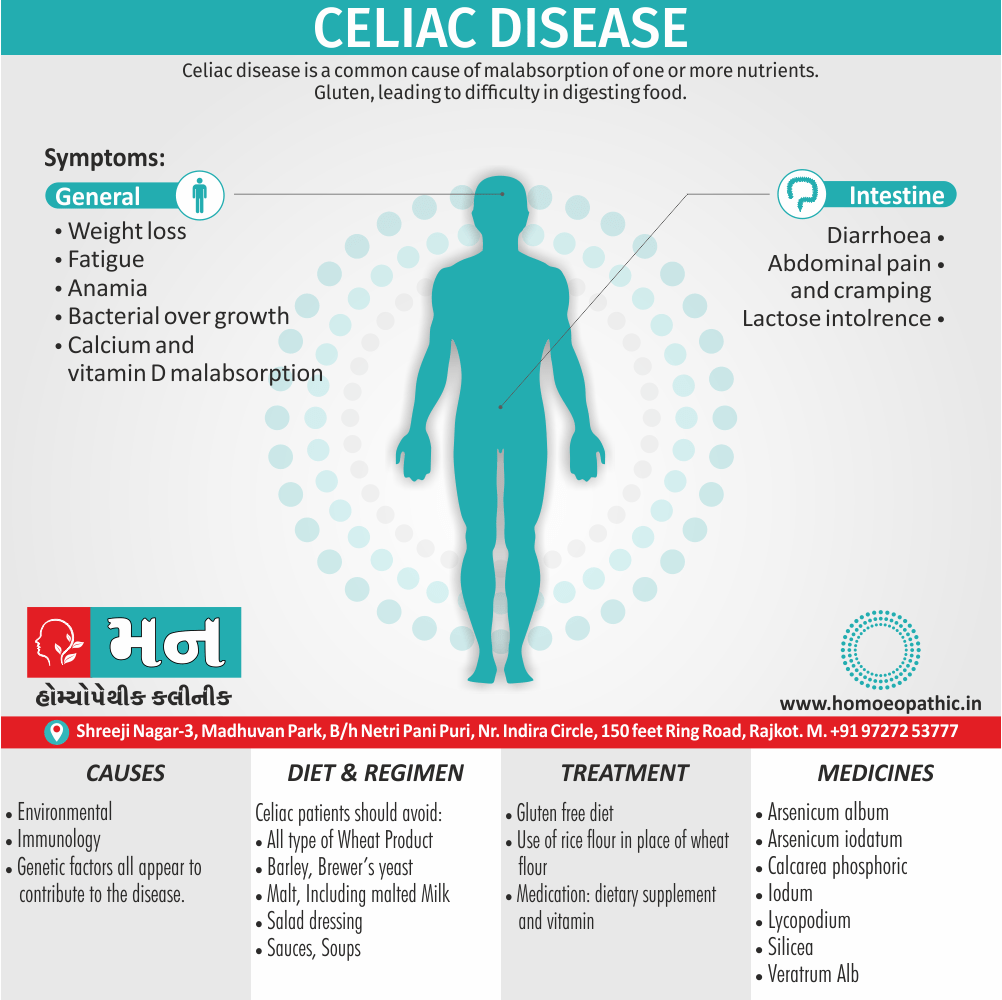
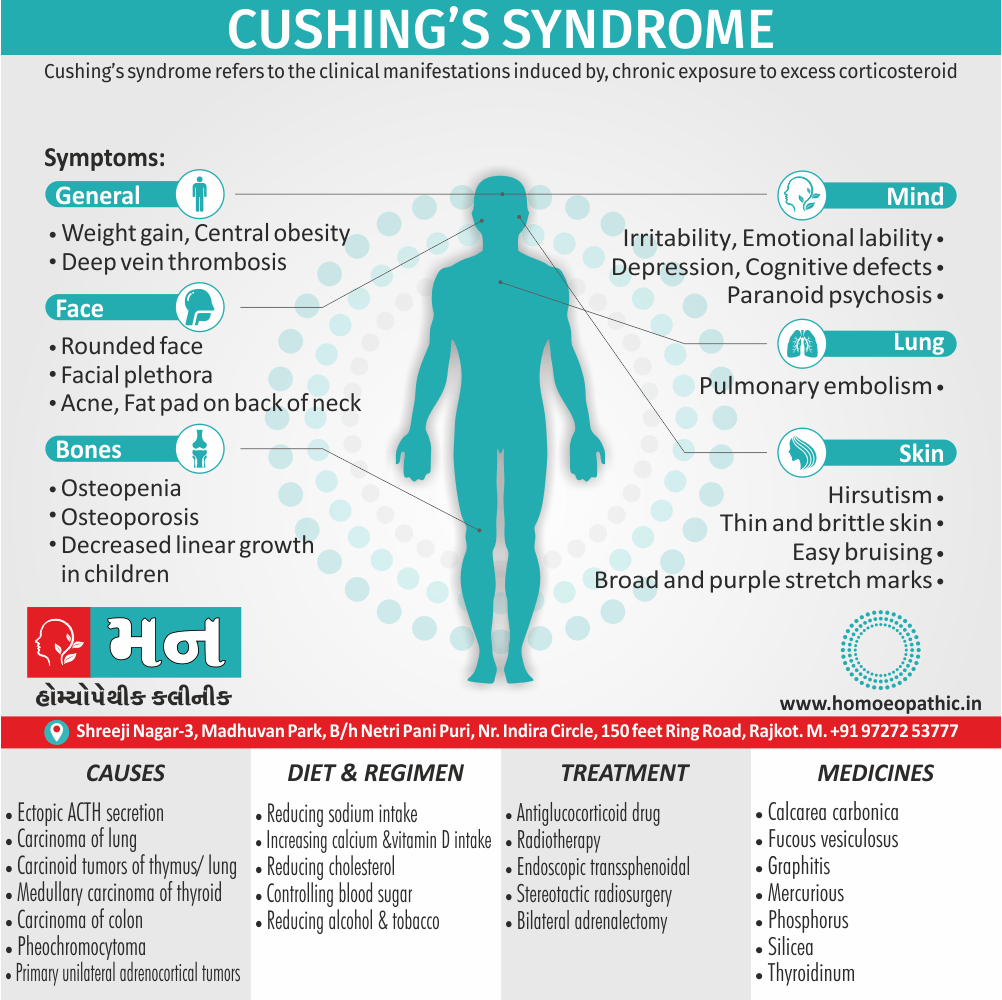
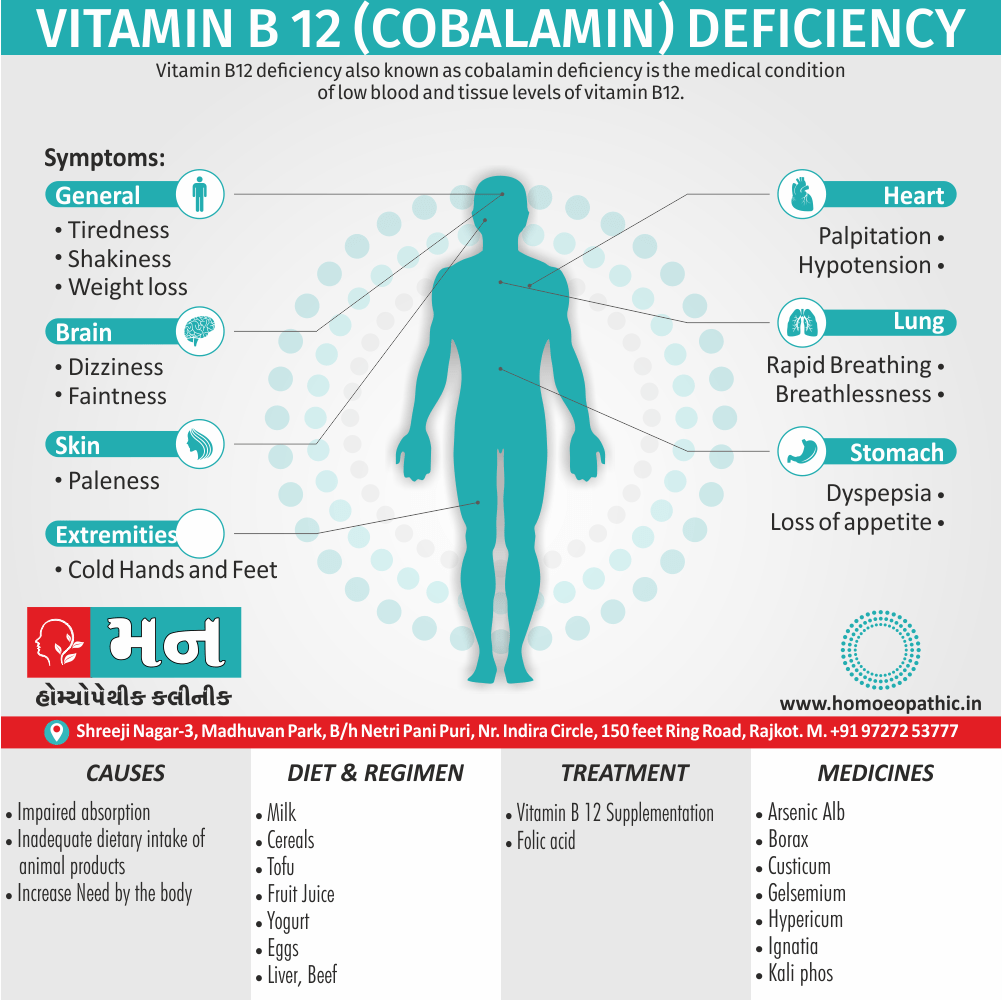
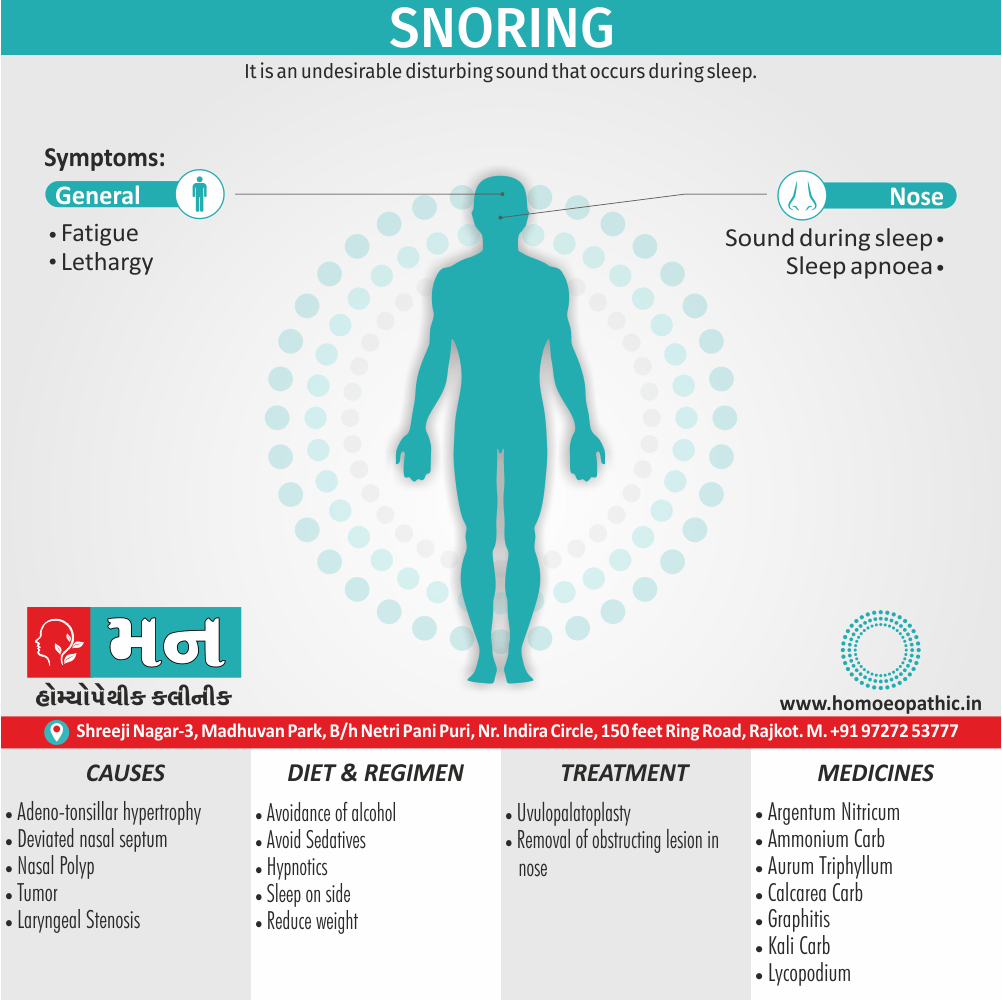
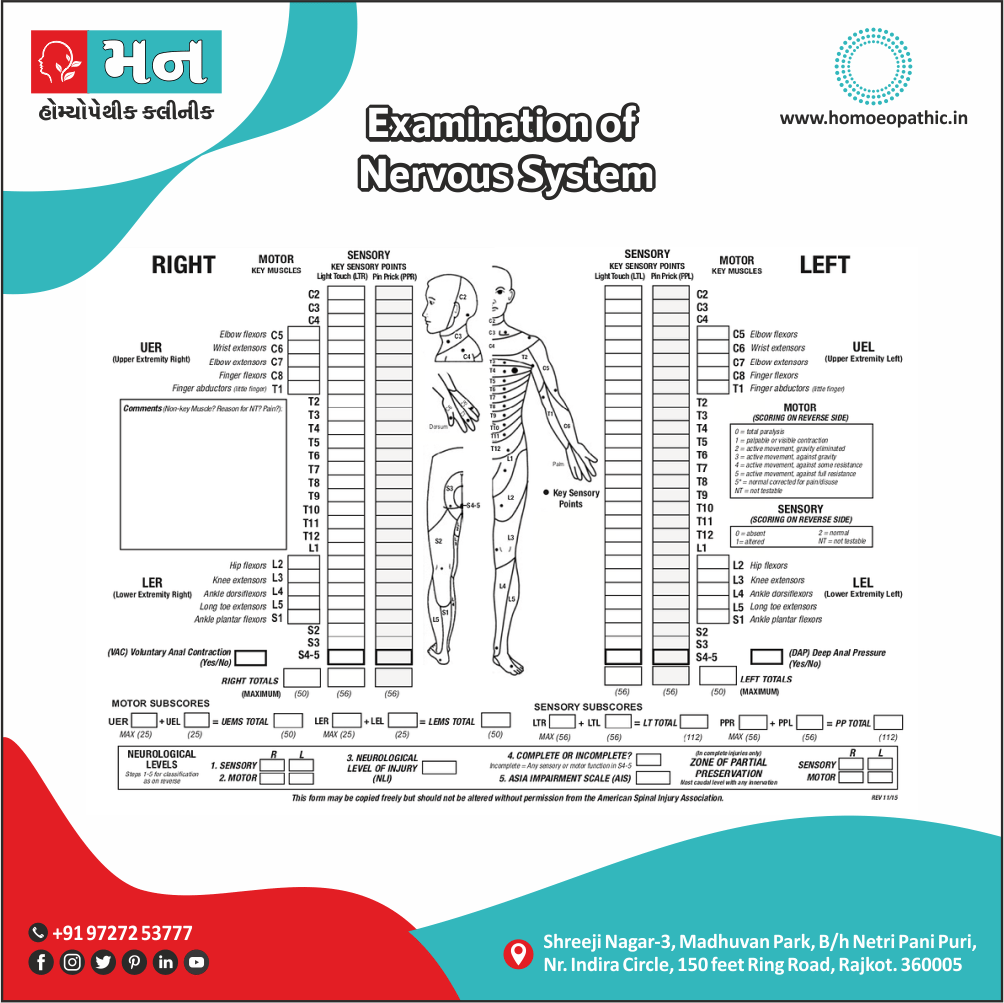
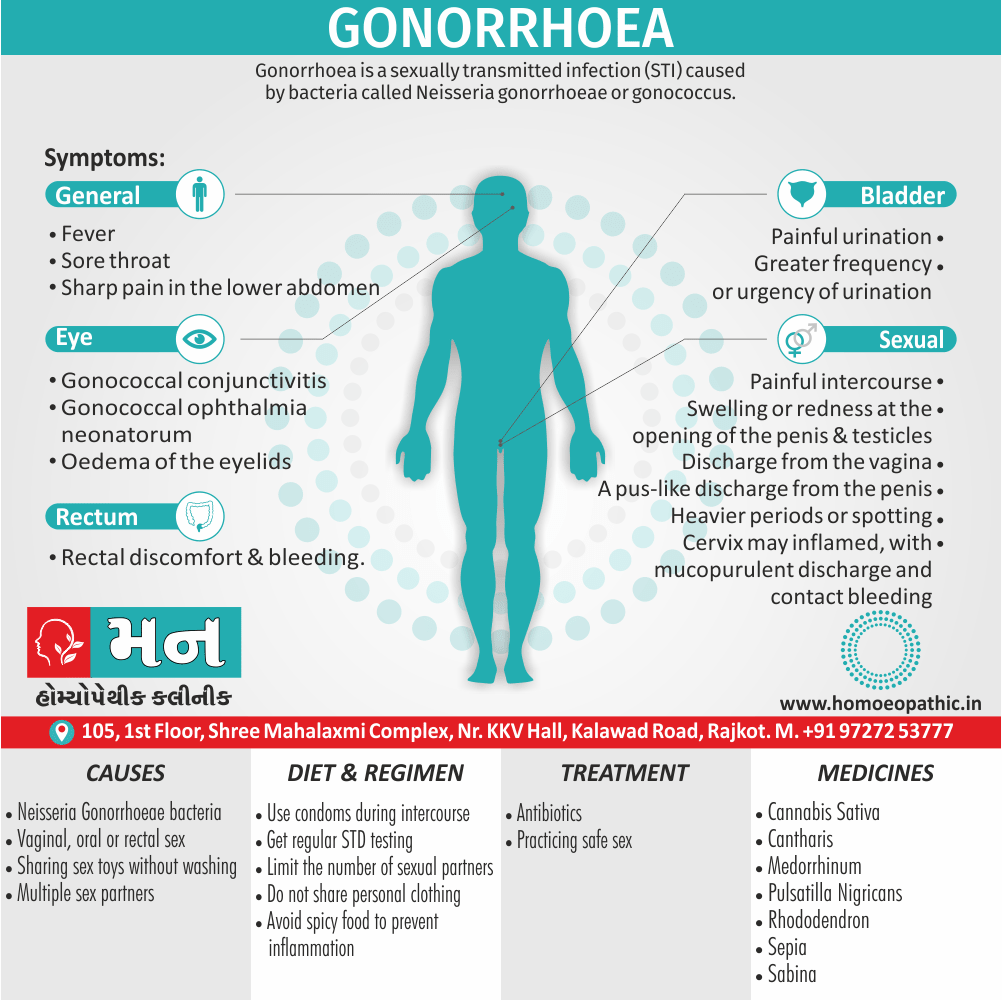
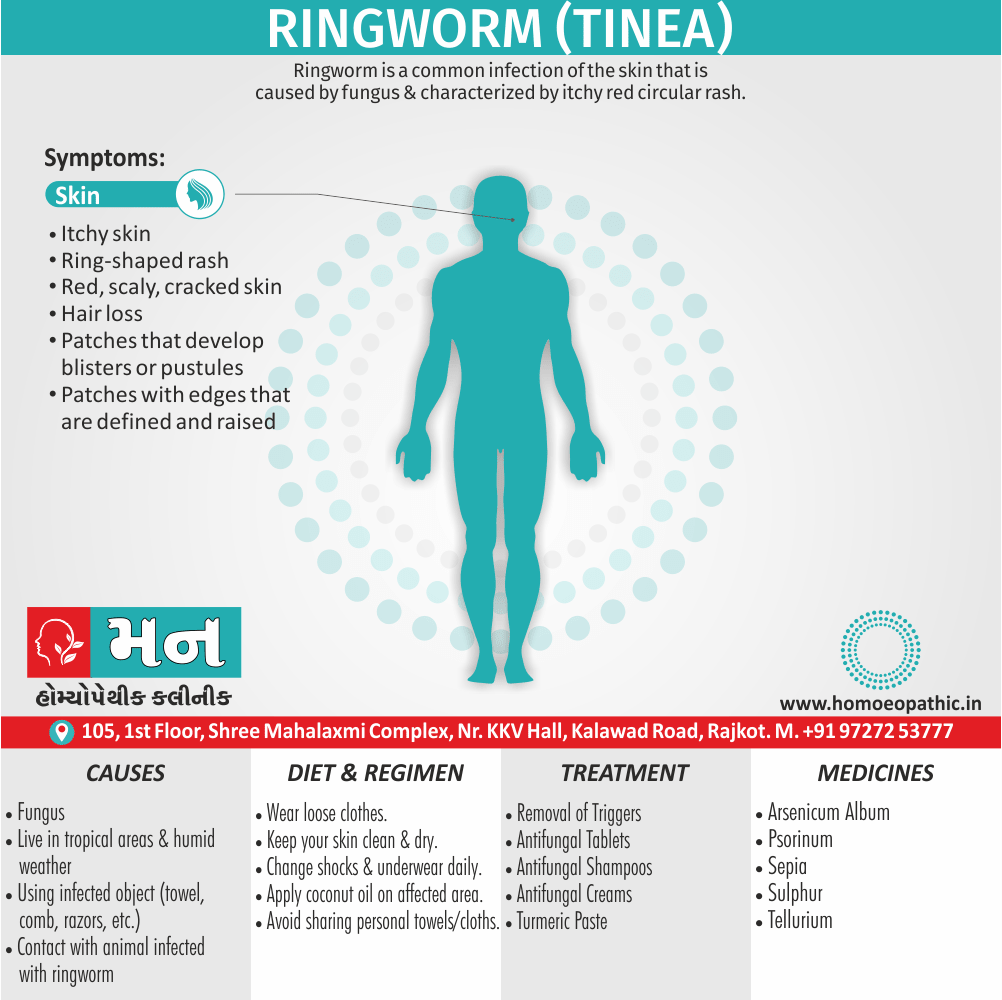
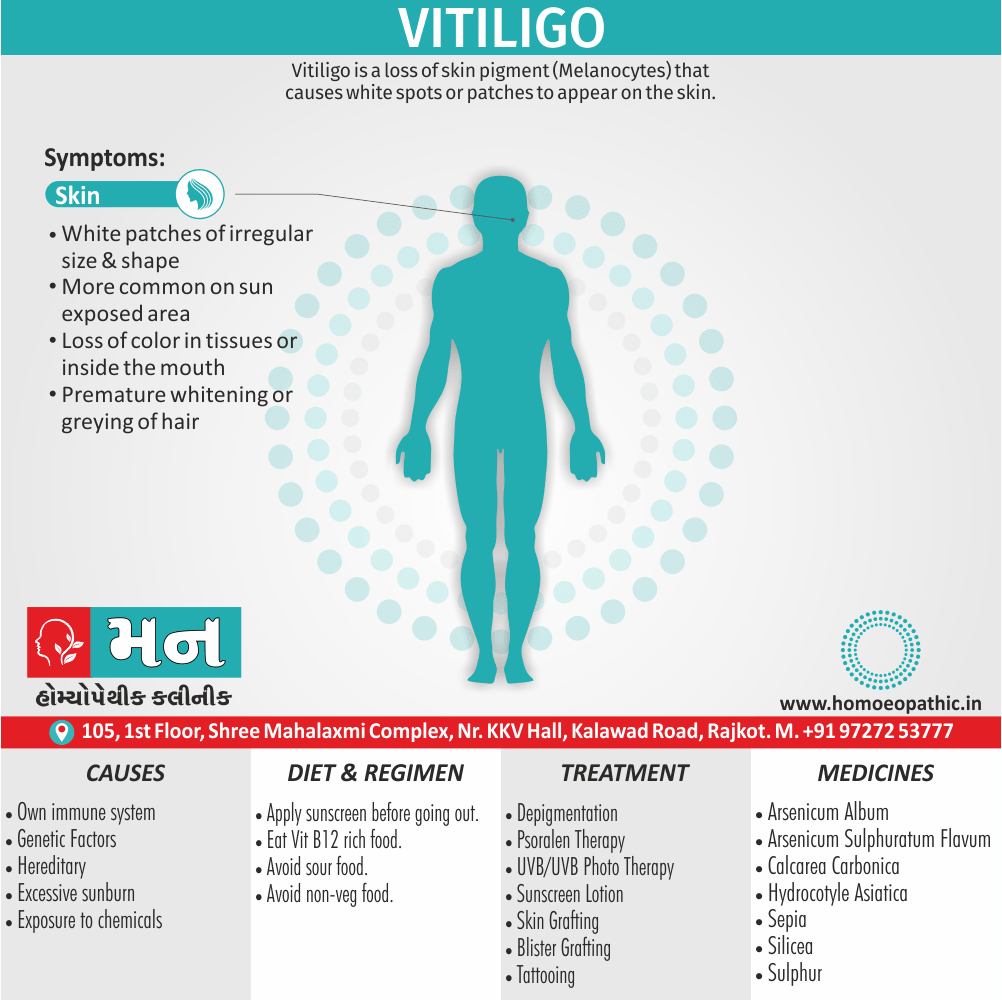
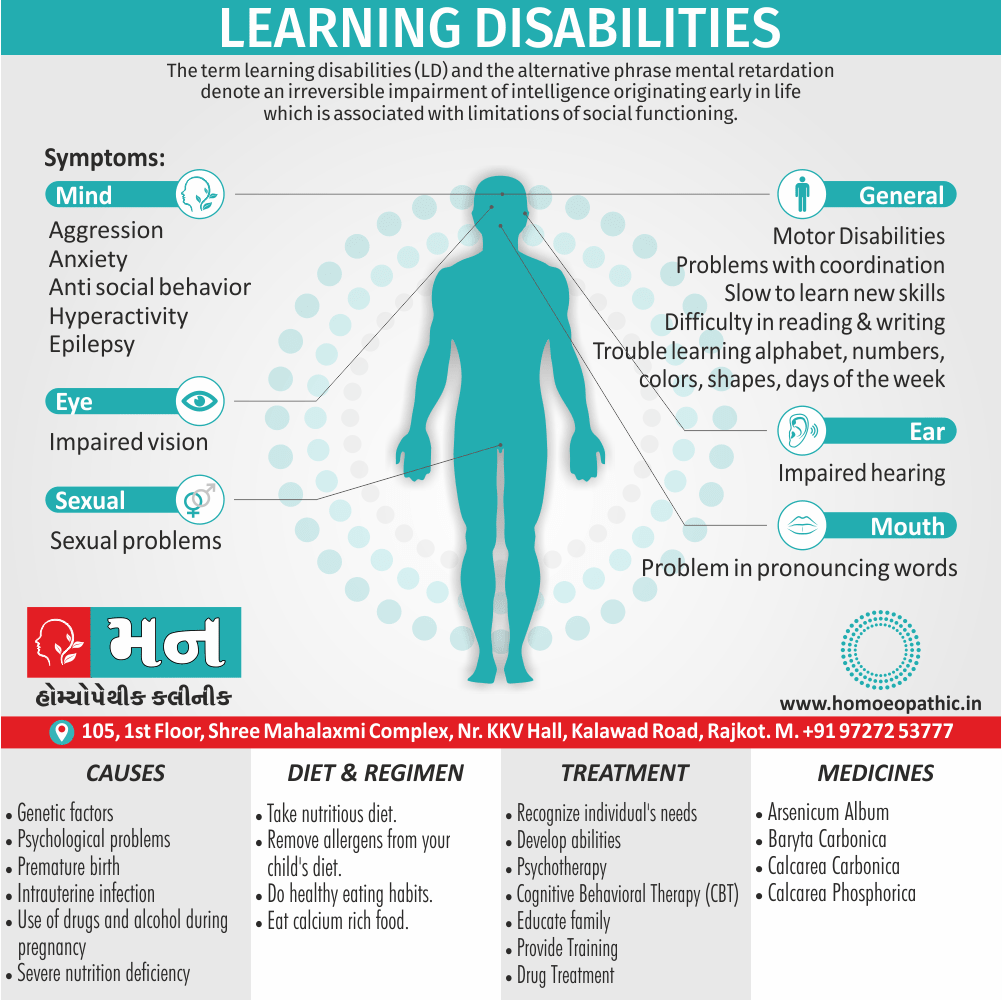
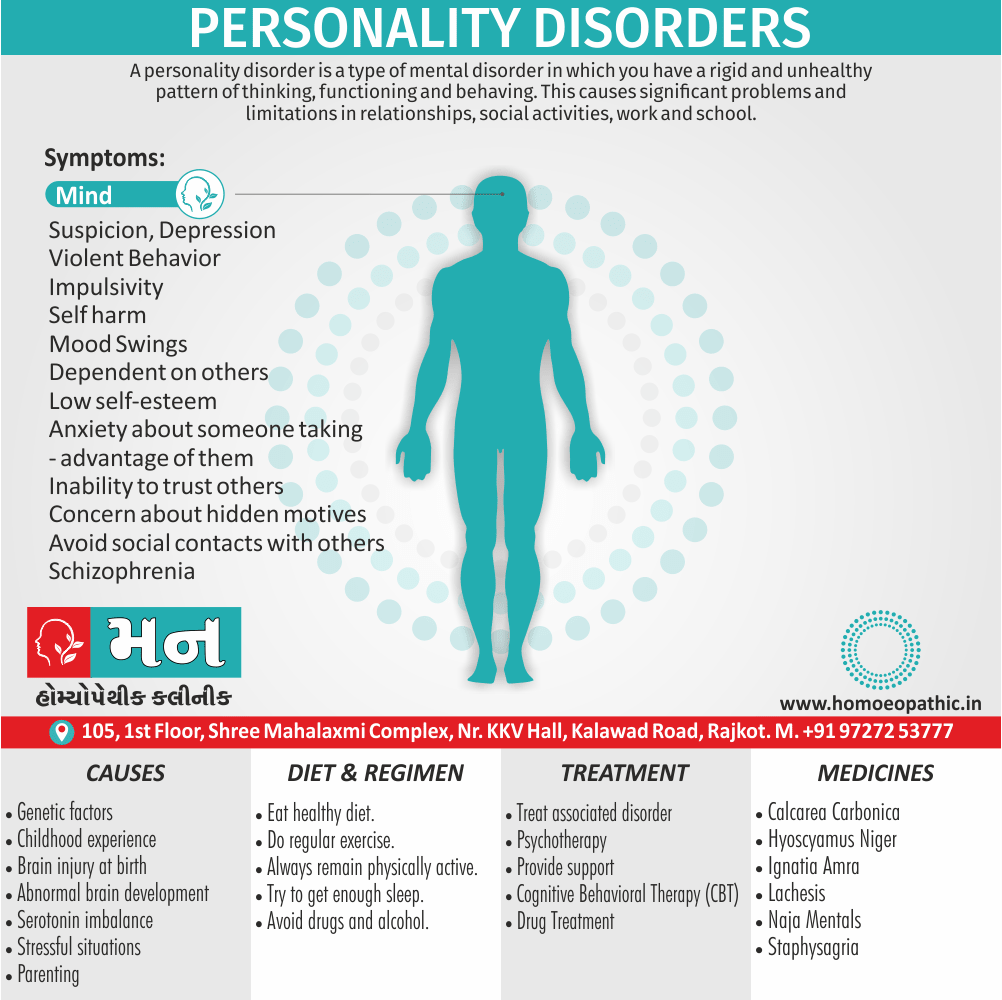
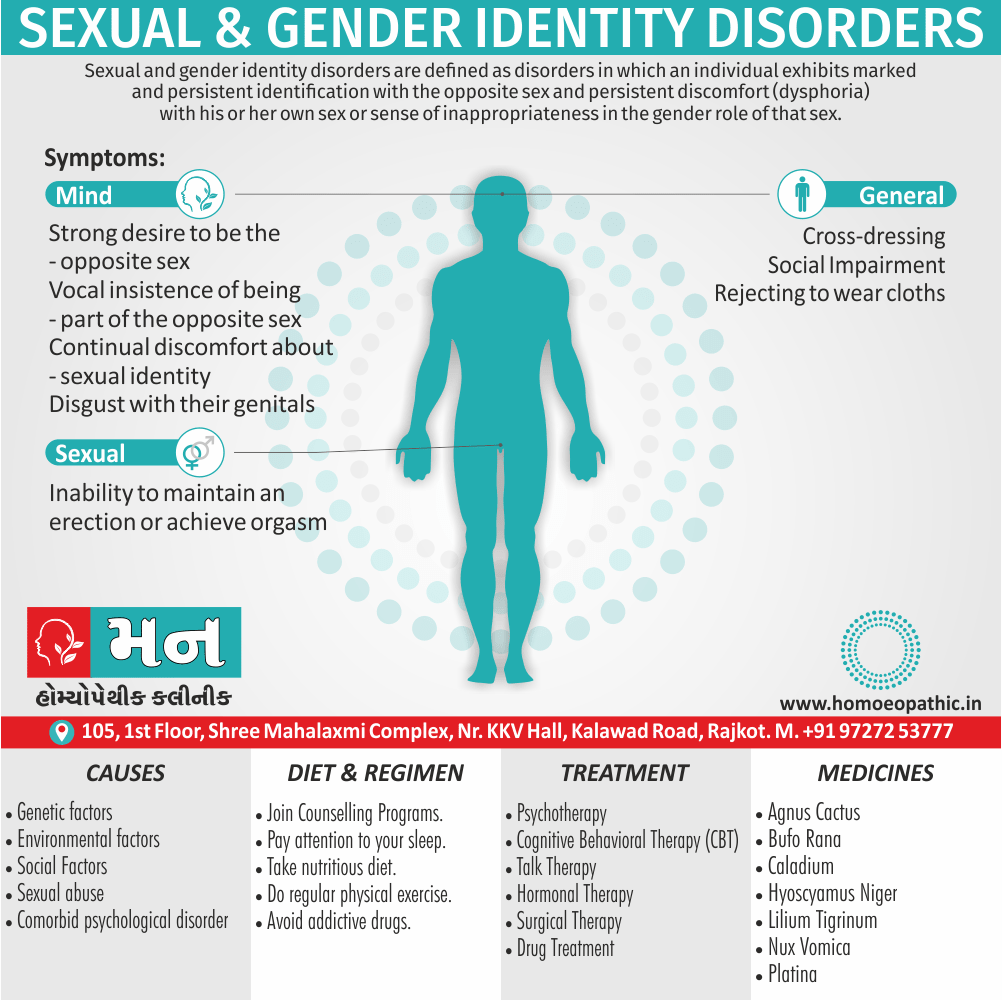
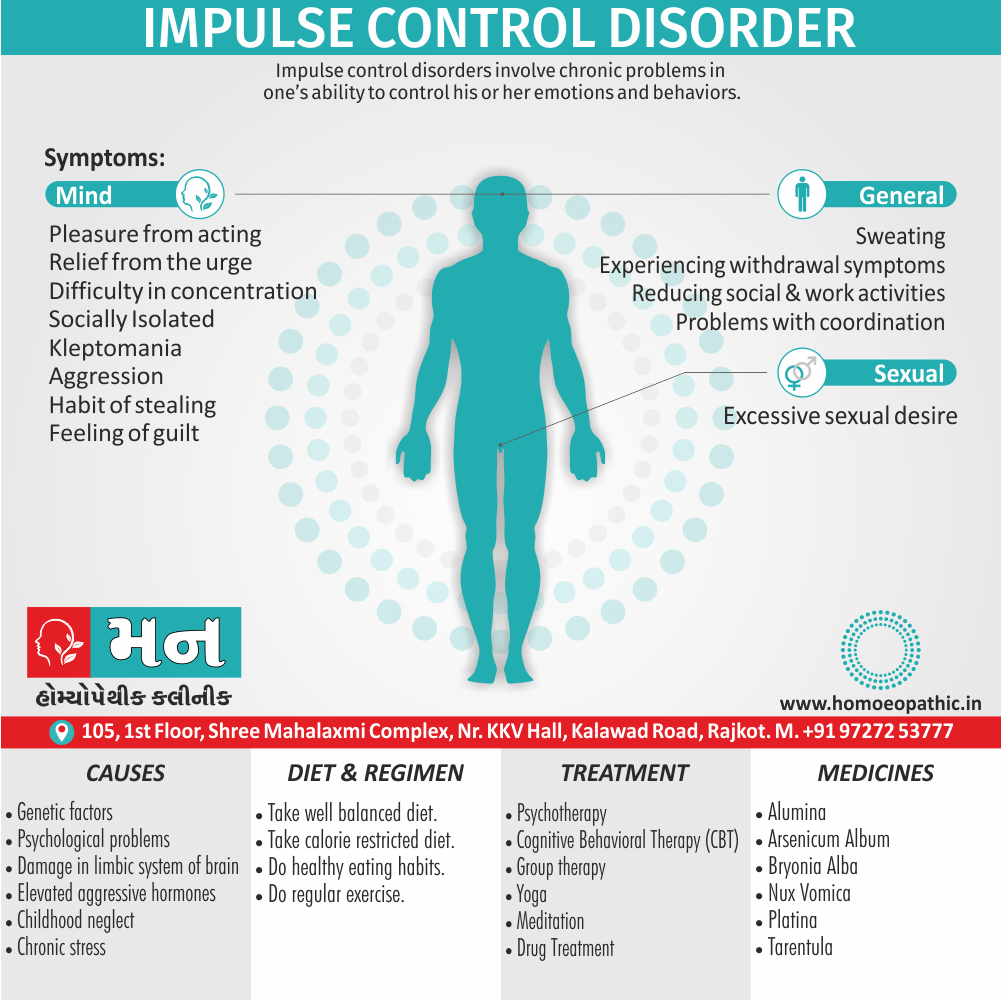
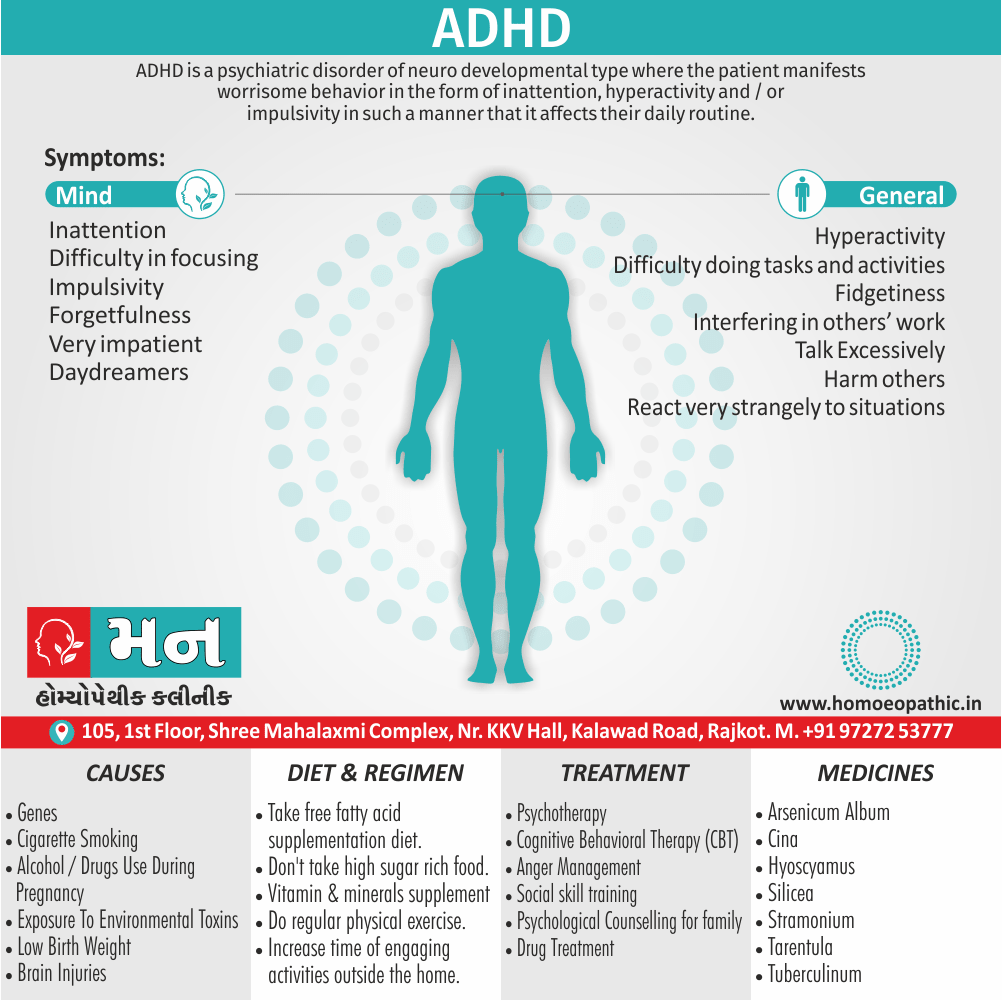
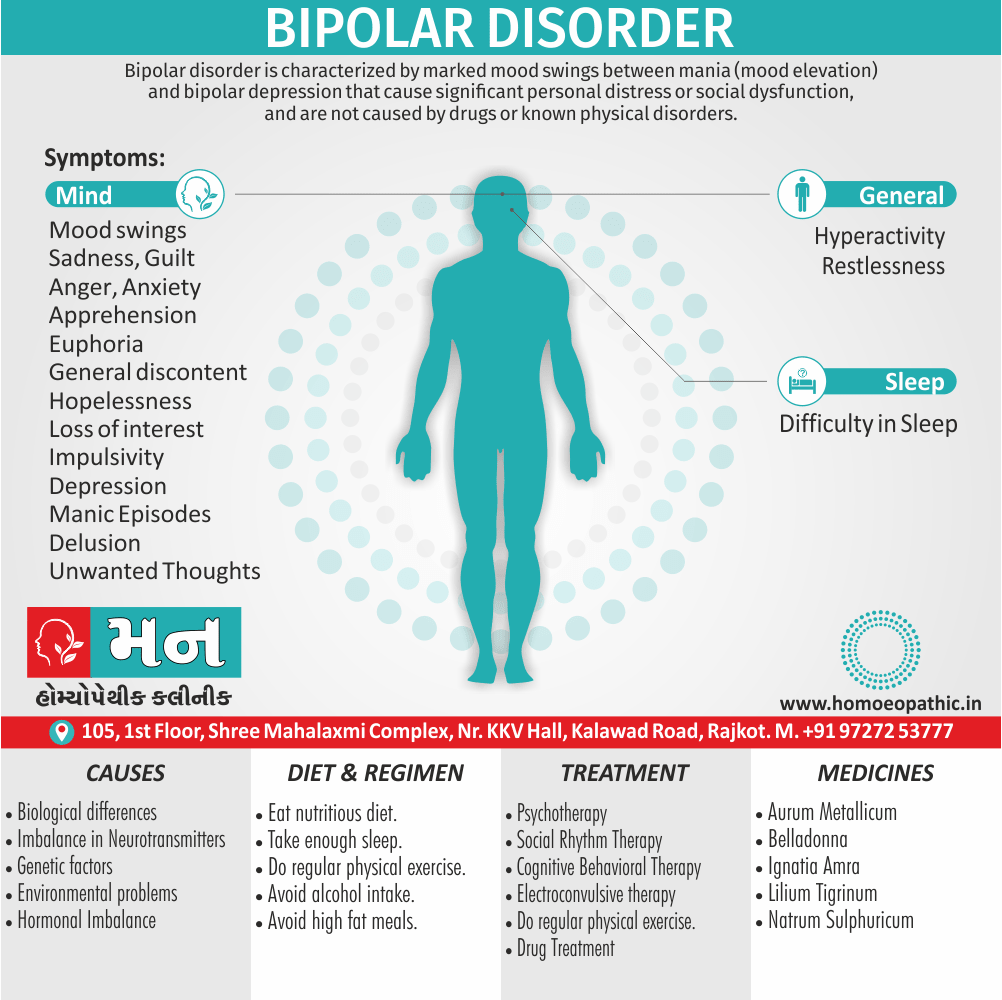
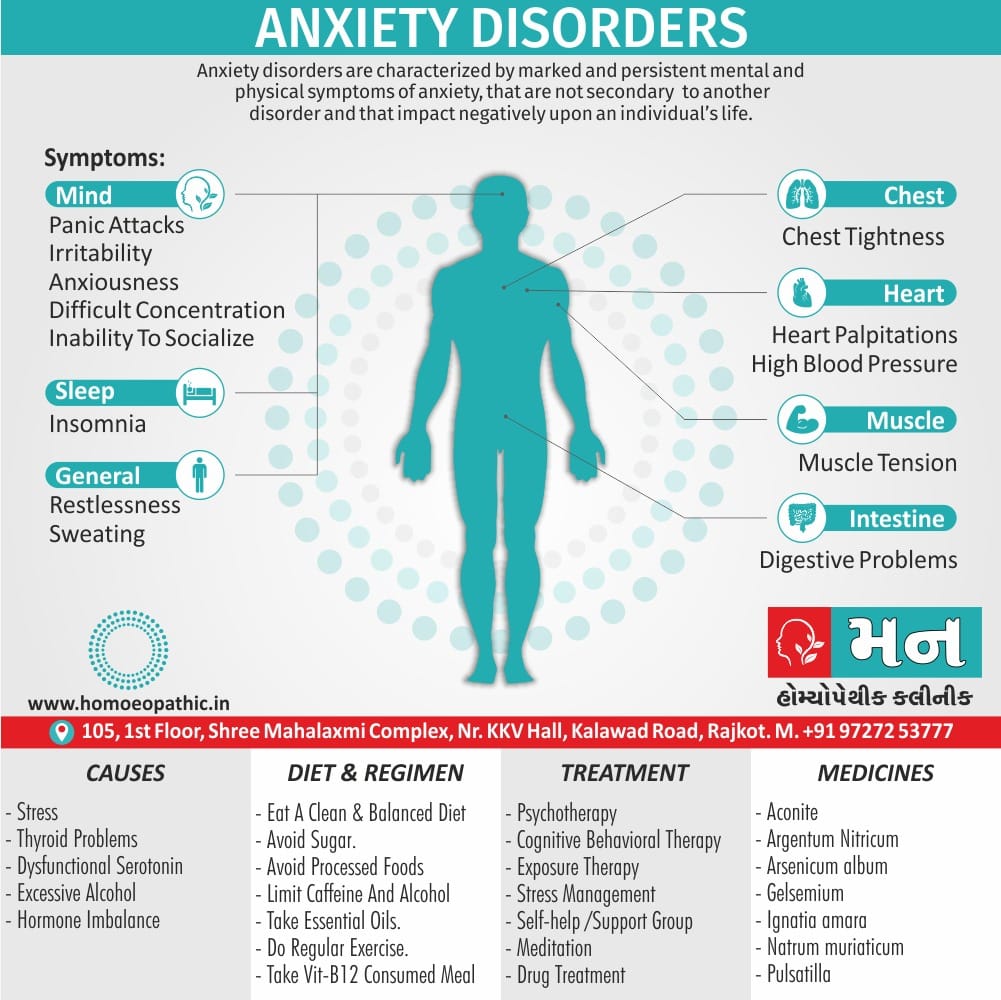
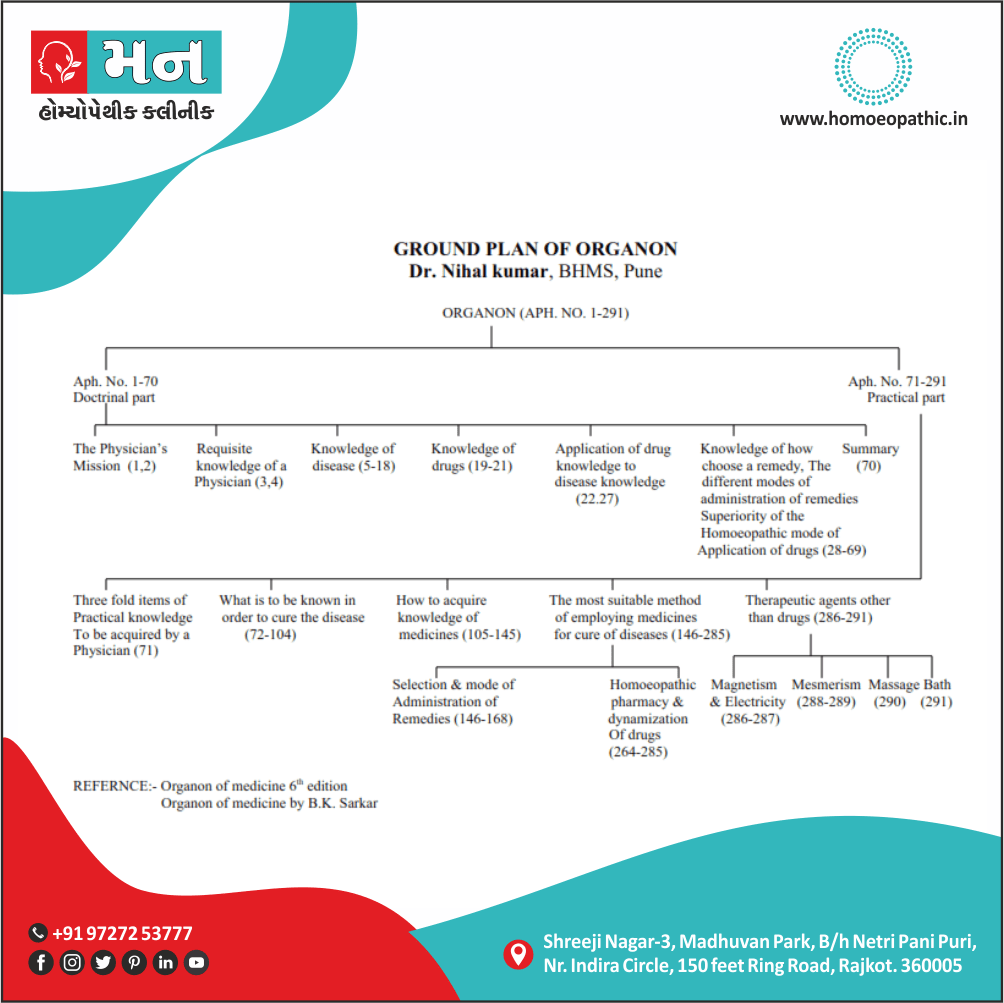
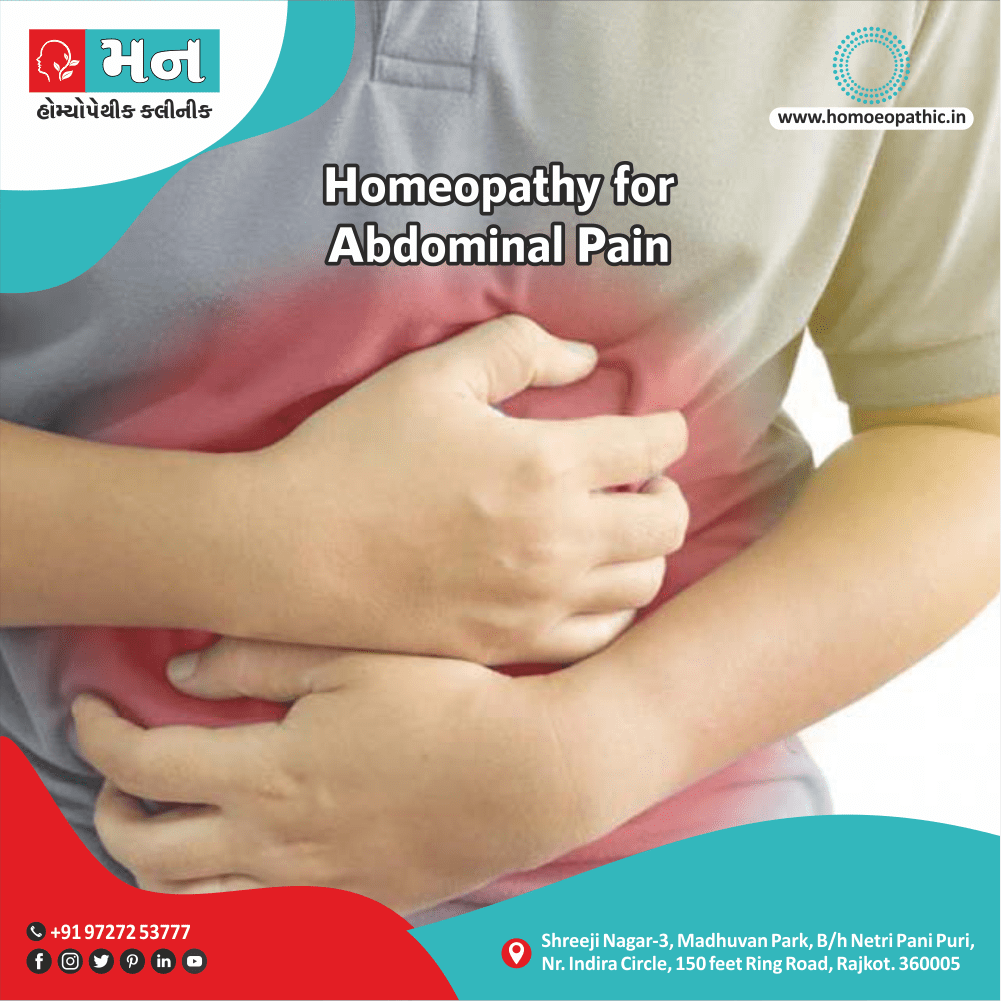
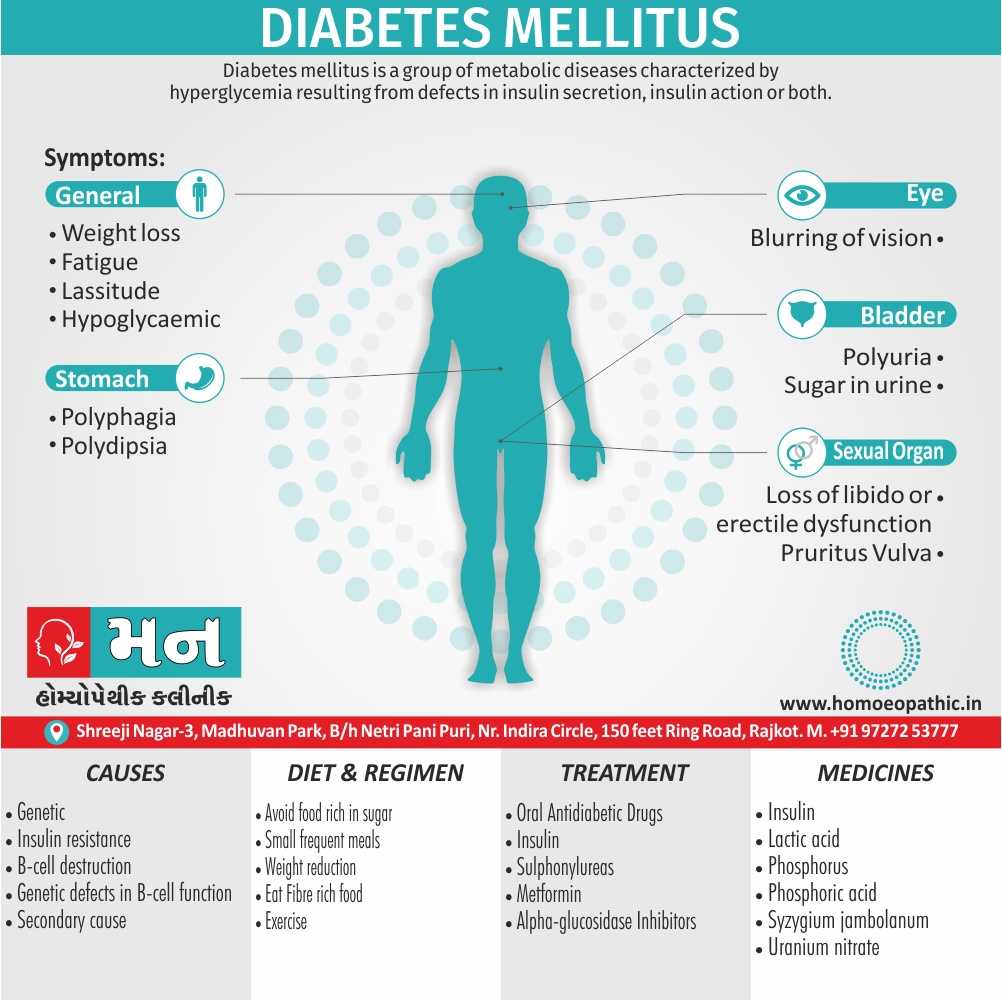
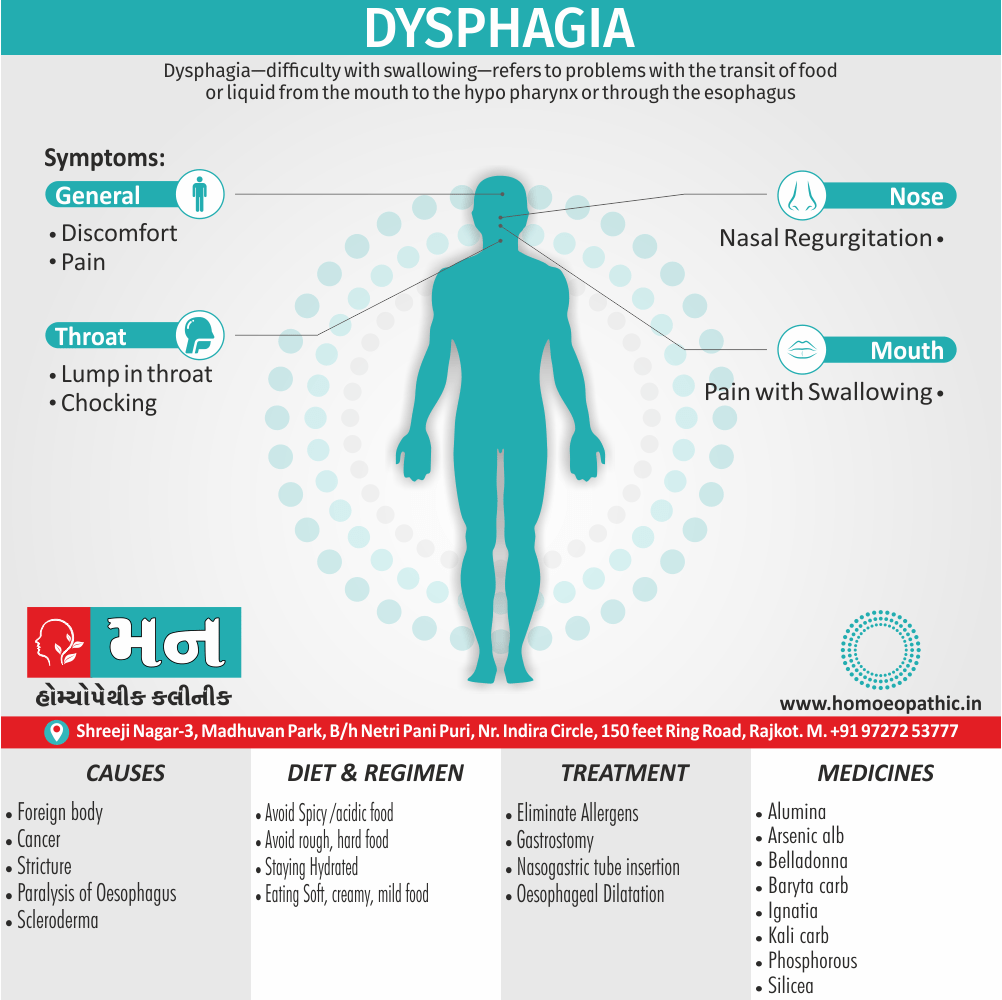
Memory Tips for Guiding Symptoms
Hi Friends Let’s memorize guiding symptoms of Apis Mellifica through name of Medicine ‘Apis Melifica‘.
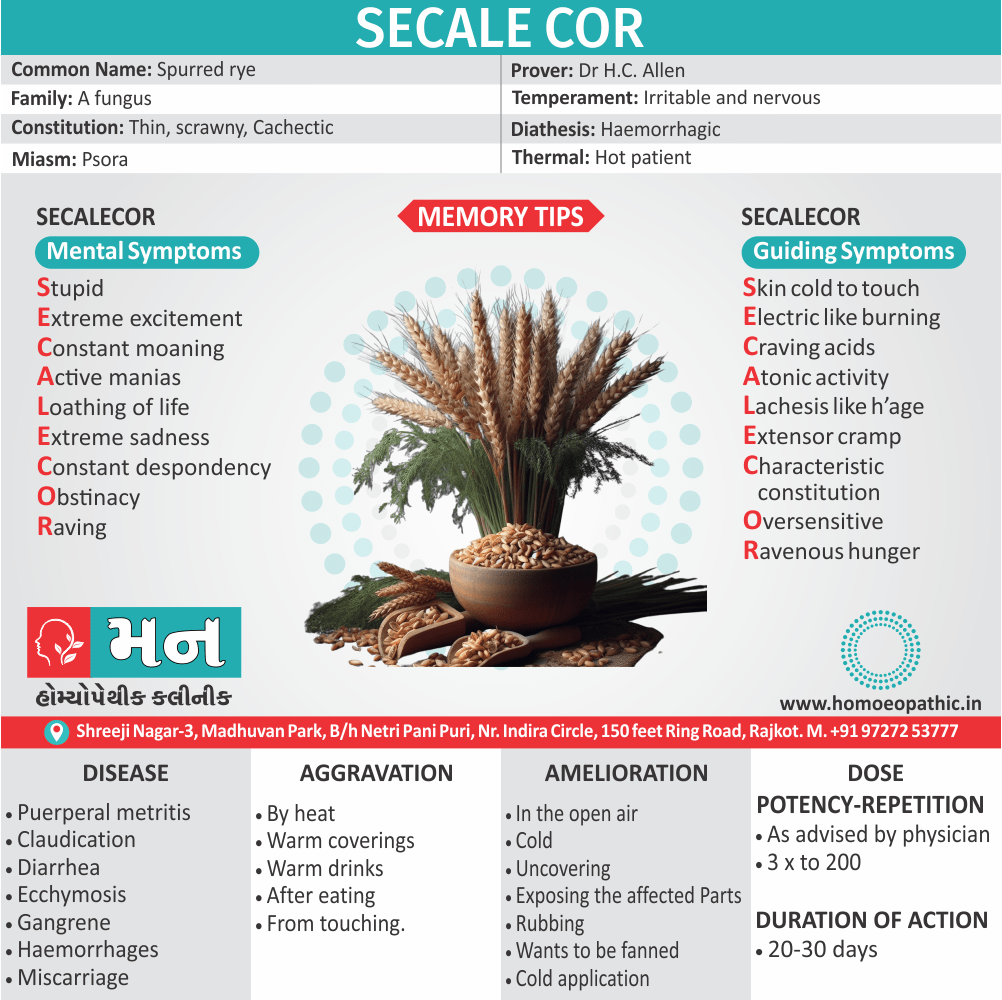
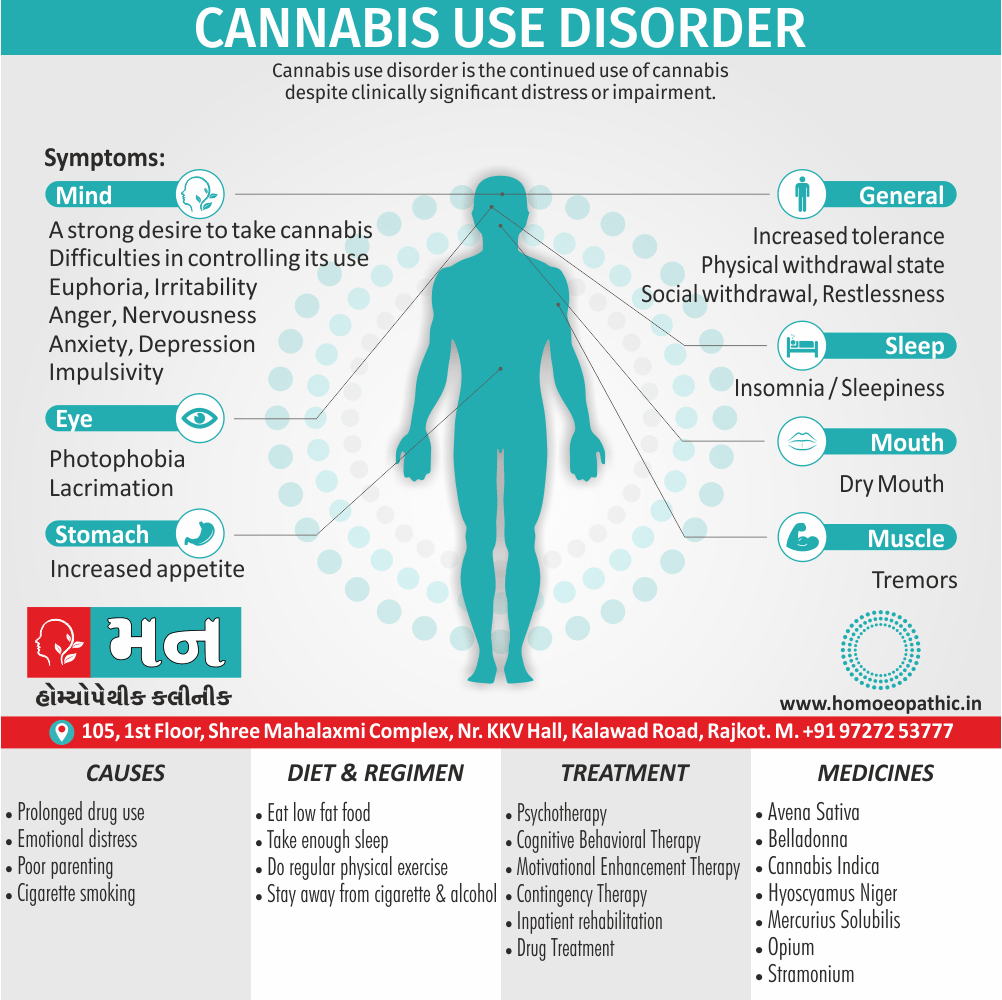
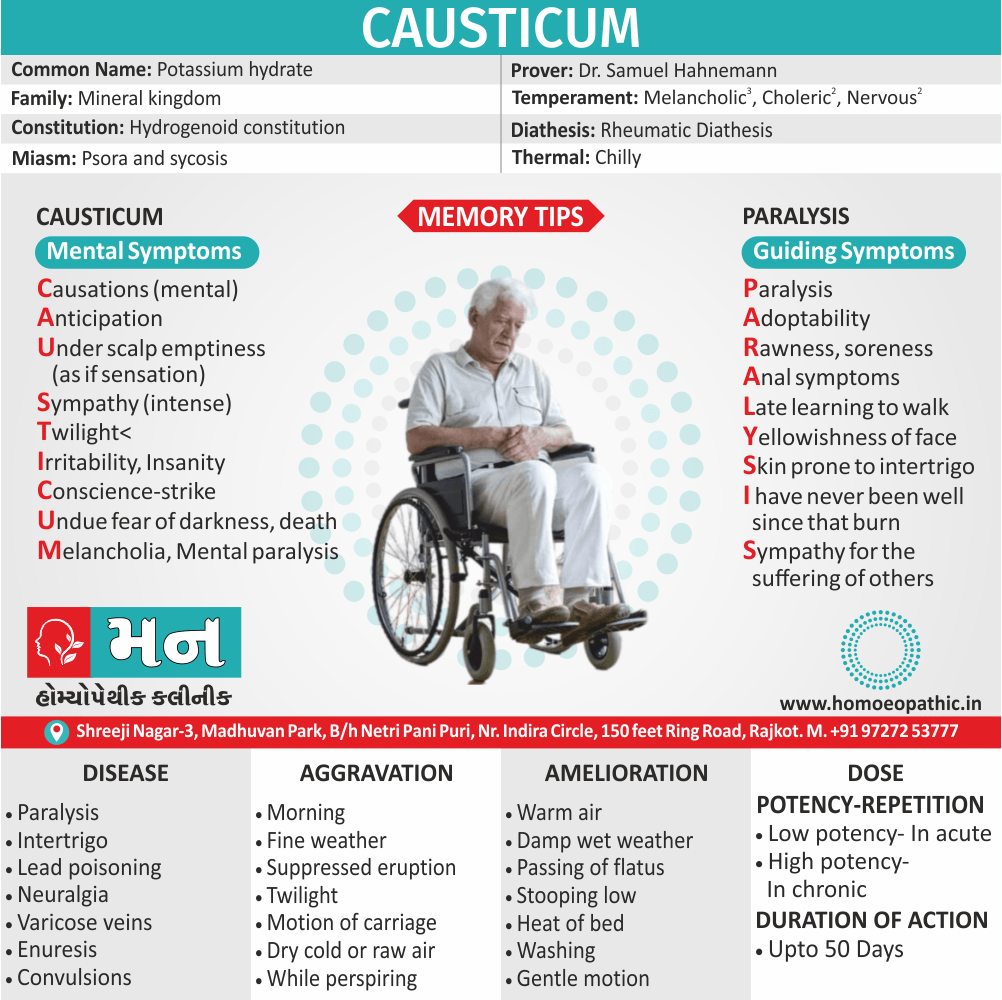
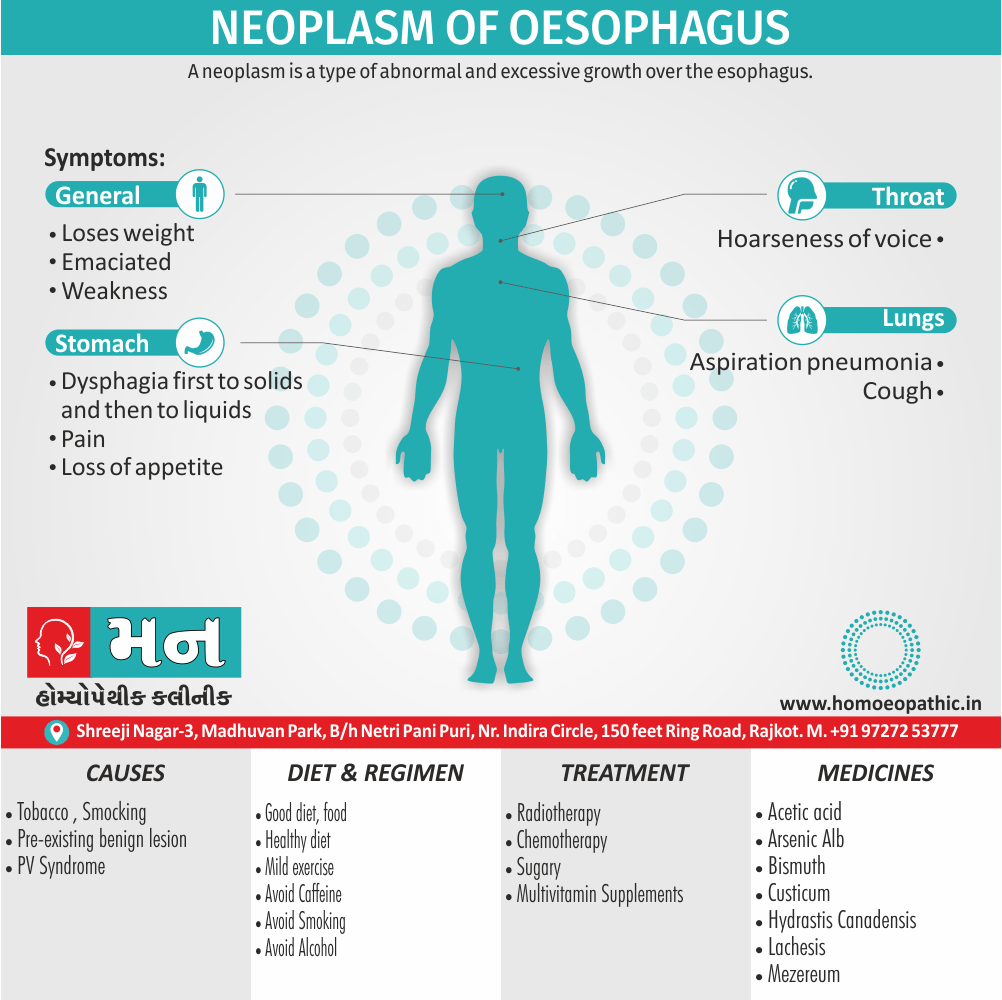
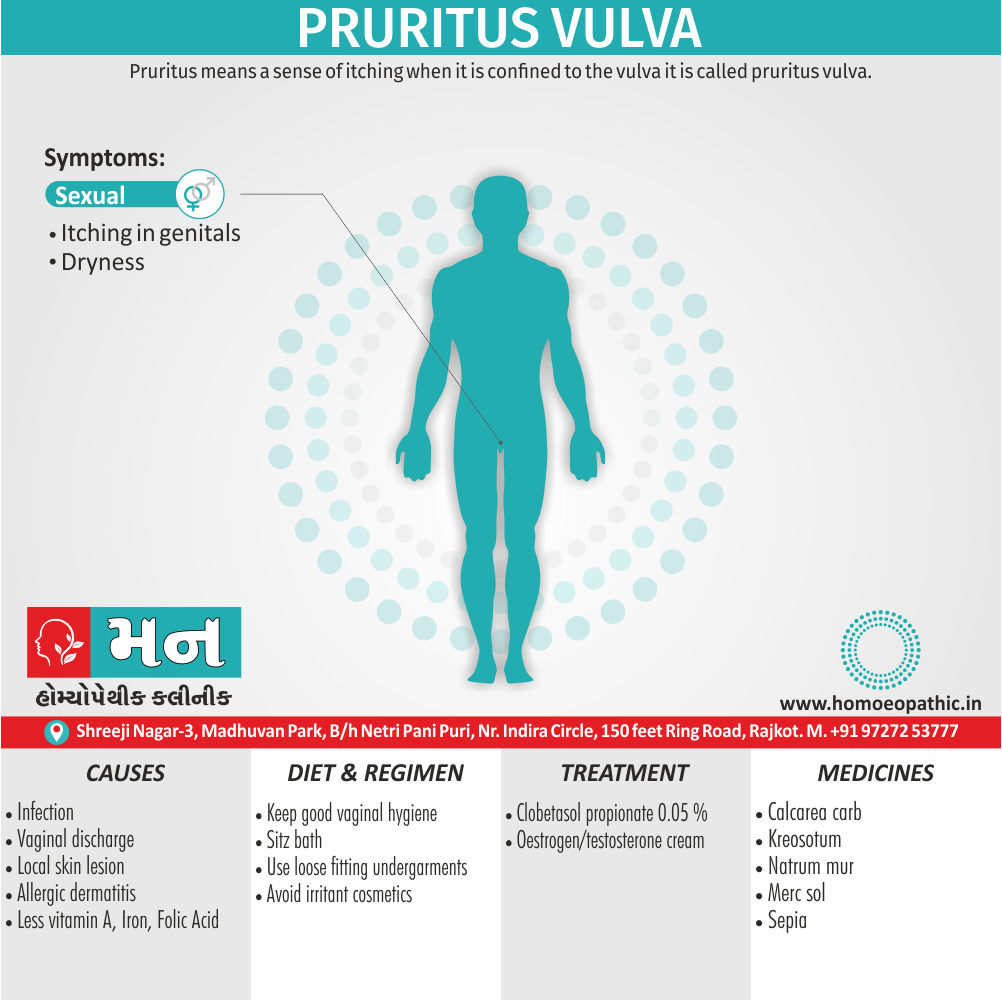
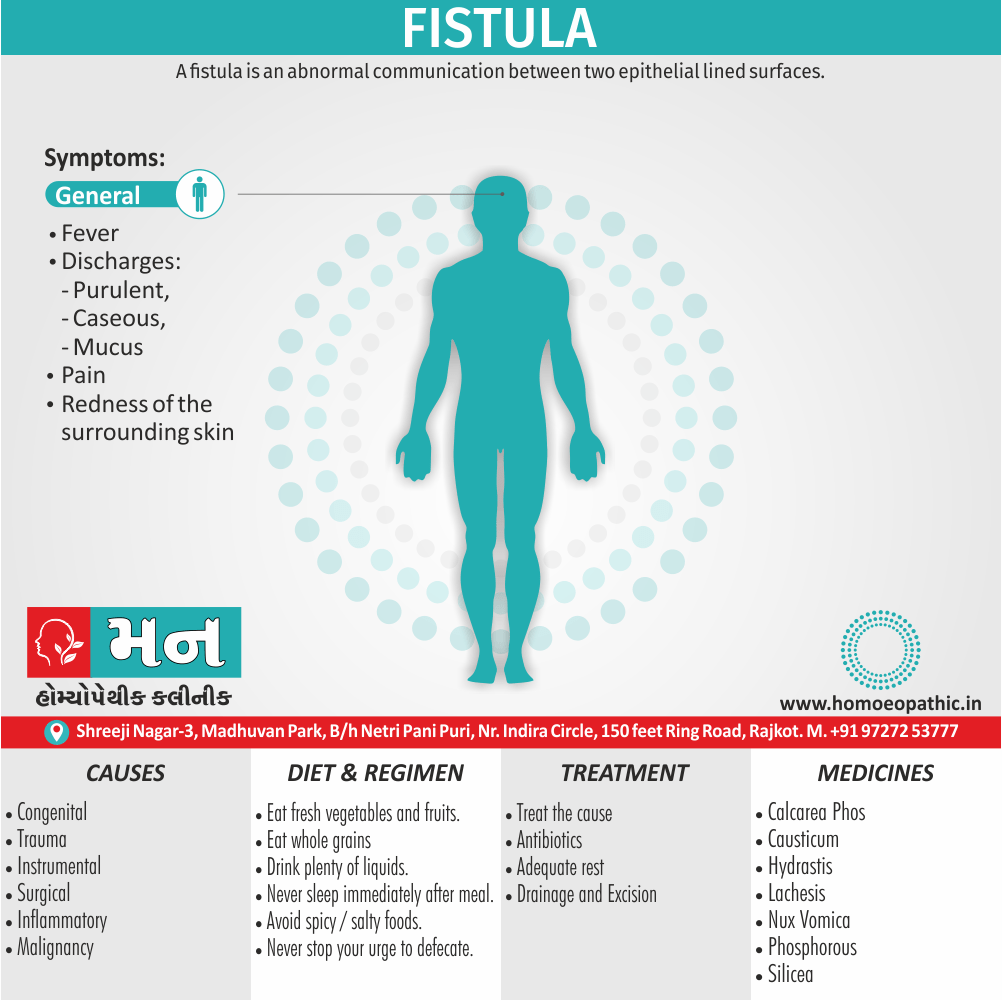
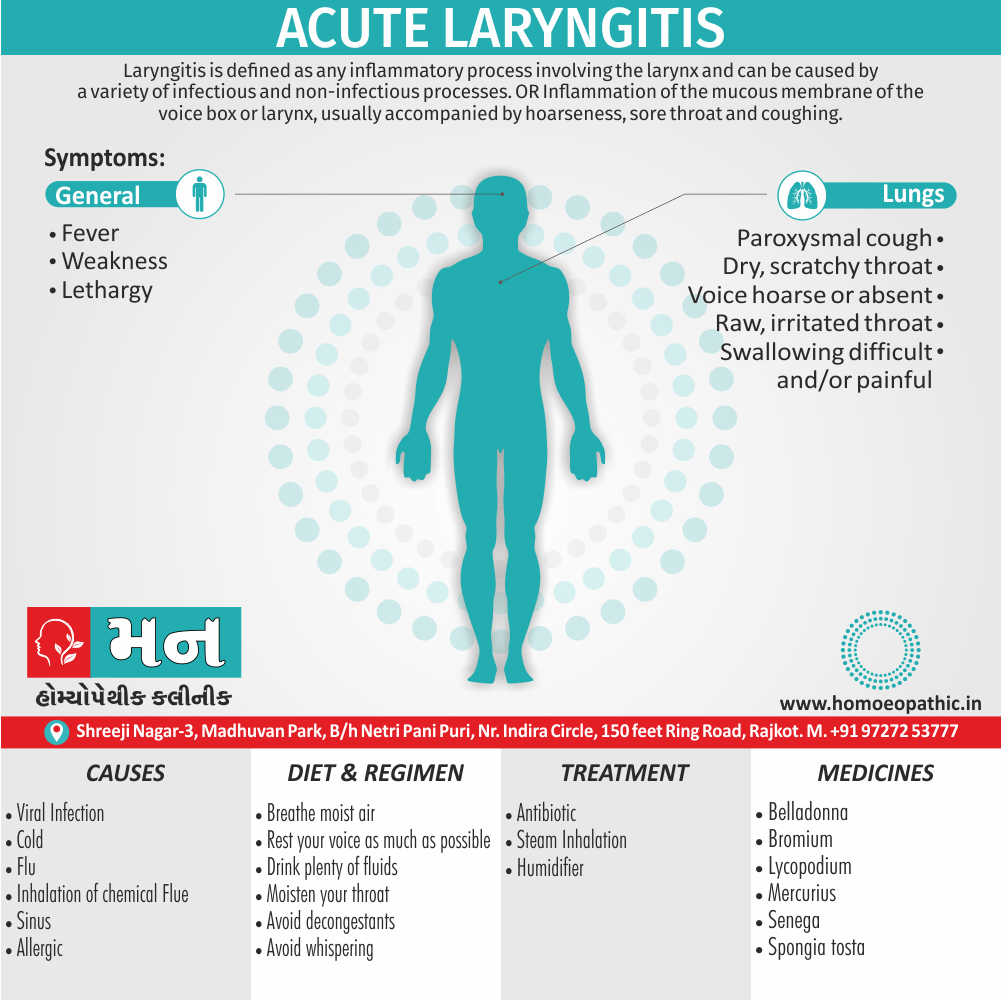
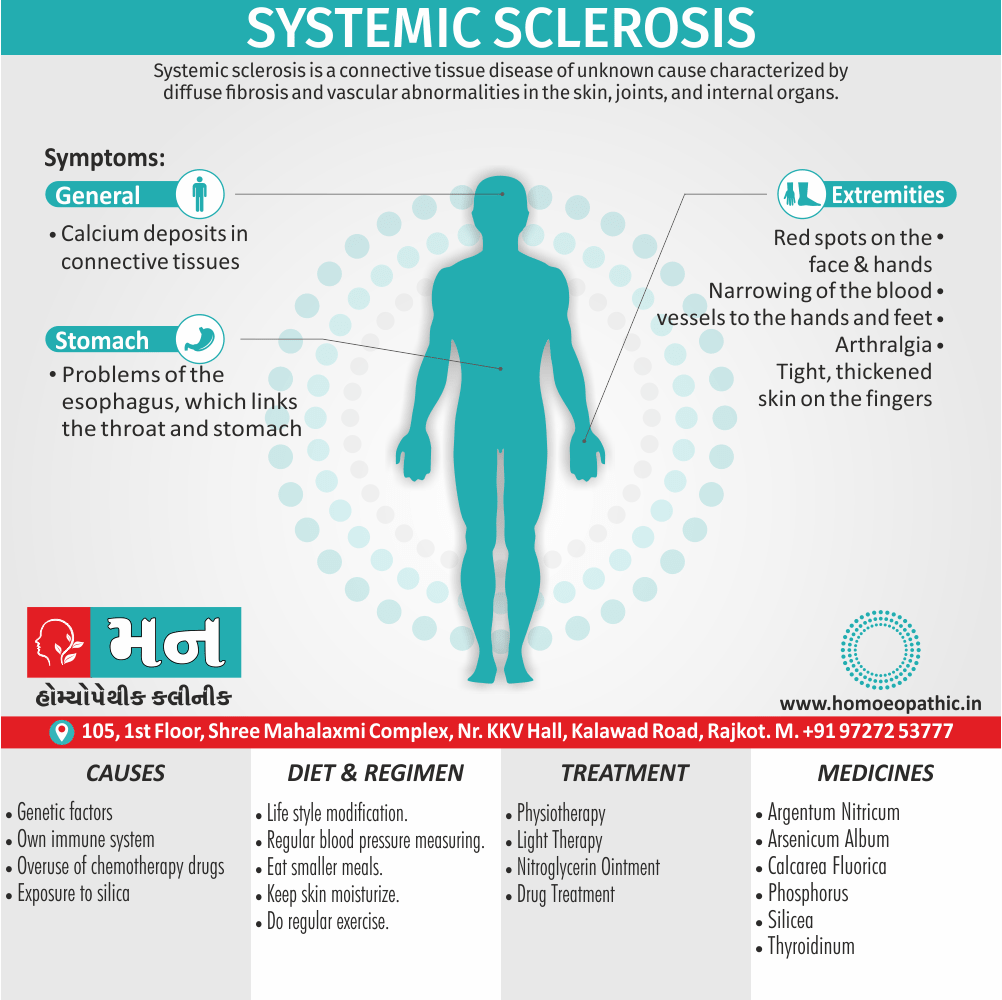
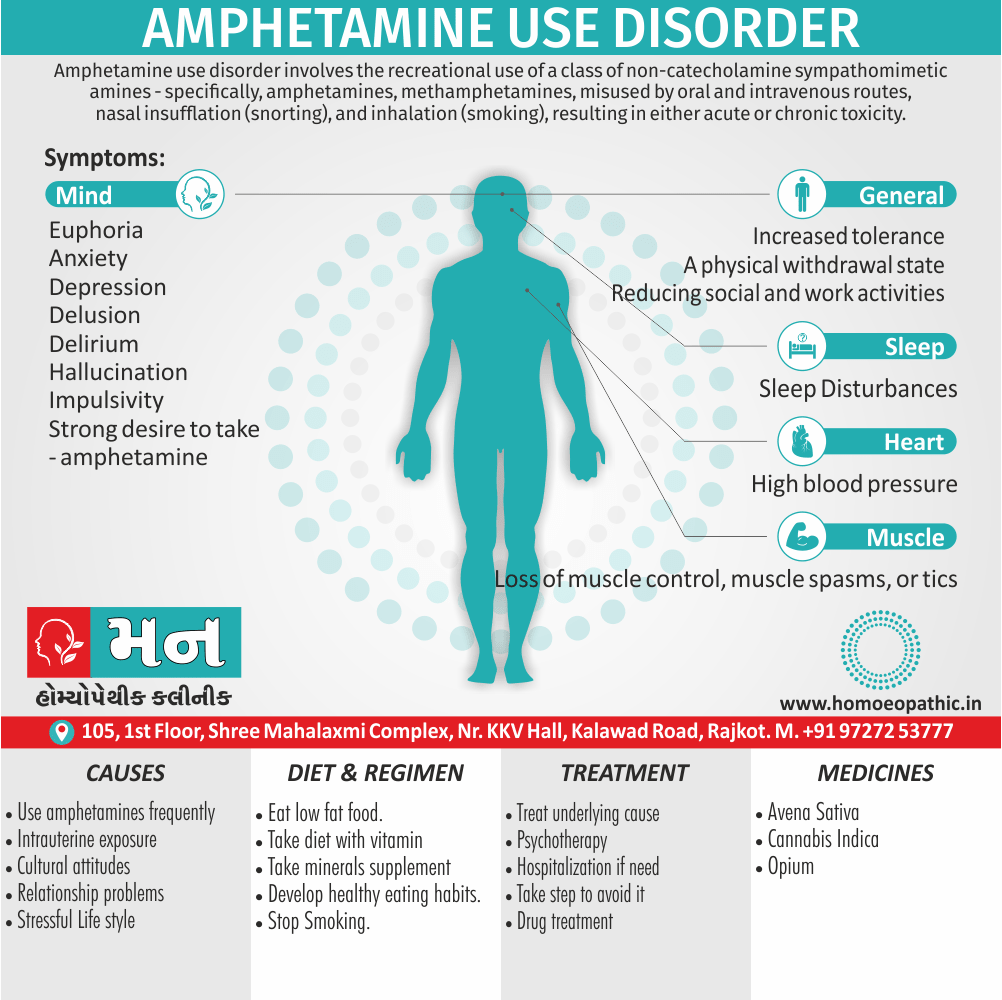
Ailments from :
- Ailments from jealousy, fright, rage, vexation, bad-news. grief (Ref. Clarke).
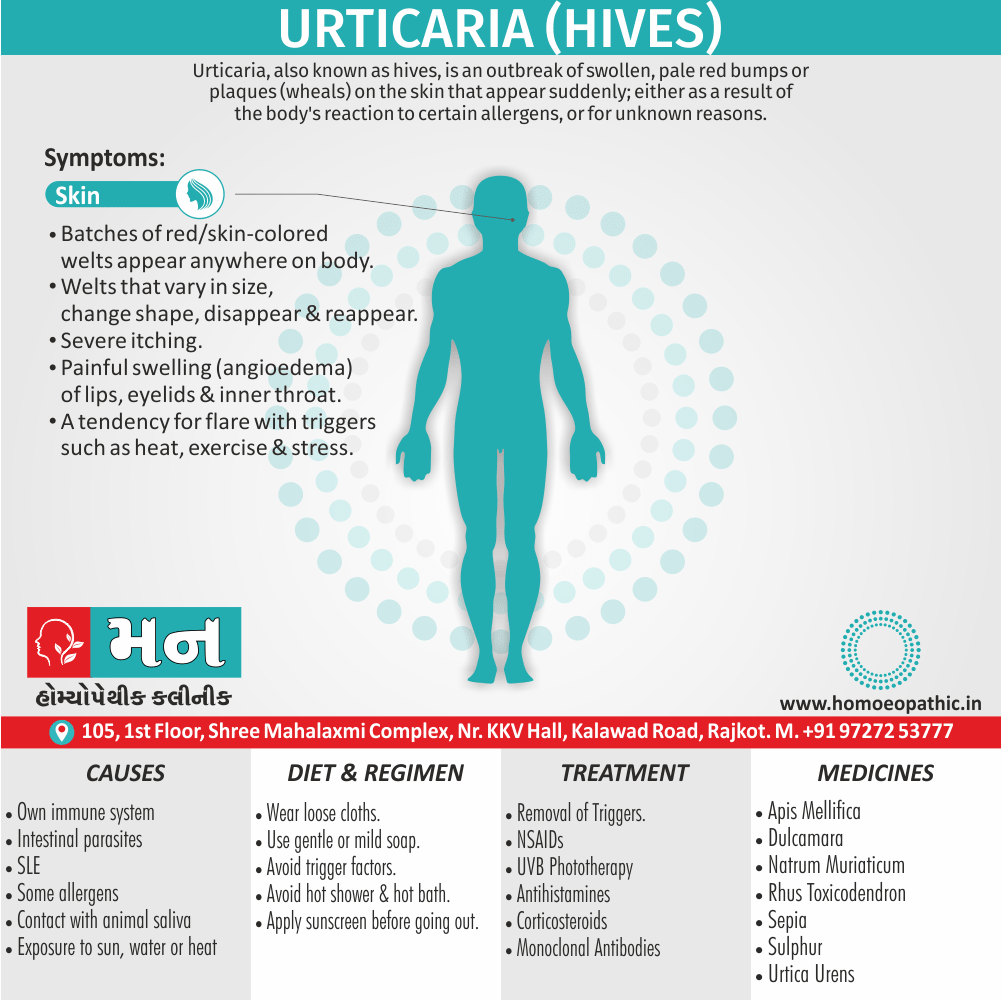
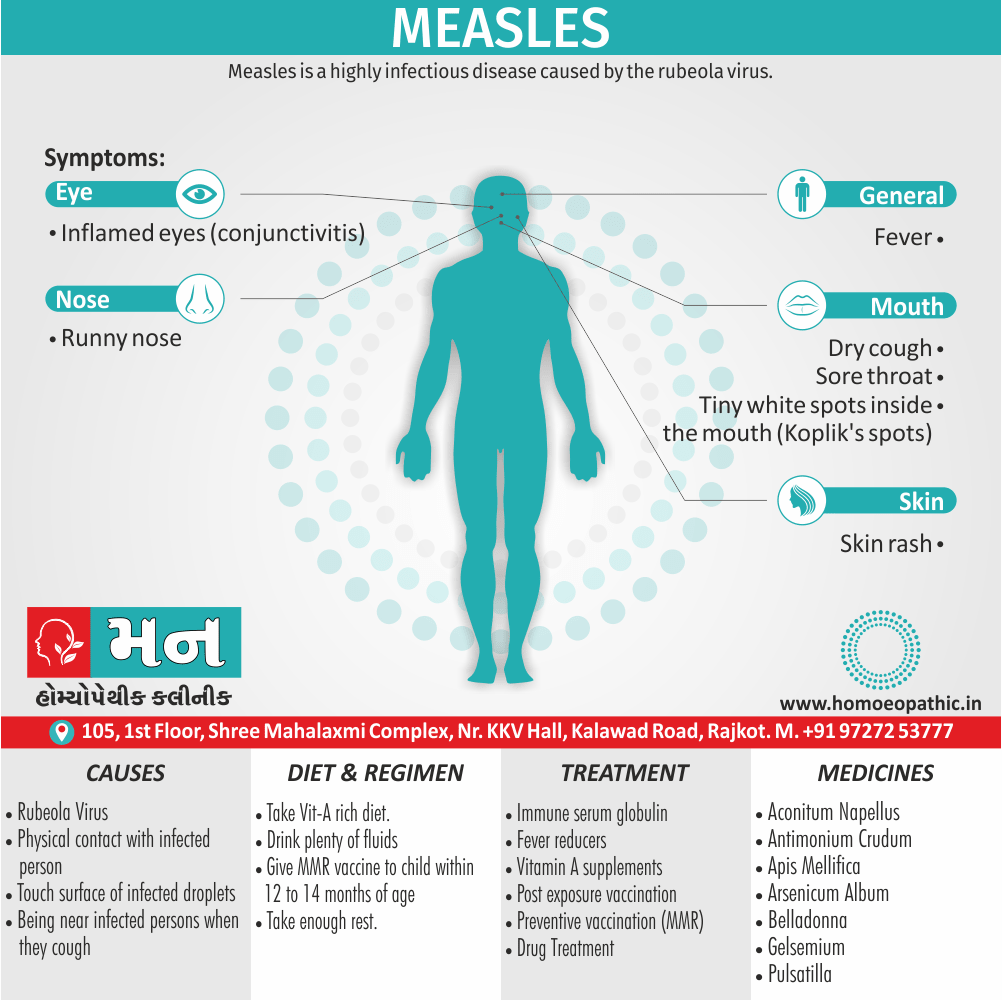
- Bad effects of acute exanthema –imperfectly developed or suppressed (Zinc.), from measles, scarlatina, urticaria, etc. [1]
Pains :
- Dr. E. B. Nash said, ‘It seems to me that in this remedy also the leading characteristic is to be found in its sensation -burning, stinging pains.
- They are sharp and quick, like the sting of the bee.
- These pains are characteristic of this remedy.
- The pains may shift suddenly from one part to another and may be associated with remedies such as Kali Bichromicum, Kali Sulphuricum, Magnesium Phosphoricum, Lac Caninum, Phytolacca, Pulsatilla and Manganum Aceticum. These pains may have a burning quality and may worsen with heat, as seen with Sulphur.[1]
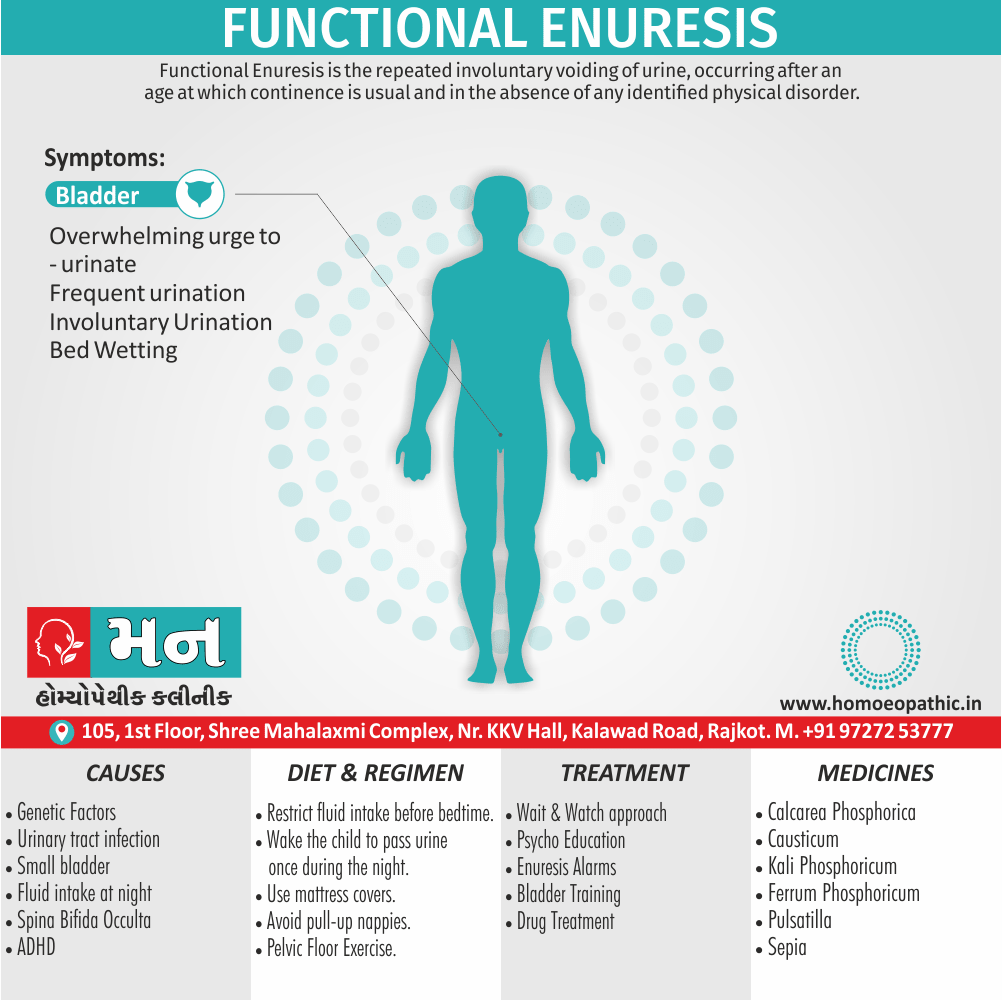
Incontinence of urine :
- Apis Mellifica is associated with urinary incontinence and significant irritation of the urinary tract. The individual may have difficulty retaining urine and may experience a severe burning sensation when urinating. Urination may be frequent, painful, and scanty, and may contain blood.
- Master Kent said much straining before the urine will start, and then only a few drops, -strangury, agony in voiding urine; retention of urine in nursing infants.
- Note: Increased flow of urine shows it is having a favourable effect (Ref. Clarke). [1]
Sensitiveness :
- Extreme sensitiveness to touch (Apis. ¹, Bell.’, China.’, Hep.’, Lach., Merc., Petrol.’, Phos Ac., Plb., Sil.’, Sulph.’).
- Dr. Clarke said, general soreness – every pain is painful to contact.
- This sensitiveness and sorness is also manifested as an aversion to tight things like Lach. [1]
Most jealous :
- Dr. Clarke said as the queen bee is the most jealous thing in nature thus our Apis pt. is also jealous.
- Apis is also a very valuable remedy for ailments resulting from jealousy.
- Master Kent said foolishly suspicious and jealous. [1]
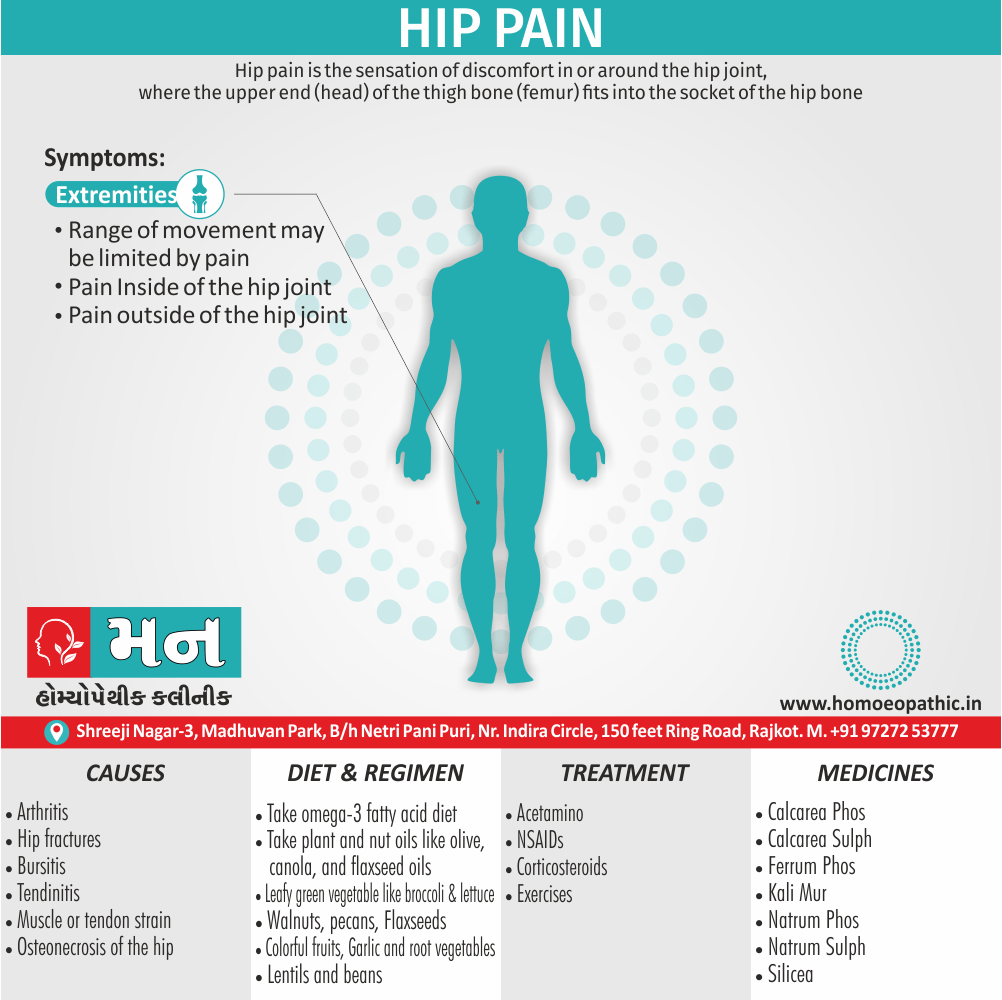
Extremities are dropsical:
- Master Kent said, in the extremities we have a marked dropsy, swelling with pitting upon pressure.
- A general anasarca may appear. The face is greatly swollen, puffy or oedema, bag like swelling under the eyes (- over the eyes, Kali Carb: – around the eyes or Nash said whole face, Phos), of the hands and feet, dropsy without thirst (-with thirst, Acet. ac., Apoc. and Dr. Nash said Ars.).
- Dr. Kent explained that this general puffiness may be present in any inflammatory state. [1]
Lack of thirst:
- Our Apis is a thirstless remedy and can be bracketed with, Aethusa., Gels., Puls., Nux Mos.
- Dr. E. B. Nash said this particular symptom which helps to choose between it and other remedies in dropsy, is the almost absence of thirst. [1]
Memory Tips for Mental Symptoms
- Hi Friends Let’s memorize mental symptoms of Apis Mellifica through name of Medicine ‘WABGirlFriend’.
Workaholic:
Mentally the Apis personality is quite like a bee – busy and active constantly. May be a workaholic, “task oriented”. [1]
Absentminded:
Awkward, lets things fall from her hands and laughs sillily at the mishaps. [1]
Busy & Restless:
Busy and active constantly. May be a workaholic, “task oriented”. [1]
Great restlessness:
Great restlessness and fidgetiness. [1]
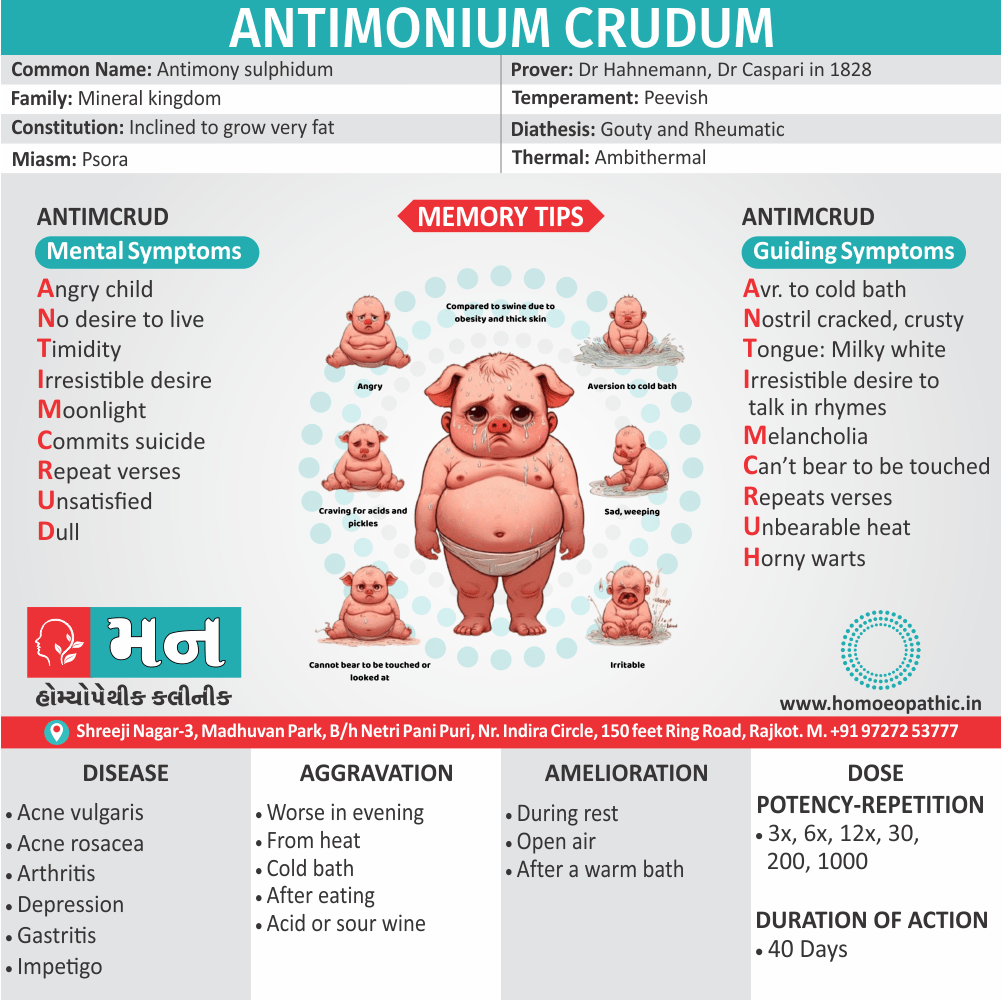
Foolishly suspicious :
Apis Mellifica Introduction
Hi Friends, Now we describing Drug picture of Apis Mellifica
Common name : Honeybee poison
Synonyms : Madhu Makhi
Family / Group / Class / Order : Apidae
Habit and habitat / Description :
Oedematous, puffy, bag-like swelling under the eyes) Dropsy without thirst, and fever with thirst) Sensation as though anus was wide open in diarrhoea
Name of prover :
- Dr Frederick Humphries in 1852.
- It is also proved by Brauns and introduced by E.E. Marey to homeopathy
Introduction and history :
- Apis is an invaluable acquisition to our materia medica.
- The genus Apis is of European origin and is widely distributed all over the world.
- Female bees are distinguished from the males by their shorter abdomen.
- Only the female bees have poisonous stings.
- In males, the mouth parts are well developed.
- Honey bees are found in India and other parts of the world.
Parts used :
- Live honey bees are used for preparation of the drug.
- Bees are put into a bottle and irritated by shaking.
- Dilute alcohol is poured five times and this is kept closed for a week.
- The bottle should be shaken two times a day.
- The tincture is then poured off and from this mother tincture, potentized medicine is prepared.
Active principles :
- Honey bee poison contains toxalbumin and the effects are similar to those of other animal poisons, such as the toxalbumin of snakes, spiders and lizards.
- The following table includes the active principles and their respective actions.
- Haemolytic enzyme- It causes destruction of the haemoglobin part of RBC’s causing anaemia.
- Zinc oxide- It affects peripheral nerves causing paralysis of the organs. [2]
- Formic acid- It causes burning, so there is a burning sensation in the patient.
- Toxalbumin -It has a toxic effect on the albuminous parts of the body; albuminuria.
Preparation :
- Live honey bees are used for preparation of the drug.
- Bees are put into a bottle and irritated by shaking.
- Dilute alcohol is poured five times and this is kept closed for a week.
- The bottle should be shaken two times a day.
- The tincture is then poured off and from this mother tincture, potentized medicine is prepared. [2]
Constitution
Physical make up:
- Scrofulous constitution.
- It is characterized by oedematous swelling of the face, especially under the lower eyelids.
- The face is pale and waxy.
- Women, especially widows are very adaptable to this remedy.
Temperament :
Sanguine 2, Choleric 2 , Nervous 1,Phlegmatic 1
Diathesis:
Scrofulous
Relation with heat & cold:
Hot patient
Miasm : Psora [2]
Clinical Features
Clinical conditions
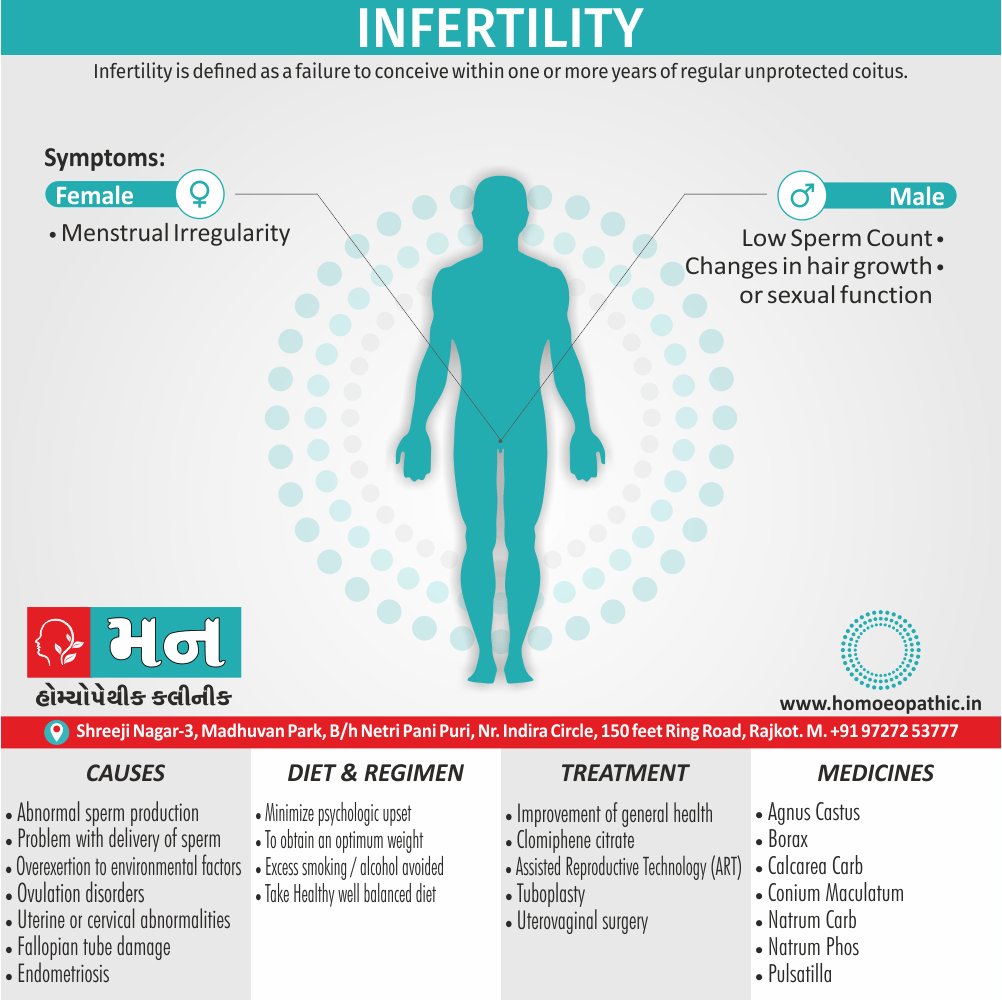
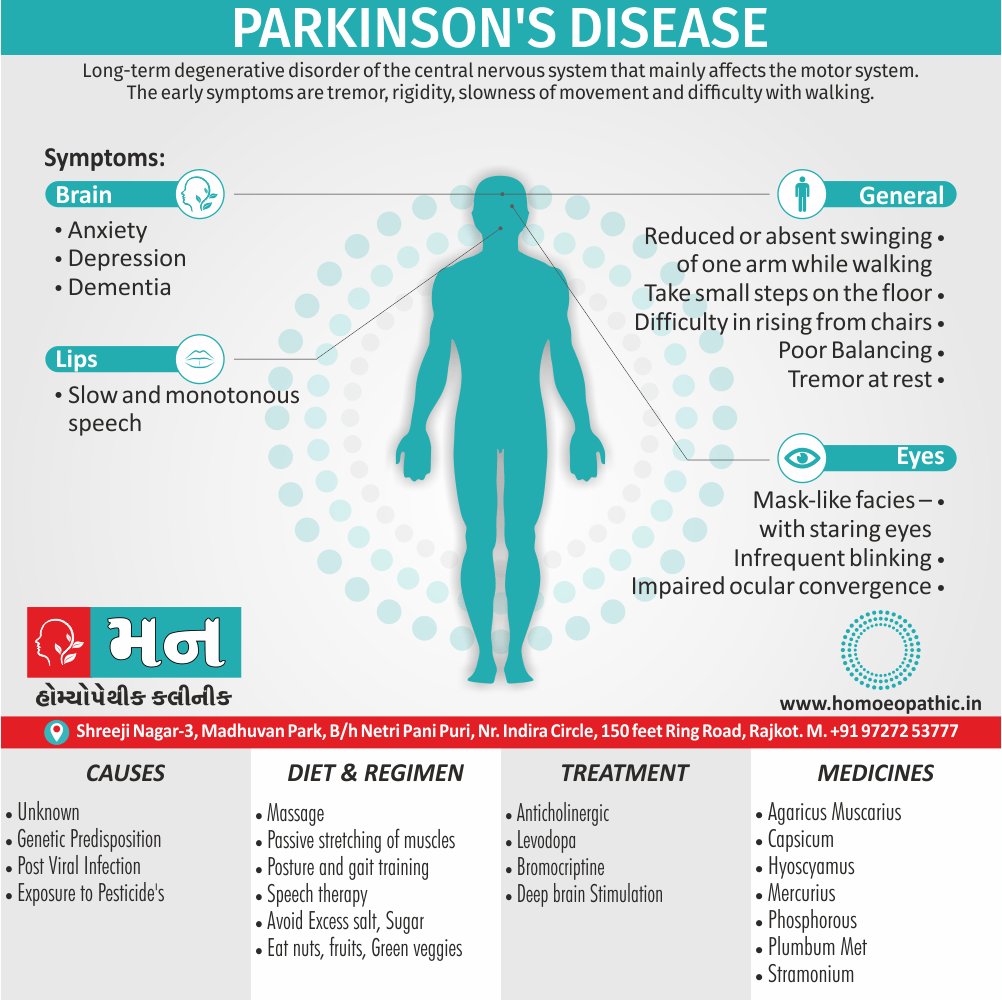
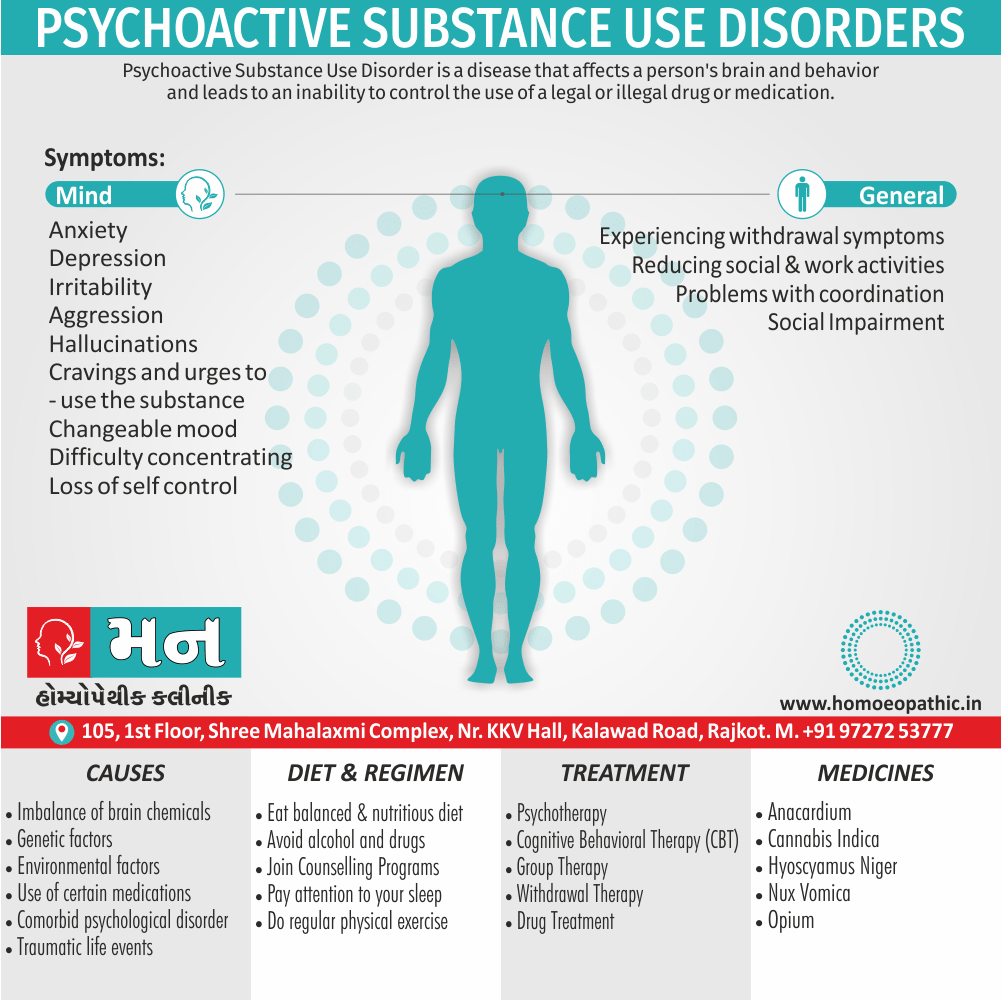
In Homeopathy Apis Mellifica medicine use by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of following Disease Conditions
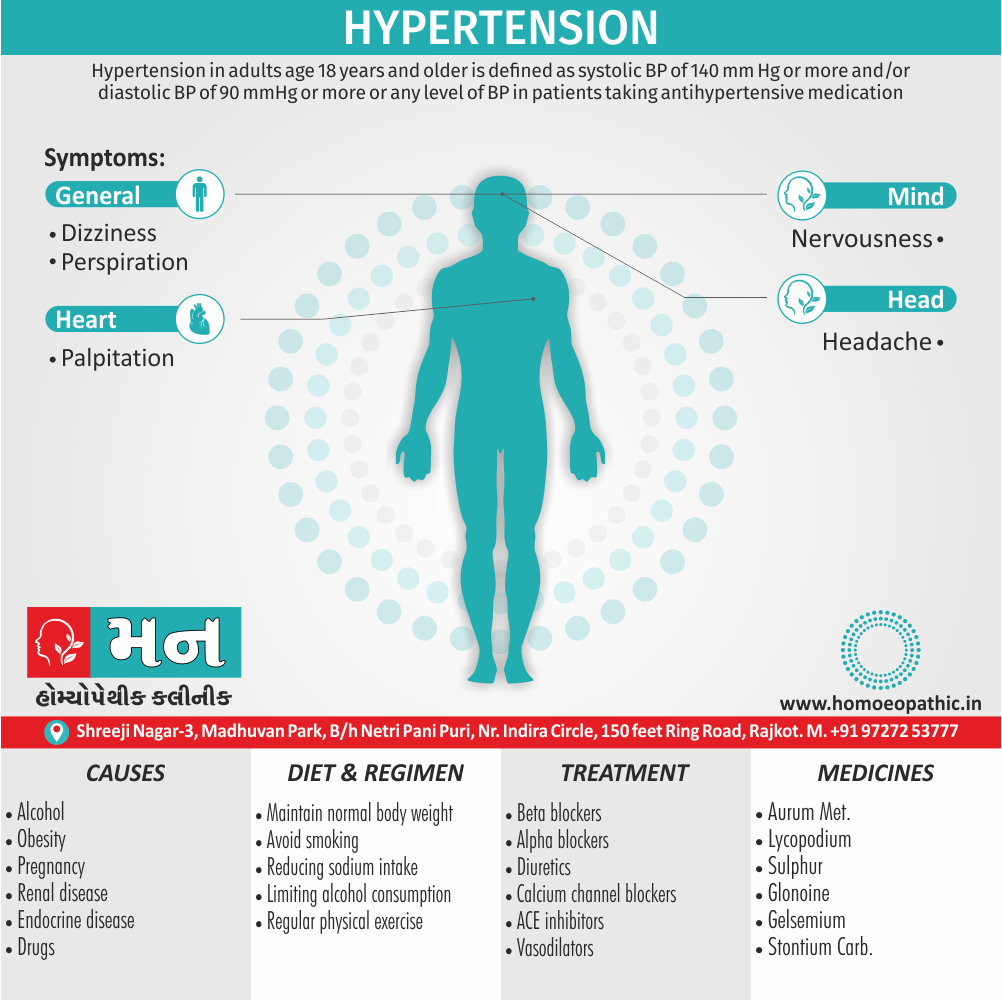
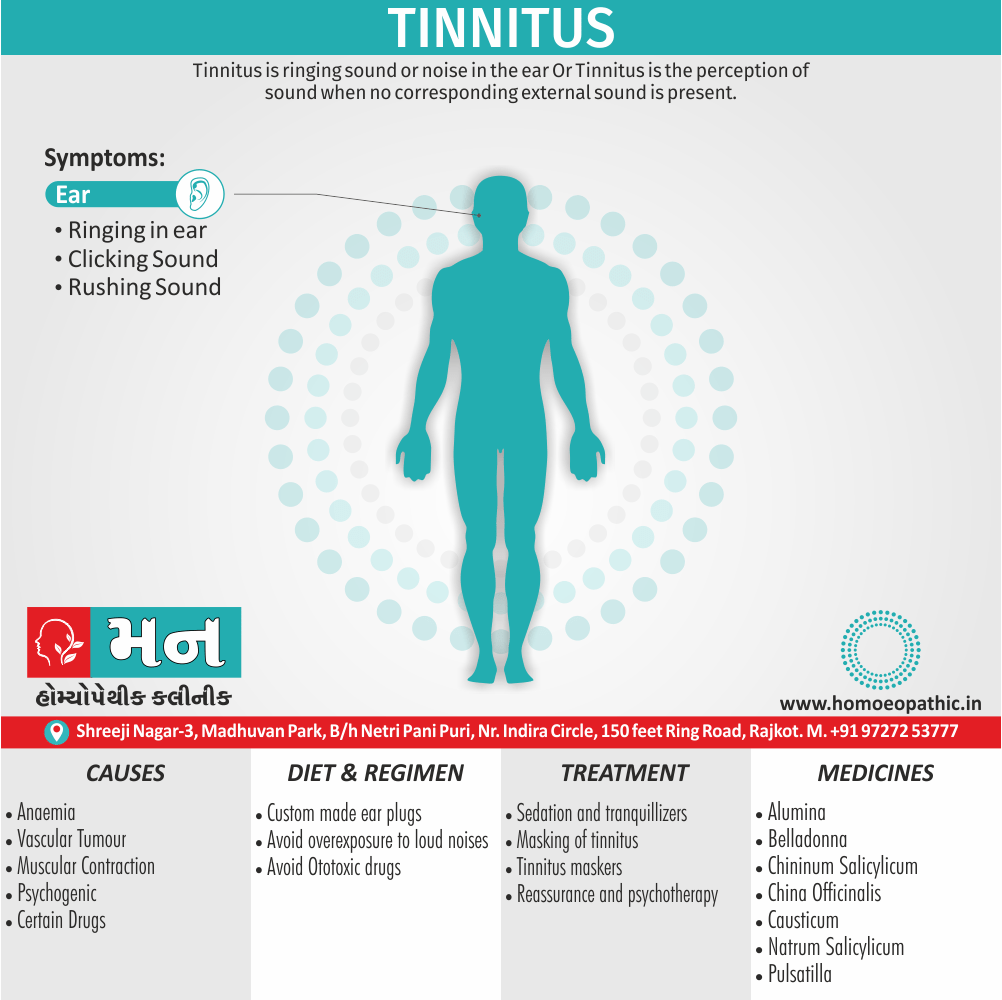
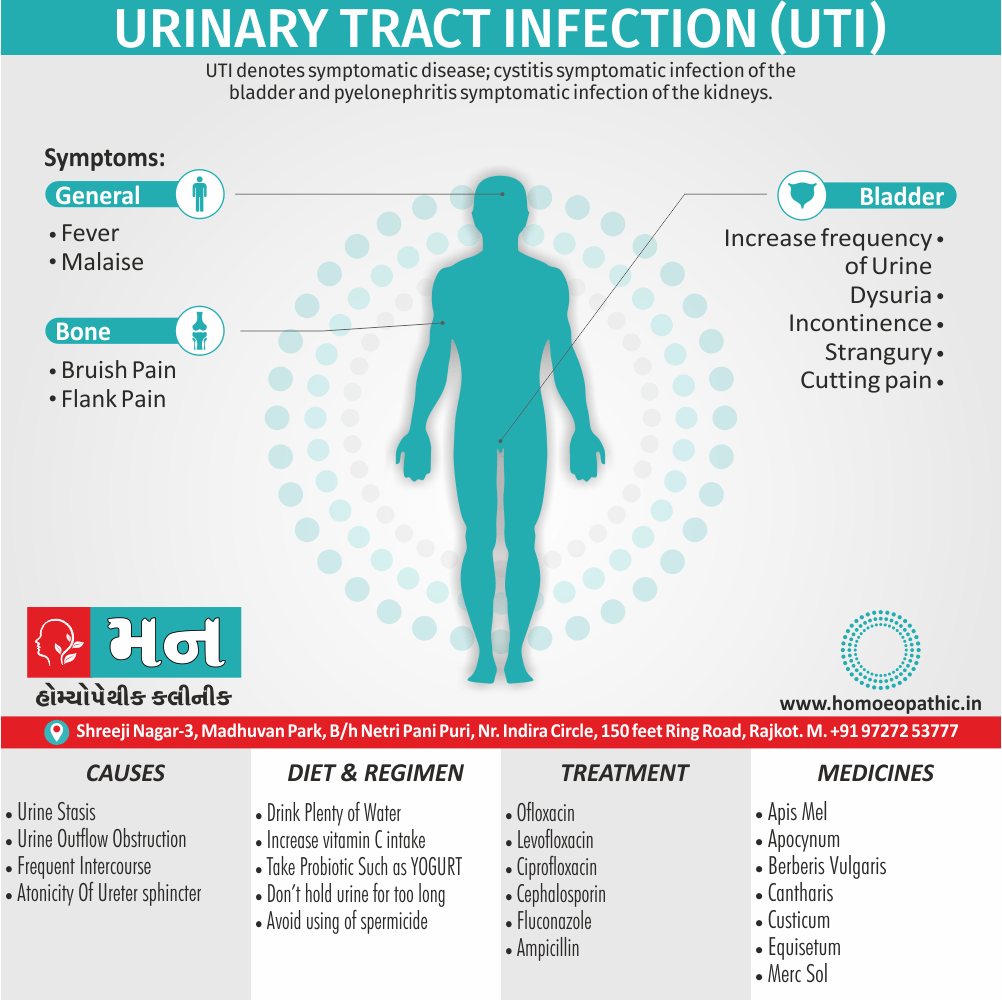
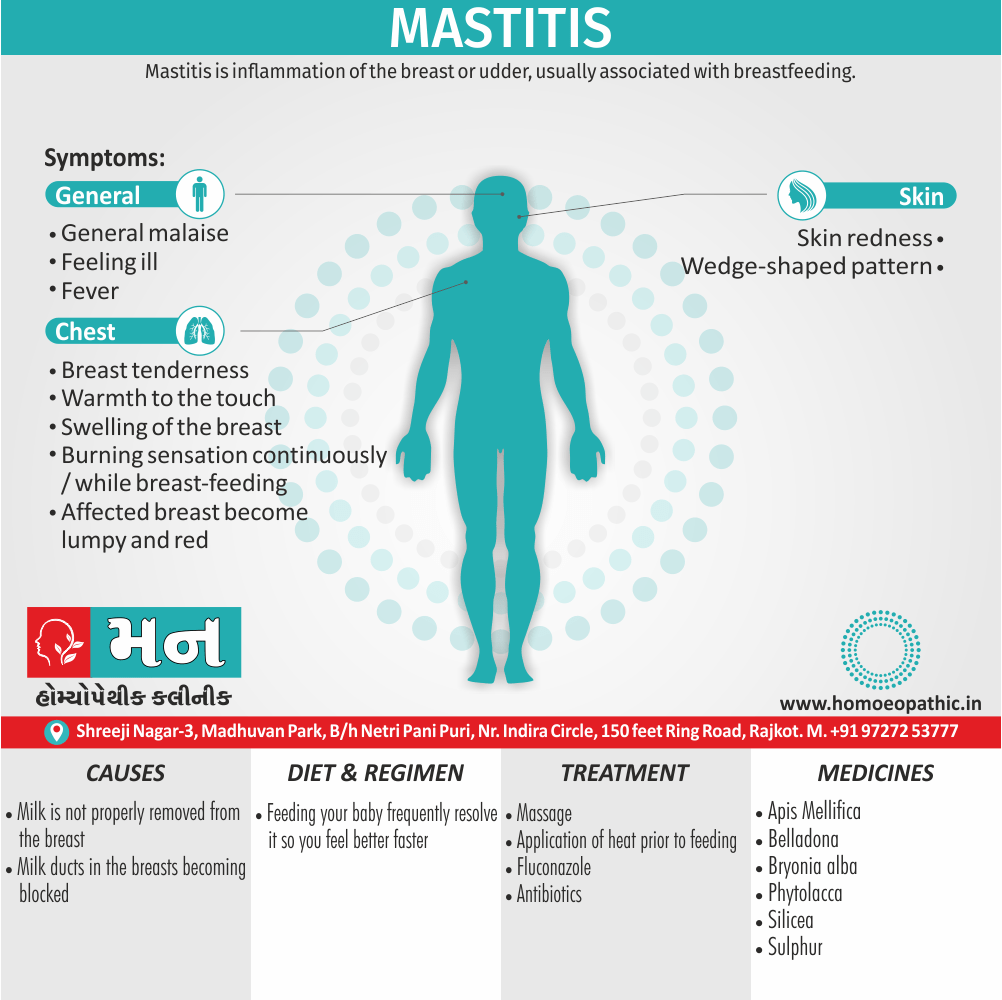
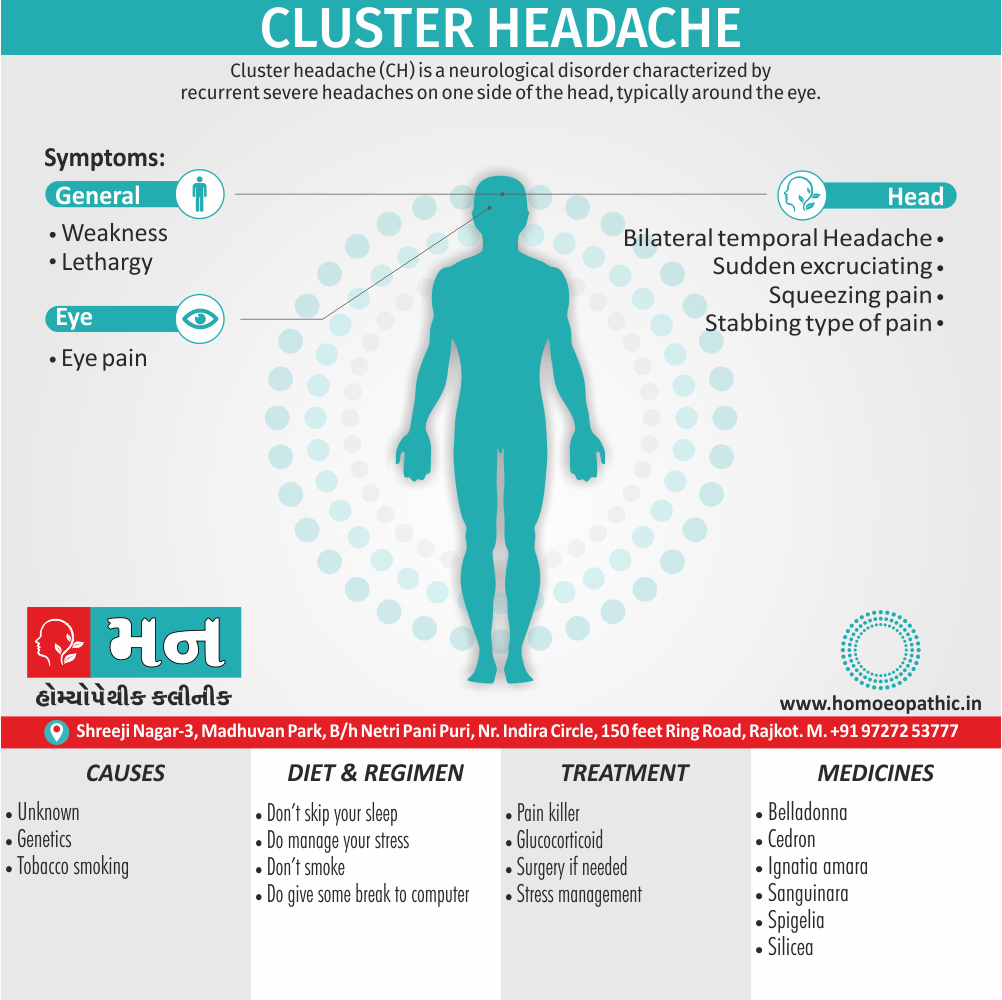
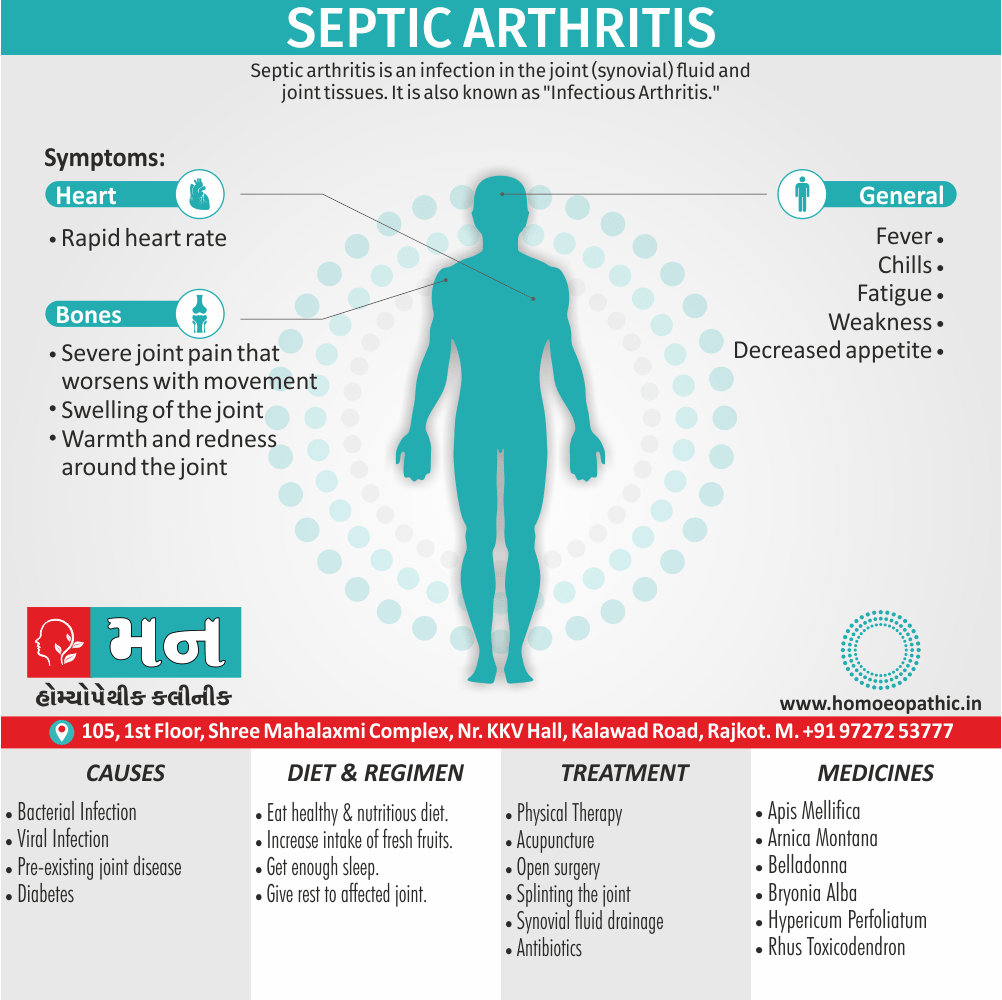
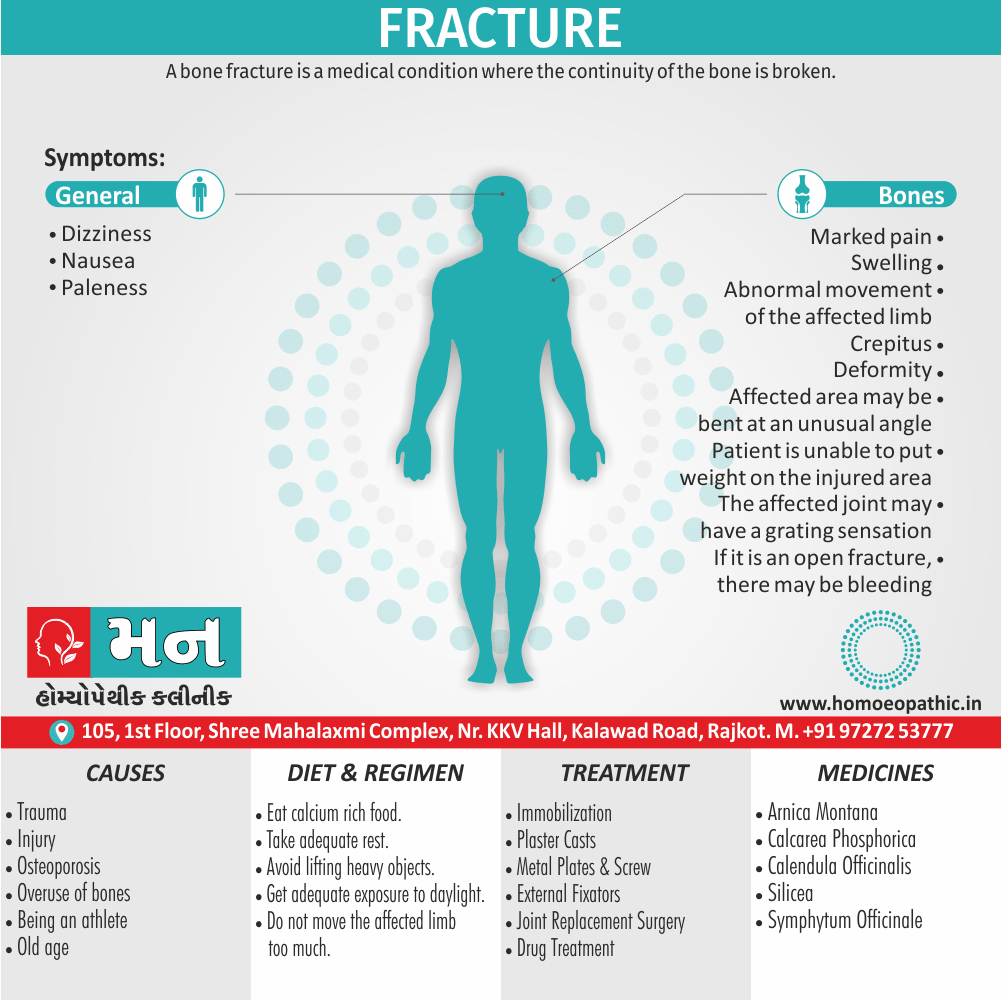
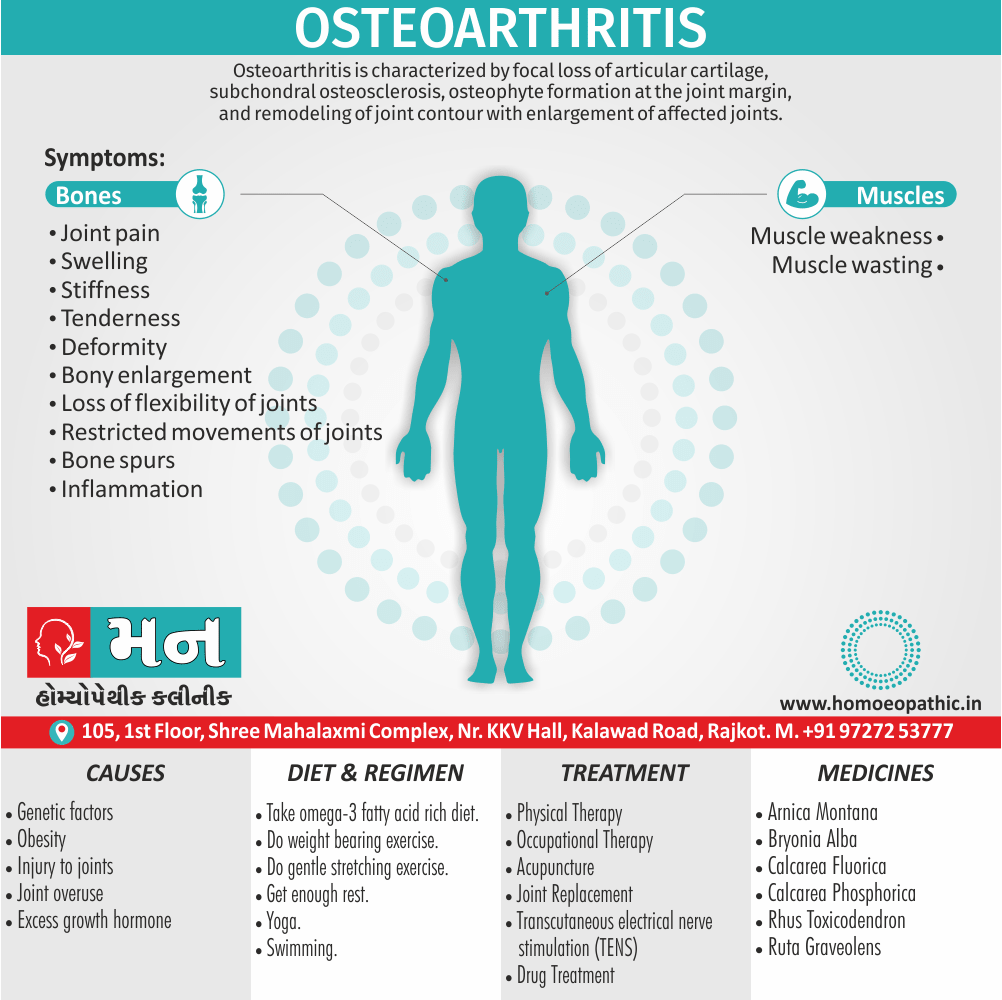
- Abortions, Angioneurotic oedema, Arthritis, Cystitis, Herpes zoster, Meningitis, Nephritis, Pharyngitis, Pleurisy, Pneumonia, Pyelonephritis, Urticaria.
- Apis has a slow action and must not be changed too soon.
- Increased flow of urine shows that the remedy has started acting favourably.
- A complete stupor yields to Apis after Opium phase.
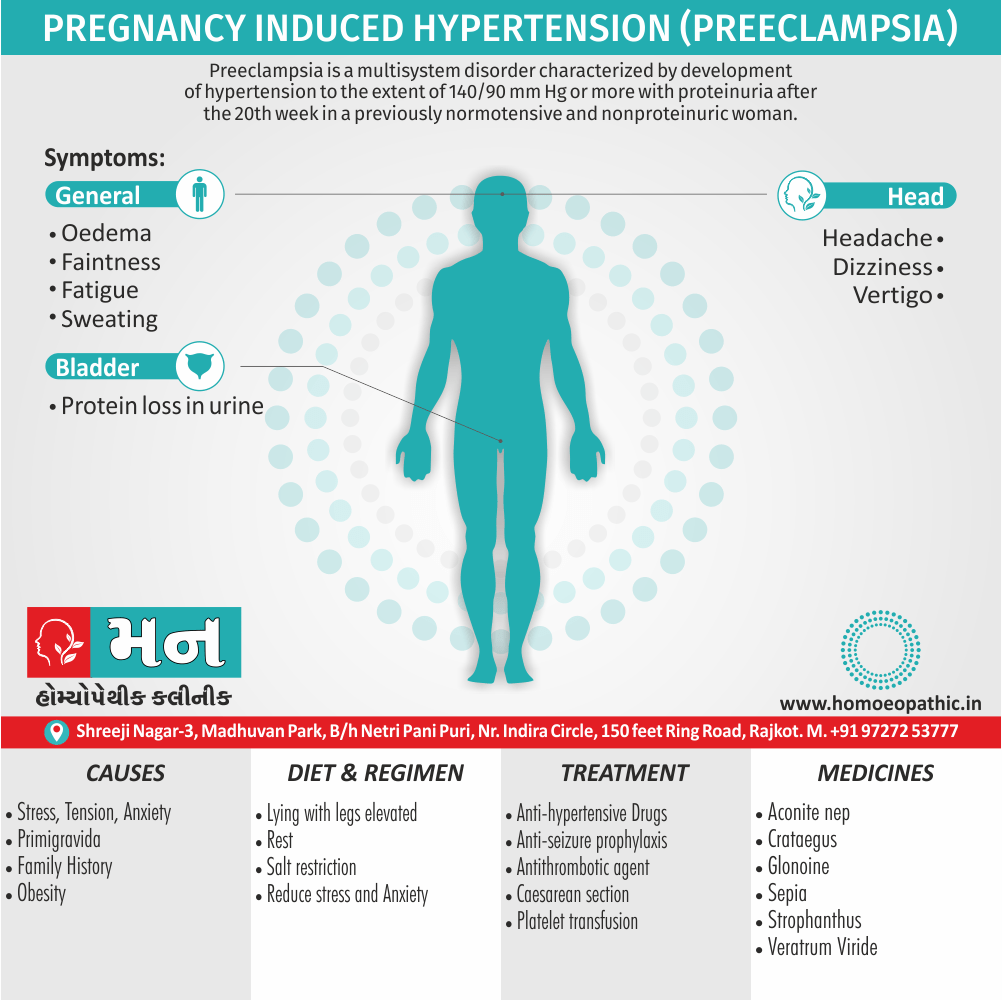
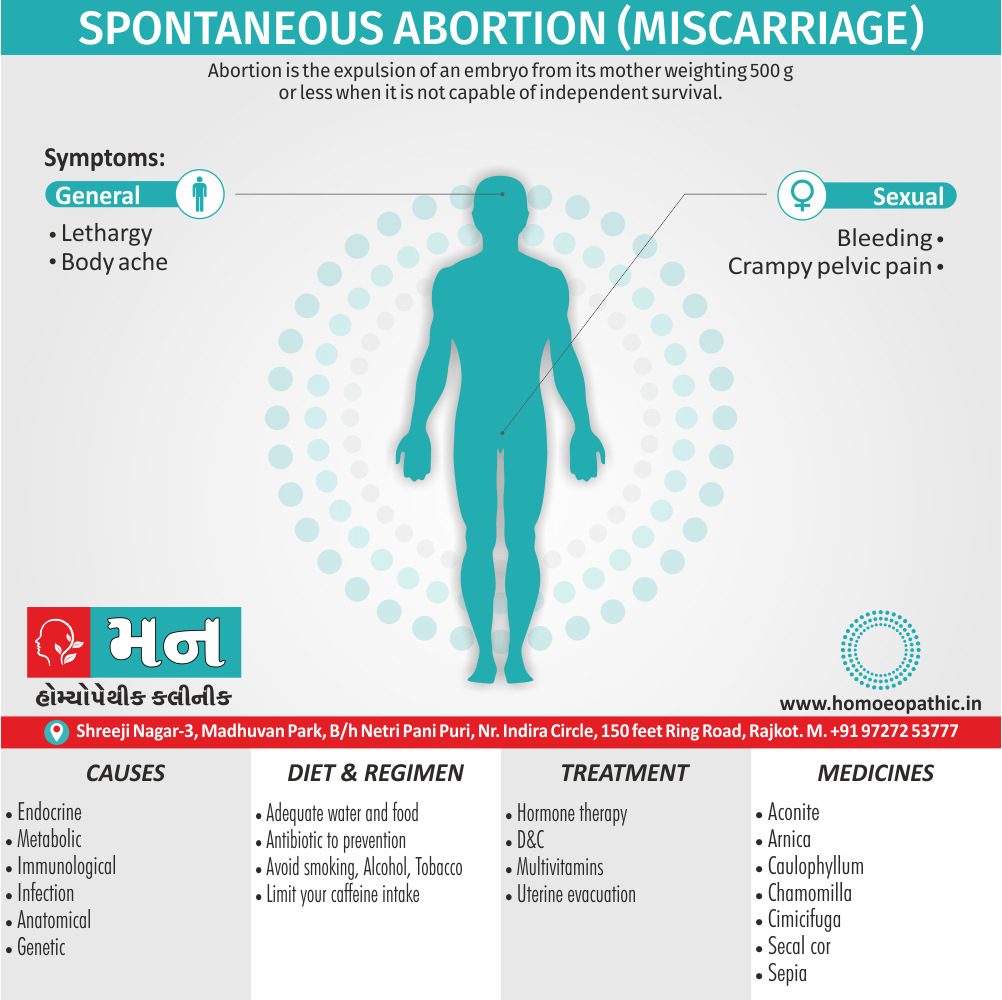
- Should be given cautiously during the first 3 months of pregnancy- In low potency liable to produce miscarriage -Dr. Cowperthwaite.
- Apis for drug burns, iodine, chloroform etc. – Dr. Pulford. [6]
Sites of action / Pharmacodynamics
Mind, glands, brain, kidneys, bladder, skin, heart, serous cavities, eyes, ovaries, cellular tissues, etc.
Causation (Causes / Ailments from)
Shock, from bad news, disappointments, jealousy, rage, fright, vexation, suppressed urticaria, suppressed rash, getting wet.
Physiological action
- The main action of the poison is on the skin and on the nervous system.
- Affected part swells up, is hot and red, with a stinging, burning and itching sensation. Intense pain, skin appears like urticarial patches, red and shining; mucous membranes become inflamed and swollen, especially that of the eyes or loose tissues; urinary system gets inflamed with a burning sensation; scanty urine with a feeling as if there is a stricture in the urethra; rheumatic pain in the joints of the wrist, shoulders, etc.
- Sensorium is depressed; sleepy or drowsiness, sometimes unconsciousness.
Patho-physiological changes / Pathogenesis
- It acts on the nervous system; sensorium is depressed to the point of drowsiness, even to unconsciousness.
- It acts on the skin, mucous membranes, which get affected – swollen and inflamed; particularly in the eyes and where there is loose tissue; thus, it causes oedema and anasarca.
- Urticarial patches with burning, stinging; redness and a shiny surface of the skin are seen.
- Also acts on the urinary system producing inflammation; burning and scanty urine with a feeling of stricture in the urethra.
- Acts on the glands, causing induration and enlargement.
- It acts on the lungs that is, on the pleura and produces wet pleurisy.
- Acts on joints like wrists, shoulders, ankles, etc. producing rheumatic pains. [2]
Characteristic mental symptoms (psychology) of Apis Mellifica
- Patient is absentminded with impaired memory.
- Moaning and whining; weeping disposition, cannot help crying; discouraged and despondent.
- Patient is very restless, constantly changes his occupation.
- The patient is very nervous and irritable. They are fidgety and very hard to please. They are also sad and melancholic.
- Patient is very awkward, drops things while handling them.
- Very jealous, especially widows. Apathetic, listless, fault-finding, joyless.
- Indolent and suspicious.
- There is a kind of constricted feeling. Stretched, ‘tight feeling’; sensation in abdomen as if something is tight.
- Dreams full of care and toil, of flying through the air [2]
Guiding Symptoms of Apis Mellifica
Generalities of Apis Mellifica:
- The well-known effects of a bee sting; burning, stinging, smarting, prickling, lancinating pain, with excessive swelling; are the leading symptoms for the selection of this remedy.
- The well-known effects of a bee sting include burning, stinging, smarting, prickling, and lancinating pain with excessive swelling. These are the leading symptoms for the selection of this remedy.
- It acts on Cellular Tissue esp. of eyes, face, throat, ovaries, causing oedema of skin and mucus membranes.
- In the SEROUS MEMBRANES of heart, brain, pleura etc. it produces inflammation with effusion.
- Various parts are swollen, PUFFED UP; become oedematous and of shiny, red-rosy colour. The burning is like hot needles.
- There is great debility, as if he had worked hard; is compelled to lie down.
- Symptoms develop rapidly.
- The pains are sudden that extort cries.
- Sudden shrill Cries in hydrocephalus and meningitis.
- Extreme sensitiveness to touch and general bruised Soreness is marked; of brain; Abdomen; ovaries; bladder.
- Sensation of constriction.
- Sensation of stiffness and as of something torn off the interior part of the body.
- Great restlessness and fidgetiness.
- Trembling, jerking and twitching.
- One half of the body twitching, the other, boring or paralyzed.
- Neuralgia of lips, tongue, gums.
- Great prostration even to faintness.
- Infections.
- Ill effects of grief; fright; rage; jealousy; hearing bad news; mental shock; suppressed eruptions.
- Right side is affected more.
- Symptoms go from right to left.
- Numbness.
- Thrombosis.
- Lymphangitis.
- Inflammation of kidneys, bladder.
- Oedema; of eyelids, of lips; red, succular.
- BURNING
- itching.
- Paralysis after dipheria and other severe diseases.
- Worse – Heat of room; of weather; of fire; hot drinks, bath, bed.
- Touch, even of hair.
- Pressure. [2]
Head of Apis Mellifica:
- Brain feels very tired.
- Vertigo, with sneezing worse lying or closing eyes.
- Sudden stabbing in head, or as of a blow worse occiput, with occasional Sharp Shrieks.
- Numb, tired headache better pressure.
- Flow of tears, with headache.
- Rolling of the head from side to side in hydrocephalus; boring of the head backward in pillow in meningitis.
- Fontanelles sunken Painful hair.
- Musty head sweat. Inability to hold the head, in meningitis.
- Head feels swollen.
- Hair falls out; bald spots. [3]
Eye of Apis Mellifica:
- Puffy; lids or conjunctiva red; oedematous like water‐bags, red, chemosed.
- Hot lachrymation.
- Eyes brilliant.
- Burning, stinging, shooting pain in.
- Staphyloma of cornea.
- Bag like swelling under eyes.
- Photophobia, yet covering intolerable.
- Blindness better stool.
- Squint.
- Myopia.
- Puffy or red about eyes.
- Cannot look fixedly at any object; or cannot read in artificial light.
- Cornea opaque.
- Styes prevents their recurrence.
- Perforating corneal ulcer. [3]
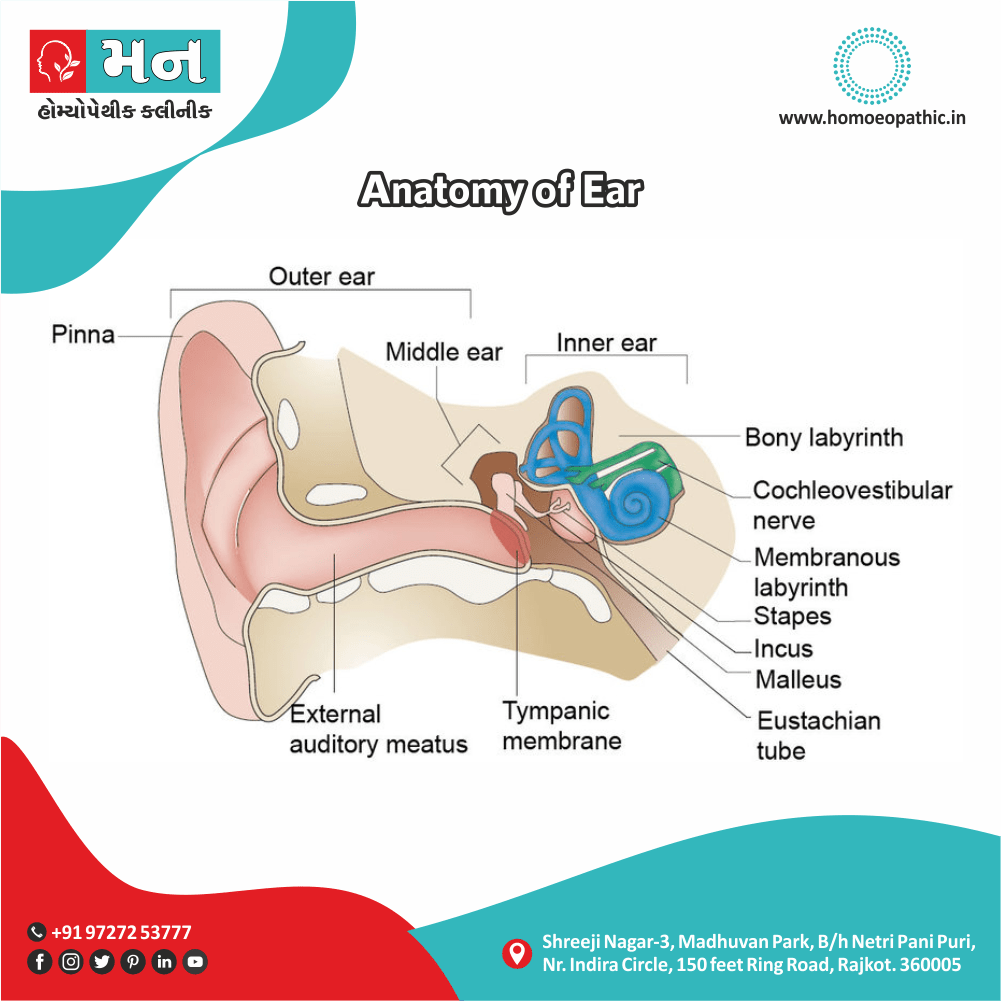
Ears of Apis Mellifica:
- External ear red and inflamed.
- Raises the hand to the back of ear with each scream.
- Scarlatinal otitis.
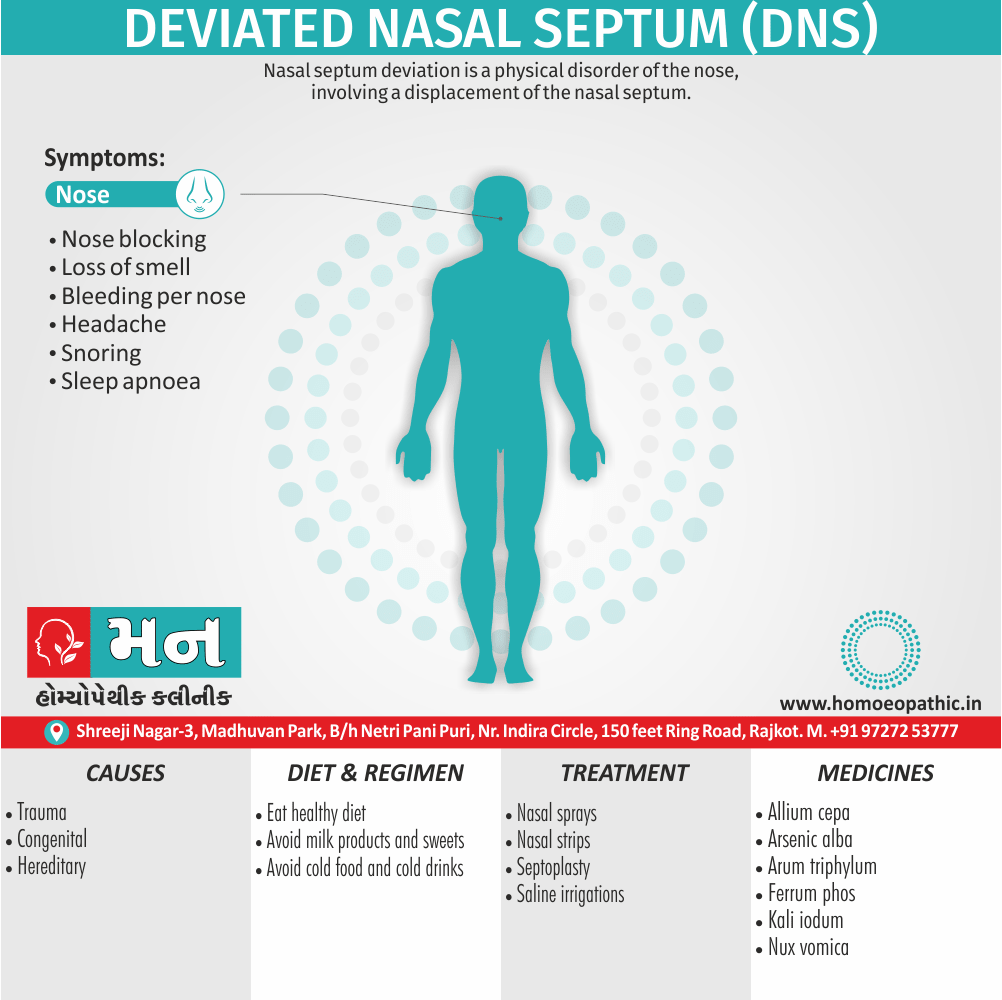
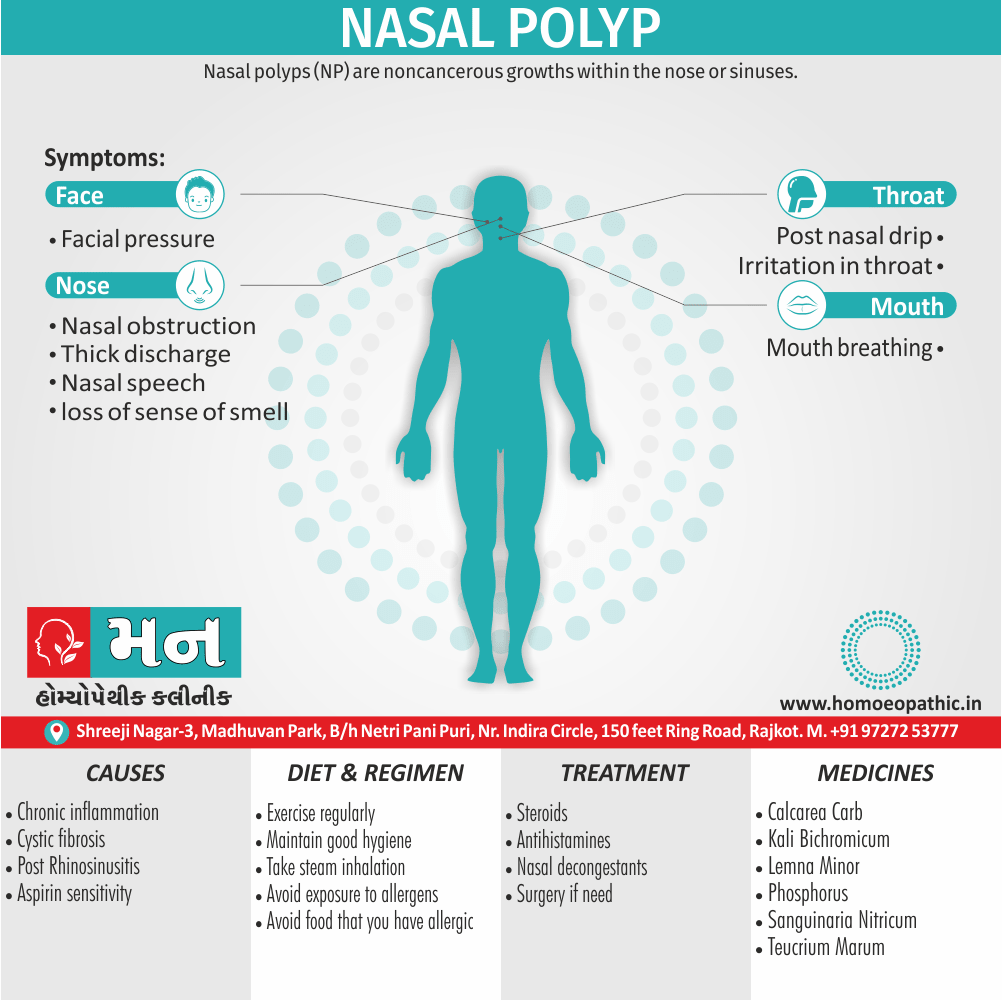
Nose of Apis Mellifica:
- Swollen, red and oedematous.
- Nose and tip cold. Boils in nostril better cold.
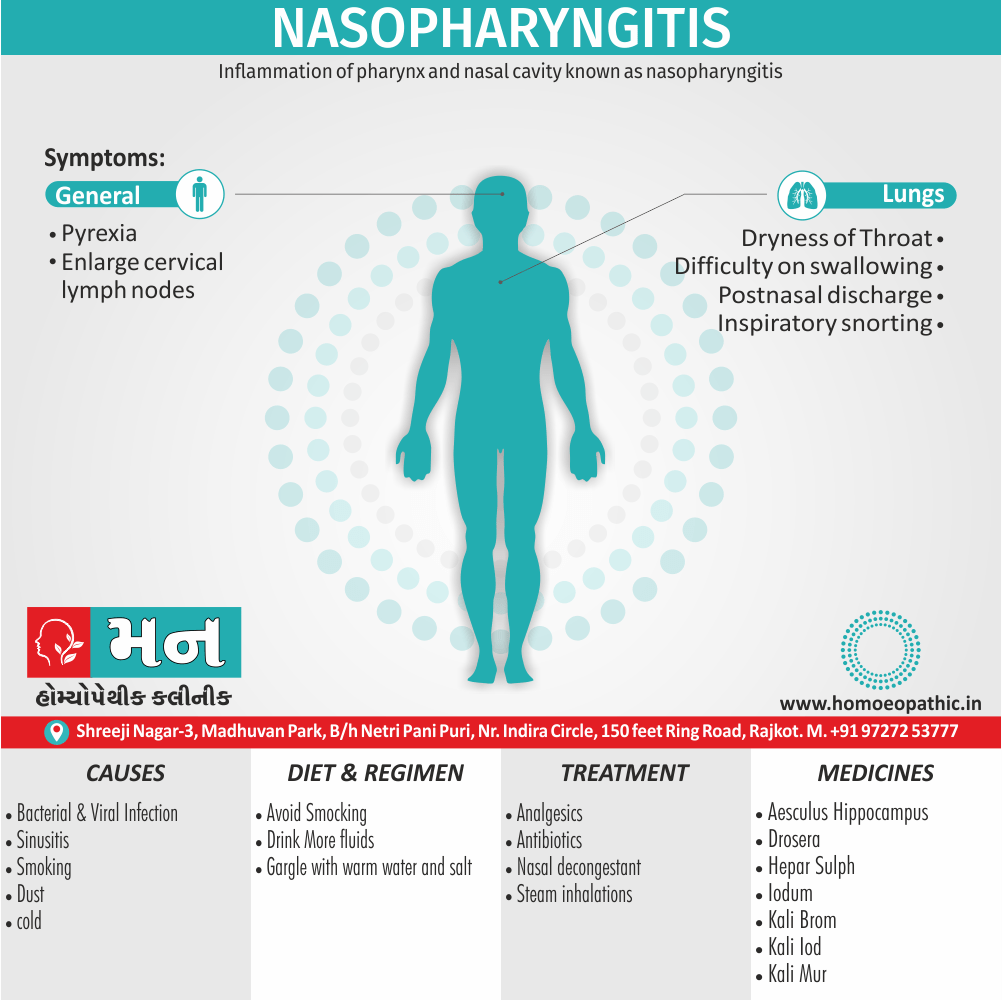
- Coryza, with feeling of swelling in nose. [4]
Face of Apis Mellifica:
- Expression; happy, terror stricken or apathetic.
- Face red, hot, swollen and oedematous with piercing pains; or waxy pale and oedematous.
- lips; bluish, oedematous, upper.
- Jaws stiff, with stiffness of tongue.
- Paralysis of right side, with right eye closed.
- Desire for washing face with cold water.
- Formication and prickling in face. [4]
Mouth of Apis Mellifica:
- Tongue; red or vesicles on edge; swelled, raw; feels, as if burnt; as if wooden; sore; stiff.
- Grinding of the teeth.
- Mouth glossy as if varnished.
- Tongue hangs out; or cannot be protruded.
- Sudden involuntary biting teeth together.[3]
Throat of Apis Mellifica:
- Sandy, glossy or translucent amel.
- Cold, swollen inside and outside, Throat purple.
- Tonsils; swollen, fiery red, stinging pain, while swallowing, amel.
- Cold drinks.
- Angina.
- Diphtheria with early prostration; dirty membrane, oedema of uvula.
- Throat sore, swallowing painful agg.
- Solids, sour or hot substances.[3]
Stomach of Apis Mellifica:
- Thristless, with dropsy, Craving; from sour things, for milk, which amel.
- Child nurses by day, refuses at night.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Soreness in the pit of stomach when touched.
- Neither eats nor drinks; for weeks.
- Eructation; tasting of ingesta agg.
- Drinking water; flow of water [4]
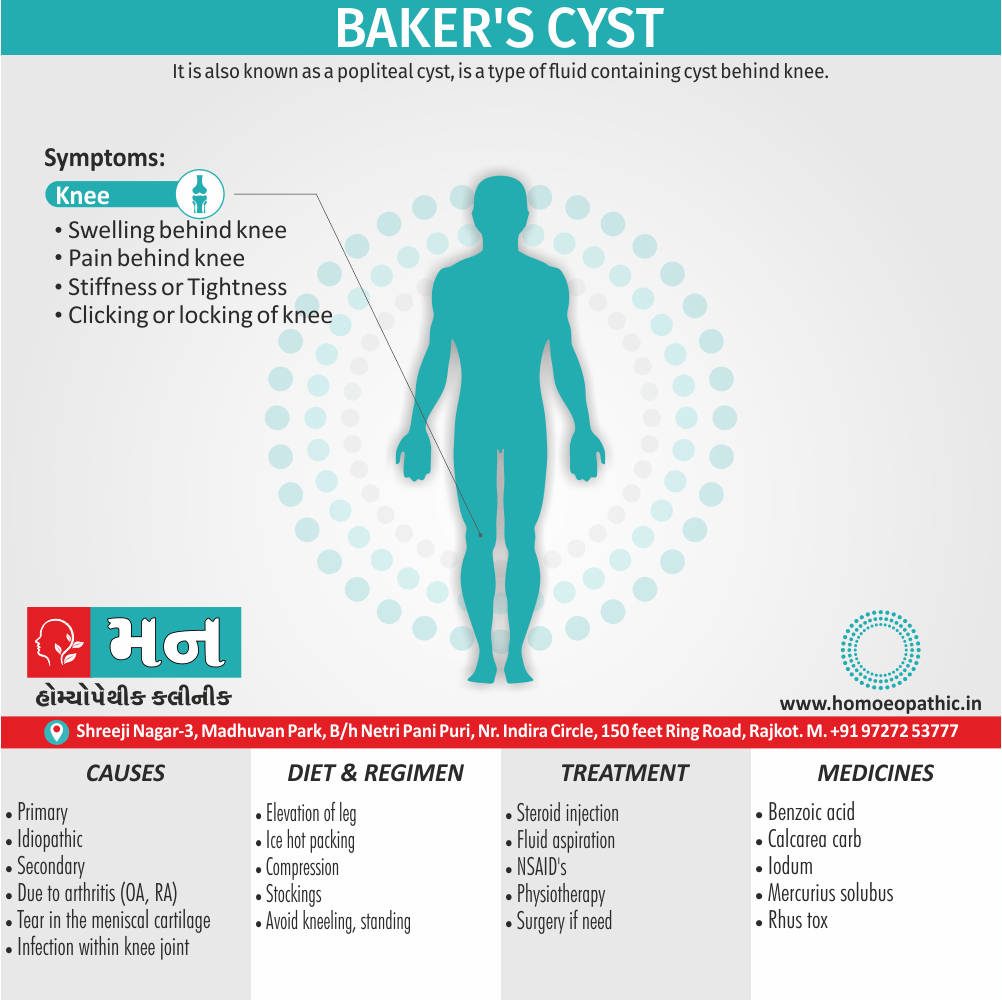
Abdomen of Apis Mellifica:
- Feels tight as if to break, straining at stool.
- Sore; bruised on pressure, when sneezing.
- Dropsy.
- Peritonitis.
- Diarrhoea; watery yellow, orange yellow or tomato-sauce like stools.
- Stools; odourless, or offensive, involuntary agg.
- Motion.
- Anus; sore, swelled, profuse haemorrhage from; remains open; prolapsus ani.
- Electric shocks in rectum before urging to stool.
- Burning, pain and tenderness in epigastrium.
- Pains from below ribs going upwards.
- Burning or soreness below ribs. [3]
Rectum & Anus of Apis Mellifica:
- Anus seems open.
- Anus is sore, swollen with profuse hemorrhage.
- Anus feels raw, remains open.
- Prolapsed anus.
- Hemorrhoids with stinging pain after confinement.
- Cholera infantum.
- Cannot urinate without a stool Constipation, feels as if something would break on straining.
- Feels tight as if to break, on straining at stool.
- Electric shocks in rectum before urging to stool. [5]
Stool of Apis Mellifica:
- Profuse haemorrhage from anus. Dark, fetid stool, worse after eating.
- Bloody, painless stools.
- Stools odourless. Stools, blackish-brown, green or whitish.
- Stools, odourless or offensive involuntary worse motion.
- Diarrhea, watery yellow orange-yellow or tomato-sauce like stools.
- Stools, olive-green, slimy.[5]
Urinary Organ of Apis Mellifica:
- Burning urination.
- Dysuria with stinging pains.
- Urine, scanty foul, high coloured; last drops burn and smart; milky in hydrocephalus.
- Albuminuria.
- Urine profuse, more than he drinks.
- Coffee ground sediment.
- Incontinence of urine worse night, coughing.
- Cannot urinate without a stool.
- Nephritis.
- Cystitis.
- Retention of urine in new born.
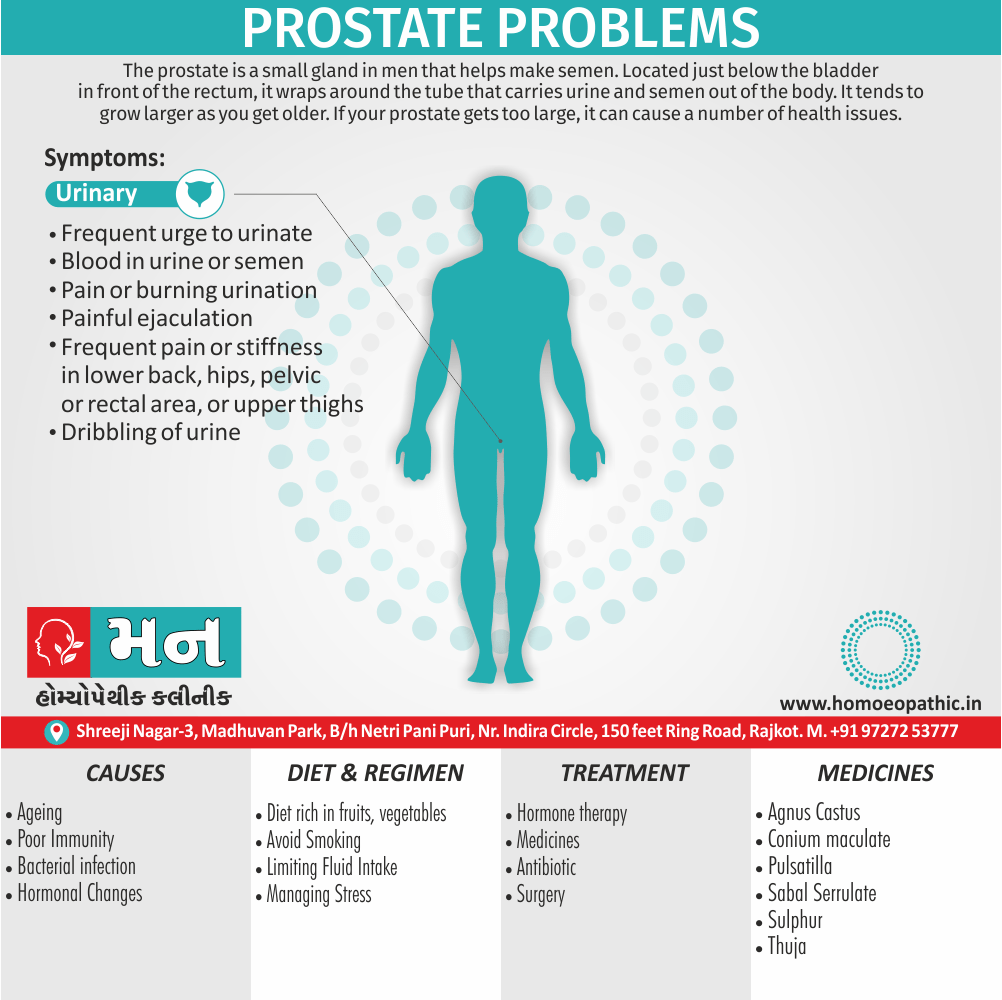
- Difficult, frequent or slow urination, must press to pass urine, in prostatic affections. [3]
Sexual Organ of Apis Mellifica:
Male
- Dropsy of the scrotum.
- Hydrocele, in multilocular cysts.
- Affections of prostate gland
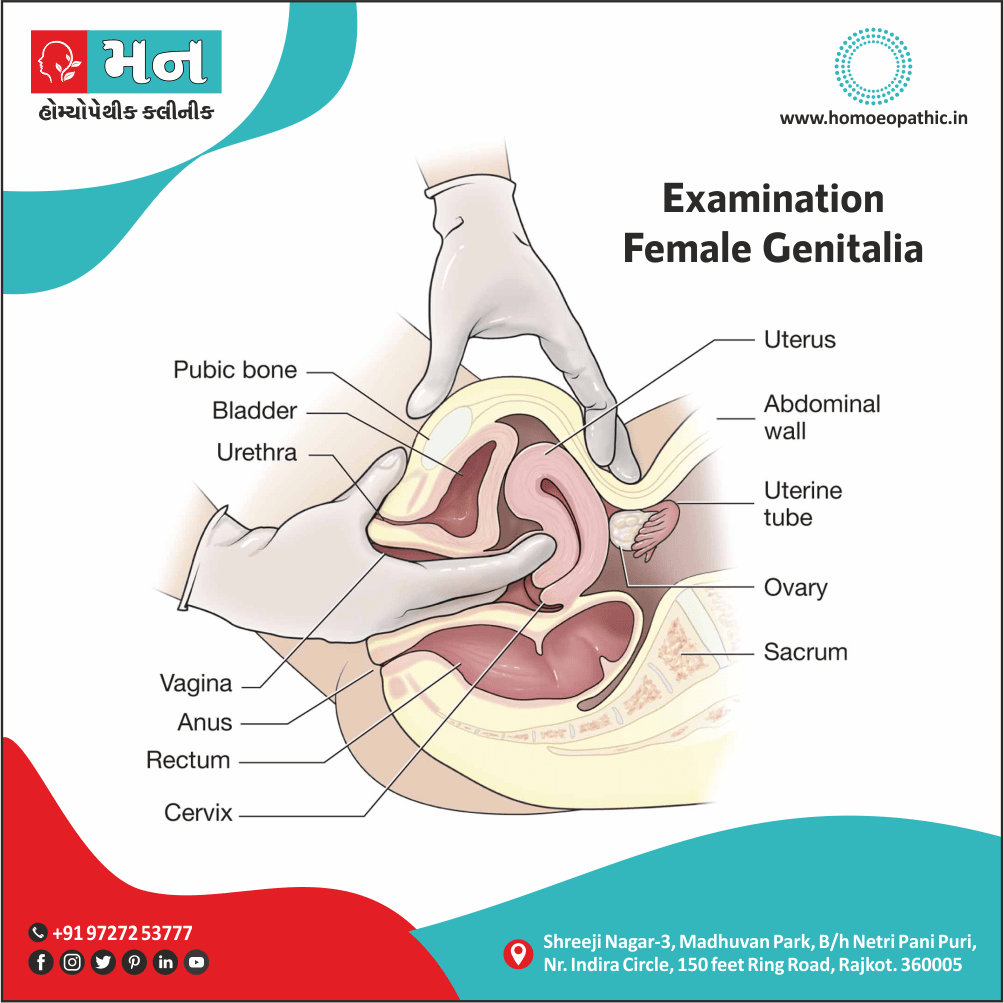
Female
- Amenorrhoea of puberty.
- Ovaries; numb, or congested, with suppressed menses. Ovarian cysts.
- Oedema of labia.
- Burning, stinging pains in ovaries or uterus.
- Dysmenorrhoea, with scanty discharge of slimy blood or with ovarian pains.
- Menorrhagia, with abortion.
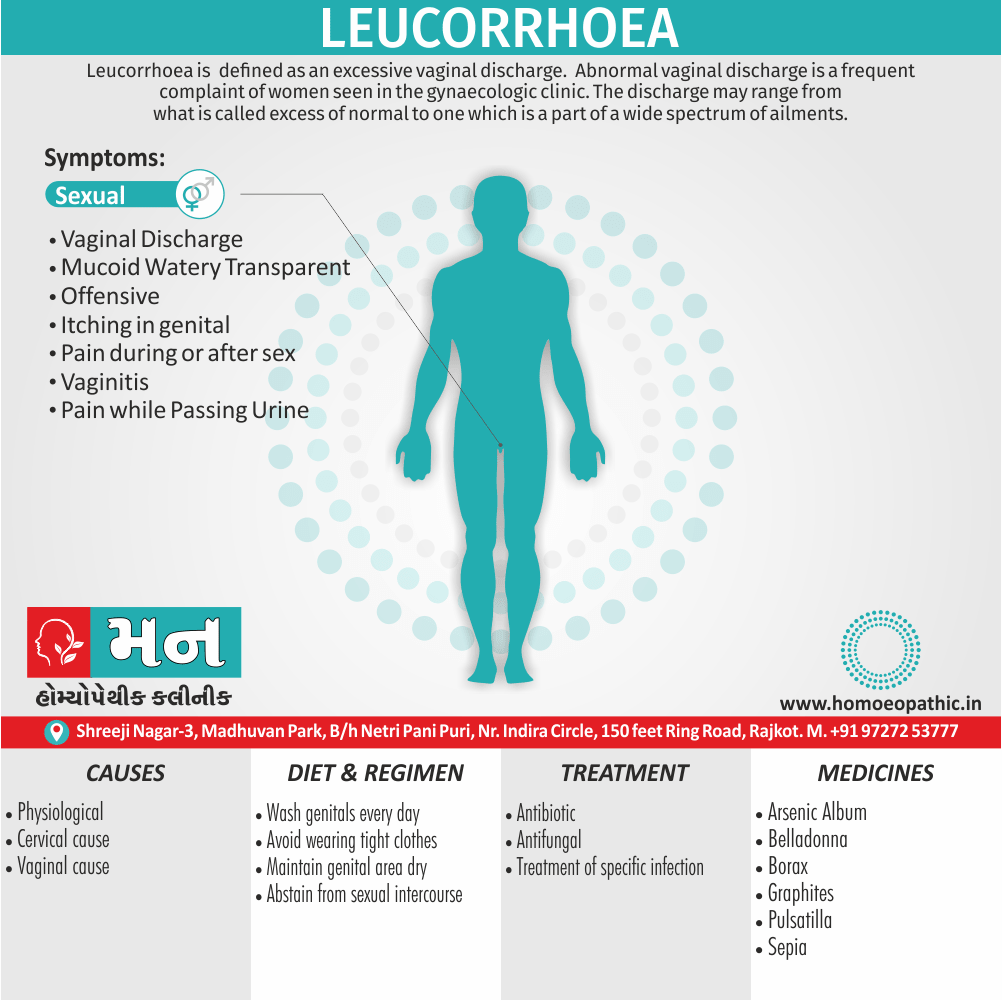
- Leucorrhoea; profuse, acrid, green.
- Stinging burning pains in mammae.
- Tumour or open cancer of mammae.
- Abortion, during early months.
- Dropsy in later parts of pregnancy, with puerperal convulsions. Mania in women from sexual excesses or suppressed menses. Pain in ovaries agg. coition.
- Menses last a day or appear at intervals of one day.
- Ulceration of navel in new born [4]
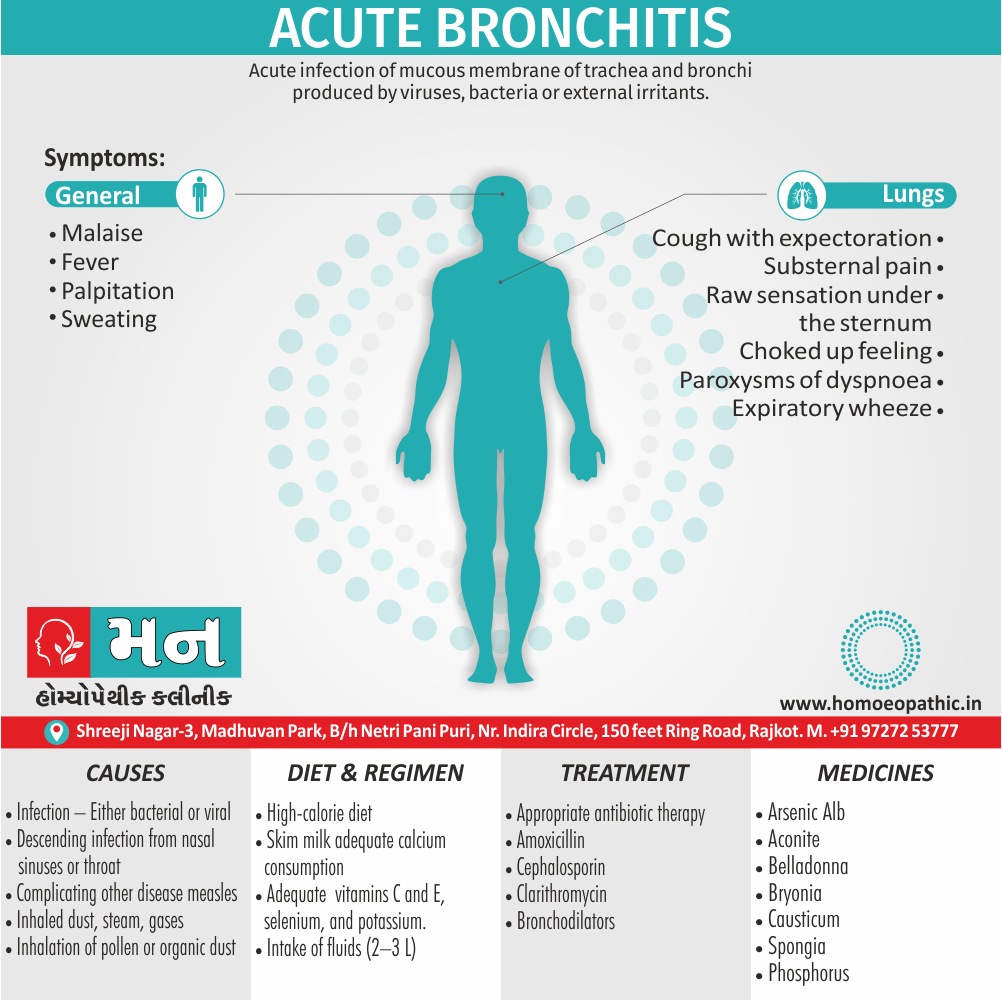
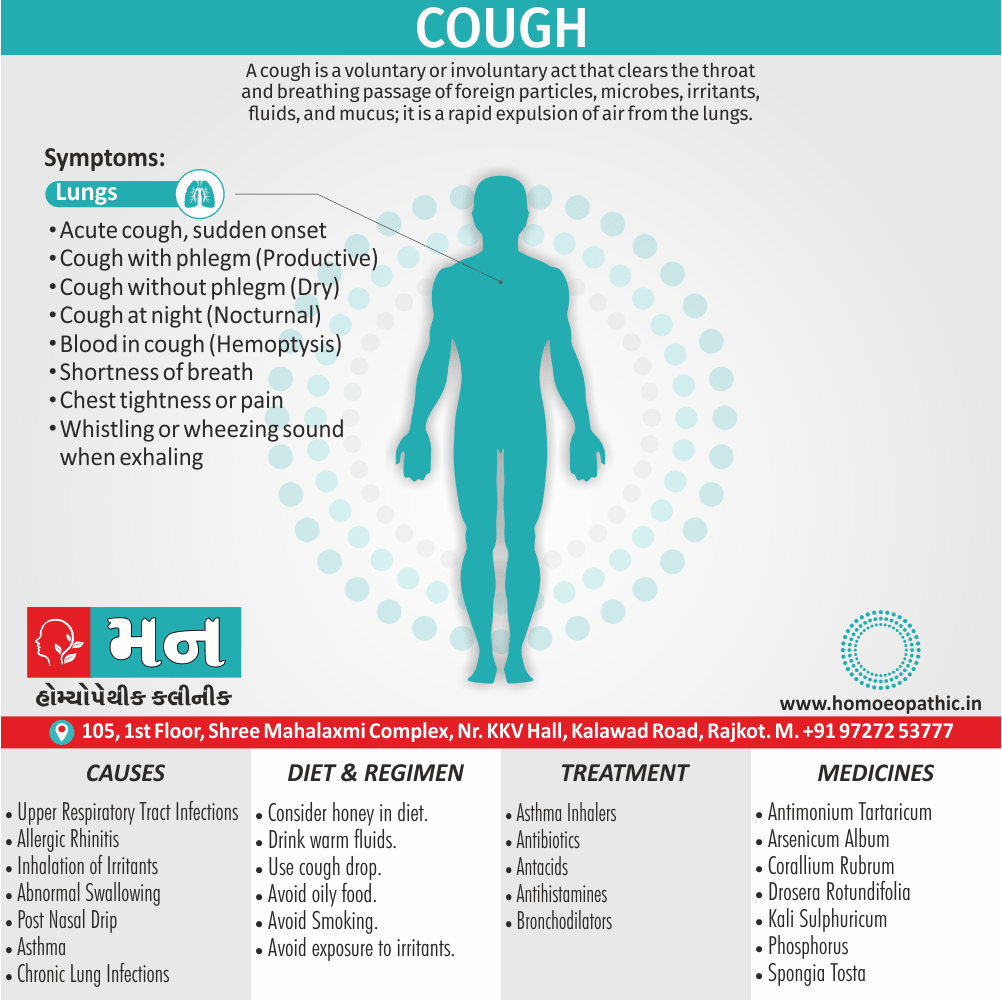
Respiratory System of Apis Mellifica:
- Panting breathing, feels every breath would be his last.
- Air hunger.
- Oedema of larynx.
- Burning stinging pains throughout entire front of the chest.
- Hydrothorax, after pleurisy.
- Chest feels as if beaten or bruised.
- Painful shock in head and chest from every cough.
- Asthma, from hives amel. small quantity of expectoration.
- Larynx drawn in.
- Hoarseness.
- Expectoration sweetish [3]
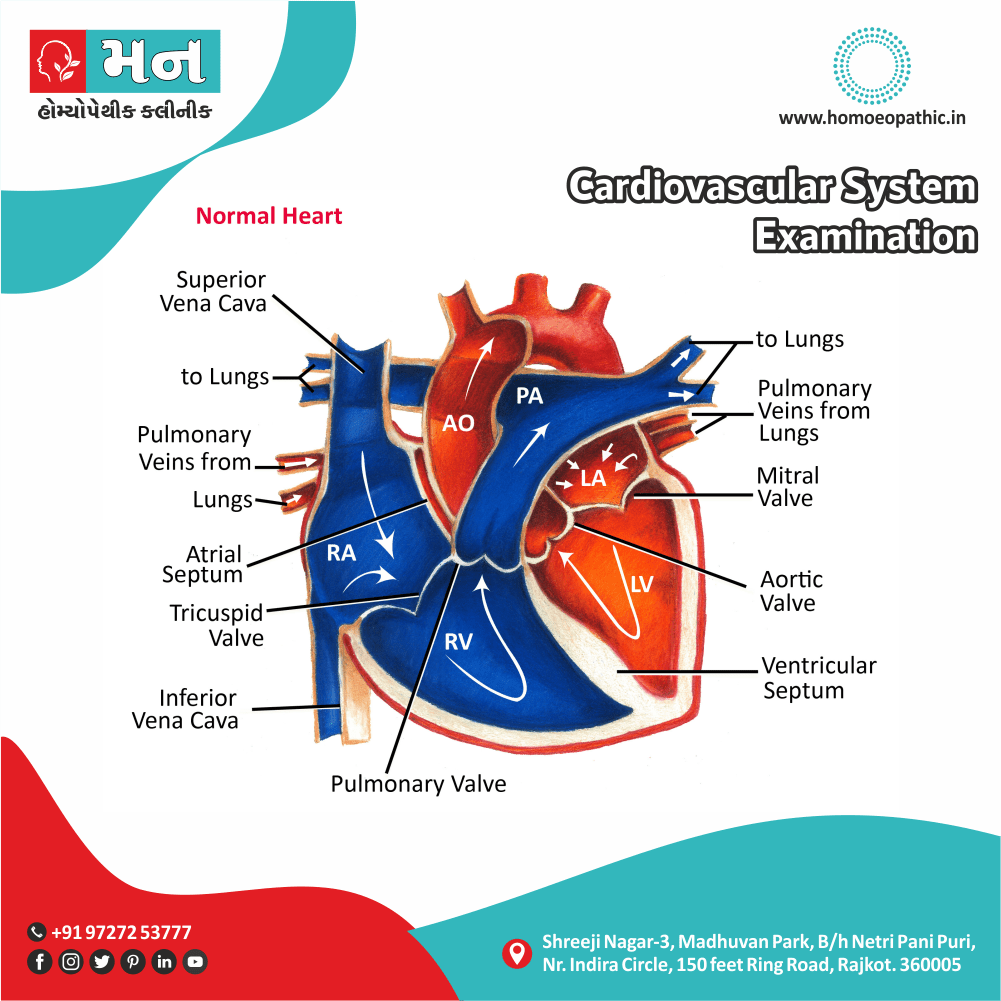
Heart & Pulse of Apis Mellifica:
- Beats, shake the whole body.
- Heart stitches backward from apex.
- Palpitation of heart from scanty secretion of urine.
- Pulse; hard small, intermittent, and quick, weak.
- Insufficient of mitral vales.
- Organic heart disease [3]
Neck & Back of Apis Mellifica:
- Back of the neck stiff.
- Rheumatic pain in back.
- Burning pressing in coccyx worse when sitting down.
- Back tired and bruised.
- Vascular goitre. [4]
Extremities of Apis Mellifica:
- Numbness of hands and tips of fingers.
- Palms hot.
- Oedema of hands.
- Person who has been incarcerated. in the beginning, with burning stinging throbbing pains. Limbs; immovable, heavy, numb.
- Feet numb and stiff.
- Legs and feet waxy, pale swollen oedematous.
- Trembling of hands and feet.
- Nails feel loose.
- Hemiplegia from severe mental shock.
- Staggers when eyes are shut.[3]
Skin of Apis Mellifica:
- Rosy red, sensitive, sore.
- Rough eruptions or stinging‐like spots on skin.
- Large urticaria.
- Skin dry; hot, alternating with gushes of sweat.
- Oedematous swellings.
- Erysipelas.
- Scarlatina.
- Carbuncles. [4]
Sleep of Apis Mellifica:
- Great Inclination to Sleep; but cannot sleep from nervous restlessness.
- Drowsiness during fever.
- Dreams, during sleep and suddenly starts from sleep.
- Kicks off covers during sleep.
- Dreams full of care and toil. [3]
Fever of Apis Mellifica:
- Chill; anticipating, with dyspnoea, urticaria, desire to uncover; alternate with heat.
- Burning Heat, but chilly when moved.
- Thirstless during fever.
- Heat of one part with coldness of another.
- Sweat in gushes, partial.
- Sweat breaks out and dries frequently.
- Thirst during chill.[3]
Important characteristic feature
Keynotes / Redline:
- Oedematous, puffy bag like swelling under the eyes.
- Dropsy without thirst, and fever with thirst. Sensation as though anus was wide open in diarrhoea.
Guiding:
- All complaints aggravated by heat and better by cold application.
- Pains-burning, stinging lancinating, with excessive swelling, with redness and swelling and pain in eyes, eyelids, ears, face, lips, tongue, anus, throat, testicles.
- Trembling jerking and twitching of one half of the body. Hemiplegia.
Most often the RIGHT side is affected. Symptoms proceed from right to left.
Great SENSITIVENESS to touch with a general soreness, even the touch of hair is painful.
- Anasarca with thirstlessness. But intermittent chill at 3 p.m. with thirst.
Head-Menopausal flushings of heat. - Herpes zoster of face, especially of the left side.
- Angioneurotic oedema with tense swelling of the face, lips, tongue and larynx.
- Eyes-Recurrent suppurating styes.
- Swelling around the eyes.
- Conjunctival swelling.
- Throat-Pharyngitis > cold drinks.
- Pharyngitis with bag-like swelling of the uvula.
- Throat pain extends to ears.
- Angioneurotic oedema.
- G.I.T.-Constipation as if something would break on straining.
- Diarrhoea with involuntary stools on every motion.
- Anus seems wide open.
- Cholera infantum, Prolapsus ani.
- Haemorrhoids with burning, stinging pains with profuse bleeding.
- Chest-Pneumonia, Pleurisy.
- Extreme pain on inspiration.
- Feels he cannot take another breath.
- Female genitalia-Ovarian cysts (right) in women,
- especially widows with specific pains.
- Female complaints with soreness and stinging pains.
- Oedema of labia > cold water.
- Dysmenorrhoea with scanty, slimy blood, sensation of tightness in abdomen.
- Leucorrhoea profuse, acrid, green.
- tumours or open cancer of mammae.
- Abortion in early months.
- Eczema, urticaria, carbuncles with burning, stinging pains.
- Urticaria with burning pains.
- Eczema with marked swelling > cold applications.
- Sleep-Great drowsiness with all complaints.
- C.N.S.-Hydrocephalus, meningitis. < heat. [6]
PQRS:
i) Constipation; sensation in abdomen as if something tight would break if much effort were used.
ii) Intermittent fever; chill at 3 P.M., always with thirst (Ign.).
1) Cellular tissue: Apis produces oedema & It produces irritation which leads to inflammation. dropsy.
2) Skin: It has irritant action on skin lead to carbuncle, urticarious inflammation, erysipelas.
3) Serous membrane: Apis affects the serous mem brane of the brain, chest, abdomen & testes results meningitis. hydrocephalus, pleurisy, hydrothorax, ascites & hydrocele.
4) Mucous Membrane: It affects the throat which causes diphtheritic infiltration, congestion i.e., inflammation & oedema of the uterus & ovary.
5) Glandular System: It produces enlargement & induration of the gland & causes hypertrophy.
6) Uro-genital Organs: It produces acute inflammation of the kidney & bladder.
7) Nervous System: It acts on motor nerves & produces weak & wearied condition. In the sensory nerves produce irritability & hypersensitiveness. [1]
Confirmatory:
- Hot patient
- Thirstlessness
- Right sided
- Oedematous, dropsical states
- Burning and stinging pains > cold [6]
Nucleus symptoms:
- Jealous, suspicious, awkward, intense women especially widows with A/F rage, vexation, bad news, jealousy.
- Burning, stinging, sore pains > cold water.
- Pains migrating. [6]
- Oedematous puffiness, swellings local or general, without thirst, but fever with thirst – 3 p.m.
- Associated strangury or urinary complaints.
Therapeutic value
- Abscesses
- Anasarca
- Asthma
- Boils
- Bright’s disease
- Cancer
- Constipation
- Convulsions
- Diarrhoea
- Diphtheria
- Dysuria
- Eye troubles
- Gangrene
- Hydrocoele
- Kidney affections
- Malarial fever
- Meningitis
- Menstrual disorders
- Retention of urine in nursing infants
- Rheumatism
- Skin diseases
- Tonsillitis
- Typhoid fever
- Urinary complaints. [6]
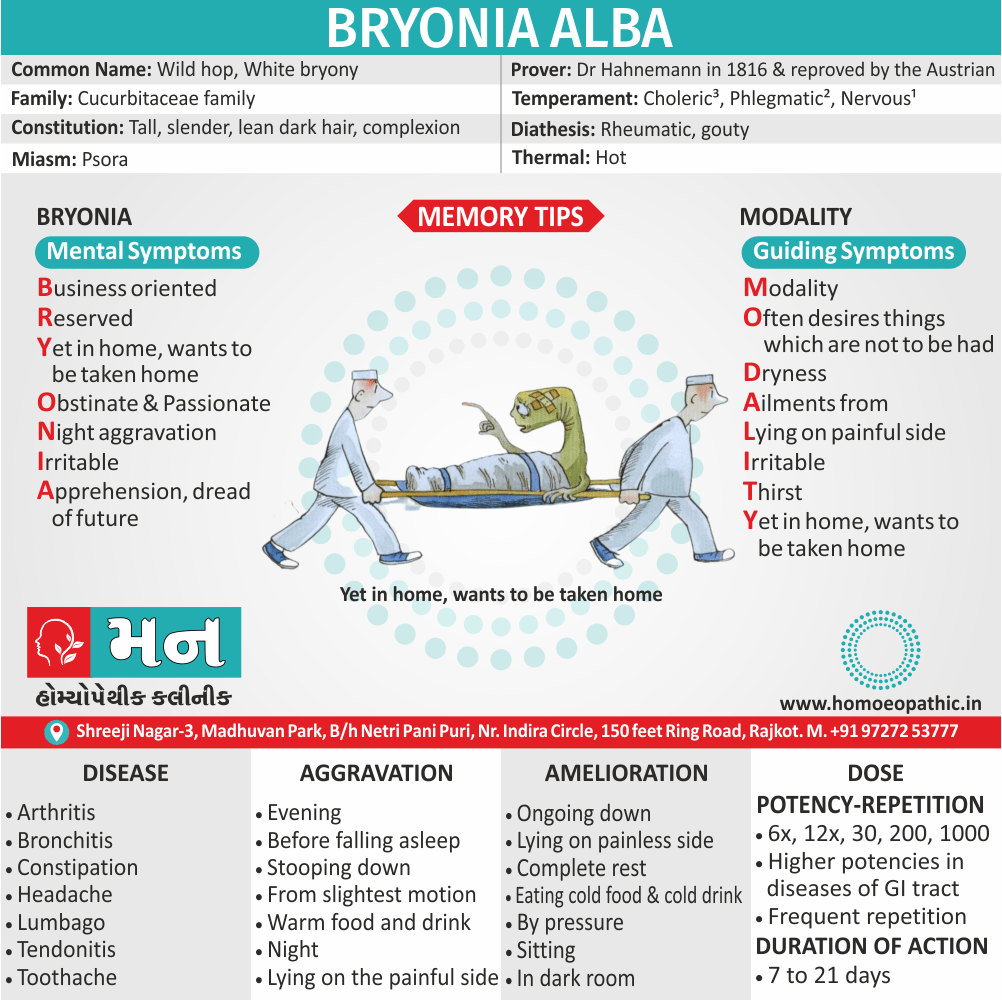
Modality
- Aggravation: Worse from heat, hot bath, by lying down, after sleep, afternoon at 3 pm, in a hot and warm room, from touch, pressure, getting wet.
- Amelioration: Cold applications, cold bathing, open air, changing position, uncovering, getting erect, cool open air, expectoration, cold water. [2]
Remedy Relationship
Complimentary
Ars, Puls, Nat-m
Follows Well
Puls, Ars
Inimical
Rhus-t
Antidoted By
Ip, Lach, Led, Nat-m
It Antidotes
Canth, Chin, Dig, Iod
Comparison
Acet-ac, Acon, Anac, Apoc, Arn, Ars, Bell, Brom, Bry, Canth, Cinch, Colch, Croto-t, Euphr, Ferr, Graph, Hep, Hyos, Iod, Lach, Lyc, Merc, Nat-a, Nat-m, Puls, Rhus-t, Rumx, Sabin, Sep, Sil, Urt-u, Vesp, Zinc. [2]
Posology (Dose)
Potency
3x, 6x, 12x, 30, 200, 1000. [2]
Repetition
It gives good results from 6c to 200c
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. Apis Melifica is used for which diseases?
Ans. In Homeopathy Apis Mellifica medicine use by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of following Disease Conditions:
- Abortions, Angioneurotic oedema, Arthritis, Cystitis, Herpes zoster, Meningitis, Nephritis, Pharyngitis, Pleurisy, Pneumonia, Pyelonephritis, Urticaria.(6)
Q 2. From which source the medicine Apis Melifica is prepared?
Ans. From poison of the honey bee.
Q 3. How can you know that Apis. has acted esp. in a urinary case?
Ans. Increased flow of urine shows that it is producing a favourable effect.
Q 4. Discuss the skin symptoms of Apis mel.
Ans.
1) Causation: -Due to imperfectly developed or suppressed acute exanthema, such as measles, urticaria, scarlatina etc.
2) Look of the skin: –
i) White and almost transparent-waxy, pale.
ii) Oedematous.
iii) Alternate sweat & dryness of the skin (Nash).
3) Urticaria:
i) Looks like bee stings, red, swollen and
ii) Great sensitiveness to touch and Urticaria esp. during chill (Kent).
iii) Intolerable itching agg. at night amel. by cold.
iv) Rash of rosy colour (Kent).
v) Urticaria esp. after violent exercise (Apis., Calc. sulph., Nat. mur.).
4) Oedema: Oedematous condition of the face. [1]
Q 5. What is strumous constitution?
Ans. It’s an old term and denotes any enlargements, characterized by scrofulous swelling.
Q 6. In your house your maid is constantly breaking the crockeries as they fall out of her hand: what are the medicines you can think of?
Ans. i) Apis mel. ii) Natrum mur. iii) Bovista.
Q 7. Mention three medicines for bad effects of suppressed exanthema?
Ans. i) Apis mel. ii) Bryonia. iii) Helleborus.
Q 8. Mention two medicines for oedema.
Ans.
i) Oedema under the eyes: –
ii) Oedema around the eyes-Phosphorus.
Q 9. Mention three medicines for extreme sensitiveness to touch.
Ans. i) Apis mel. ii) Belladonna. iii) Lachesis.
Q 10. Name five right-sided medicines.
Ans.
i) Ammon. carb.
ii) Apis mel.
iii) Causticum.
iv) Lycopodium.
v) Podophyllum.
Q 11. Mention two medicines for craving for cold milk.
Ans. i) Apis mel. ii) Rhus tox.
Q 12. Mention the uncommon-peculiar symptoms of Apis.
Ans.
i) Constipation, sensation in abdomen as if something tight would break if much effort were used.
ii) Intermittent fever, chill at 3 P.M. always with thirst.
Q 13. Describe the pain symptoms of Apis.
Ans.
i) Onset: –
ii) Character: -a) Burning. b) Stinging.
iii) Radiation-Suddenly migrate from one part to another.
iv) Modalities: –
- Agg. from sleep, in warm room, moistening the part with cold water.
- Amel. in open air.
v) Concomitant-Soreness of the affected part.
Q 14. Mention the tongue symptoms of Apis.
Ans.
i) Fiery red tongue.
ii) Swollen and sore feeling.
iii) Tongue feels scalded.
iv) Some author suggests-clean tongue (Cina, Ipecac.).
Q 15. State the child symptoms of Apis mel.
Ans.
i) Sudden shrill, piercing screams from children while wake or during sleep.
ii) Children awake suddenly, screaming and grasping sides of cradle, without apparent
iii) Irritable; nervous fidgety; hard to please.
iv) Weeping disposition; cannot help crying.
v) Children who though generally careful, become awkward, and let things, fall while handling them.
Q 16. Name three medicines where headache is >by pressure or tight bandaging.
Ans. i) Arg. nit. iii) Apis mel. iii) Puls.
Q 17. Name three medicines where eyes are agglutinated in the morning.
Ans. i) Arg. nit. ii) Apis mel. iii) Rhus tox.
Q 18. Mention two medicines where patient awakens often from cold limbs and suffers from coldness at night.
Ans. i) Apis mel. ii) Carbo veg.
Q 19. Mention five medicines where urticaria results esp. after violent exercise.
Ans. i) Apis mel. ii) Calc. carb. iii) Hep. sulph. iv) Nat. mur. v) Urtica Urens.
Q 20. State the oedema of Apis mel.
Ans.
i)Oedema: bag like puffy swelling, under the eyes.
ii) Oedema of hands & feets; without thirst.
iii) Dropsy after scarlatina (Hell, Lach.).
iv) Dropsy from suppressed exanthemata (Hell., Zinc.).
v) Note: Colchicum often cures in dropsy after Apis. and Arsenic alb. has failed.
Q 21. State the diarrhoea of Apis mel.
Ans.
a) Causation:
i) After suppression of eruptive diseases.
ii) From taking alcohols.
iii) From jealousy, rage and vexation etc.
b) Character of the stool:
i) Stool is watery, greenish, yellowish, offensive.
ii) Stool slimy, contains bloody mucus. Involuntary with every motion, as if anus remains wide open.
c) Before stool: -Sudden darting pain in rectum, with rumbling of flatus.
d) During stool: Gripping tenesmus and rawness & soreness in the anus.
e) After stool: -Burning & stinging pain in rectum.
f) Concomitants:
i) Thirstlessness.
ii) Craving for cold milk.
iii) Bag like swelling on the lower eye-lids.
iv) Burning, stinging pain in the rectum.
- Synoptic Memorizer Materia Medica Part 1⇒ Chap Apis Melifica
- J.D. Patil Materia Medica⇒ chap Apis Melifica
- PHATAK S. R., Materia Medica of Homeopathic Medicines⇒ Chap Apis Mleifica
- MM of Homeopathy Medicine By pathak ⇒ Chap Apis Melifica
- Nature’s Materia Medica by Robin Murphy, Md ⇒ Chap Apis Melifica
- Zomeo Lan version⇒ Materia medica⇒ chap Apis mellifica ⇒ Keynotes