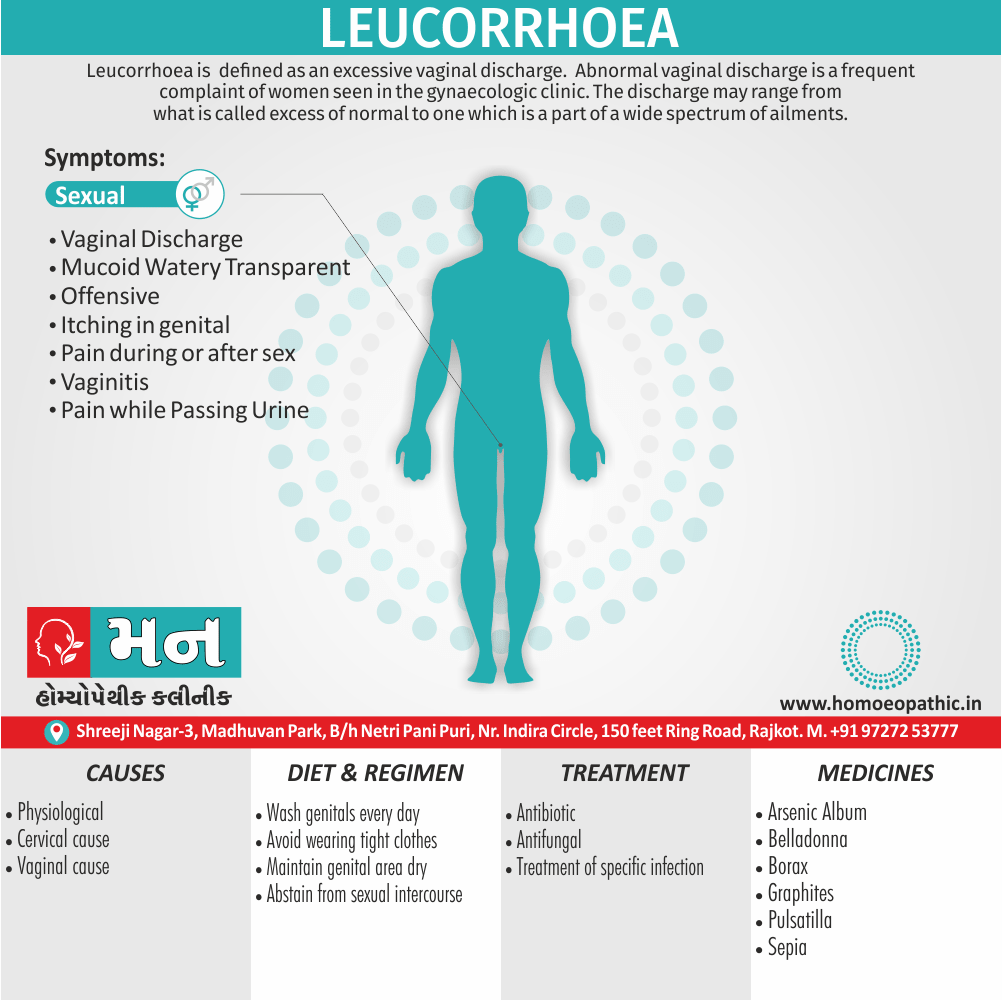
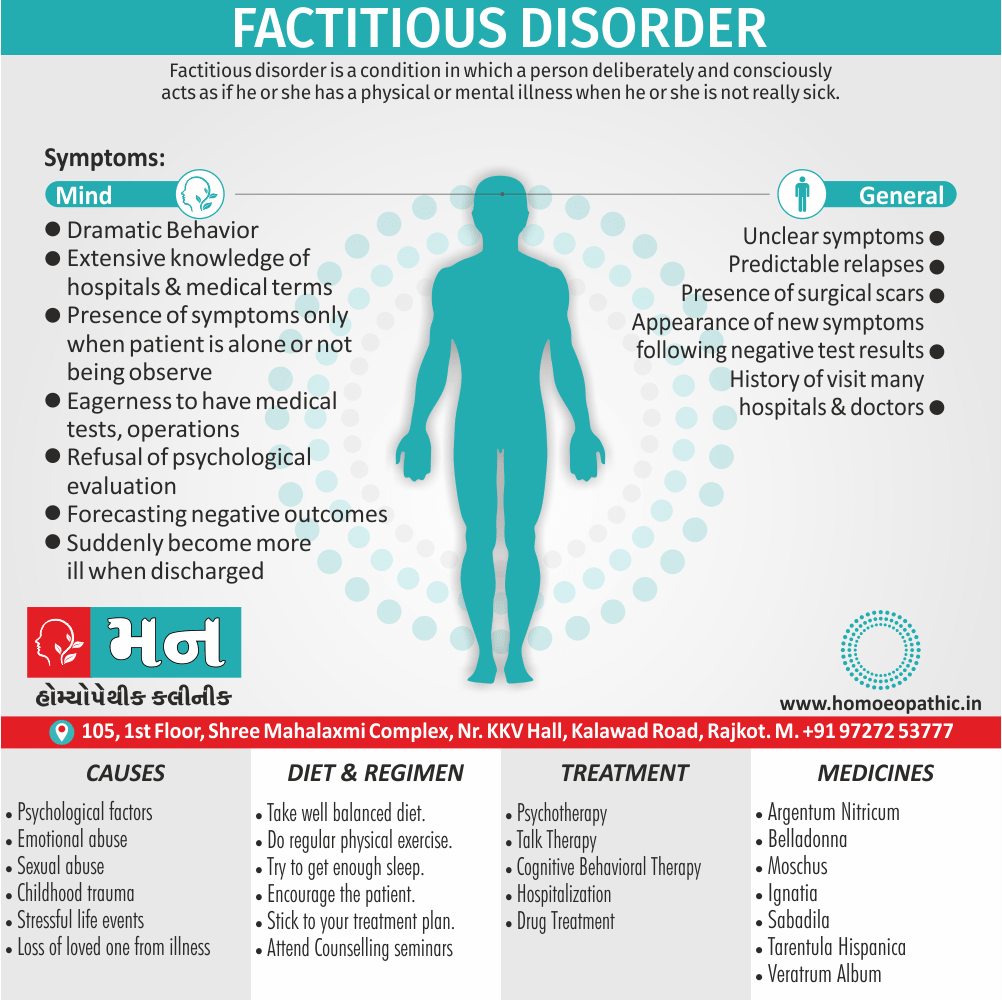
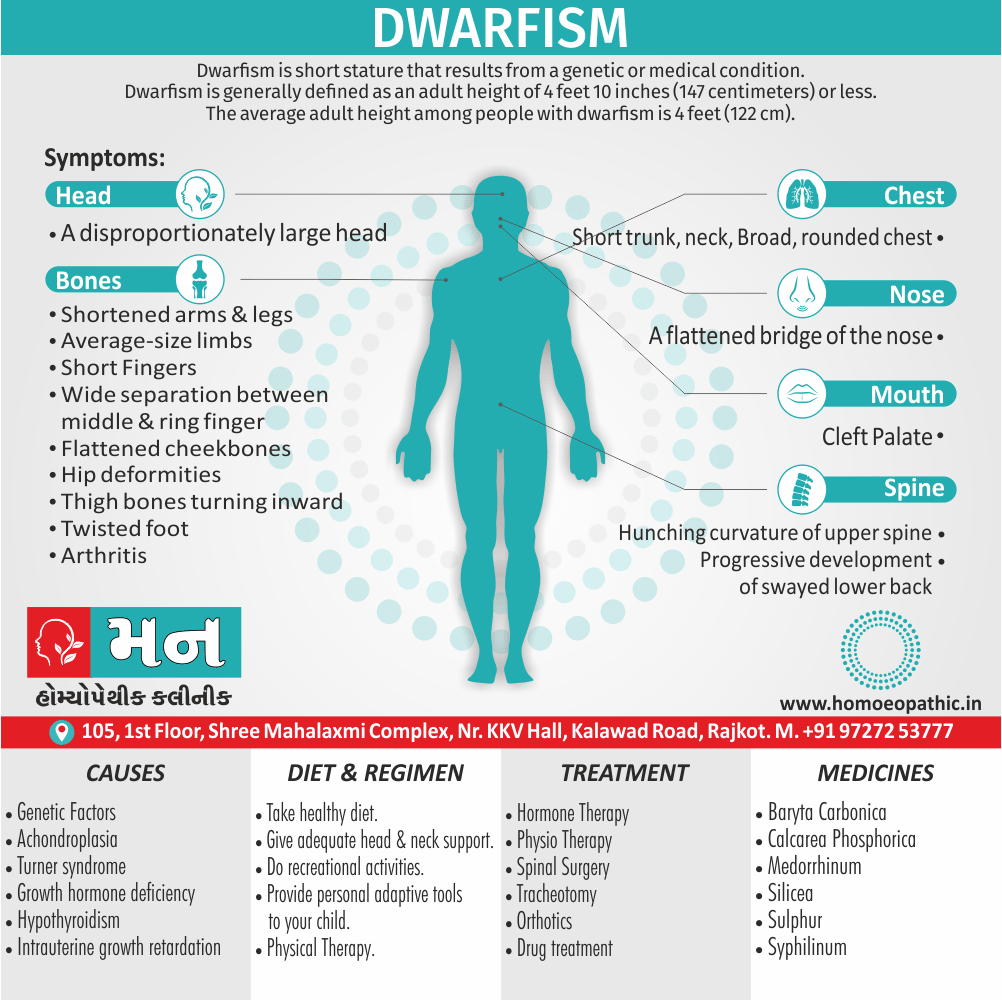
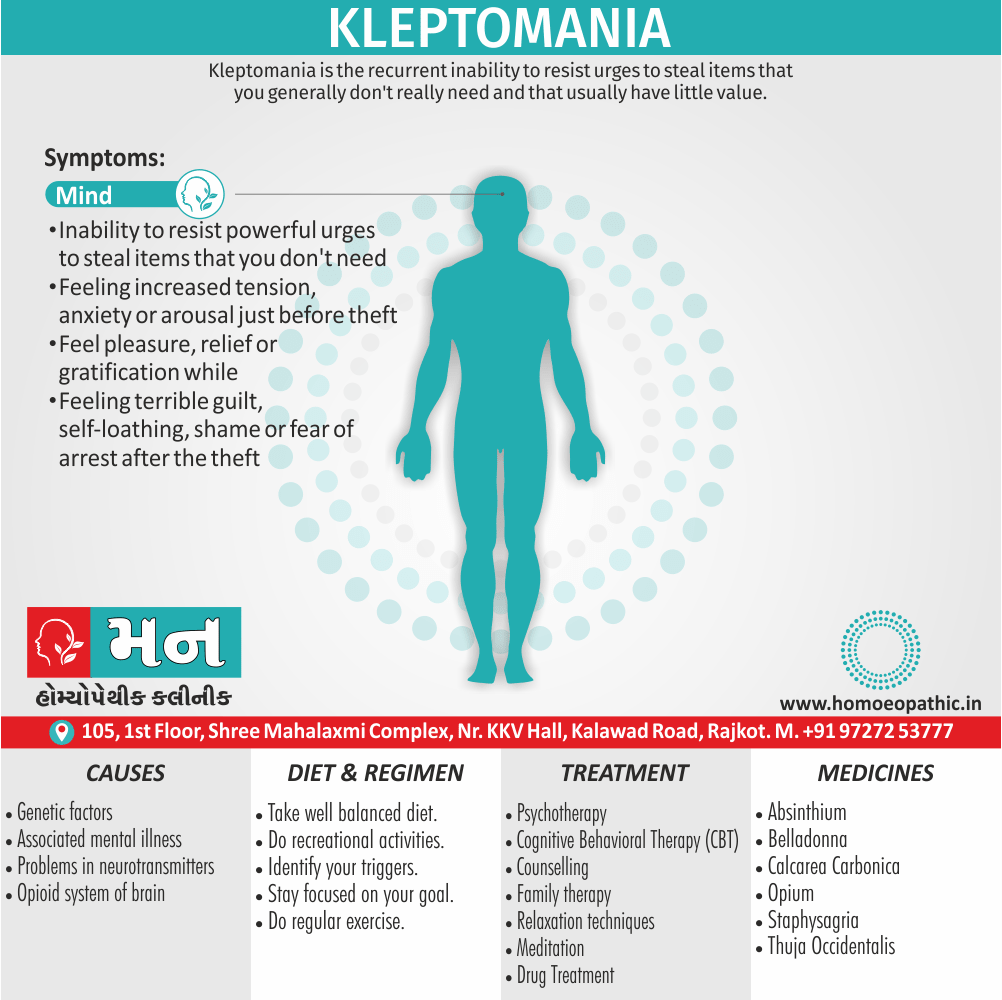
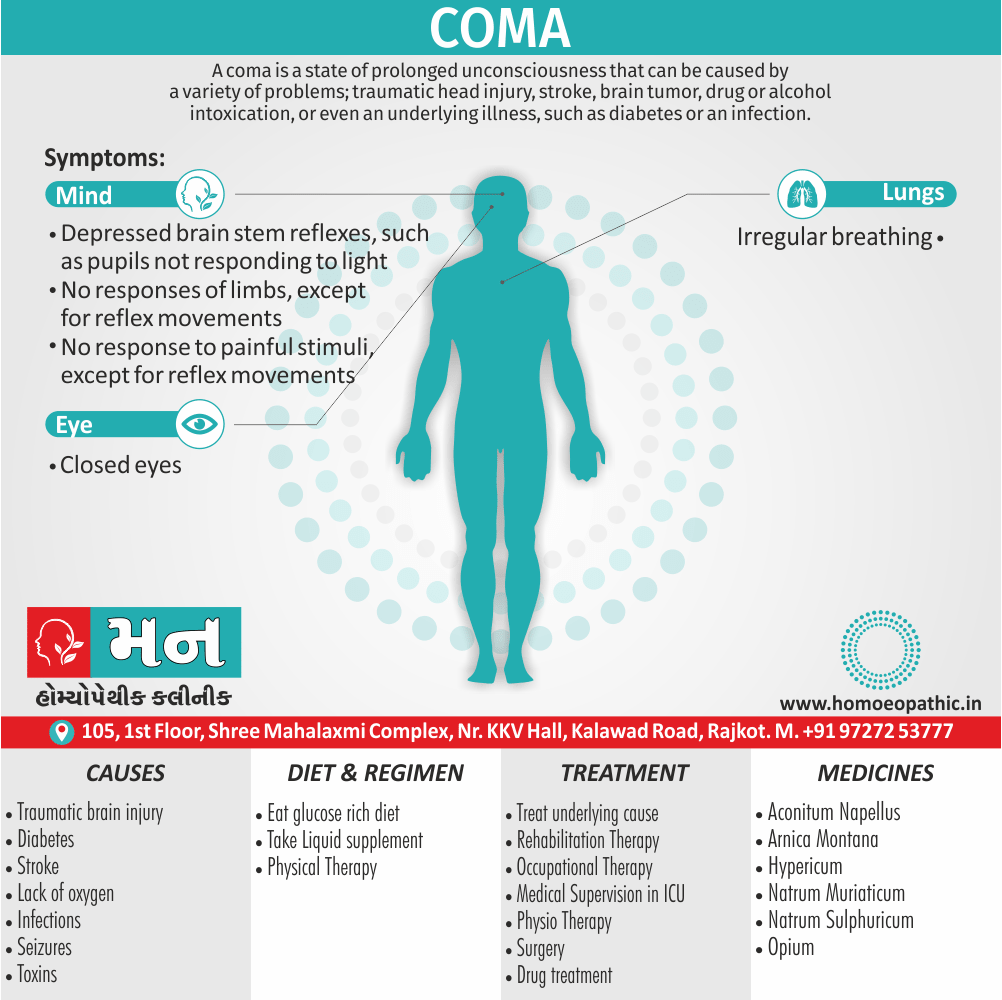
Definition of Sickle cell Disease
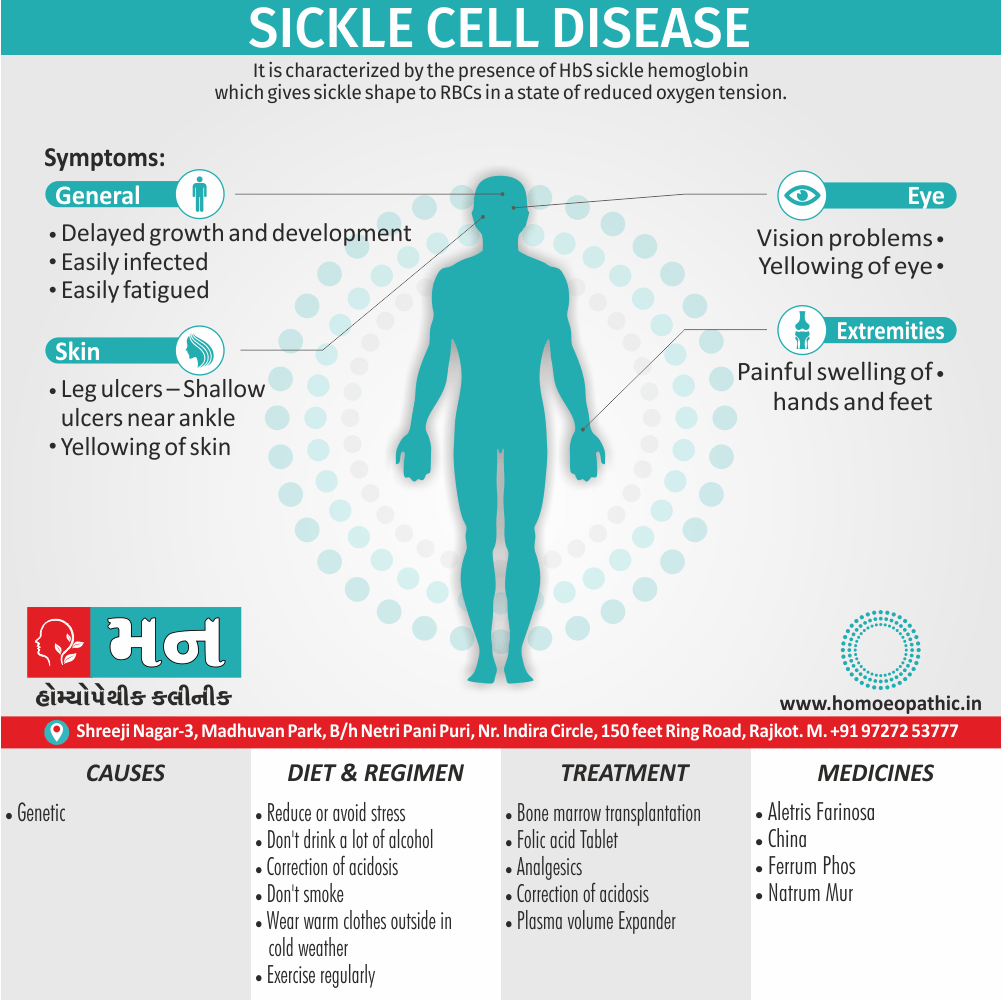
Genetic Sickle Cell Disorders or Sickle cell Disease are characterized by presence of HbS sickle hemoglobin which give sickle shape to RBCs in a state of reduced oxygen tension. [2]
Overview of Sickle cell Disease
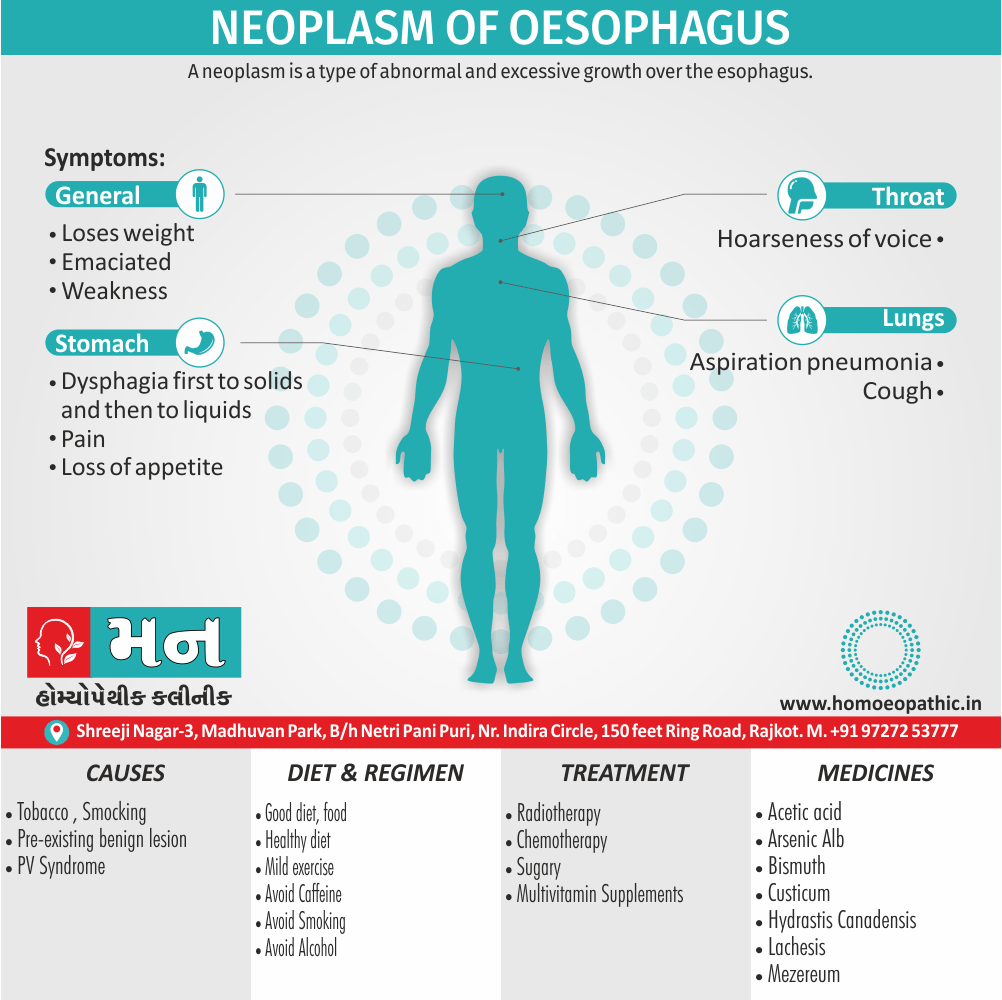
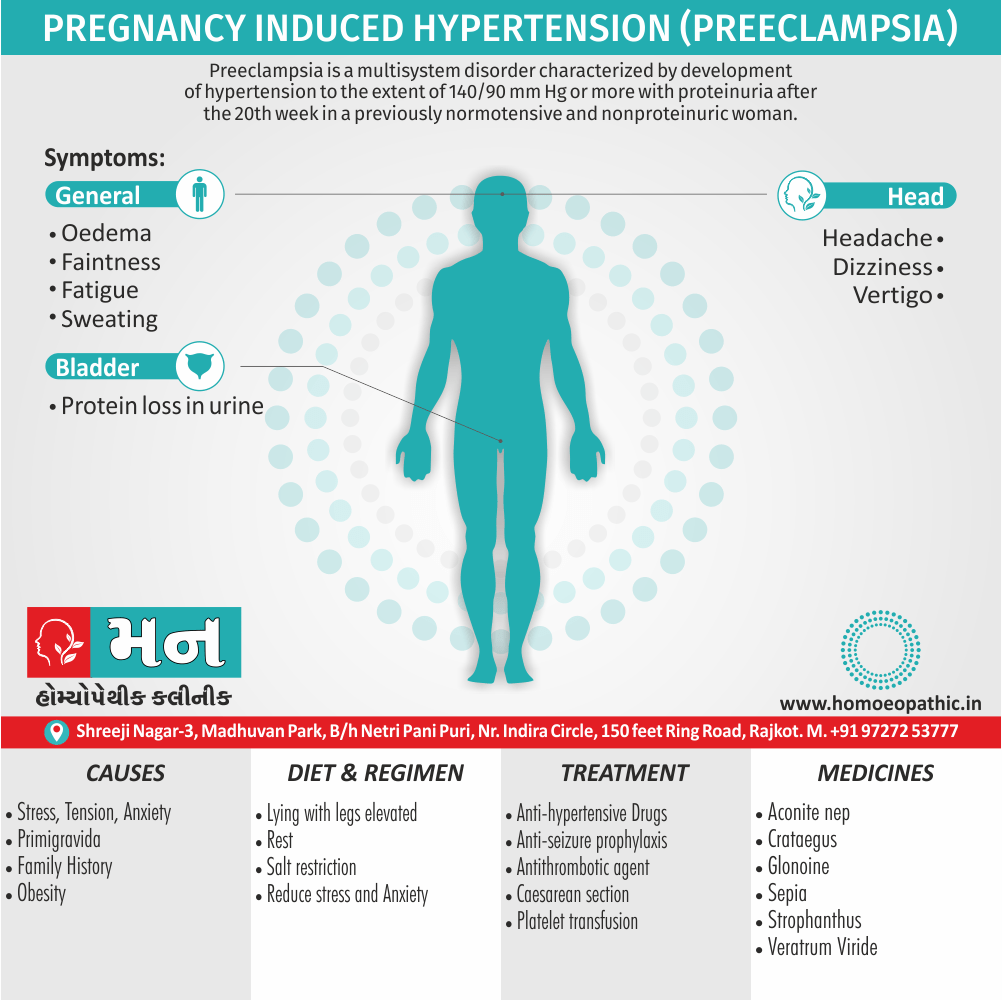
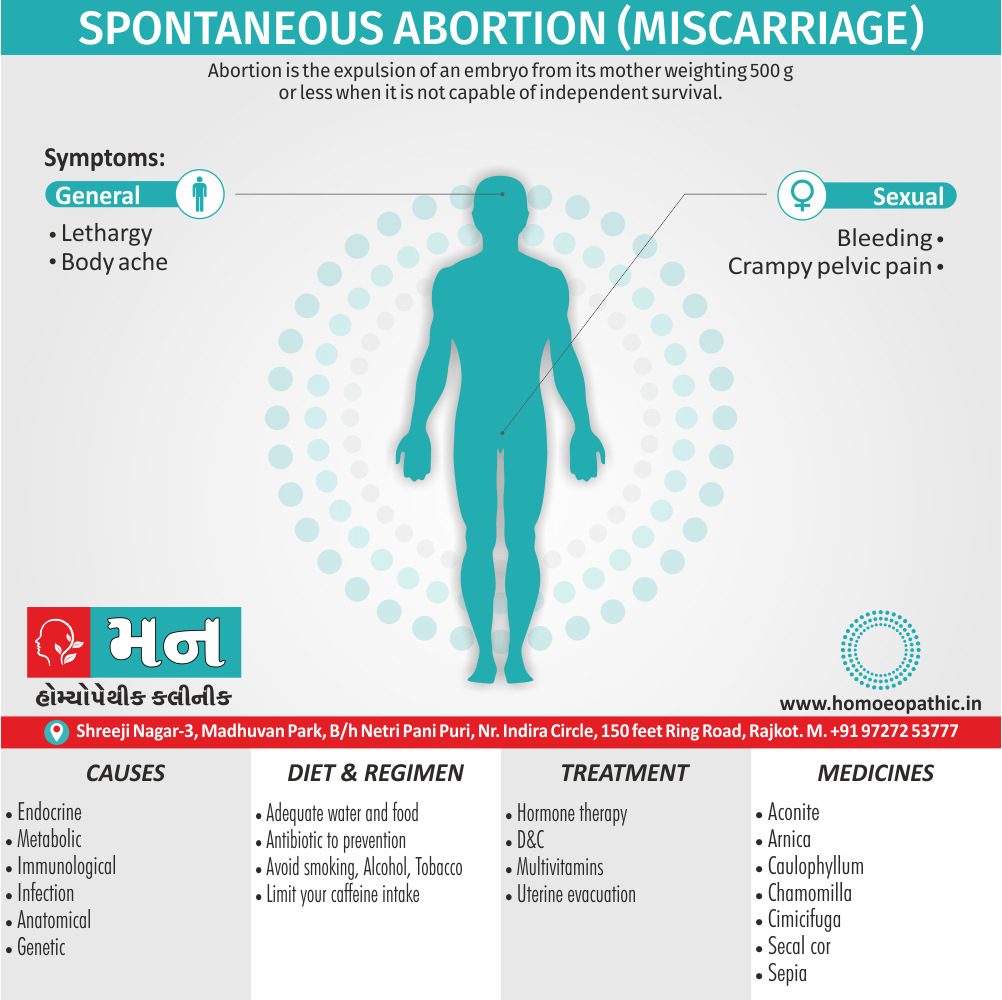
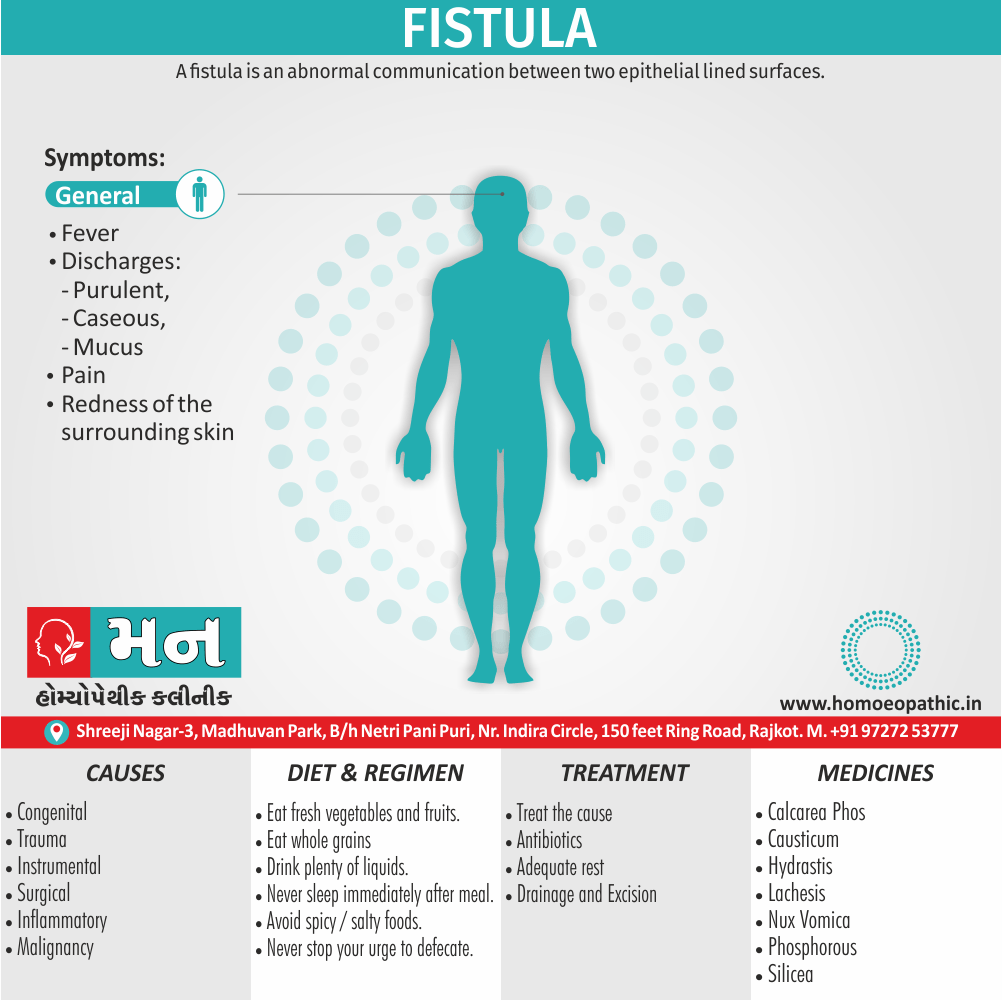
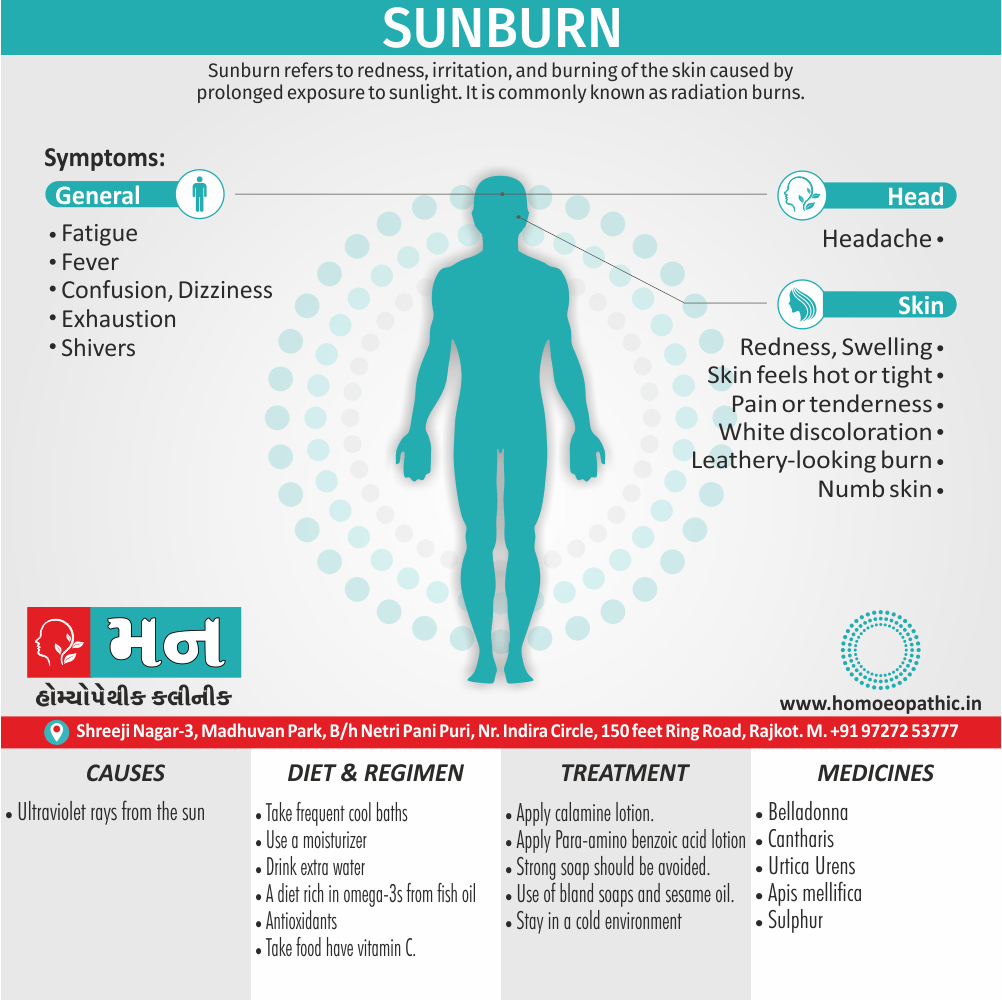
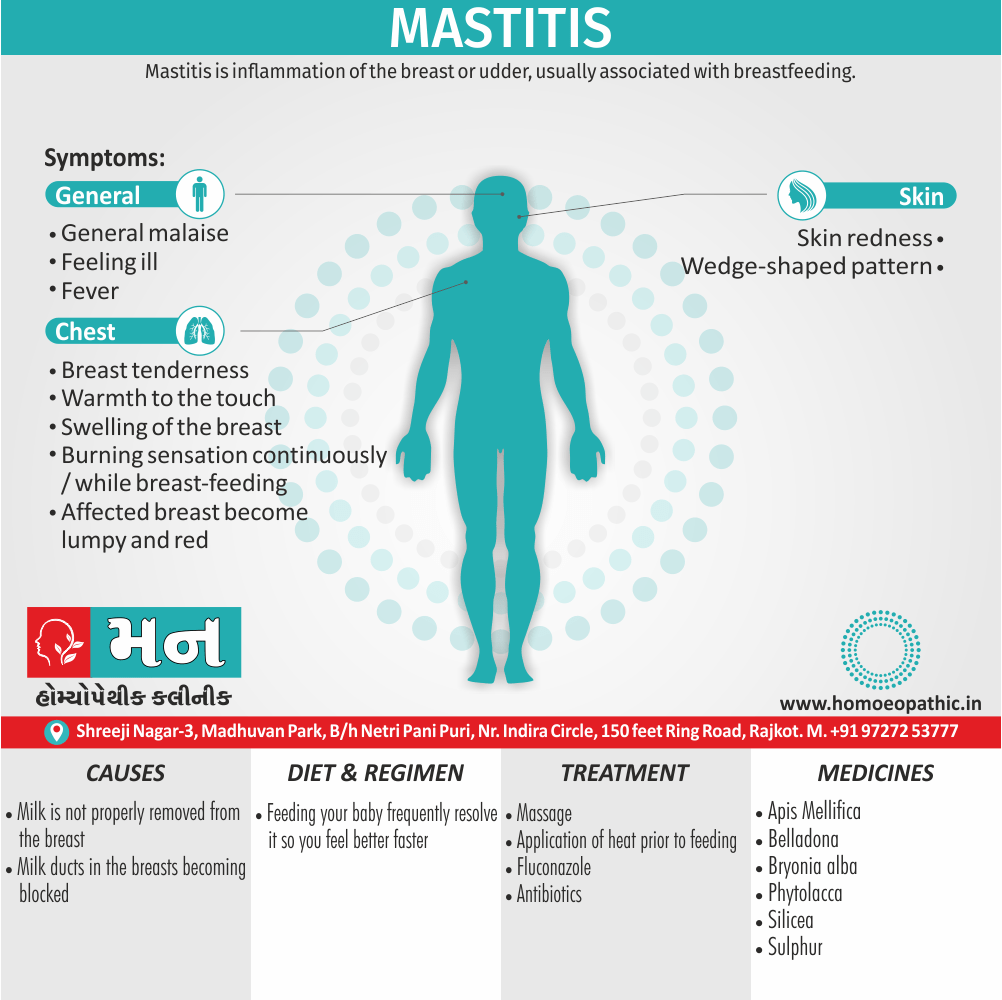
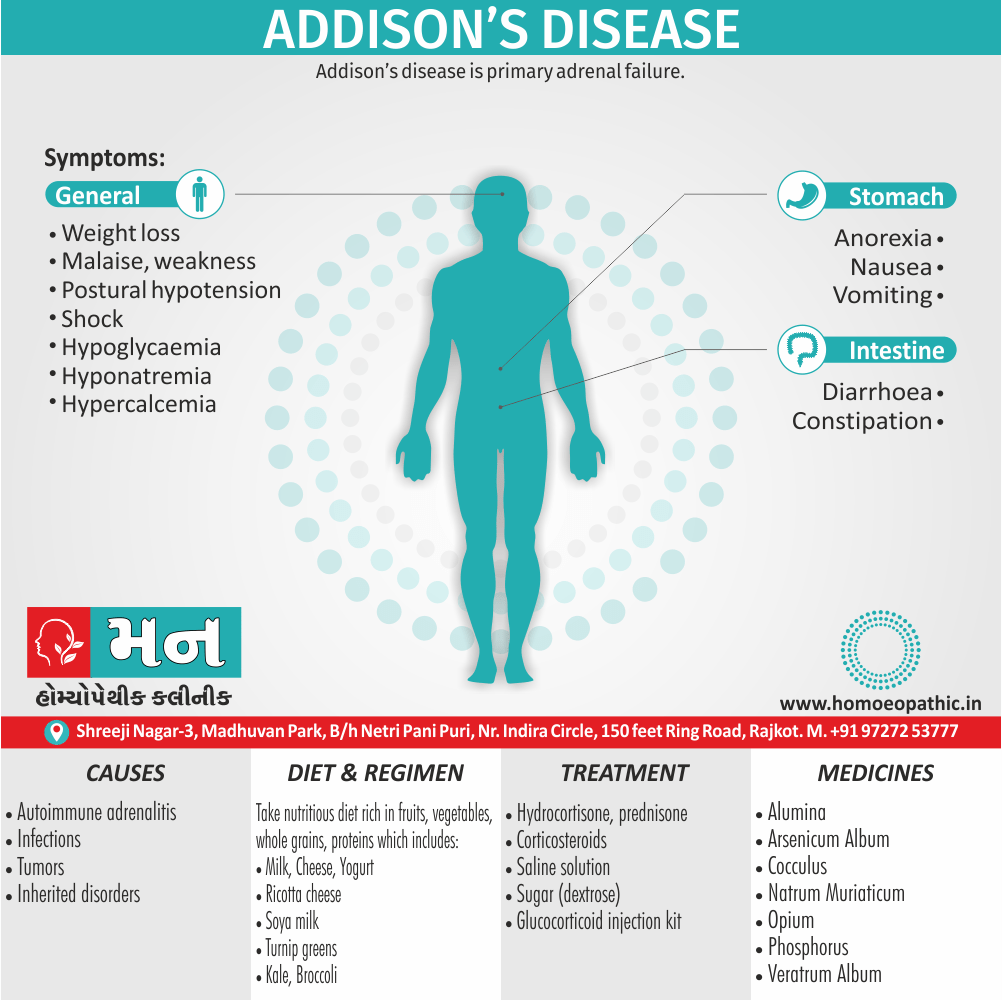
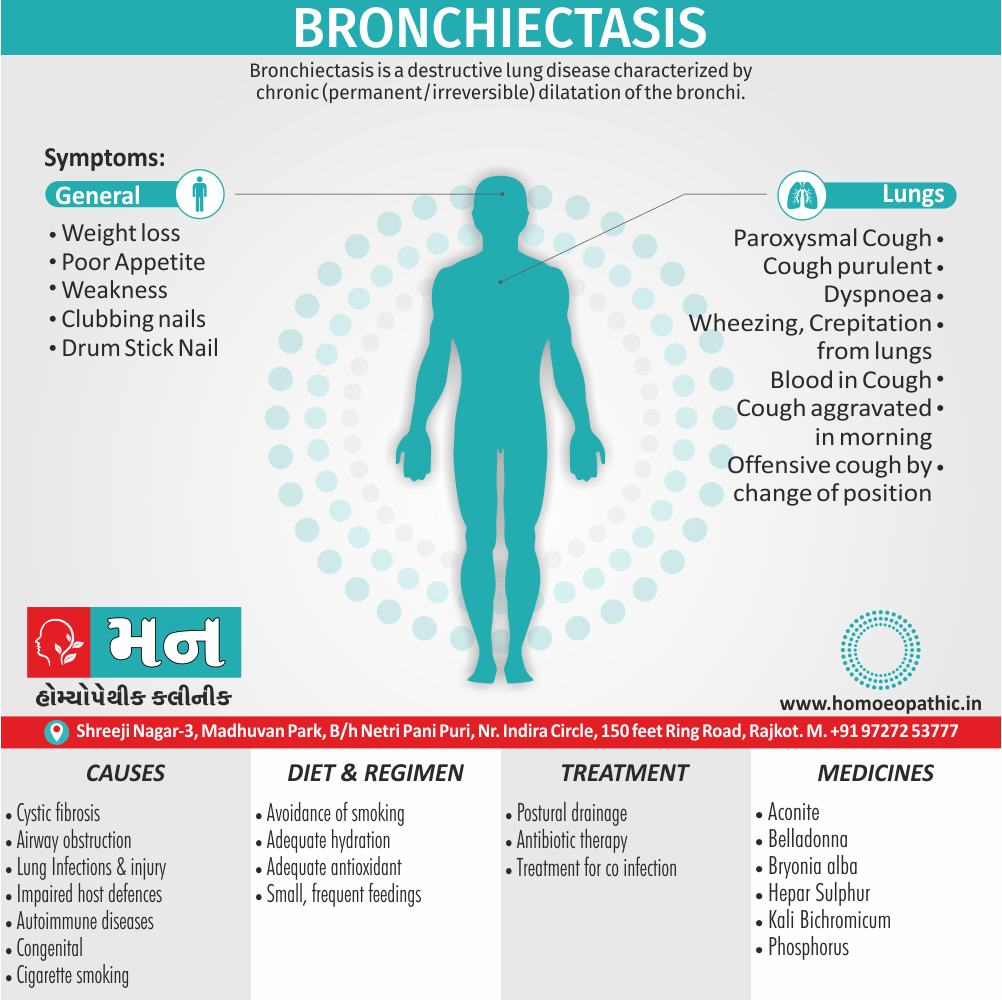
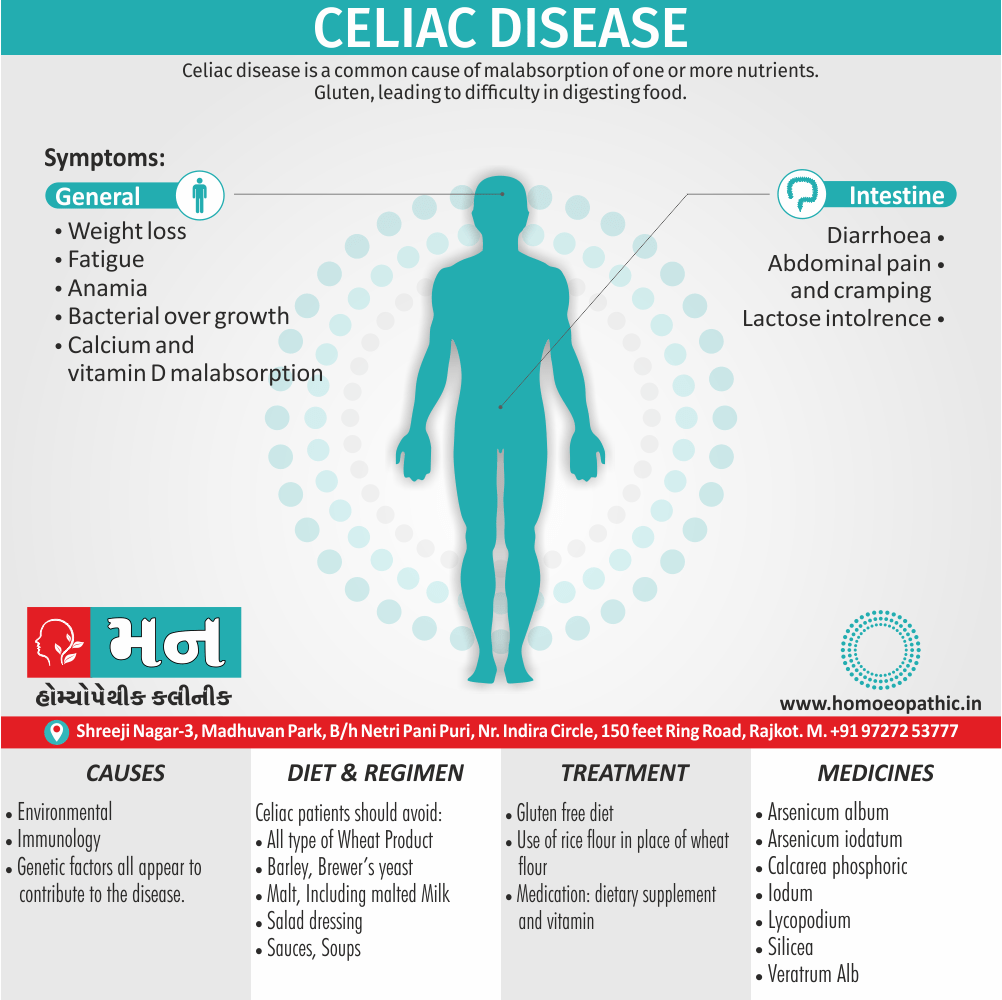
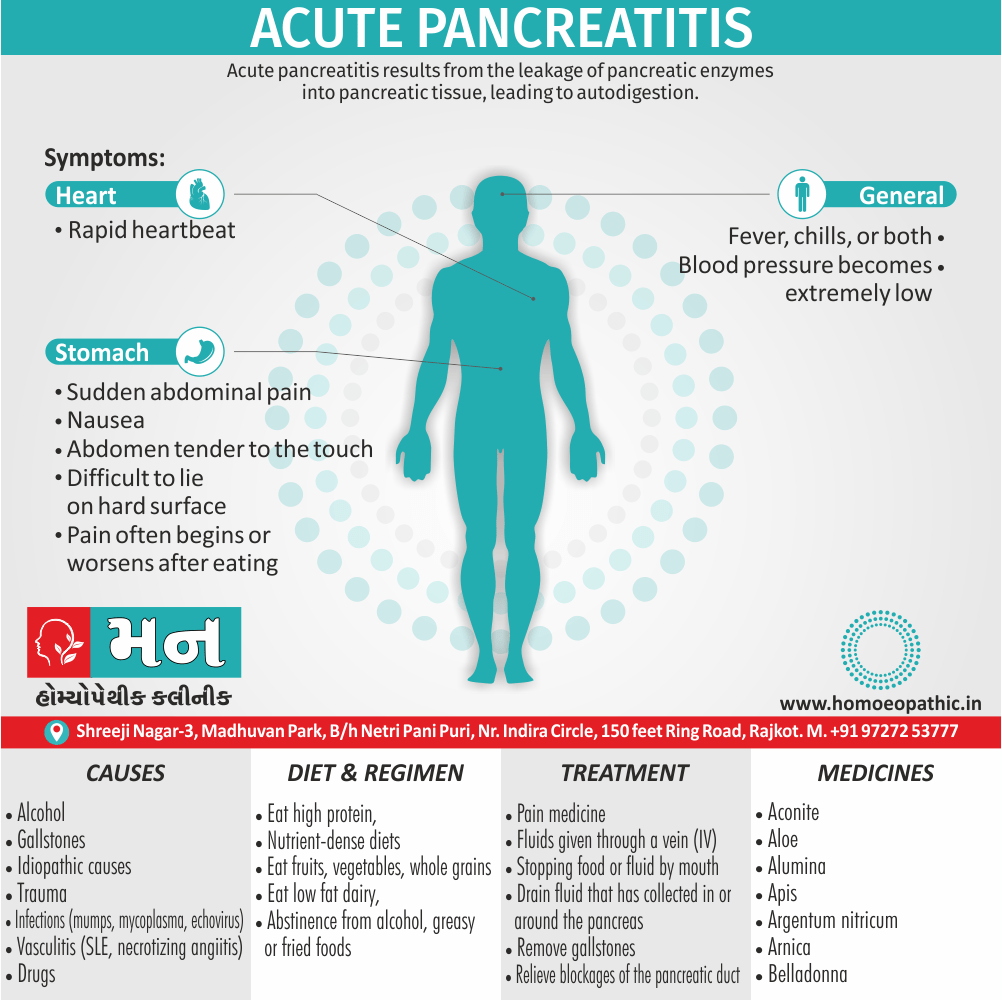
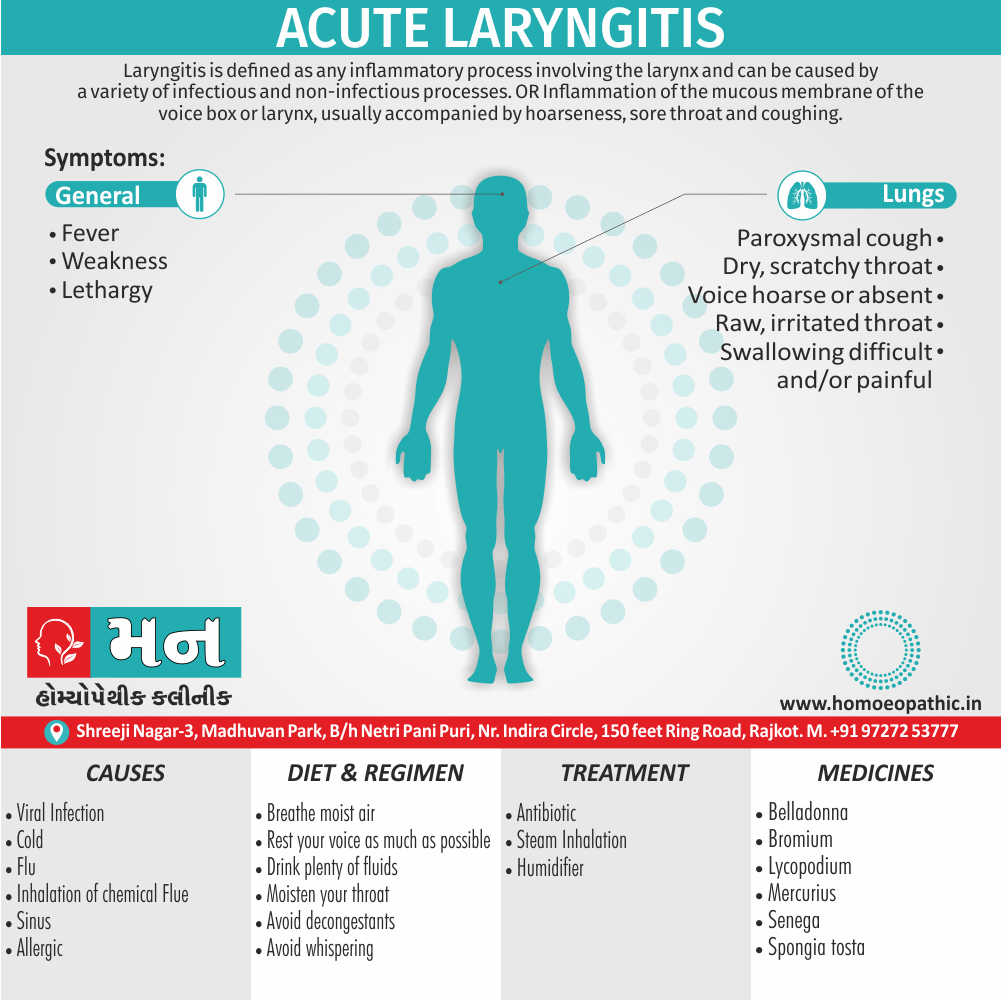
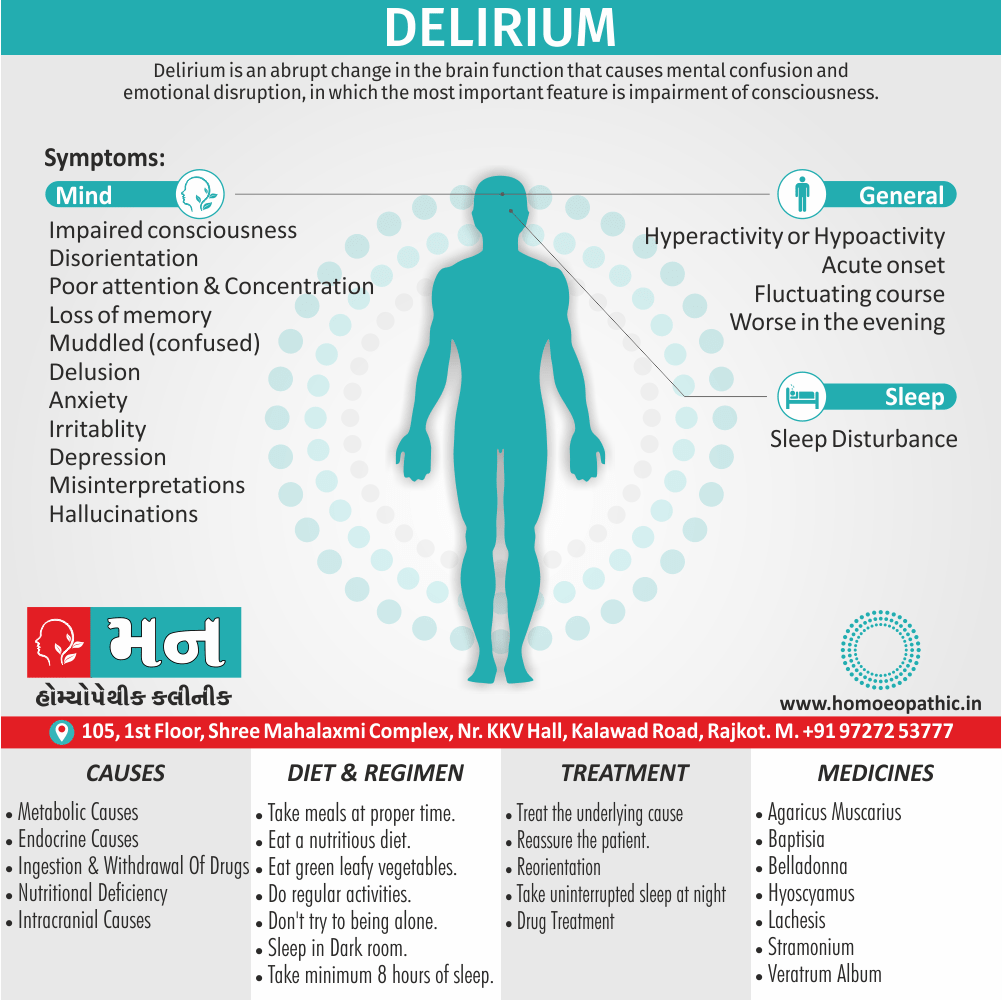
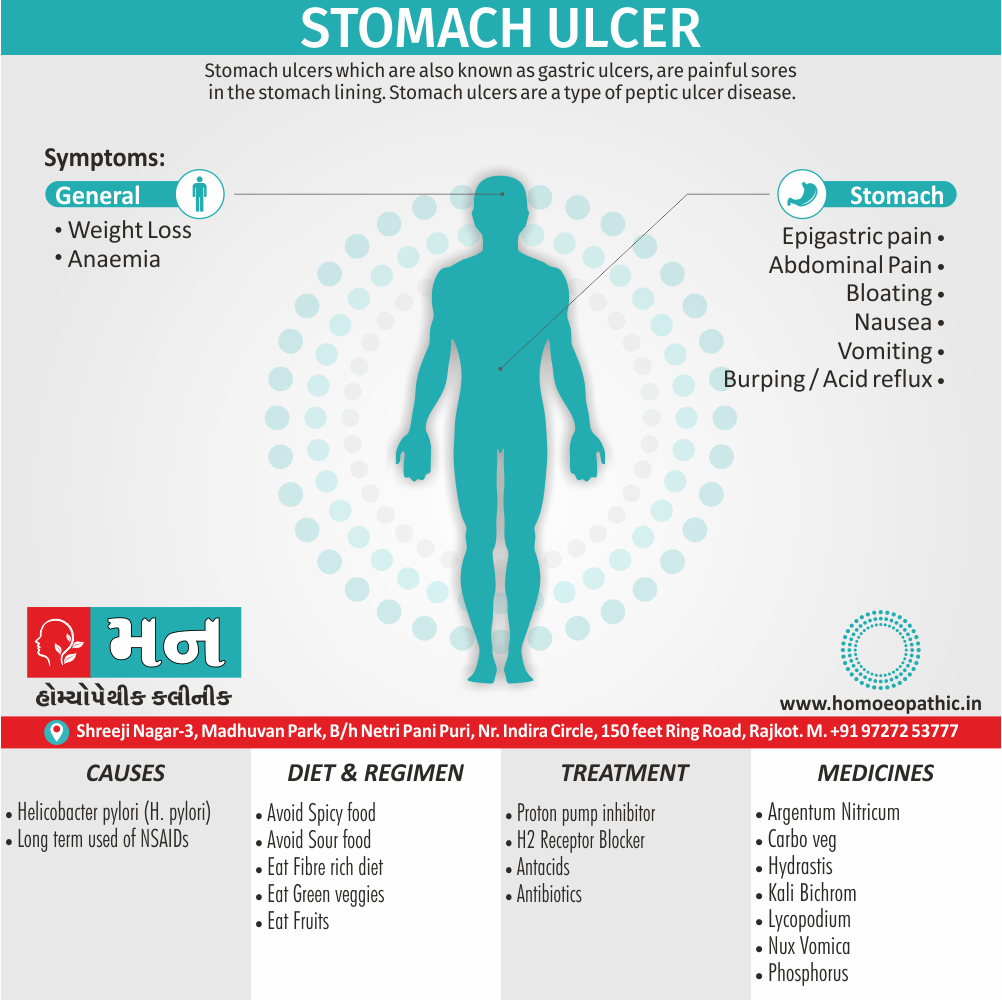
Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years.[2]
Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene that makes hemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each hemoglobin gene.
An attack can be set off by temperature changes, stress, dehydration, and high altitude. A person with a single abnormal copy does not usually have symptoms and is said to have sickle cell trait.
Such people are also referred to as carriers. Diagnosis is by a blood test, and some countries test all babies at birth for the disease. Diagnosis is also possible during pregnancy.
The care of people with sickle cell disease may include infection prevention with vaccination and antibiotics, high fluid intake, folic acid supplementation, and pain medication. Other measures may include blood transfusion and the medication hydroxycarbamide (hydroxyurea). A small percentage of people can be cured by a transplant of bone marrow cells.
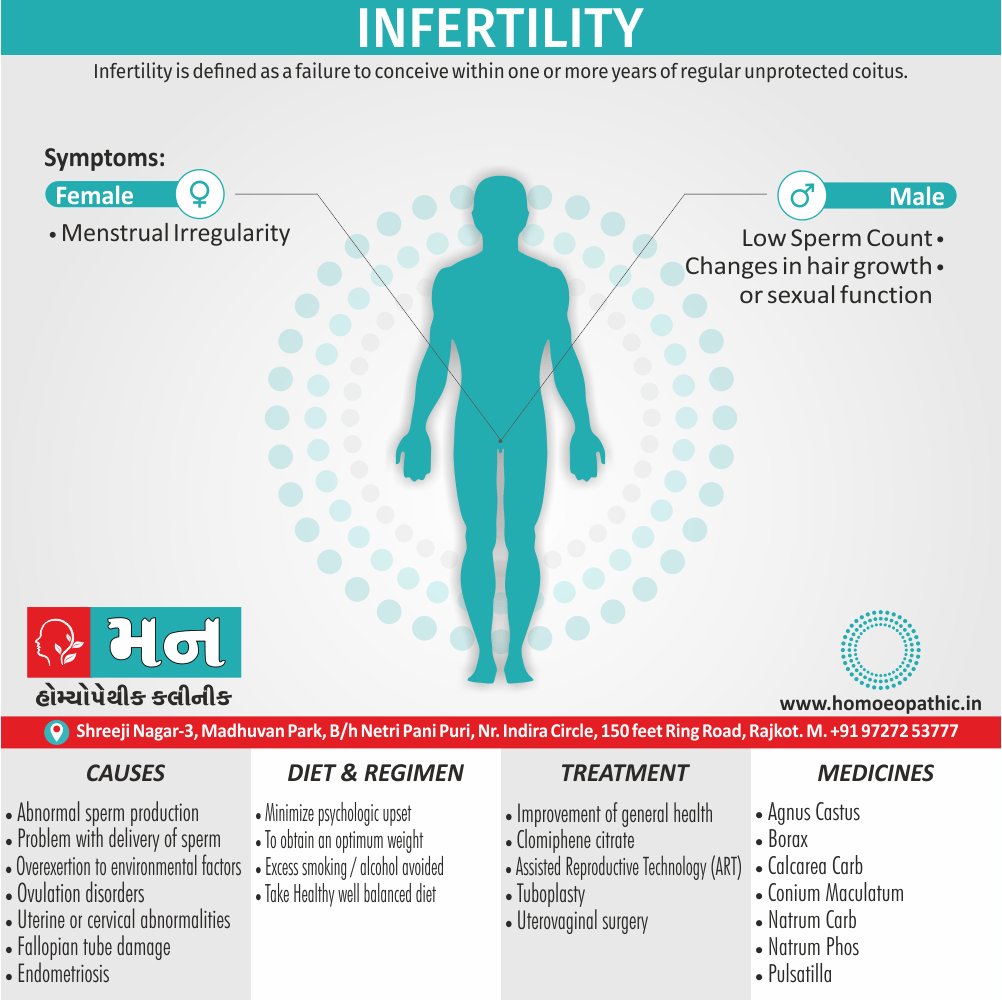
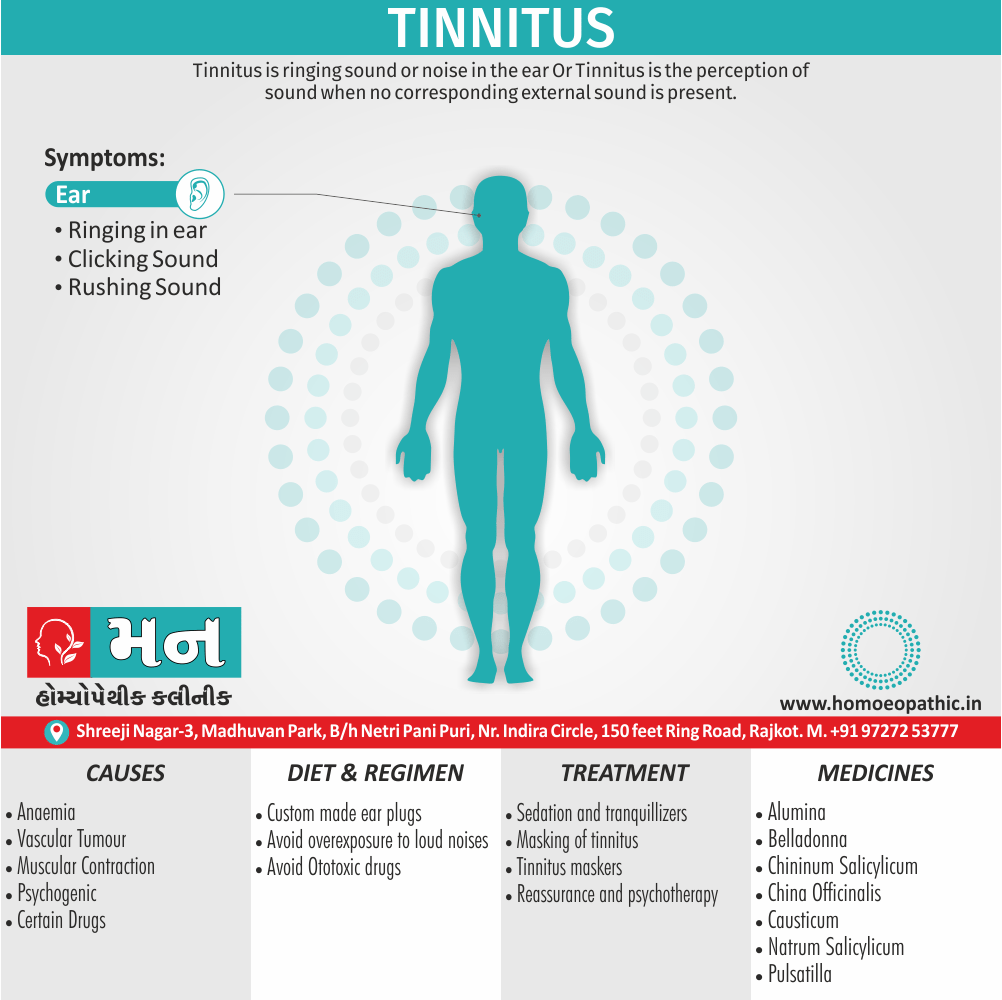
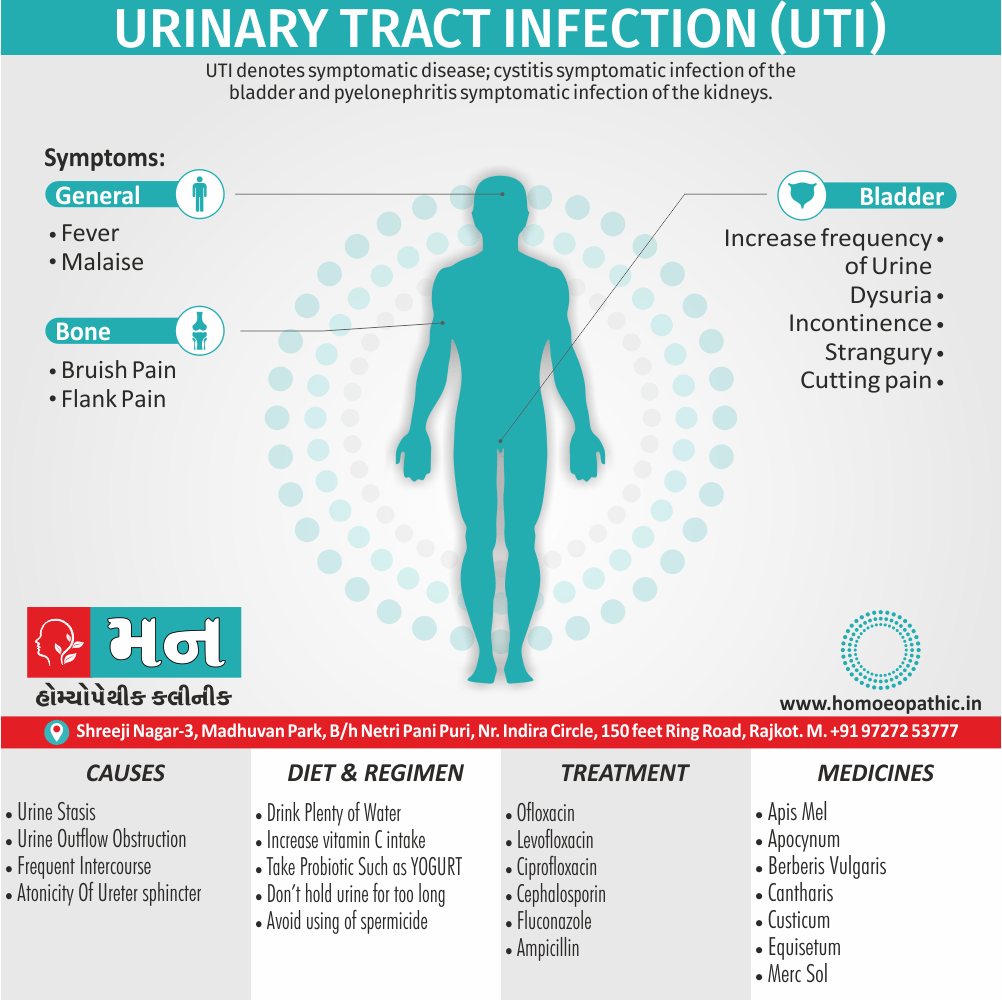
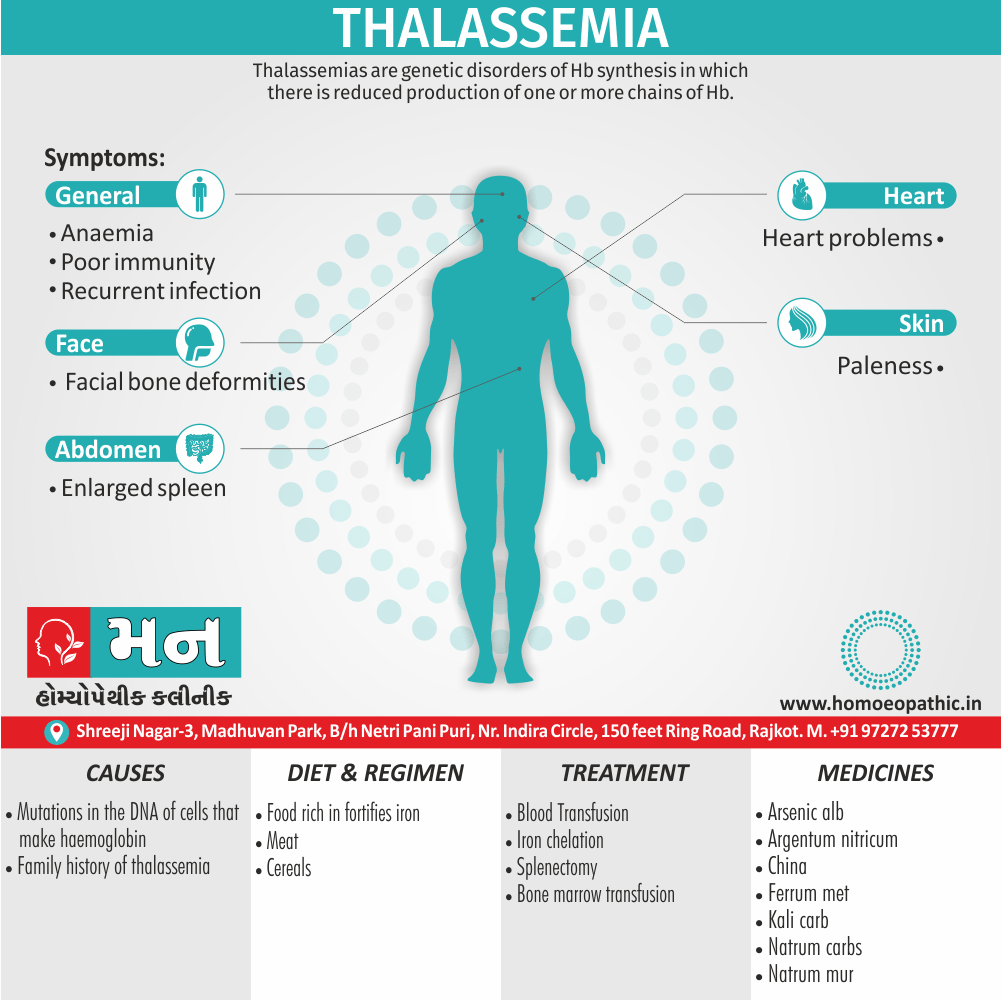
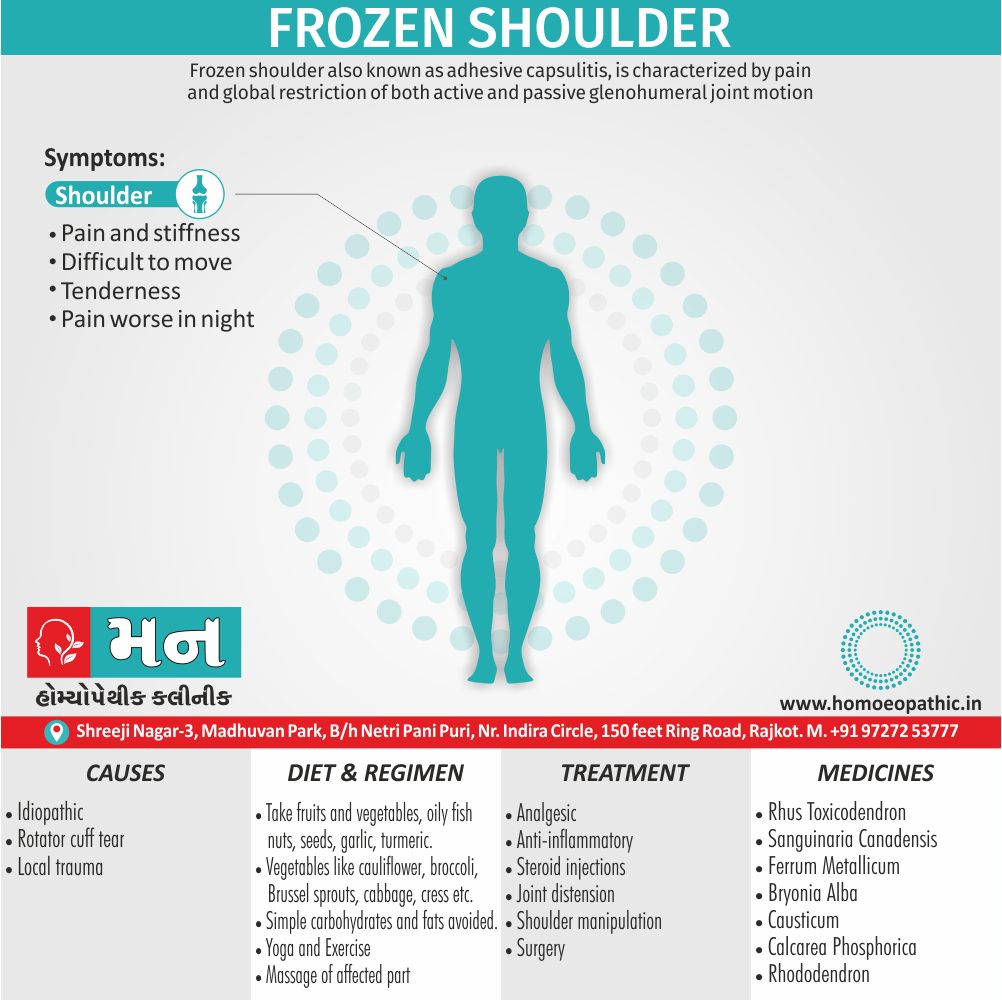
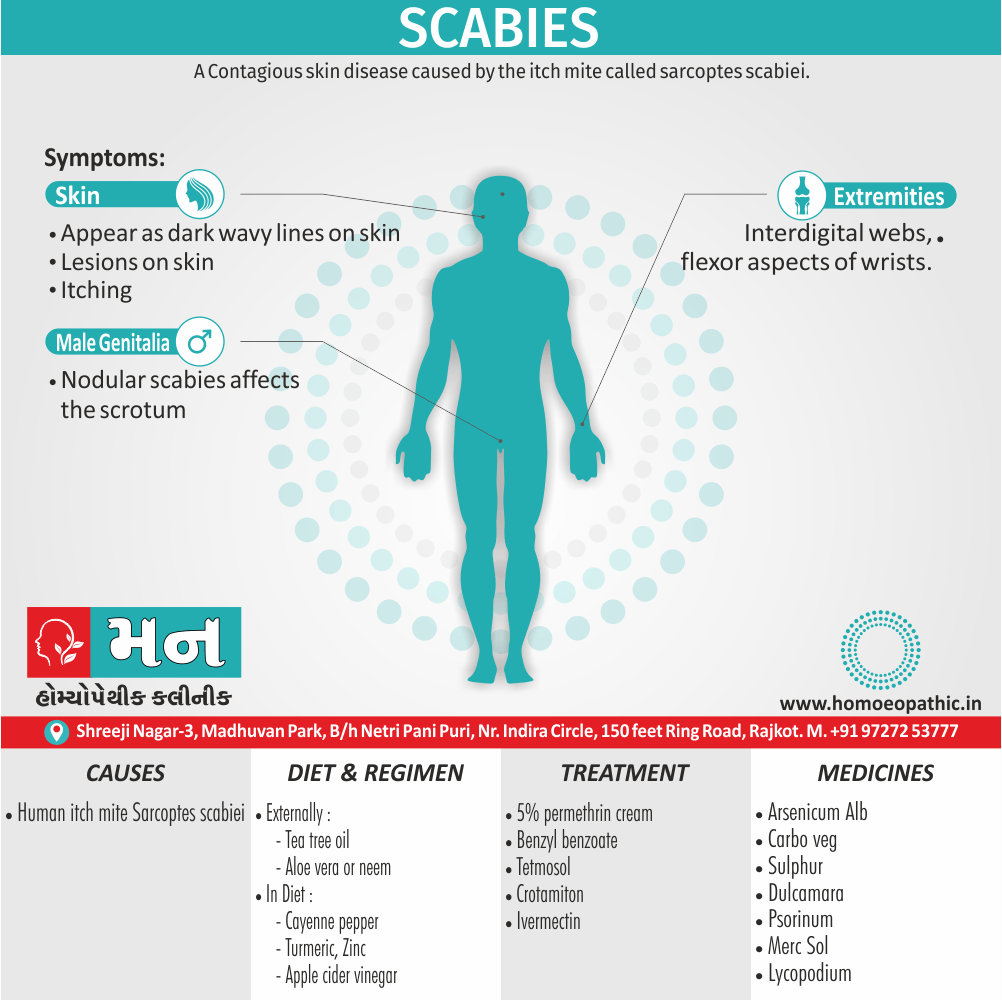
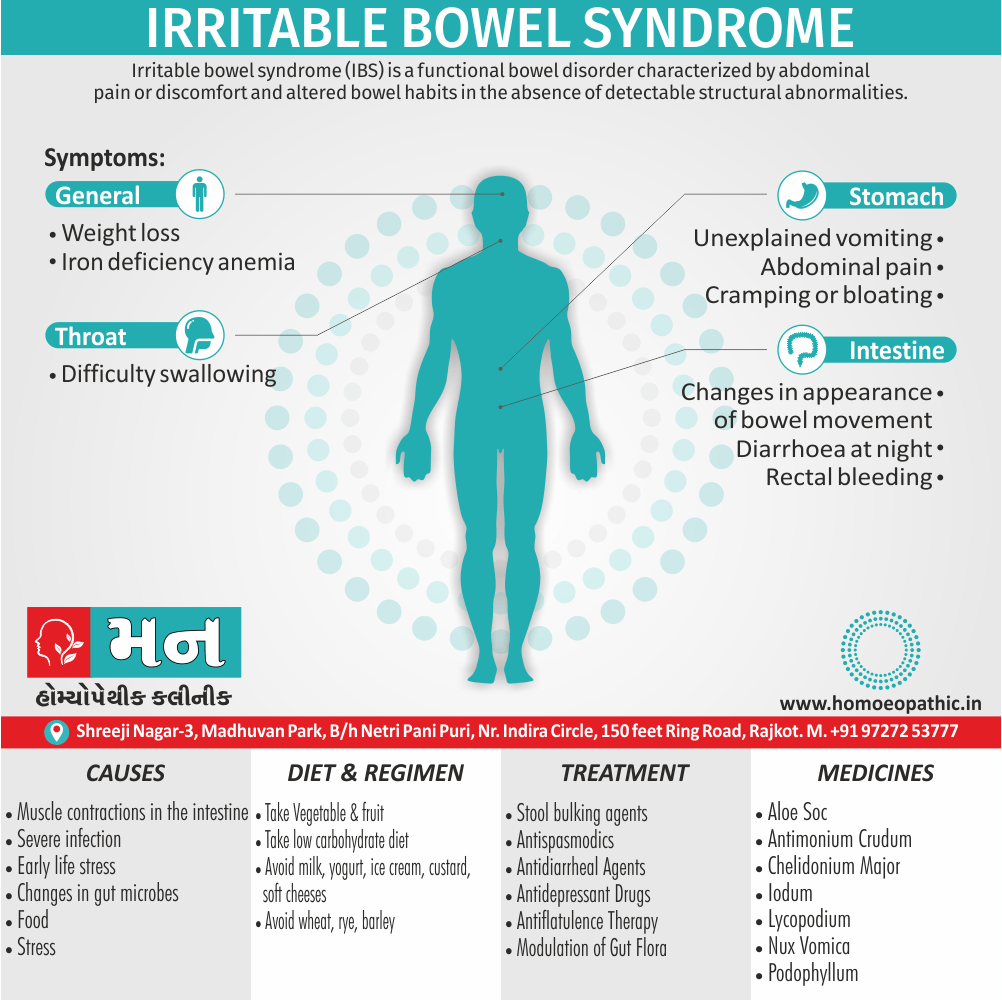
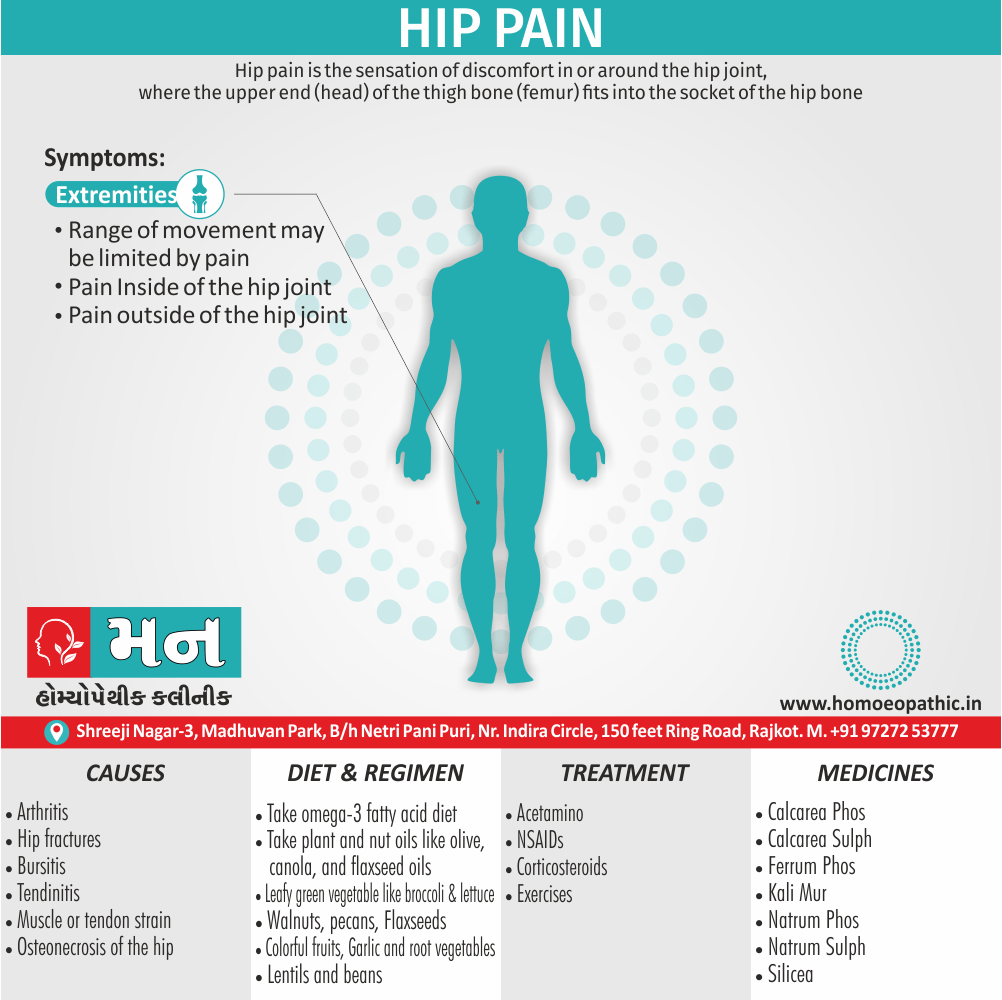
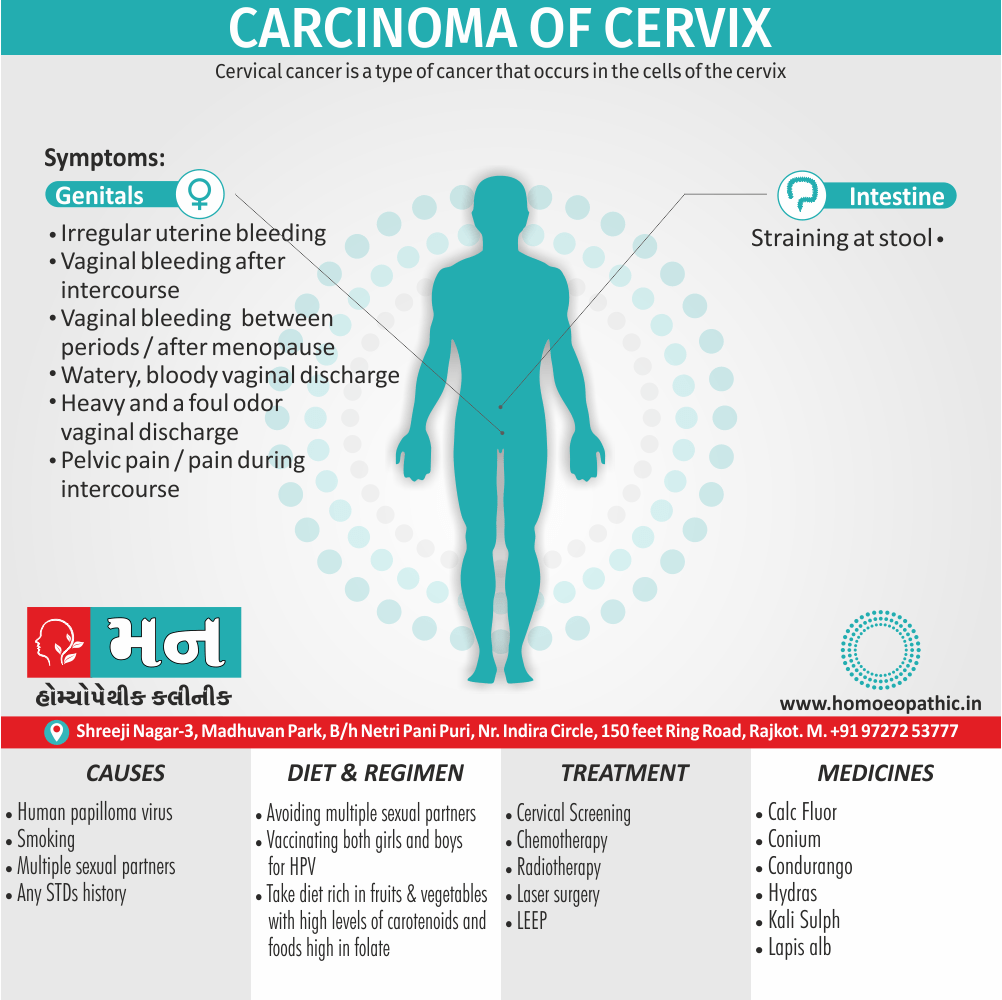
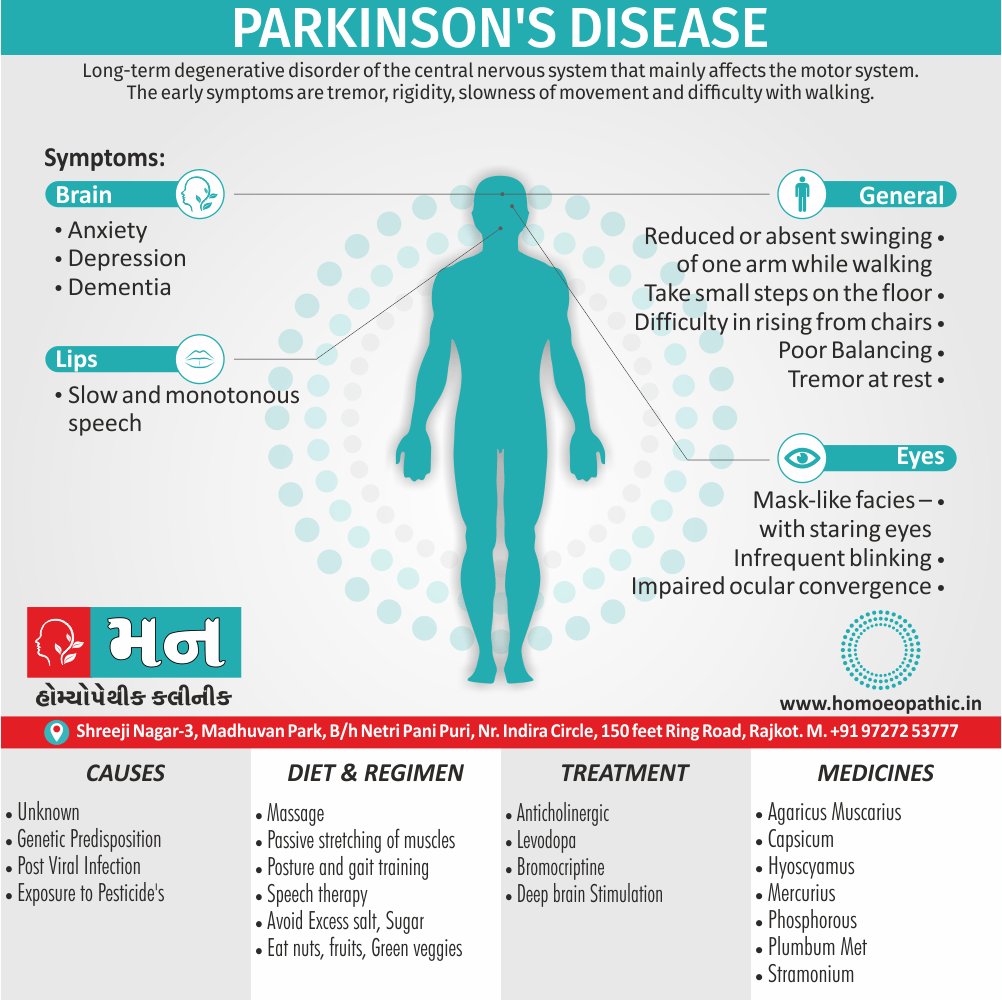
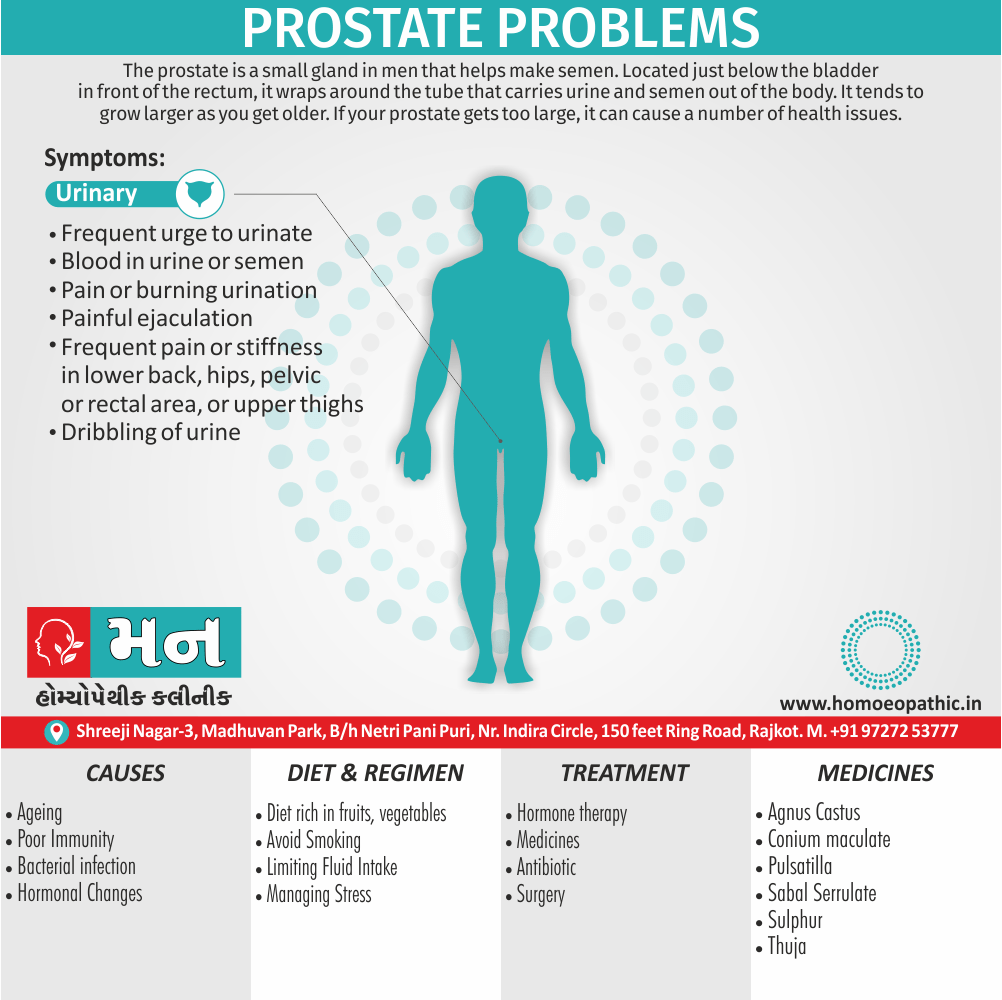
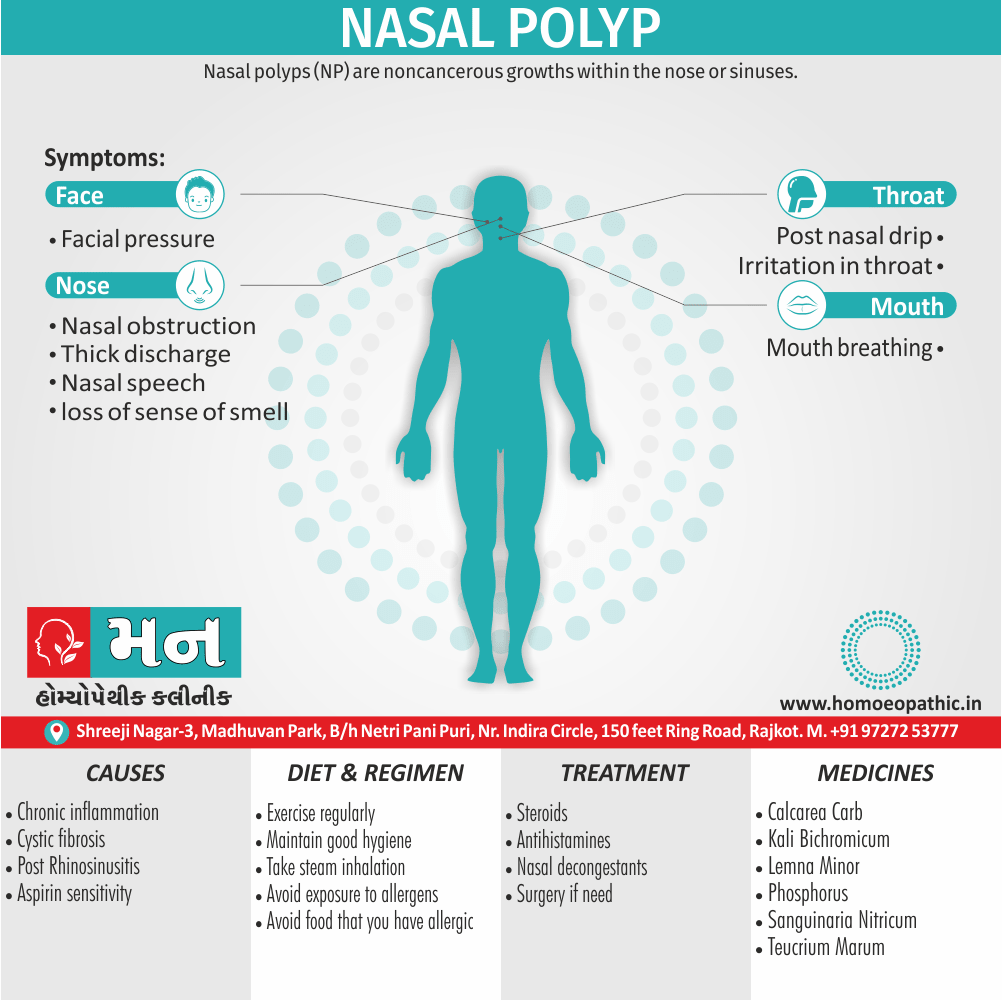
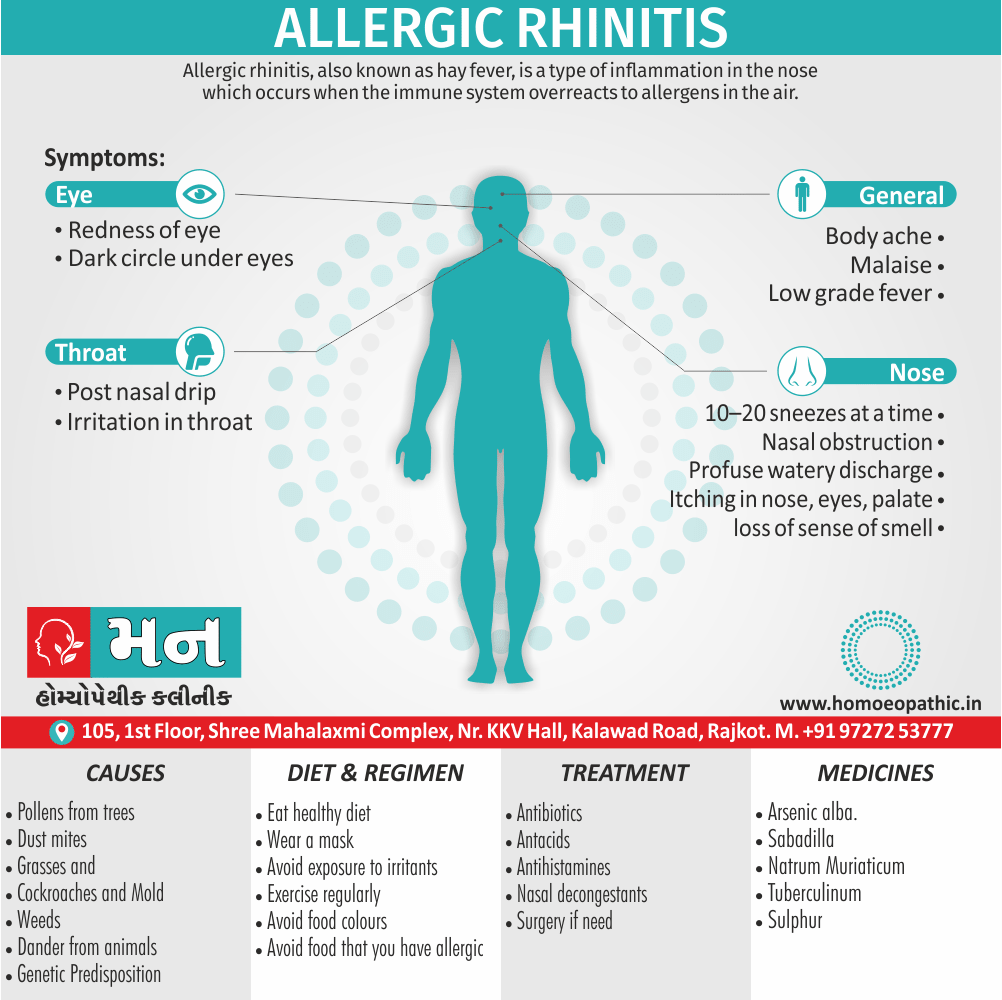
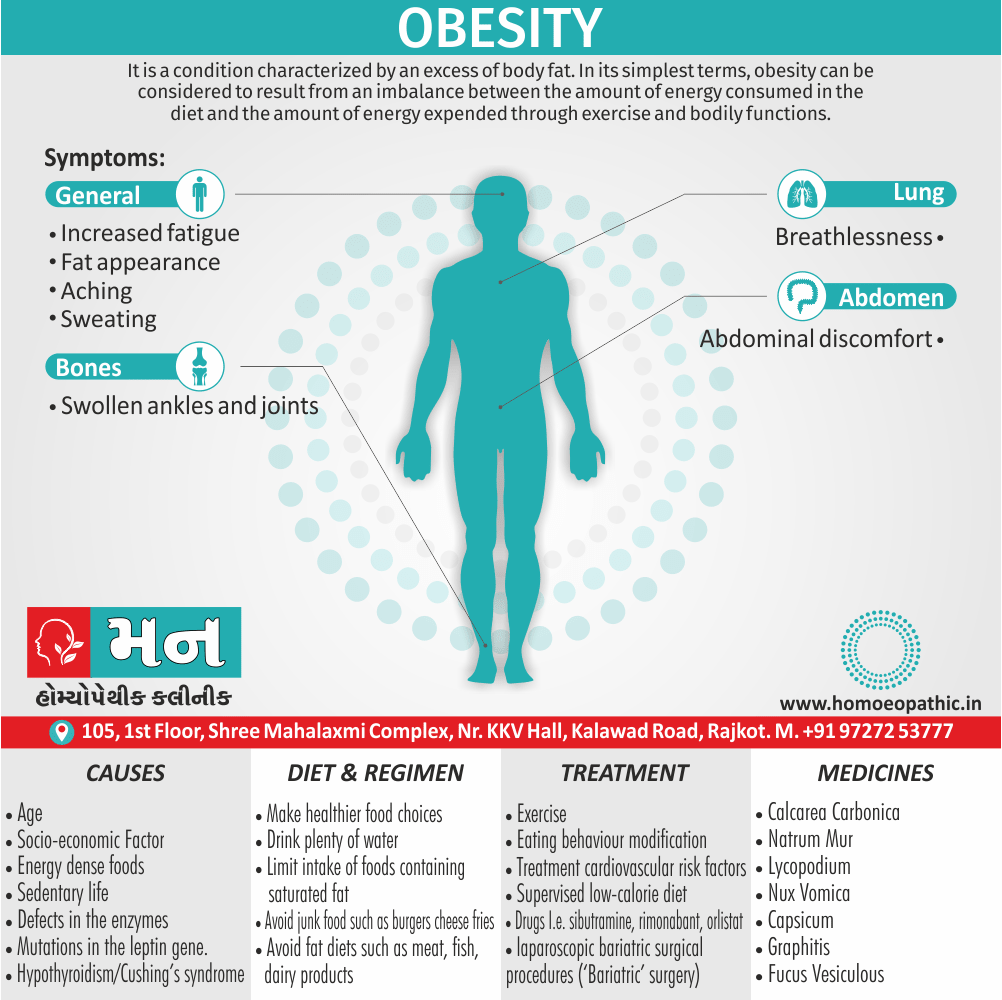
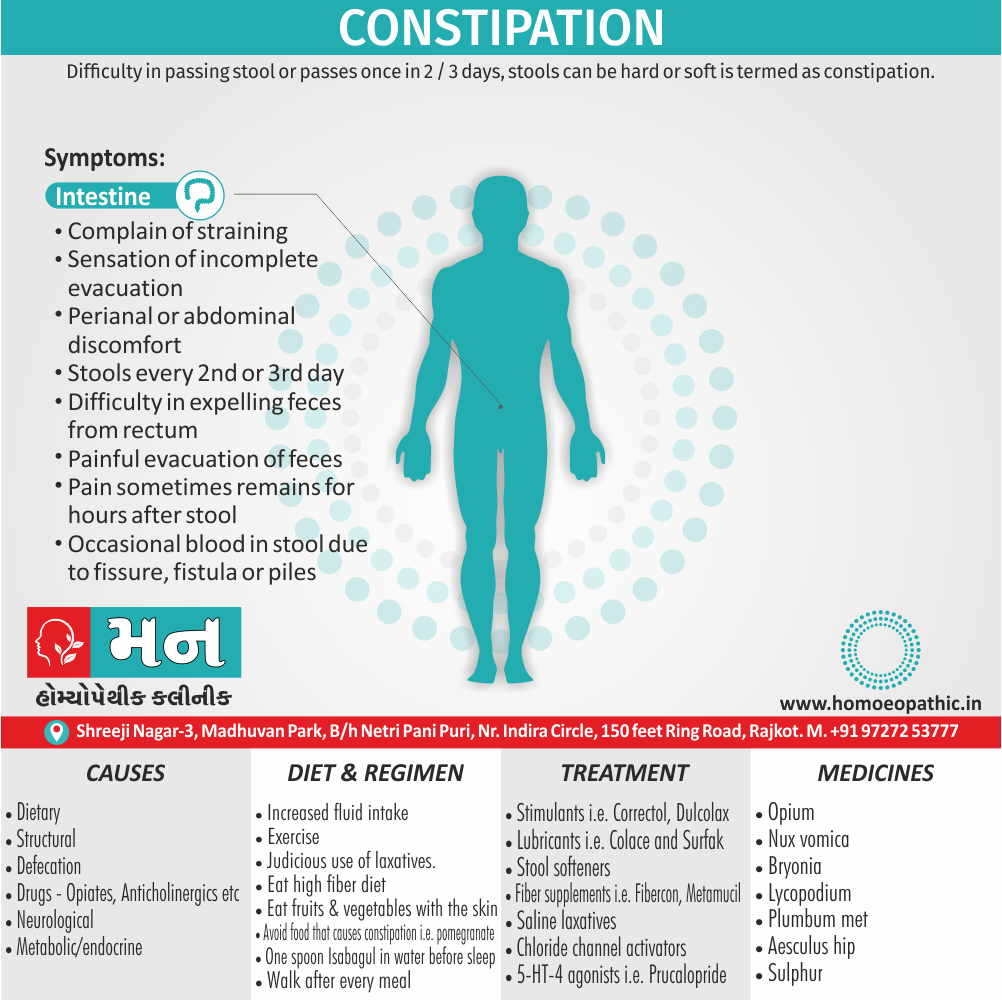
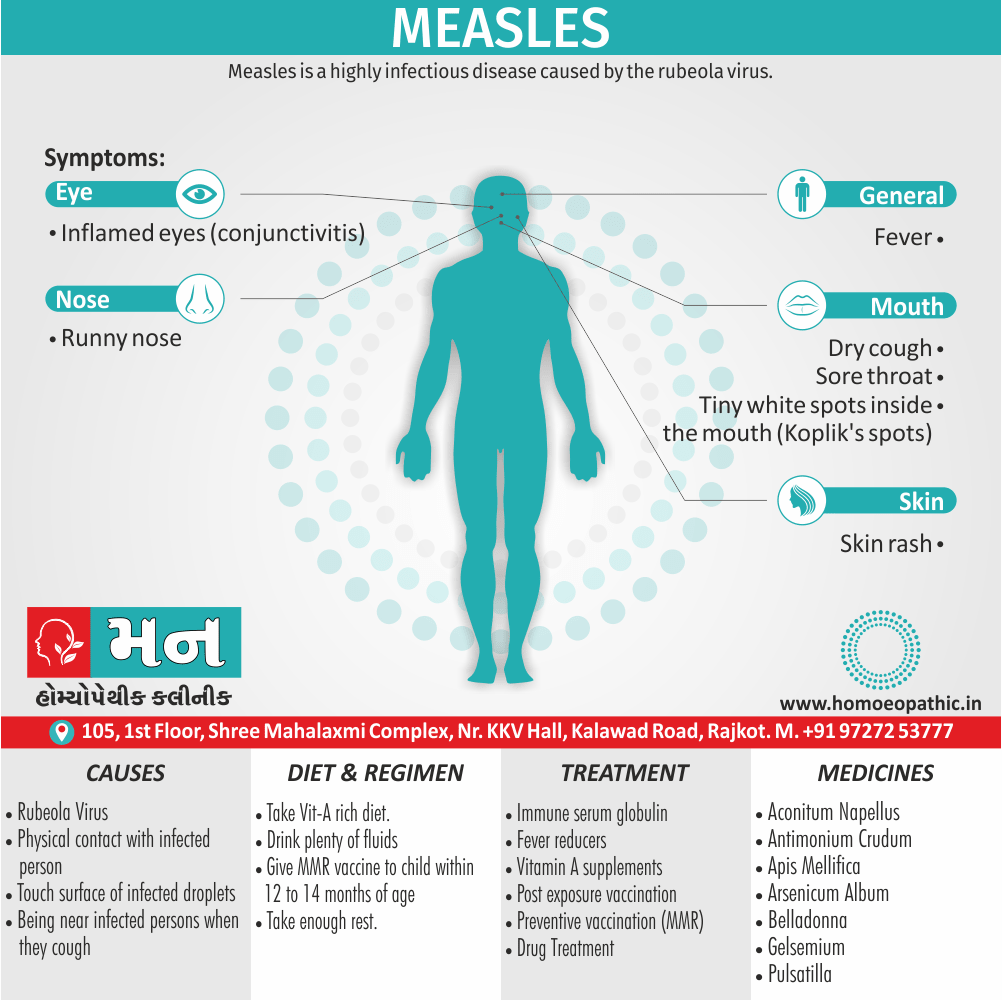
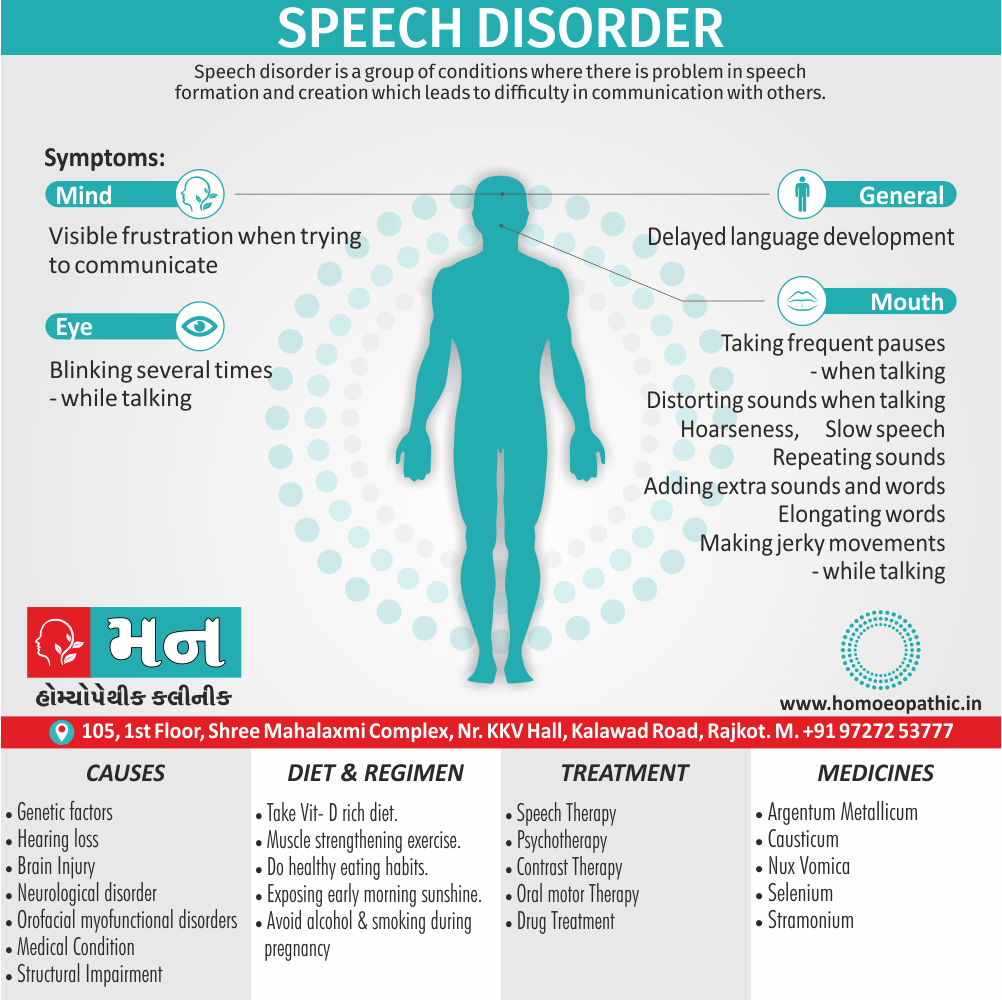
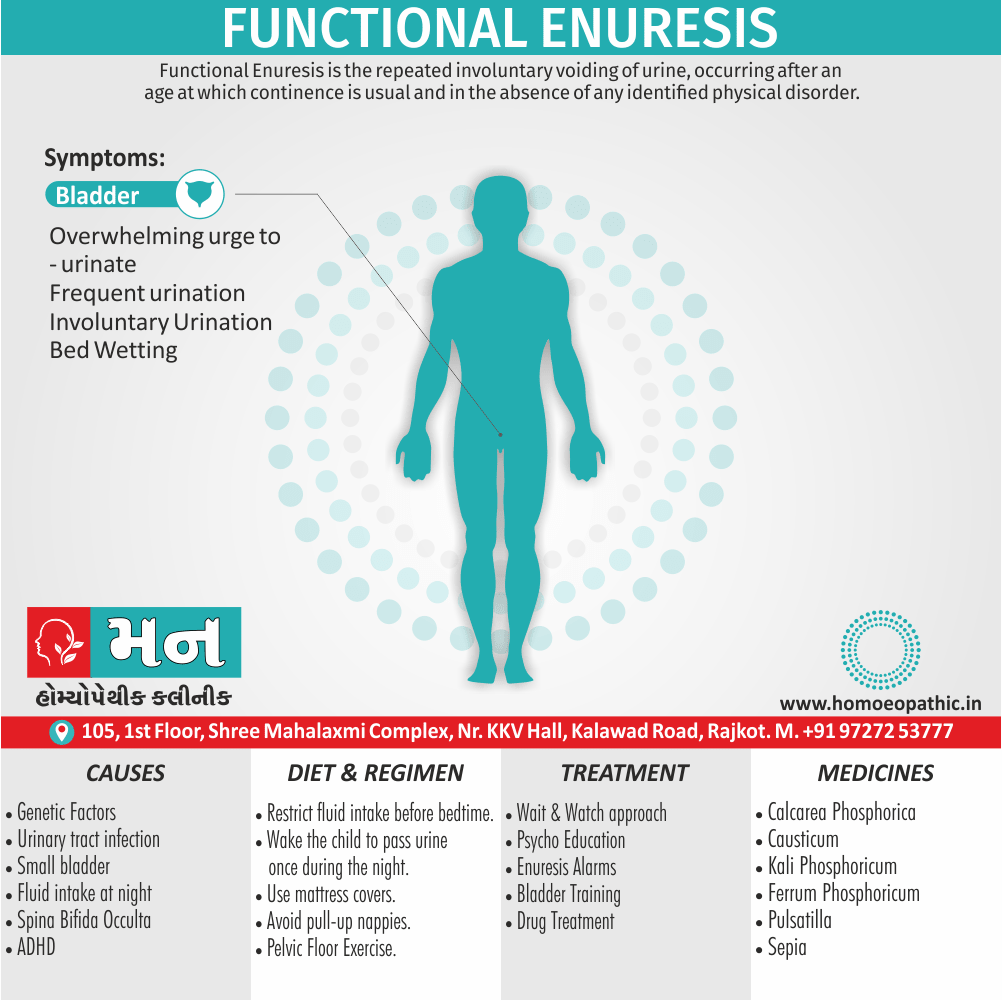
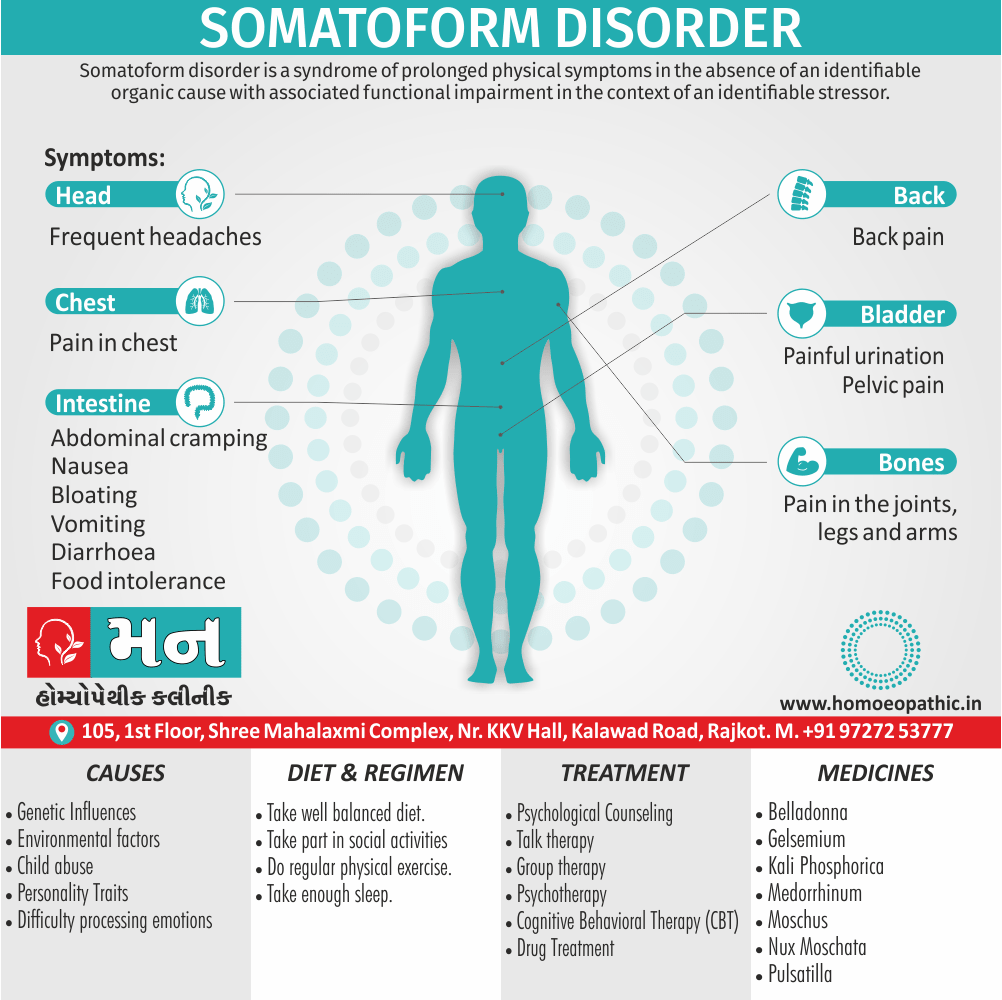
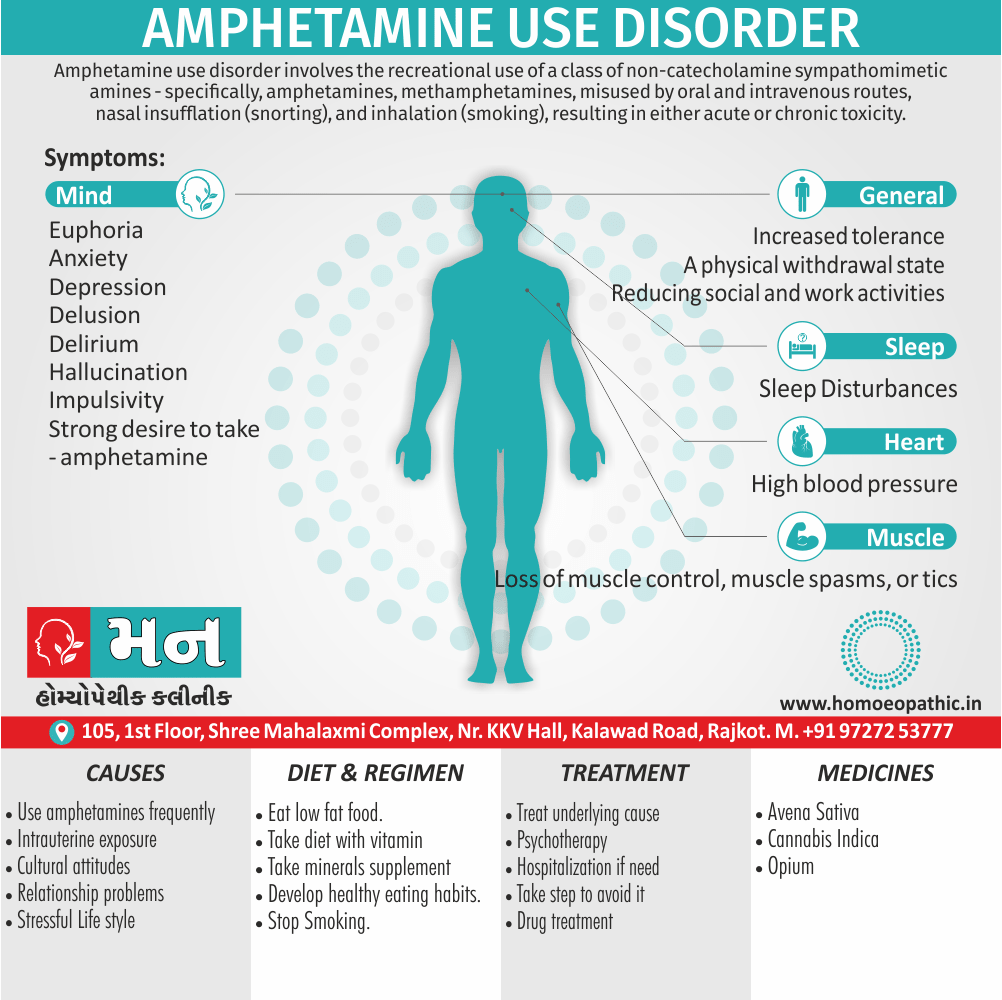
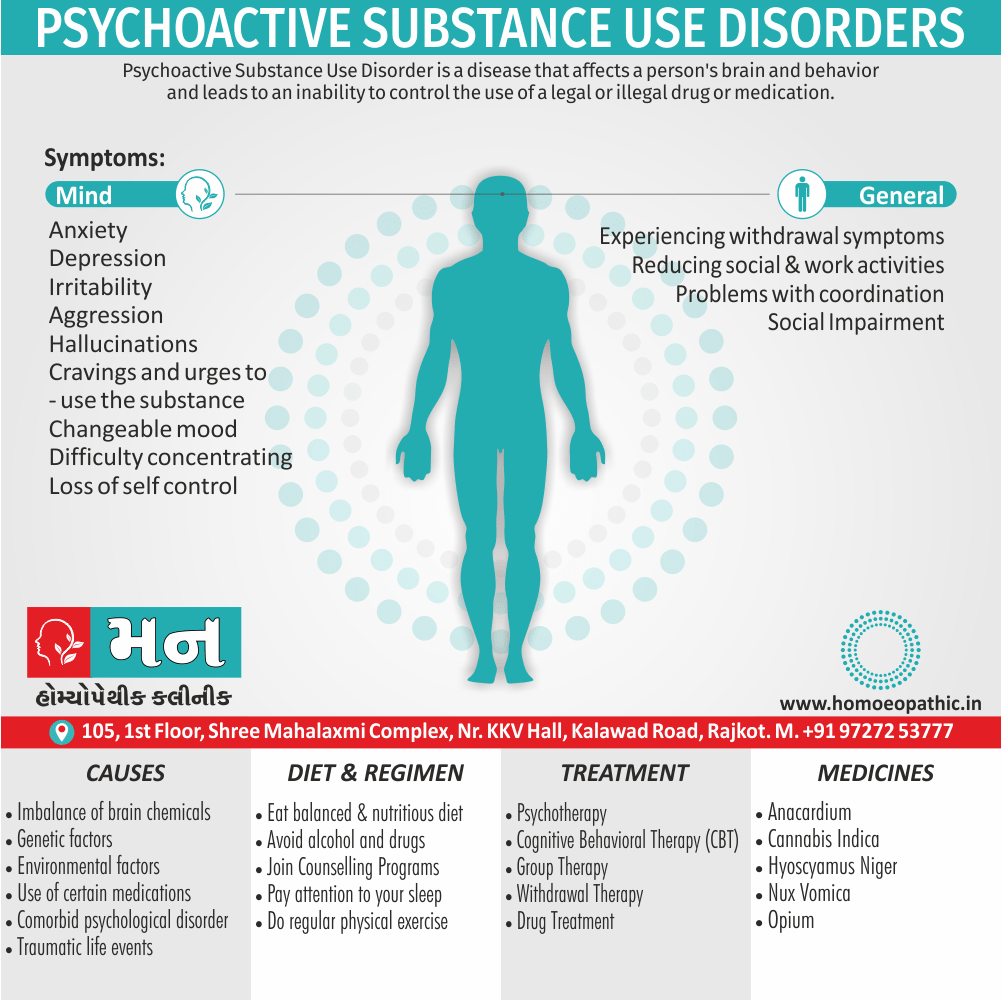
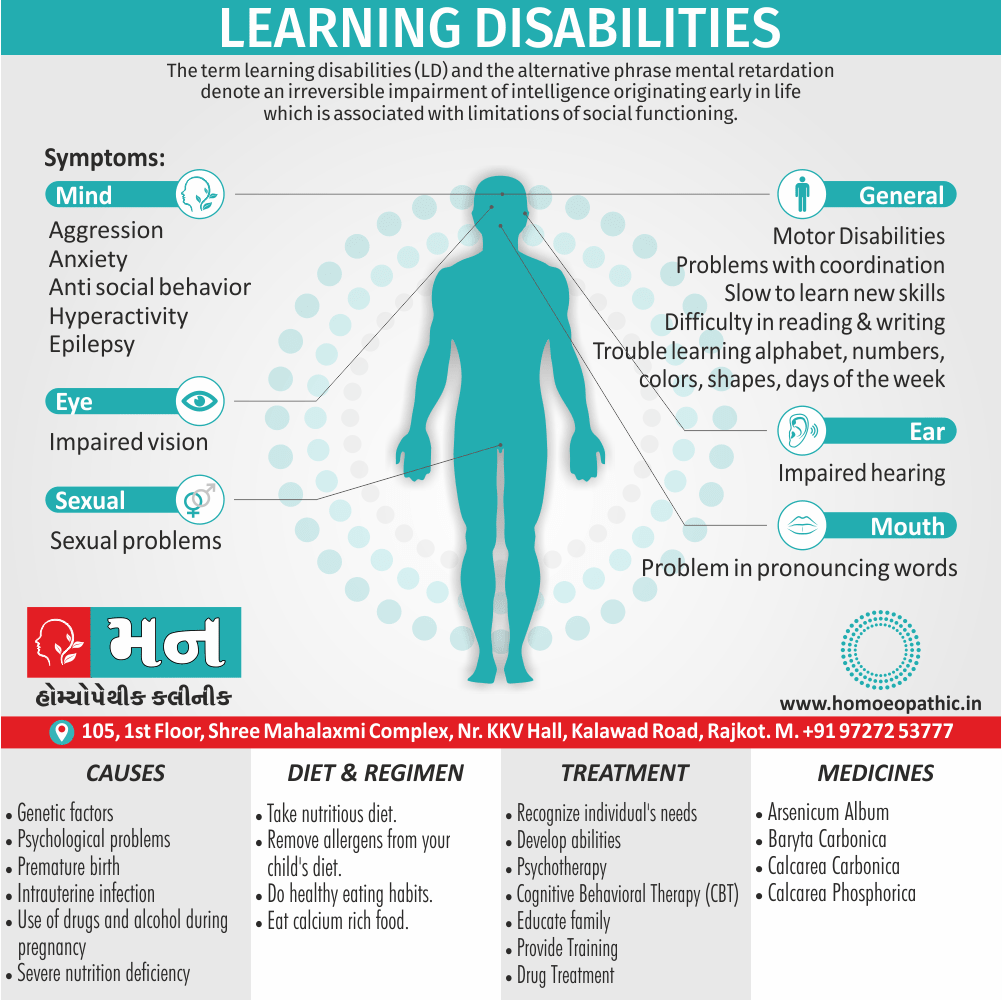
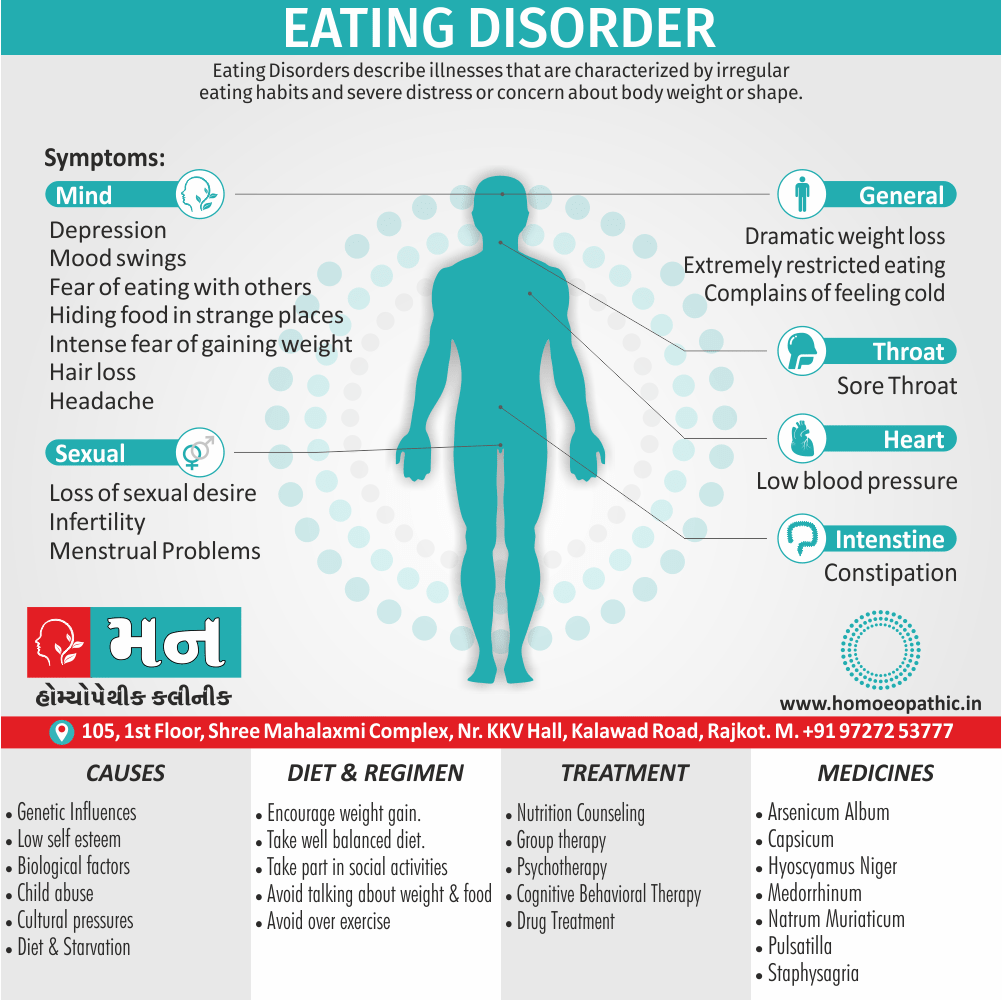
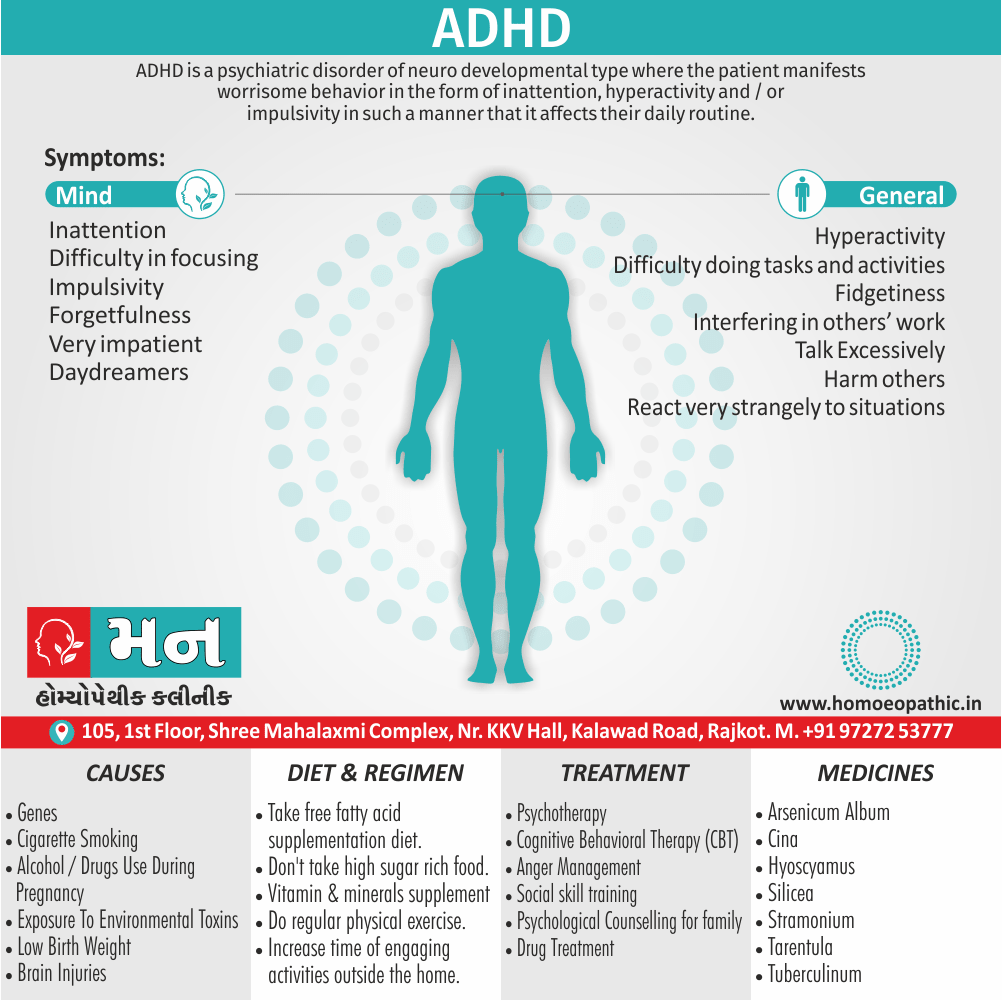
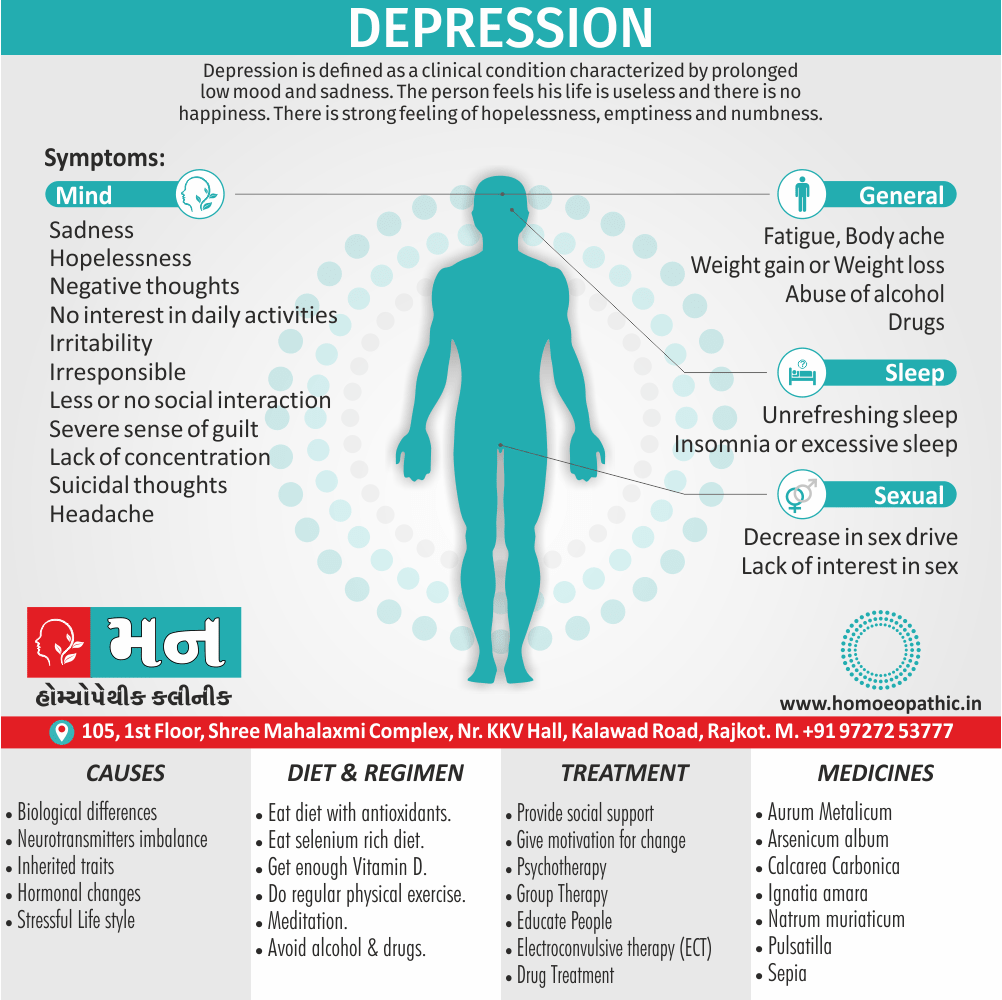
Causes of Sickle cell Disease
- Sickle cell anemia cause by a change in the gene that tells the body to make the iron-rich compound in red blood cells called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin enables red blood cells to carry oxygen from the lungs throughout the body. The hemoglobin associated with sickle cell anemia causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky and misshapen.
- For a child to affect, both mother and father must carry one copy of the sickle cell gene — also known as sickle cell trait — and pass both copies of the altered form to the child.
- If only one parent passes the sickle cell gene to the child, that child will have the sickle cell trait. With one typical hemoglobin gene and one altered form of the gene, people with the sickle cell trait make both typical hemoglobin and sickle cell hemoglobin.
- Their blood might contain some sickle cells, but they generally don’t have symptoms. They’re carriers of the disease, however, which means they can pass the gene to their children.[3]
Pathophysiology of Sickle cell Disease
Clinical problems in sickle cell disease relate to veno-occlusion caused by polymerization of deoxygenated hemoglobin S.
This results in the pathognomonic change in the shape of erythrocytes to the sickle shape that stiffen the RBC membrane, increase viscosity and cause dehydration due to potassium leakage and calcium influx.
The most common clinical feature is the painful vaso-occlusive crisis resulting from blockage of small vessels.
However, large vessels disease also occurs, resulting in – Thrombotic cerebrovascular accidents, acute sickle chest syndrome, and placental infarction. [2]
Classification of Sickle cell Disease
- Sickle cell trait – Less than 50% HbS per cell is usually not associated with clinical abnormality. Infarction of spleen may occur during anesthesia, and hematuria is not uncommon.
- Sickle-cell anemia – Anemia from about third month of life, since HbS is more than 70% in red cells. 3. Sickle cell disease – This refers to all disease states in which at least one gene is of HbS.
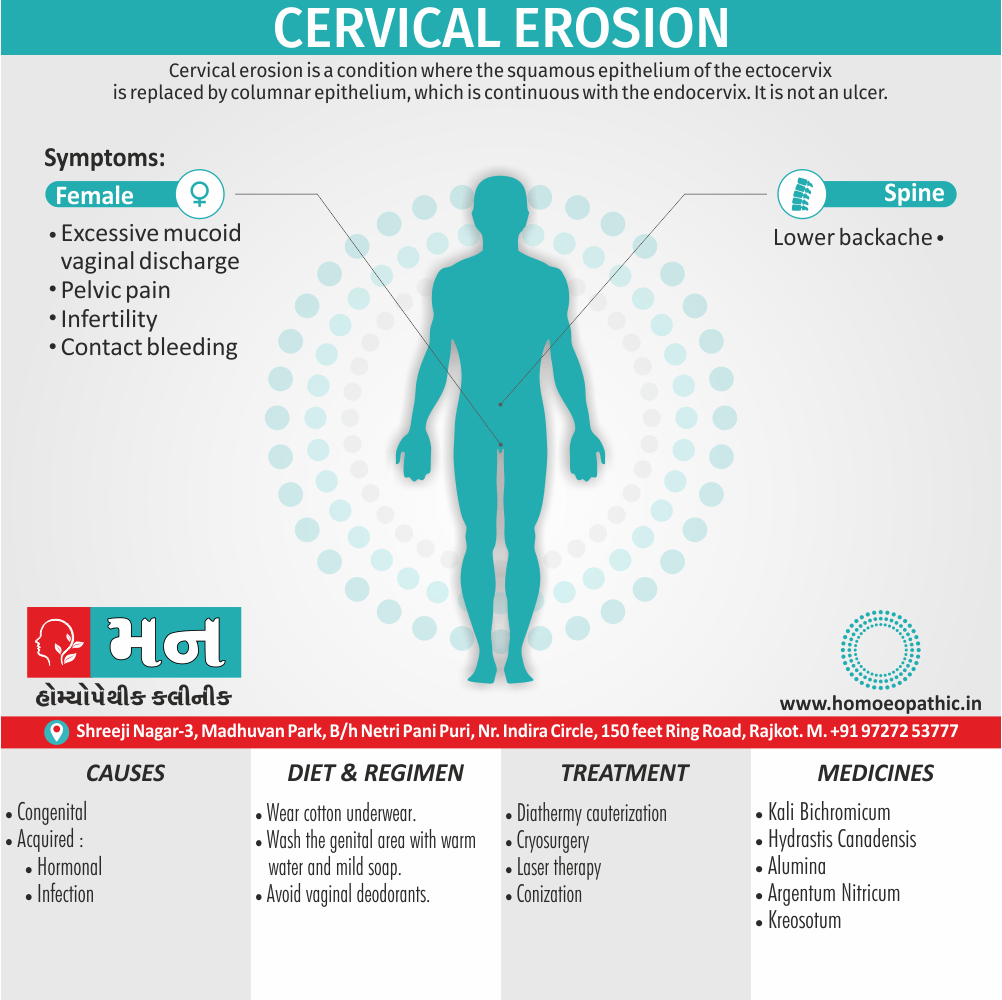
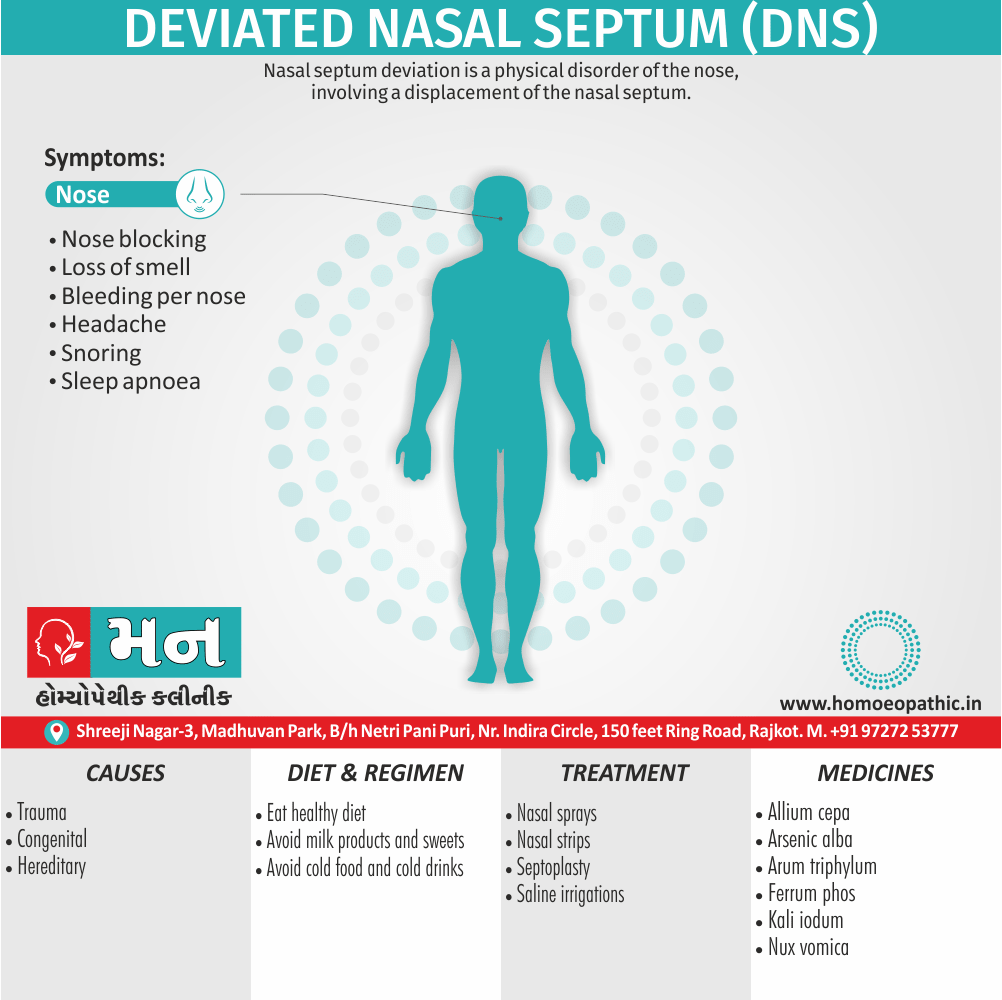
Sign & Symptoms of Sickle cell Disease
- Delayed growth and development
- Enlargement of spleen after 6 months. Later at 5-6 yrs of age, reduction in size due to multiple infarcts from veno-occlusion of branches of splenic artery. In adults, spleen may be totally replaced by fibrous tissue.
- Leg ulcers – Shallow ulcers near ankle due vascular stasis and often after trauma.
- Hand-foot syndrome – Painful swelling of hands and feet. Vaso-occlusive crisis and dactylitis leads to destruction of metacarpals, metatarsals and phalanges. [2]
- CNS – Brain syndrome in a few children, occlusion of cerebral vessels leads to stroke.
- Infections – Pneumococcal pneumonia, meningitis due to hyposplenism, osteomyelitis due to salmonella from repeated bone infarcts.
- Cardiomegaly due to hyperdynamic circulation as a result of chronic anemia.
- Hepatomegaly
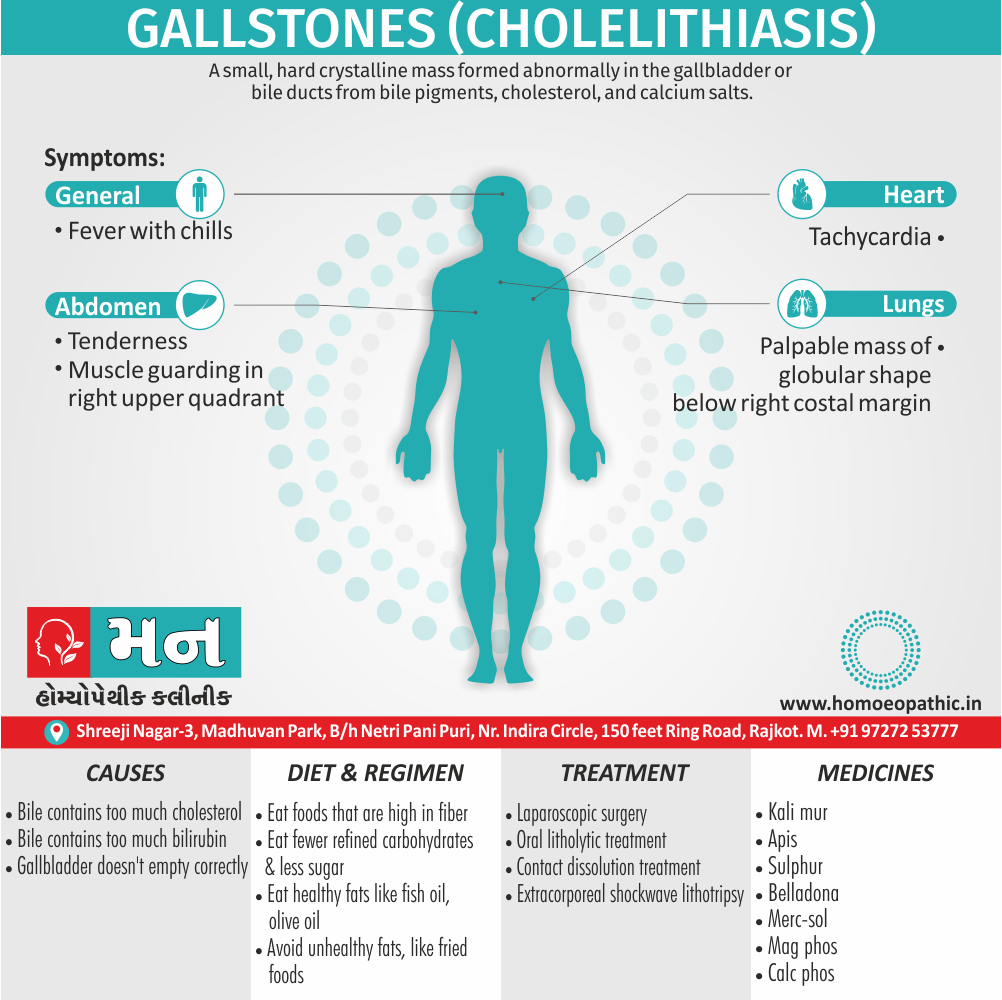
- Gall stones – Pigment gall stones increase in frequency from childhood to adult.
- Ocular complications – Occlusion of retinal vessels causes retinal changes such as ‘salmon patches’, intraretinal hemorrhages, A-V anastomosis.
- Abdominal pain occurs due to infarcts of abdominal viscera due to vaso-occlusive crises.
- Priapism – due to stagnation of blood in corpora cavernosa.
- Skeletal changes – In a young child there is widening of the diploe of the skull leading to new bone formation with resultant ‘crew cut appearance’ in X-ray. Bone and joint ischemia leading to aseptic necrosis seen in femoral and humeral head. Unusually susceptibility to osteomyelitis, caused by salmonella.
Investigation of Sickle cell Disease
- Sickling test – Sickling is induced by adding reducing agent like 2% sodium metabisulphite to blood.
- Hb electrophoresis can be performed on cellulose acetate membrane or starch agarose. HbS is a slow moving Hb as compared to HbA and HbF. In HbS, HbS constitutes 70-90% of total Hb but HbA is nil. This differentiates homozygous (SS) from heterozygous state (SA), since the latter demonstrates two bands of HbS and HbA.
- HbF estimation since HbF is 10-30% in homozygous state and is helpful in assessing course of the disease.
- High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) gives exact amount of HibA, HbS, HbF and HbA2.
- Globin chain analysis may be required to assess the genetic basis of disease and differentiate it from various heterozygote states.
- HbS solubility is based on the fact that sickle Hb is insoluble in deoxygenated state. [2]
Diagnosis of Sickle cell Disease
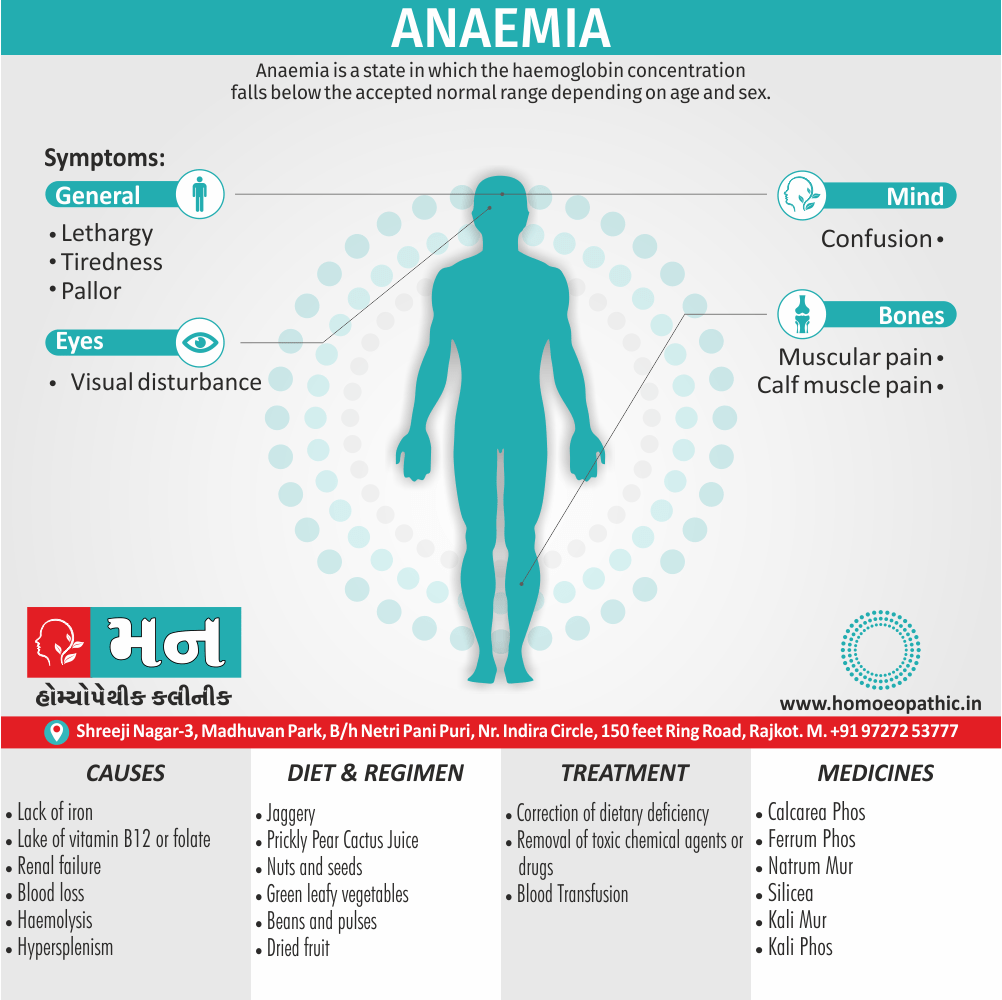
Hematology in Sickle Cell Anemia
- Anemia – moderately severe
- WBC – slightly elevated
- Platelets – elevated
- Peripheral smear – Anisopoikilocytosis There are sickle cells, target cells and ovalocytosis. Also polychromatophilia with few stippled RBCs. [2]
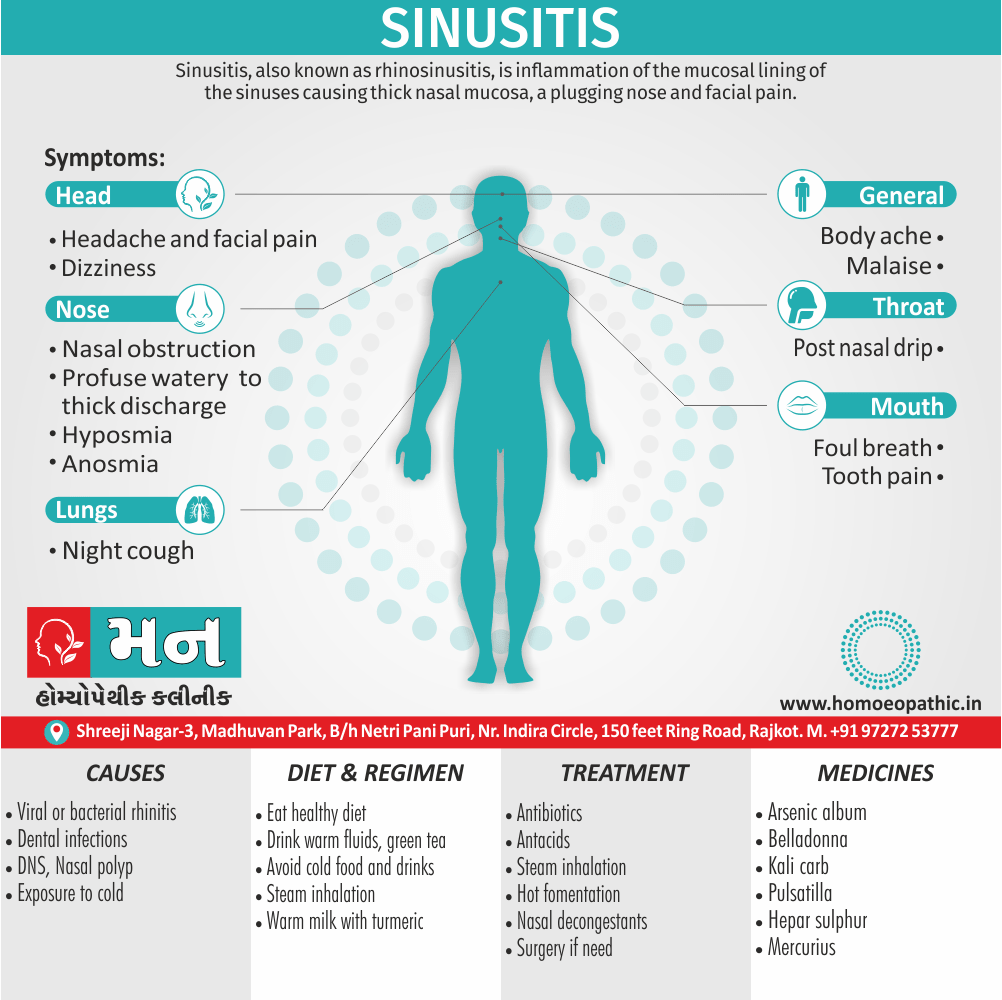
Treatment of Sickle cell Disease
Between crises – Patient should be given folic acid regularly, and infection treated early with antibiotics.
Hydroxyurea helps by –
- Reducing incidence of sickling crises.
- Increase in HbF levels in RBCs which can carry more O2 and reduce tissue hypoxia.
- Lowering of blood viscosity thereby reducing occurrence of veno-occlusive crises [2]
- During crises – Rest, analgesics, hydration, correction of acidosis, plasma volume expander and oxygen.
- Blood transfusions – if PCV fails dangerously, cerebrovascular symptoms in early childhood, recurrent pulmonary thrombotic episodes, and to suppress the sickling process, e.g. to permit major surgery, during pregnancy or to ‘break’ a cycle of painful crises.
- Further management – Bone marrow transplantation offers opportunity for cure.
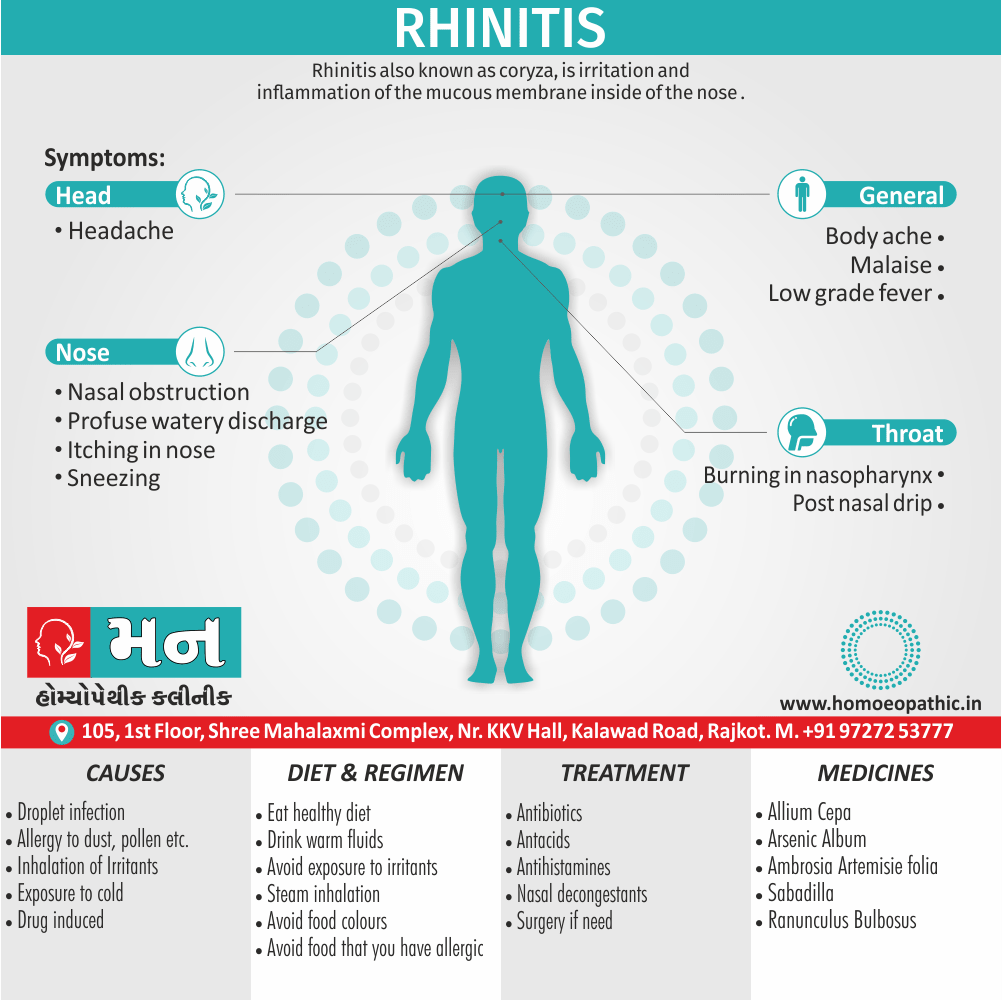
Complications of Sickle cell Disease
- Extreme hypoxia vaso-occlusive syndromes [2]
- Tissue infarction, or sequestration of sickled RBCs in various organs.
- Dehydration
- Exposure to low temperatures
- Hand-foot syndrome
- cerebral or pulmonary infarction
- Parvovirus B19 infection
- Splenic enlargement
- Profound hypoxemia
- Proliferative retinopathy due to retinal Ven occlusion. [2]
Homeopathic Treatment of Sickle cell Disease
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
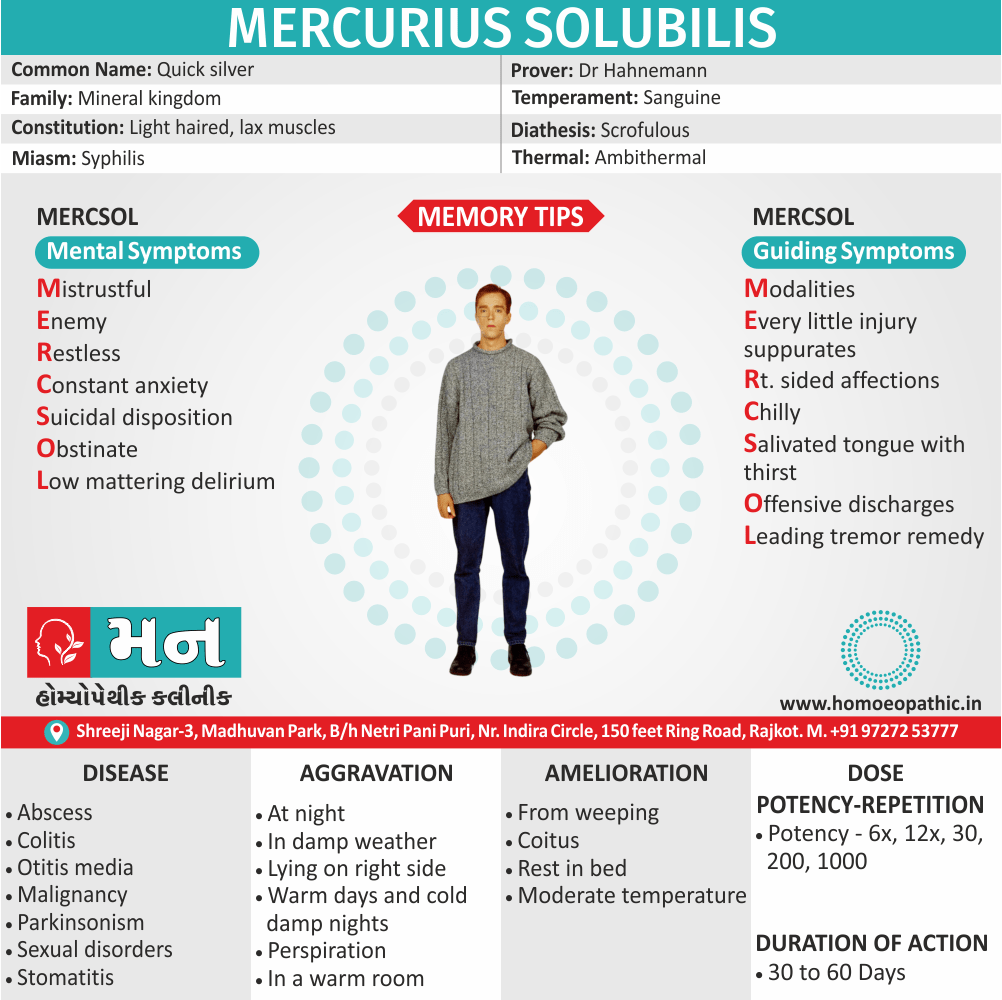
Homeopathic Medicines for Sickle cell Disease:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Medicines:
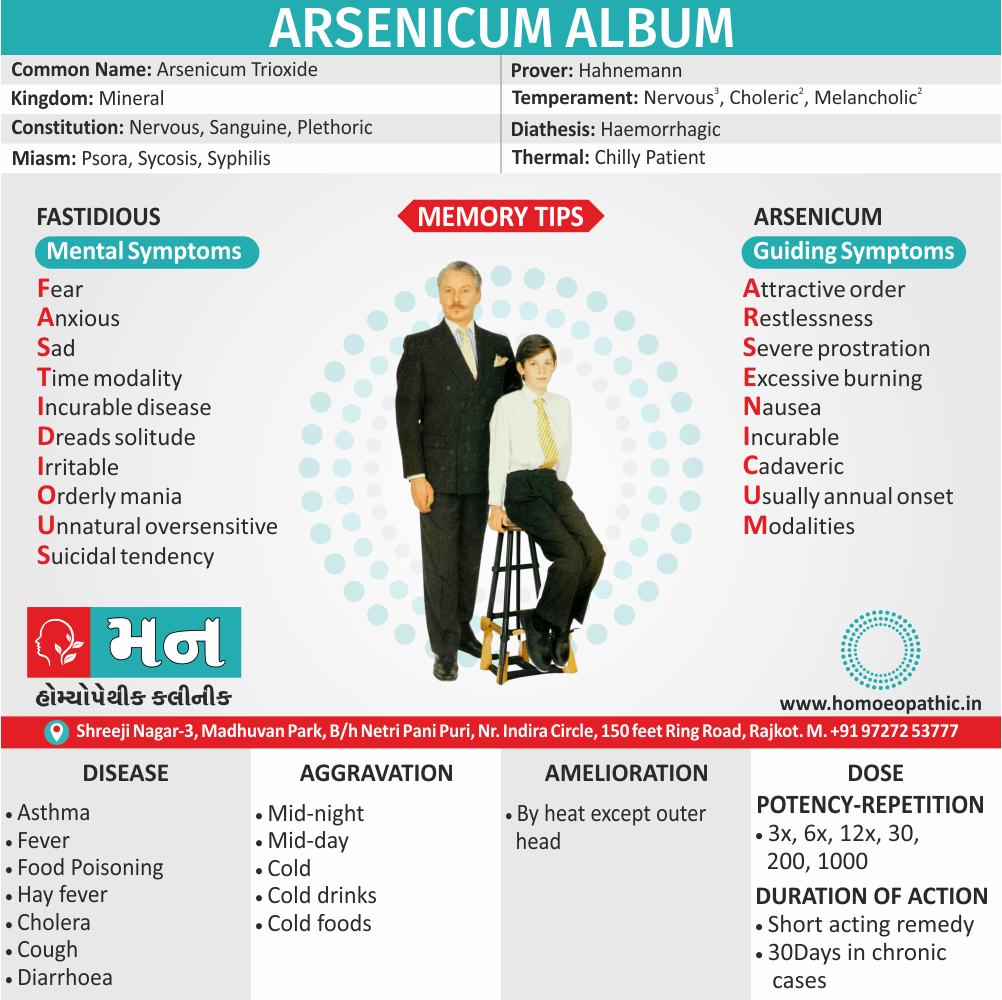
Alteris Ferinosa
- Aletris Farinosa is the best natural Homeopathic medicine for women suffering from Anemia with extreme weakness and fatigue.
- There is a marked weariness and tiredness all day in such patients.
- The energy level seems to markedly reduced and the body feels powerless.
- Frequent episodes of faintness and vertigo are common and even the face appears very pale.
- Anemia in women due to repeated abortions best treat with Homeopathic remedy Aletris Farinosa.
- Vaginal discharge due to Anemia can also correct with this Homeopathic medicine.
- Aletris Farinosa is also the ideal Homeopathic mode of treatment for women with Anemia due to abundant bleeding during periods [1]
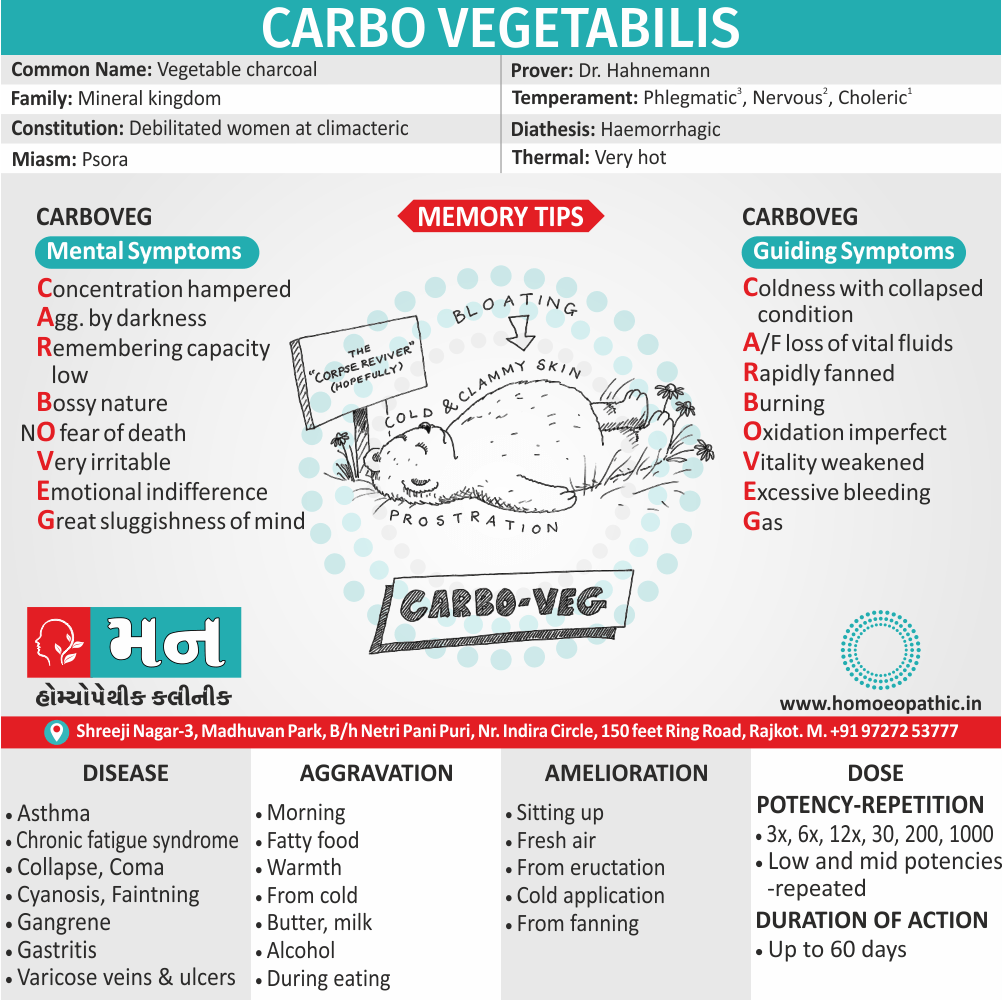
China
- Sickle cell Disease due to extreme blood loss best treated with natural Homeopathic medicine China.
- The bleeding can the result of a traumatic injury, excessive bleeding in periods or bleeding from any part of body like throat, bowels, nose, etc.
- The person exhausted and even fainting spells occur due to extreme anemic conditions consequent to blood loss. Episodes of vertigo with marked weakness also experienced.
- The body feels cold and pallor mark.
- The face especially appears pale with sunken features.
- Homeopathic medicine China acts both as a hemorrhage controller as well as enhances the amount of blood after the bleeding episodes.
Ferrum Phos
- Ferrum Phos is the most frequently used natural Homeopathic medicine to increase the hemoglobin level.
- It can safely used among people of all age groups.
- Even during Anemia in pregnancy, Ferrum Phos is a safe Homeopathic remedy though the dosage is to properly handled by the physician during pregnancy.
- The skin appears pale in persons needing Ferrum Phos and they also experience palpitation of heart and weakness.
- The pulse rate quicken. Vertigo and headache also appear as symptoms.
- Ferrum Phos is also the best Homeopathic remedy for controlling sweat in anemic patients especially at night.
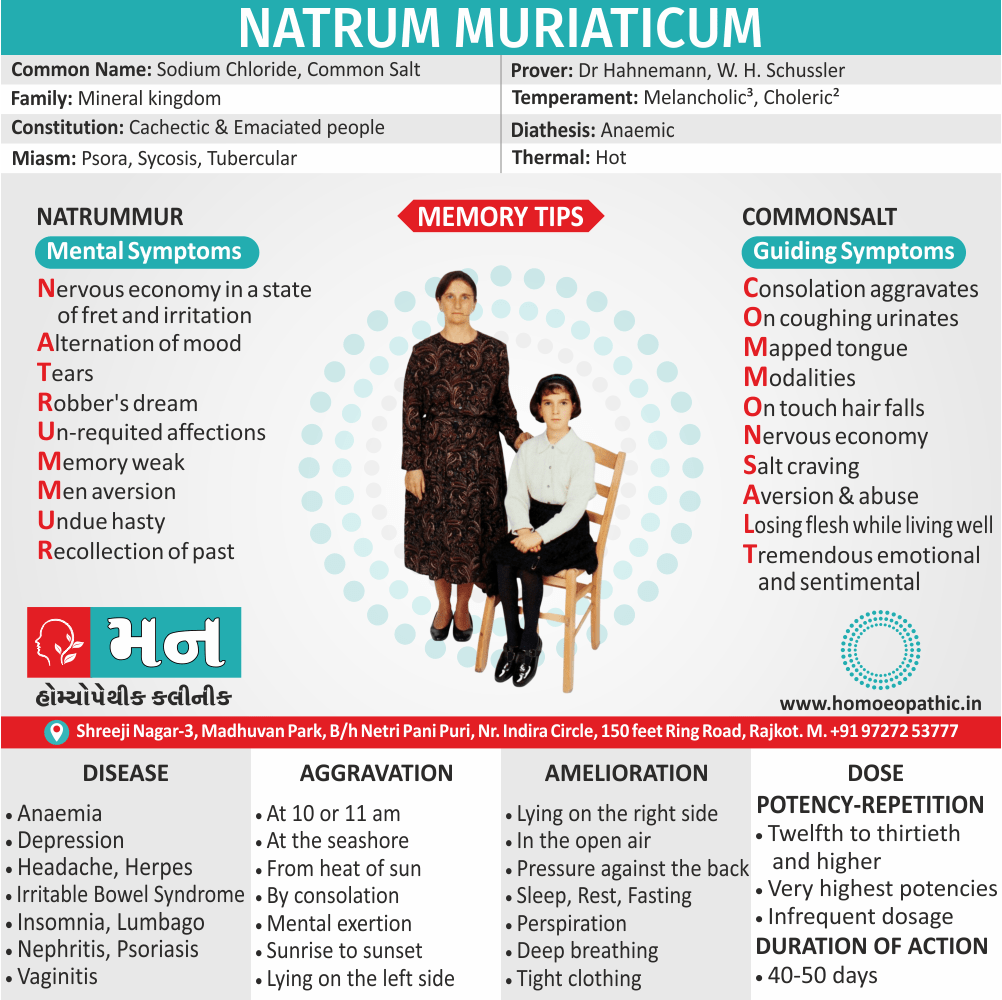
Natrum Mur
- Natural Homeopathic medicine Natrum Mur acts very efficiently to control weight loss as a result of Anemia.
- The person appears very lean and emaciated with loss of flesh.
- The headache due to Sickle cell Disease is also best treated with Natrum Mur. The headache is mainly bursting in character.
- Nausea and vomiting may accompany the pain in head.
- Natrum Mur is also the Homeopathic cure when anemic patients experience palpitations.
- Natrum Mur has a great ability to control palpitations due to decreased blood.
- Anemia due to longstanding grief is also best treated with Homeopathic remedy Natrum Mur.
- There is also a marked desire for extra salt in persons needing Natrum Mur to cure Anemia.[1]
Diet & Regimen of Sickle cell Disease
- Don’t drink a lot of alcohol and smoke.
- Exercise regularly but not so much that you become really tired. When you exercise, drink lots of fluids.
- Drink at least eight 12-ounce glasses of water a day during warm weather.
- Reduce or avoid stress. Talk to your doctor if you’re depressed or have problems with your family or job.
- Treat any infection as soon as it occurs
- Wear warm clothes outside in cold weather and inside in air-conditioned rooms during hot weather. Also, don’t swim in cold water.
- Try to be positive about yourself.
- Tell your doctor if you think you might have a sleep problem, such as snoring or if you sometimes stop breathing during sleep
- If you have another medical condition, like diabetes, get treatment and control the condition.
- If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, get early prenatal care.
- Only travel in commercial airplanes. If you have to travel in an unpressurized aircraft, talk to your doctor about extra precautions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Sickle cell Disease?
Genetic Sickle Cell Disorders or Sickle cell Disease are characterized by presence of HbS sickle hemoglobin which give sickle shape to RBCs in a state of reduced oxygen tension.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Sickle cell Disease?
- Alteris Ferinosa
- China
- Ferrum Phos
- Natrum Mur
What are the main causes of Sickle cell Disease?
Change in the gene that tells the body to make the iron-rich compound in red blood cells called hemoglobin.
What are the symptoms of Sickle cell Disease?
- Delayed growth and development
- Enlargement of spleen after 6 months.
- Leg ulcers
- Hand-foot syndrome
- Infections
- Cardiomegaly
- Hepatomegaly
- Gall stones
- Ocular complications
Reference:
[1] https://www.drhomeo.com/homeopathic-treatment/homeopathic-medicines-anemia/
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sickle_cell_disease
[3] https://www.mayoclinic.org/
Definition:
Definition of Sickle cell Disease
Genetic Sickle Cell Disorders or Sickle cell Disease are characterized by presence of HbS sickle hemoglobin which give sickle shape to RBCs in a state of reduced oxygen tension. [2]
Overview
Epidemiology
Causes
Risk Factors
Pathogenesis
Pathophysiology
Types
Clinical Features
Sign & Symptoms
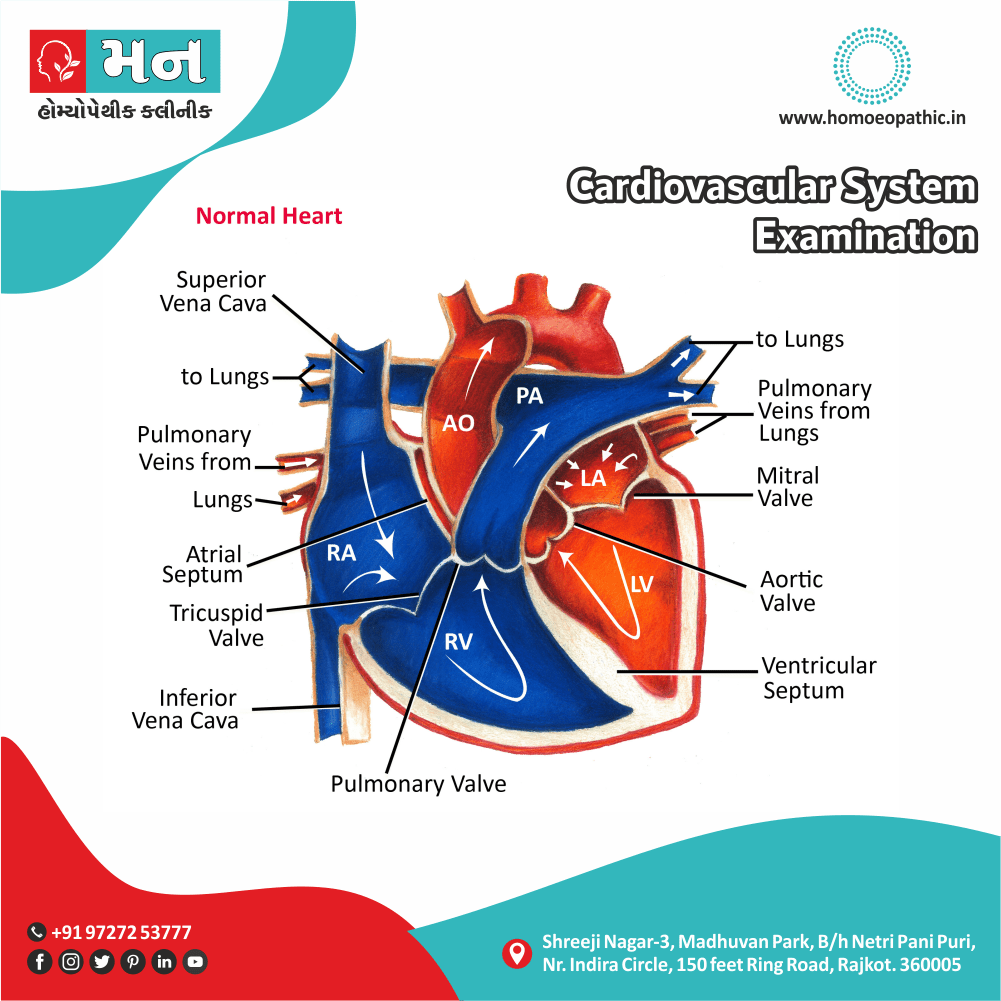
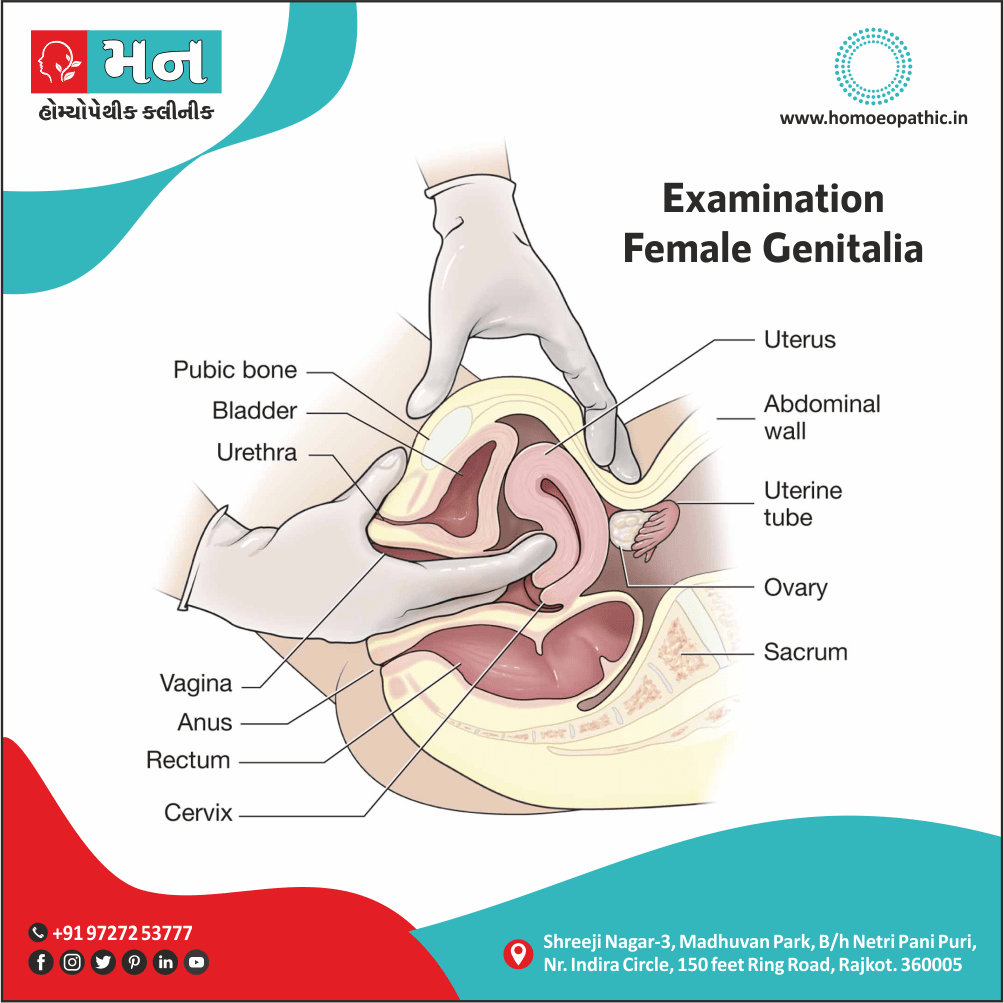
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Complications
Investigations
Treatment
Prevention
Homeopathic Treatment
Diet & Regimen
Do’s and Dont’s
Terminology
References
FAQ
Also Search As
Overview
Overview of Sickle cell Disease
Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years.[2]
Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene that makes hemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each hemoglobin gene.
An attack can be set off by temperature changes, stress, dehydration, and high altitude. A person with a single abnormal copy does not usually have symptoms and is said to have sickle cell trait.
Such people are also referred to as carriers. Diagnosis is by a blood test, and some countries test all babies at birth for the disease. Diagnosis is also possible during pregnancy.
The care of people with sickle cell disease may include infection prevention with vaccination and antibiotics, high fluid intake, folic acid supplementation, and pain medication. Other measures may include blood transfusion and the medication hydroxycarbamide (hydroxyurea). A small percentage of people can be cured by a transplant of bone marrow cells.
Epidemiology
Indian epidemiology then other
Causes
Causes of Sickle cell Disease
- Sickle cell anemia cause by a change in the gene that tells the body to make the iron-rich compound in red blood cells called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin enables red blood cells to carry oxygen from the lungs throughout the body. The hemoglobin associated with sickle cell anemia causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky and misshapen.
- For a child to affect, both mother and father must carry one copy of the sickle cell gene — also known as sickle cell trait — and pass both copies of the altered form to the child.
- If only one parent passes the sickle cell gene to the child, that child will have the sickle cell trait. With one typical hemoglobin gene and one altered form of the gene, people with the sickle cell trait make both typical hemoglobin and sickle cell hemoglobin.
- Their blood might contain some sickle cells, but they generally don’t have symptoms. They’re carriers of the disease, however, which means they can pass the gene to their children.[3]
Risk Factors
Risk factors are things that make you more likely to develop a disease in the first place.
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis refers to the development of a disease. It’s the story of how a disease gets started and progresses.
This is the entire journey of a disease, encompassing the cause but going beyond it.
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology of Sickle cell Disease
Clinical problems in sickle cell disease relate to veno-occlusion caused by polymerization of deoxygenated hemoglobin S.
This results in the pathognomonic change in the shape of erythrocytes to the sickle shape that stiffen the RBC membrane, increase viscosity and cause dehydration due to potassium leakage and calcium influx.
The most common clinical feature is the painful vaso-occlusive crisis resulting from blockage of small vessels.
However, large vessels disease also occurs, resulting in – Thrombotic cerebrovascular accidents, acute sickle chest syndrome, and placental infarction. [2]
Types
Classification of Sickle cell Disease
- Sickle cell trait – Less than 50% HbS per cell is usually not associated with clinical abnormality. Infarction of spleen may occur during anesthesia, and hematuria is not uncommon.
- Sickle-cell anemia – Anemia from about third month of life, since HbS is more than 70% in red cells. 3. Sickle cell disease – This refers to all disease states in which at least one gene is of HbS.
Clinical Features
Tab Content
Sign & Symptoms
Sign & Symptoms of Sickle cell Disease
- Delayed growth and development
- Enlargement of spleen after 6 months. Later at 5-6 yrs of age, reduction in size due to multiple infarcts from veno-occlusion of branches of splenic artery. In adults, spleen may be totally replaced by fibrous tissue.
- Leg ulcers – Shallow ulcers near ankle due vascular stasis and often after trauma.
- Hand-foot syndrome – Painful swelling of hands and feet. Vaso-occlusive crisis and dactylitis leads to destruction of metacarpals, metatarsals and phalanges. [2]
- CNS – Brain syndrome in a few children, occlusion of cerebral vessels leads to stroke.
- Infections – Pneumococcal pneumonia, meningitis due to hyposplenism, osteomyelitis due to salmonella from repeated bone infarcts.
- Cardiomegaly due to hyperdynamic circulation as a result of chronic anemia.
- Hepatomegaly
- Gall stones – Pigment gall stones increase in frequency from childhood to adult.
- Ocular complications – Occlusion of retinal vessels causes retinal changes such as ‘salmon patches’, intraretinal hemorrhages, A-V anastomosis.
- Abdominal pain occurs due to infarcts of abdominal viscera due to vaso-occlusive crises.
- Priapism – due to stagnation of blood in corpora cavernosa.
- Skeletal changes – In a young child there is widening of the diploe of the skull leading to new bone formation with resultant ‘crew cut appearance’ in X-ray. Bone and joint ischemia leading to aseptic necrosis seen in femoral and humeral head. Unusually susceptibility to osteomyelitis, caused by salmonella.
Clinical Examination
Tab Content
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Sickle cell Disease
Hematology in Sickle Cell Anemia
- Anemia – moderately severe
- WBC – slightly elevated
- Platelets – elevated
- Peripheral smear – Anisopoikilocytosis There are sickle cells, target cells and ovalocytosis. Also polychromatophilia with few stippled RBCs. [2]
Differential Diagnosis
Complications
Complications of Sickle cell Disease
- Extreme hypoxia vaso-occlusive syndromes [2]
- Tissue infarction, or sequestration of sickled RBCs in various organs.
- Dehydration
- Exposure to low temperatures
- Hand-foot syndrome
- cerebral or pulmonary infarction
- Parvovirus B19 infection
- Splenic enlargement
- Profound hypoxemia
- Proliferative retinopathy due to retinal Ven occlusion. [2]
Investigations
Investigation of Sickle cell Disease
- Sickling test – Sickling is induced by adding reducing agent like 2% sodium metabisulphite to blood.
- Hb electrophoresis can be performed on cellulose acetate membrane or starch agarose. HbS is a slow moving Hb as compared to HbA and HbF. In HbS, HbS constitutes 70-90% of total Hb but HbA is nil. This differentiates homozygous (SS) from heterozygous state (SA), since the latter demonstrates two bands of HbS and HbA.
- HbF estimation since HbF is 10-30% in homozygous state and is helpful in assessing course of the disease.
- High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) gives exact amount of HibA, HbS, HbF and HbA2.
- Globin chain analysis may be required to assess the genetic basis of disease and differentiate it from various heterozygote states.
- HbS solubility is based on the fact that sickle Hb is insoluble in deoxygenated state. [2]
Treatment
Treatment of Sickle cell Disease
Between crises – Patient should be given folic acid regularly, and infection treated early with antibiotics.
Hydroxyurea helps by –
- Reducing incidence of sickling crises.
- Increase in HbF levels in RBCs which can carry more O2 and reduce tissue hypoxia.
- Lowering of blood viscosity thereby reducing occurrence of veno-occlusive crises [2]
- During crises – Rest, analgesics, hydration, correction of acidosis, plasma volume expander and oxygen.
- Blood transfusions – if PCV fails dangerously, cerebrovascular symptoms in early childhood, recurrent pulmonary thrombotic episodes, and to suppress the sickling process, e.g. to permit major surgery, during pregnancy or to ‘break’ a cycle of painful crises.
- Further management – Bone marrow transplantation offers opportunity for cure.
Prevention
Tab Content
Homeopathic Treatment
Homeopathic Treatment of Sickle cell Disease
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Sickle cell Disease:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Medicines:
Alteris Ferinosa
- Aletris Farinosa is the best natural Homeopathic medicine for women suffering from Anemia with extreme weakness and fatigue.
- There is a marked weariness and tiredness all day in such patients.
- The energy level seems to markedly reduced and the body feels powerless.
- Frequent episodes of faintness and vertigo are common and even the face appears very pale.
- Anemia in women due to repeated abortions best treat with Homeopathic remedy Aletris Farinosa.
- Vaginal discharge due to Anemia can also correct with this Homeopathic medicine.
- Aletris Farinosa is also the ideal Homeopathic mode of treatment for women with Anemia due to abundant bleeding during periods [1]
China
- Sickle cell Disease due to extreme blood loss best treated with natural Homeopathic medicine China.
- The bleeding can the result of a traumatic injury, excessive bleeding in periods or bleeding from any part of body like throat, bowels, nose, etc.
- The person exhausted and even fainting spells occur due to extreme anemic conditions consequent to blood loss. Episodes of vertigo with marked weakness also experienced.
- The body feels cold and pallor mark.
- The face especially appears pale with sunken features.
- Homeopathic medicine China acts both as a hemorrhage controller as well as enhances the amount of blood after the bleeding episodes.
Ferrum Phos
- Ferrum Phos is the most frequently used natural Homeopathic medicine to increase the hemoglobin level.
- It can safely used among people of all age groups.
- Even during Anemia in pregnancy, Ferrum Phos is a safe Homeopathic remedy though the dosage is to properly handled by the physician during pregnancy.
- The skin appears pale in persons needing Ferrum Phos and they also experience palpitation of heart and weakness.
- The pulse rate quicken. Vertigo and headache also appear as symptoms.
- Ferrum Phos is also the best Homeopathic remedy for controlling sweat in anemic patients especially at night.
Natrum Mur
- Natural Homeopathic medicine Natrum Mur acts very efficiently to control weight loss as a result of Anemia.
- The person appears very lean and emaciated with loss of flesh.
- The headache due to Sickle cell Disease is also best treated with Natrum Mur. The headache is mainly bursting in character.
- Nausea and vomiting may accompany the pain in head.
- Natrum Mur is also the Homeopathic cure when anemic patients experience palpitations.
- Natrum Mur has a great ability to control palpitations due to decreased blood.
- Anemia due to longstanding grief is also best treated with Homeopathic remedy Natrum Mur.
- There is also a marked desire for extra salt in persons needing Natrum Mur to cure Anemia.[1]
Diet & Regimen
Diet & Regimen of Sickle cell Disease
- Don’t drink a lot of alcohol and smoke.
- Exercise regularly but not so much that you become really tired. When you exercise, drink lots of fluids.
- Drink at least eight 12-ounce glasses of water a day during warm weather.
- Reduce or avoid stress. Talk to your doctor if you’re depressed or have problems with your family or job.
- Treat any infection as soon as it occurs
- Wear warm clothes outside in cold weather and inside in air-conditioned rooms during hot weather. Also, don’t swim in cold water.
- Try to be positive about yourself.
- Tell your doctor if you think you might have a sleep problem, such as snoring or if you sometimes stop breathing during sleep
- If you have another medical condition, like diabetes, get treatment and control the condition.
- If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, get early prenatal care.
- Only travel in commercial airplanes. If you have to travel in an unpressurized aircraft, talk to your doctor about extra precautions.
Do’s and Dont’s
Tab Content
Terminology
Tab Content
References
Reference:
[1] https://www.drhomeo.com/homeopathic-treatment/homeopathic-medicines-anemia/
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sickle_cell_disease
[3] https://www.mayoclinic.org/
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Sickle cell Disease?
Genetic Sickle Cell Disorders or Sickle cell Disease are characterized by presence of HbS sickle hemoglobin which give sickle shape to RBCs in a state of reduced oxygen tension.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Sickle cell Disease?
- Alteris Ferinosa
- China
- Ferrum Phos
- Natrum Mur
What are the main causes of Sickle cell Disease?
Change in the gene that tells the body to make the iron-rich compound in red blood cells called hemoglobin.
What are the symptoms of Sickle cell Disease?
- Delayed growth and development
- Enlargement of spleen after 6 months.
- Leg ulcers
- Hand-foot syndrome
- Infections
- Cardiomegaly
- Hepatomegaly
- Gall stones
- Ocular complications
Also Search As
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
XYZ
XXX
XYZ
XXX
XYZ
XXX
How can I find reputable homeopathy clinics or homeopathic doctors in my area?
You can found Homeopathic Clinic For XXXX by searching for
Specific city Examples are
You can also search for near you Examples are