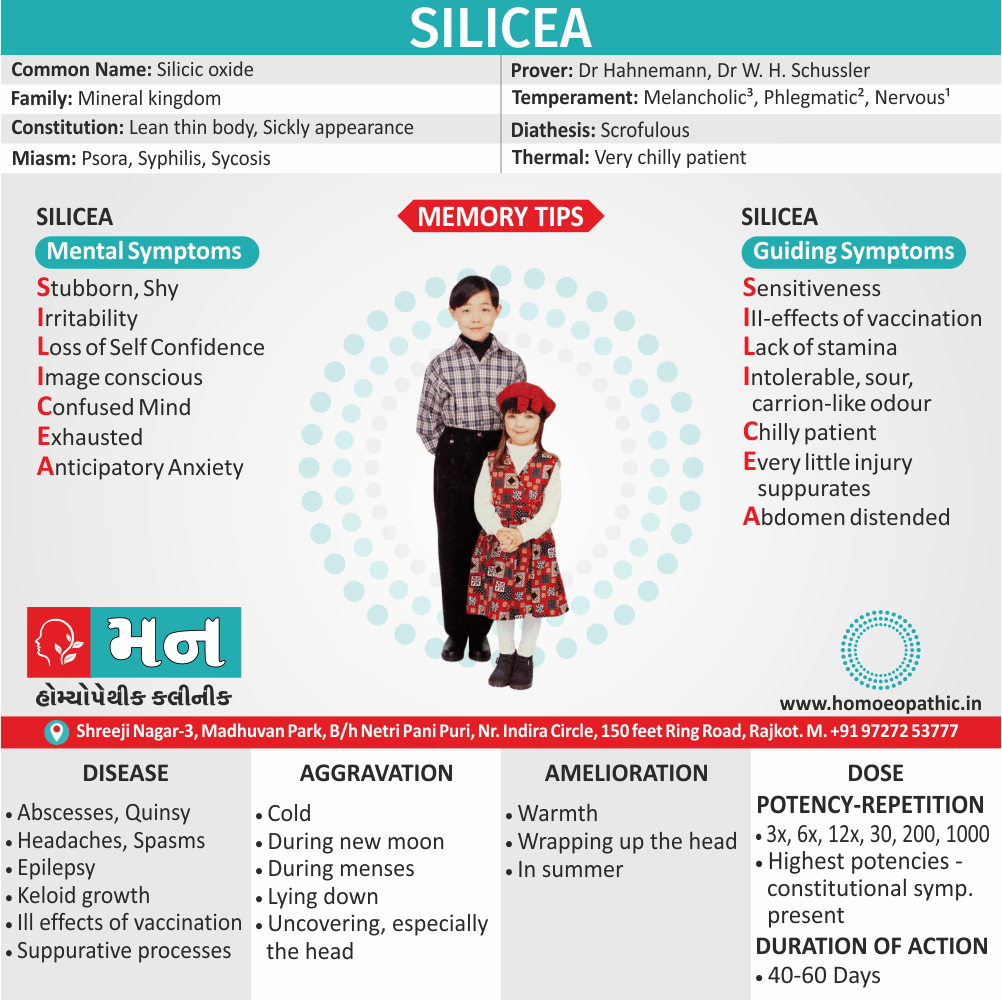
Silicea
Definition
Silicea, in homeopathic medicine, is also known as:
- Silica: This is the most common synonym and refers to the chemical compound silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
- Pure Flint: This is the source material from which homeopathic Silicea is often prepared.
It is important to note that while these are synonyms, they are not always interchangeable. When referring specifically to the homeopathic remedy, Silicea is the preferred term.
In addition to these synonyms, Silicea is sometimes referred to by its common name, "The Surgeon’s Knife," due to its ability to promote the expulsion of foreign objects from the body and to heal wounds.
Overview:
S
I
L
I
C
E
A
S
Stubborn, Shy
Children are obstinate, headstrong, cry when kindly spoken to.
Shy, refuses to answer, instead whispers to the mother. (3)
I
Irritability
Irritable and irascible when aroused; when let alone he is timid, retiring, wants to shirk everything; mild, gentle, tearful women. (6)
L
Loss of Self Confidence
Loss of self confidence; dreads failure, but unfounded.(8)
I
Image conscious
Silicea people stand defiant, obstinate, and try to retain the fixed image they have created for themselves.
The most important feature of a Silicea person is his concern: What do others think about me.
It is not important that people should think of him as a good or a nice person (in Palladium there is longing for the good opinion of others), but that he is thought of in a particular way, in a fixed manner–(5)
C
Confused Mind
Confusion of mind; difficulty in fixing the attention.(9)
E
Exhausted
Nervous exhaustion coming on from business brain-fag, but more for such brain-fag as belongs to professional men. (5)
A
Anticipatory Anxiety
Anxious conscientiousness over small details.
Stage fright, performance anxiety, test phobia, conscious about self image. Want of self-confidence. Irresolution. Timid.
Fears public speaking, examinations.
Complaints from long mental exertion. Brain fag. (3)
S
I
L
I
C
E
A
S
Sensitiveness
Dr. John Henry Clarke reported that the sensitiveness of Silicea is one of its keynote.
This is a state of an over-susceptibility to nervous stimuli is a frequent accompaniment of conditions-requiring Sil..
The surface to tender and the least touch is painful.
The senses are morbidly keen.
Brain and spine even can’t bear the ordinary vibrations.
Dr. Clarke has clearly emphasized that the condition may be caused by losses of fluids an in spermatorrhoea, or due to over-worked brain.
Dr Harvey Farrington said the special senses rendered more acute. The pts restless, and fidgety is marked: easily made anxious by nose or the confusion of much company.
Sudden or unexpected sounds cause him to start violently: every jar or jolt hurts his head, causes roaring in the ears, or Increases the pain in his spine Ulcers, abscesses and other lesions and in some cases, the entire surface of the skin are sensitive to touch, he s oversensitive to pain, wherever located.
I
III-efforts of vaccination
Silicea is one of our leading remedy to cope with the consequences of bad-effects of vaccination (Maland, Sulph, Thuja, others, Ant Tart, Mex, Crot Hor, Variol, Vaccininum.).
Note: For bad-effects of vaccination, when Thuja fails and Silicea is not indicated, AntIm Tart. to be thought of.
L
Lack of stamina
Dr. Clarke said, want of grit, moral or physical is a leading indication for Silicea in homoeopathic practice. Master Kent said pt. lacks stamina.
i) In mental sphere: Master Kent elucidated it in a masterly fashion, a young man who has studied for years and is now nearing the end of his course, he dreads the final examination, i.e, the lack of stamina or confidence, yet he goes through them all right.
ii) In physical sphere: This state is characterized by great weariness and debility, wants to lie down (Ref. Allen). Constitutions which suffer from deficient nutritions, not because food is lacking in quality or In quantity but from Imperfect assimilation.
Note: Dr E B. Nash said, even the mind and nervous symptoms come into the general picture of "weakness", He la nervous, and irritable, weak, faint-hearted, yielding, giving up disposition, ‘grit-all-gone’ (Puls). In such a case Sil. Is grand.
I
Intolerable, sour, carrion-like odor
Dr. Clarke said, hands and feet are sweaty and the sweat is generally offensive. But the characteristic feature to note is that, the feet may give off an intolerable odor without any sweat.
Note : Master Kent said, complaints from suppressed sweet: this suppressions produce a state in the economy that threatens what little order is left. Silicea ha cured long lasting foot-sweat when the symptoms agree or complains that have lasted since the suppression of foot sweat
Master Kent in his Repertory classed the following medicines under the sub-rubric, complaints from suppressed perspiration. Bell., Bry., Calc., Chamo., China., Colch., Dulc., Poor", Rhus Tox., Sep., Stramo.3, Sulph..
C
Chilly patient
Our Sil. is very chilly pt.: can be bracketed with chilliest drugs of our Materia Medica like Hepar Sulph, Psorinum.
There is want of vital heat, always chilly, even when taking active exercise.
Master Kent said, it is especially necessary for the Sil. pt. to avoid the cold air, must have the head well wrapped up, esp. the part that is painful, and this part perspires profusely.
His symptoms develops in cold damp weather, symptoms come out after a bath.
Our lamented Dr. Constantine Hering puts the term want of vital warmth, takes cold very easily, relived by wrapping up the head (Mag Mur) or in other words, by supplying artificially the warmth that he lacks naturally.
Note: Master Kent said. Sil. pt. sometimes better in cold dry weather.
E
Every little Injury suppurates
Every little injury tends to suppurate (Hep.Sulph, Marc, Sulph., Psor.).
It has a wonderful control over the suppurative process, soft tissue, periosteum or bone, maturing abscesses when desired or reducing excessive suppuration; swelling and suppuration of glands-cervical, axillary, parotid, mammary, Inguinal, sebaceous.
Master Kent said the remedy produces inflammation about any fibrinous nidus and suppurates it out, suppurates out old wen, and indurated tumours.
Note: If a splinter or bullet lodges in the tissue, a suppuration will slough it out.
A
Abdomen distended with late learning to walk (in children)
Scrofulous, rachitic children with large heads, open fontanelles and sutures, with distended abdomen and much sweating about the head (but not of that grade like Calc Carb). which must be kept warm by external covering, is the typical appearance of Sil child.
Their milestones are delayed, esp. late learning to walk due to weak ankles.
Dr. E. B. Nash said, the Sil. child is not larger than natural anywhere, except in its big belly’ which is due to diseased mesentery. (1)
Introduction
Constitution
Clinical
Mental Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms
Characteristic
Therapeutic Value
Modality
Remedy Relationship
Dose
Reference
Terminology
Also Search As
Introduction
Intoduction of Silicea
Common name
- Silicic oxide
Synonyms
- Pure funk, Pure silica
Family / Group / Class / Order
Mineral kingdom
Habit and habitat / Description
- Sil. is a white, amorphous powder which is tasteless and odourless.
- It is insoluble in water as well as in alcohol.
- It is soluble only in hydrofluoric acid.
- Silicea is insoluble in dilute acids.
- When a small fragment of silica is introduced in a bead of microcosmic salt (sodium ammonium phosphate) and heated, silica will float in the bead while hot and after cooling, it will become opaque.
Formula / Symbols
SiO2
Name of prover
Dr Hahnemann in 1828 and Dr W. H. Schussler
Introduction and history
- Silicea is a boon to the suffering humanity serves the purpose of a ‘surgeon’s knife’ in the hands of a homeopath.
- It is a great polychrest and powerful remedy.
- It is one of the twelve tissue remedies of Schussler.
- It is a long and deep acting constitutional remedy.
- Silicea is an oxide of silicon occurring in a great variety of forms.
- It is commonly known as silicious earth flint or quartz.
- It is found in the hair, nails, skin, periosteum, nerve sheath and even in the bony tissues. It is also used in the making of dynamite Though inert in its crude state because of its insolubility, it becomes a very powerful remedial agent when potentized.
- Silicea, a chemically inert material, gives rise to foreign body reactions. It forms silicic acid, sodium silicate or silico
- fluoride compounds in living tissues.
- The hydrophilic colloid – silicic acid can retain water in varying amounts as reserves and prevents drying in plants growing in deserts and sandy areas.
- Silicea is dispersed as a negative colloid and found where chemical metabolism is very low or has ceased; for example, in connective tissues, skin and appendages, like nails, hair, etc.
- Silicea is the precursor for fluoride action. It is a supporting and structure giving component, which is a counter pole to the supporting action of Calcarea.
Parts used
- Pure silicea is triturated with sugar of milk upto 3C potency.
- Higher potencies are prepared with alcohol.
- For biochemic purposes, decimal triturations are used.
Preparation
- Pure silicea is triturated with sugar of milk upto 3c potency.
- Higher potencies are prepared with alcohol.
- For biochemic purposes, decimal triturations are used.(4)
Constitution
Constitution of Silicea
Physical make up
Silicea is best suited to persons with a lean and thin body, sickly appearance and dry skin. Suits people having a weak and lax musculature, with a pale face.
Temperament :
- Sanguine and irritable
Diathesis :
Scrofulous
Relation with heat & cold :
Very chilly patient
Miasm of Silicea:
Psora, syphilis and sycosis, but predominantly antipsoric(4)
Clinical
Clinical conditions of Silicea
In Homeopathy Silicea medicine use by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of following Disease Conditions
Abscesses, Quinsy, Headaches, Spasms, Epilepsy, Feeling of coldness before an attack, Keloid growth, Scrofulous, Rachitic children, with large head, open fontanelles and sutures, distended abdomen, slow in walking. ILL EFFECTS OF VACCINATION. SUPPURATIVE PROCESSES (7)
Sites of action / Pharmacodynamics
Mucous membranes, skin, cartilages, elastic and cellular tissues, bones, eustachian tube, nerves, lachrymal duct, glands, etc.
Causation (Causes / Ailments from)
Exposure to draught of air, vaccination, chest complaints of stone cutters, suppressed foot sweat.
Patho-physiological changes / Pathogenesis
- It acts on the nervous system producing well defined irritability with extreme sensitiveness.
- Initially, Silicea decreases phagocytosis followed by an increase in phagocytosis, due to an increase in the nuclear maturity of neutrophils and macrophages.
- Thus, it protects against pus producing bacteria like staphylococcus and streptococcus.
- It acts on the sphincters and causes remote pains.
- In lower triturations, Silicea precipitates proteins, agglutinates red blood cells, typhoid bacilli and spermatozoa. Therefore, higher triturations must be used.
- It produces perverted nutrition, thus resembling two great dyscrasia – scrofula and rachitis.
- Silicea forms sodium silicate, a thin, watery, transparent liquid around foreign bodies and provokes the opening of the tract by applying pressure, and facilitates expulsion of foreign substances. Hence, Silicea is known as a ‘surgeon’s knife.’
- Crude silicea promotes uniform connective tissue growth as silicotic nodules.
- Distinctly encapsulated in the lungs, it is called ‘chalicosis pulmonum’ by activating fibroblastic tissues, which favour the development of tuberculosis, asbestosis and fibrosis.
- It lowers the vital capacity of the lungs. It acts on fibrous tissues producing inflammation and suppuration. (4)
Mental Symptoms
Characteristic Mental Symptoms (psychology) of Silicea
- Want of grit, absentmindedness, fidgety feeling.
- Anticipatory anxiety, fear of appearing in public.
- Aversion to be spoken to or touched.
- Shy, timid, capricious, careless.
- Difficulty in concentration, lack of self-confidence.
- Confused mind; wants to be magnetized, obstinate. Cries when spoken kindly to; weeping tendency.
- Thinks of pins; pin mania during delirium state; fear of pins of being pricked by them, therefore wants to collect them.
- Fixed ideas, lack of stamina, anticipatory anxiety about his performance but once he starts, he gains back his usual self-confidence and command, and he does the task well. (3)
Guiding Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms of Silicea
1. Generalities
- It produces defective Nutrition esp. in children; due to imperfect assimilation.
- Affects the Nerves; increasing their susceptibility causing neurasthaenic states and exaggerated reflexes.
- Diseases of bones and cartilages; caries and necrosis; softening, of bones.
- GLANDS are enlarged.
- Scrofulous rachitic children; with large head, open fontanelles; distended hot and hard abdomen, slow in walking, and wasted in body esp. legs.
- Children crawl nervously; or are dragged in on their mother’s arms; on running they become pale.
- Suppurative processes; stubborn; fistulous openings; abscesses.
- Slow incomplete inflammation, of glands, cellular tissue and skin; then induration.
- Keenly sensitive to noise, pain, to cold, hugs the fire, wants plenty of warm clothing; hates drafts.
- Cachetic and old patients; persons of fair, clear complexion.
- Want of vital warmth even when taking exercise.
- Spasms, epilepsy; feeling of coldness before the attack.
- Hysteria, paralysis and obstinate neuralgias caused by dissipation, hard work, with close confinement.
- Mal-nutrition.
- Arrested development. Emaciation.
- Want of grit; moral and physical.
- Removes foreign bodies.
- Progressive locomotor ataxia.
- Sensation as if she were divided into halves and left side does not belong to her. Sensation of a hair on tongue; in trachea.
- Ill effects of vaccination; stone cuttings; loss of vital fluids; injuries; sprains, splinters. Intolerance of alcoholic stimulants.
- Cold; Air; Draft; damp; uncovering, bathing.
- Checked sweat esp. of feet.
- Nervous excitement. (3)
2. Head
- Vertigo; ascends from dorsal region agg. looking upwards, closing eyes, lying on left side.
- Ascending occipital pains amel. pressure.
- Periodical headaches.
- Headache, then blindness.
- Vertex throbs.
- Fontanelles open, with distended abdomen.
- Lumps on scalp.
- Profuse sweat on head.
- Swelling of glabella.
- Cephalohematoma.
- Profuse urination amel. headache.
- Right side as if paralysed agg. coition.
- Headache agg. by exertion, study, noise, motion, jar, light, cold air, talking and straining at stools, and amel. by wrapping warmly, and pressure.
- Moist crusty eruptions on the scalp.
- Swelling filled with grumous fluid between scalp and bone.
- Headache while fasting or when not eating at proper time.
- Migraine.
- Chronic headaches since some severe disease.
- Falling of hair, premature baldness.
3. Eye
- Affections of canthi; in the region of tearducts; swelling of lachrymal fistula; stricture of lachrymal duct.
- Spotted vision.
- Objects appear pale.
- Aversion to day light; it dazzles.
- Keratitis; pustular; perforating.
- Inflammation of eyes.
- Hypopion. Opacities of the cornea; after small pox (use 30 for months).
- Cataract in office workers, after suppressed foot sweat.
- Styes; to prevent their recurrence.
- Encysted tumours of lids.
- Letters run together while reading.
4. Ears
- Roaring in ears.
- Hissing in.
- Perforated drum.
- Itching.
- Caries of mastoid process.
- Deafness, hears again with a loud report or on blowing the nose, and coughing; agg.
- full moon.
- Foetid discharge.
- Sensitive to noise.
- Feeling of stoppage in the ear amel. when yawning or swallowing.
- Crusty formations in ears.
- Child bores into its ears when asleep.
5. Nose
- Frothy nasal discharge.
- Coryza, with epistaxis.
- Perforation of septum.
- Dry hard crusts; bleeding when loosened.
- Sneezing in morning.
- Itching of the tip.
- Bone sore.
- Nose; dry obstructed, with loss of smell.
- Epistaxis in infants.
- Cracks in nostrils.
- Obstinate colds; with ear affections.
- Nose cold
6. Face
- Pale, cachetic; waxy.
- Enlarged parotids.
- Cracks; in lips; on skin of face.
- Eruptions on chin.
- Swelling of maxillary glands.
- Indurated fissures at the corners of lips.
- Cancer of lower lip.
7. Mouth
- As of a hair on tongue.
- Abscess at the root of the teeth.
- Boils on gums.
- Pyorrhoea.
- Water tastes badly; vomits after drinking.
- Teeth; break down, lose their enamel, become rough, carious.
- Tongue; brown.
- Teeth feel too large and too long for the mouth.
8. Throat
- Bitter taste in.
- Tonsils swollen, suppurating.
- Food is ejected through nose, when swallowing.
- Pricking pain as of a pin in tonsil.
- Hawks foul lumps.
- Swallowing painful, difficult; exaggerated.
9. Stomach
- Aversion to cooked or warm food and meat; to mother’s milk, vomits it.
- Likes ice cream, ice water, feels comfortable when it is in the stomach.
- Water tastes bad; vomits after drinking.
- Induration of pylorus.
- Water‐brash with chilliness.
- Voracious appetite, but disappears on attempting to eat, or loathing of food.
- Sour eructations after eating.
- Sour vomiting.
- Gnawing, twisting pain in epigastrium worse by pressure.
- As if a cold stone were in stomach.
10. Abdomen
- Throbbing ulcerative pain in the region of liver; abscess of liver.
- Colic, cutting pain; with yellow hands and blue nails.
- Distended hard and hot,
- with thin legs esp. in children.
- Cutting, cramping pain in rectum extending to testes worse coition.
- Constipation worse before and during menses.
- Straining, with soft stools, with exhaustion. Moist anus, foul flatus.
- Stools; comes out with difficulty, when partly expelled, recedes again; retained for fear of pain. Cracks on abdominal wall.
- Fissures, fistula in ano, with chest symptoms.
- Painful spasms of sphincter.
- Intensely painful haemorrhoids protrude during stool.
- Foul diarrhoea.
- FRUITLESS urging to stool.
- Chronic diarrhoea.
- Stools offensive, painless, lienteric.
- Tapeworm.
- Diarrhoea after milk.
- Hernial tumour tender.
- Ascites; with great effusion; with frequent attacks of diarrhoea.
11. Rectum & Anus
- Feels paralyzed.
- FISTULA IN ANO. [BERB.; LACH.]
- Fissures and haemorrhoids, PAINFUL, WITH SPASM OF SPHINCTER.
- CONSTIPATION ALWAYS BEFORE AND DURING MENSES; with irritable sphincter ani. Diarrhoea of cadaverous odor.
12. Stool
- STOOL COMES DOWN WITH DIFFICULTY; WHEN PARTLY EXPELLED, RECEDES AGAIN.
- Great straining; rectum stings; closes upon stool.
- Faeces remain a long time in rectum.
13. Urinary Organ
- Profuse urination better headache.
- Frequent urination with tenesmus.
- Nocturnal enuresis; in children; from worms.
- Chronic urethritis; foul discharge from urethra, thick, curdy, purulent, bloody. Pus in urine. nightly incontinence after a blow upon the head.
- Renal and vesical calculi.
14. Sexual Organ
Male:
- Foul gonorrhoeal urethral discharge.
- After coition sensation on right side of head as if paralysed.
- Itching moist spots on scrotum. Hydrocele. Nocturnal emissions.
- Sexual appetite increases or decreases. Prostatorrhoea worse straining at stools.
- Chronic urethritis with twisting pain.
- Elephantiasis of scrotum. Extreme exhaustion after coition; takes 8 to 10 days to come to normal condition.
- Painful eruptions on mons veneris.
Female
- Increased menses with paroxysms of icy coldness over whole body. Cutting upward in vagina worse urinating.
- Leucorrhoea milky, acrid, gushing, worse during urination.
- Itching of vulva and vagina, which is very sensitive.
- Bloody discharge worse nursing; between periods.
- Nipple; retracted like a funnel, sore. Hard lumps, fistula, in mammae. Serous cyst in vagina fistulous opening and abscess about vulva. Threatened abscess of mammae. Scirrhus, with itching.
- Sharp pains in mammae and uterus.
- Menses; early, scanty. Amenorrhoea for months
- Too violent motion of foetus.
- Fistulous abscess or fistulous openings in or around vagina with thick, curdy discharge.
- Salpingitis, with accumulation of pus or serum which escapes from uterus from time to time.
- Cutting pain around the navel with leucorrhoea. Watery discharge instead of menses.
- Abortion from weakness or they do not conceive because of weakness.
- Nausea during coition.
- Bloody discharge between periods.
- Sterility. Nymphomania.
- Itching of pudenda.
15. Respiratory System
- Cough gagging,shaking, retching worse cold drinks; talking, lying and after waking.
- Dyspnoea; from draft on neck; chronic colds which settle in chest and bring on asthmatic attacks; after being over heated or exertion.
- Sycotic asthma.
- Profuse foul, yellow, lumpy sputum; granular; offensive when broken.
- Cold fails to yield.
- Slow recovery from pneumonia.
- Rattling in chest. Stitches in chest, through the back.
- Shortness of breath, from manual labour; walking fast.
- Stone‐cutter’s affections.
- Emphysema after pleurisy.
- Neglected pneumonia.
- Painless throbbing in sternum.
16. Heart & Pulse
- Throbbing all over the body, when sitting or while in motion.
- Palpitation; while sitting, with trembling of hand.
- Heart trouble from nervous exhaustion.
17. Neck & Back
- Spine; weak, very sensitive to drafts on back.
- Spina bifida.
- Caries of vertebrae.
- Psoas abscess.
- Painful coccyx.
- Backache as from riding in carriages for a long time.
- Burning in back, when body is being heated after walking in open air.
- Stiff neck; with headache.
- Painful kyphosis.
- Lameness in region of sacrum.
18. Extremities
- Axillary glandsswollen, enlarged.
- Finger tips, painful, dry asif made of paper; at night.
- Icy cold and sweaty feet. ***FOOT SWEAT FOUL; *itching, *acrid, destroying shoes; *suppressed.
- Sore ache in arch of foot.
- Distorted, ingrown, yellow nails.
- Weak ankles and feet.
- Calves tense and contracted.
- Intense throbbing pain, deep seated pain.
- Atrophy and numbness of fingers.
- Parts lain on go to sleep.
- Bunions.
- Inflammation of bones.
- Trembling of hands when attempting to do something.
- Forearm weak.
- Legs feel paralysed, trembling while walking.
- Voluptuous tingling in soles.
- Bruised feeling in whole body after coition or emission.
- Cramps in knees.
- Soft corns in between toes.
- Nails; rough, yellow, impair, brittle, white spots, blue in fever.
- Ulcers around the joints with thin, foul, bloody, purulent discharge or curdy particles.
- Slovenly gait.
- Rheumatism esp. of the soles, cannot walk.
- Cramps in calves and soles.
- Enlarged bursa over patella.
- Distorted during convulsion.
- Arms (left) shake before epilepsy.
19. Skin
- Soggy, wilted.
- Acuminate eruptions.
- Scars suddenly become painful.
- Keloid. Even little injury suppurates.
- Leprous nodes. Coppery spots. Carbuncles.
- Ulcers; painfully sensitive, foul; spongy; on feet, toes, nails better heat.
- Abscess of joints.
- Eruptions itch during daytime or evening only.
- Boils and pustules everywhere.
- Sensation of coldness in ulcers.
- Warty growths.
- Rose coloured blotces.
- Elephantiasis.
20. Sleep
- Somnambulism.
- Frightful dreams wake him on falling to sleep.
- Restless sleep.
- Dreams; lascivious, of past events.
- Awakes frightened, from sleep with trembling of the whole body.
- Talks in sleep loudly, whines or laughs.
- Violent yawning. Sleepy but cannot sleep.
- Sleep unrefreshed.
21. Fever
- CHILLY; worse lying in bed; exertion.
- Coldness; of painful part. Icy chills.
- SWEAT; profuse, on upper part of the body; head or affected parts; at night; foul; easy; acrid; as soon as he falls asleep. Hectic fever.
Characteristic
Characteristics of Silicea
Keynotes / Redline:
A/F suppressed foot sweat, which is offensive. Carrion like odour of feet, acrid eats up the shoes.
Stools recede again when partly expelled.
Discharge of blood from vagina when child takes the breast.
Promotes expulsion of foreign body from tissue eg. fish bones, needles, bone splinters.
Hair like sensation on tongue.
Guiding:
Nocturnal emission, prostatorrhoea < straining at stool.
Female-Discharge of blood from vagina every time the child takes the breast (Croto-t).
Icy coldness over whole body during menses.
Skin-Abscesses, boils and fistulous ulcers. UNHEALTHY. TENDENCY TO SUPPURATION. Every little injury suppurates.
Delicate, pale skin.
Promotes expulsion of foreign bodies through skin (Anag).
Keloid. Scars become painful, stinging and red.
Eruptions, itching > night.
Vitiligo. Ringworm. Impetigo.
Tumours and warts.
PQRS:
Much sweating about the head, which must be kept warm by external covering (Sanic.); exposing the head or back to any slight draft of air.
Want of vital heat, always chilly, even when taking
active exercise. (Led., Sep.).
Children are obstinate, headstrong, cry when spoken kindly to (lod.).
Headache draft of air or uncovering the head:>by pressure and wrapping up wramly (Mag.M., Stron.);>profuse urination.
Discharge of blood from vagina every time the child takes the breast (Crot.T.). Nipple is drawn in like a funnel (Sars.).
Night-walking; gets up while asleep, walks about and lies down again (Kali Br.).
Intolerable, sour, carrion like odor of the feet, without perspiration, every evening.
Fistula in ano alternates with chest symptoms.
Constipation: always before and during menses.
Confirmatory:
Chilly patient, wants to be wrapped up warmly. Want of grit mentally and physically.
Obstinate, head strong. Easy suppuration, tendency to fistulous burrowings.
Inflammation, swelling and suppuration of glands. Profuse, offensive sweat, especially of feet and head.
Nucleus symptoms:
Slow incomplete processes, then induration.
Every hurt festers, fixed ideas.
Keenly sensitive to external impressions.
Profuse discharges (sweating) if restricted cause problem.(3)
Fistula in ano.
Therapeutic Value
Therapeutics of Silicea
- Abdomen distended,
- Abdominal disorders,
- Boils,
- Bone affections,
- Cancer,
- Carbuncles,
- Constipation,
- Cough,
- Debility,
- Dentition,
- Diabetes,
- Enuresis,
- Epilepsy,
Other Therapeutics
- Foreign body expulsion of,
- Glandular swelling,
- Headache,
- Hernia,
- Perspiration offensive,
- Pleurisy,
- Rheumatism,
- Rickets,
- Sexual organs,
- Skin troubles,
- Somnambulism,
- Suppuration,
- Tenesmus,
- Ulcers,
- Urinary trouble,
- Vaccination,
- Vertigo, etc.(4)
Modality
Modality Of Silicea
Aggravation :
- Cold, during new moon, during menses, lying down, uncovering, especially the head.
Amelioration :
- Warmth, wrapping up the head, in summer (3)
Remedy Relationship
Remedy Relationship of Silicea
Complimentary
- Puls, Sanic, Thuj
Follows Well
- Ars, Asaf, Bell, Calc, Clem, Fl-ac, Graph, Hep, Lach, Lyc, Nux-v, Phos, Puls, Rhus-t, Sep, Sulph
Inimical
- Merc
Antidoted By
- Camph, Fl-ac, Hell.
It Antidotes
- Merc-c, Sulph
Comparison
- Ang, Ant-c, Ant-t, Apis, Ars, Asaf, Bar-c, Benz-ac, Berb, Calc, Calc-p, Caps, Caust, Cham, Chel, Cina, Con, Cupr, Gettys, Graph, Hep, Iod, Kali-bi, Kali-br, Kali-c, Lach, Led, Lob, Luna, Lyc, Mag-m, Maland, M-aust, Meny, Merc, Nat-c, Nat-m, Nat-s, Nit-ac, Nux-v, Paris, Petr, Ph-ac, Phel, Phos, Pic-ac, Plat-mur, Psor, Puls, Ran-b, Rhod, Ros-ca, Sang, Sars, Sep, Sil, Spig, Stann, Stron, Sul-ac, Sulph, Thiosin, Thuj, Vacc, Vario.(4)
Dose
Dose
Potency & Dose of Silicea
- Schussler recommends 6x and 12x potencies.
- Kent recommends high and highest potencies when the constitutional symptoms are present.
- It is to be applied externally on ulcers, carbuncles and ulcerated pyogenic parts.
- 3x, 6x, 12x, 30, 200, 1000.
Duration of action of Silicea
- 40-60 Days. (4)
Reference
References of Silicea
- Synoptic Memorizer Of Materia Medica vol.1 by Dr. Subrata Banerjee- Silicea
- Synoptic Memorizer Of Materia Medica vol.2 by Dr. Subrata Banerjee- Silicea
- ZomeoLane – Materia Medica – silicea- keynote
- Textbook of homoeopathic materia medica by Dr. J.D. Patil- Silicea
- The Soul of remedy By Dr. Rajan Shankaran- Silicea
- Lectures On Homoeopathy By Kent J. T.
- Materia Medica By Boericke W.
- Concise Materia Medica Of Hom. Remedies By S.R. Phatak
- Condensed Materia Medica By Hering C.
Terminology
Terminology
Here are some terminologies and their meanings that are commonly used in homeopathic articles about Silicea, along with images where appropriate:
1. Silicea
- It refers to a homeopathic remedy prepared from silica, or silicon dioxide.
- It is also known as Silica terra or Pure Flint.
- In homeopathy, substances are diluted and potentized, and it is believed that the resulting remedies stimulate the body’s self-healing abilities.
2. Potency
- It indicates the number of times a substance has been diluted and succussed (shaken vigorously) in the preparation of a homeopathic remedy.
- Common potencies of Silicea include 6X, 30C, 200C, etc.
- Higher potencies are considered to have a deeper and longer-lasting effect.
3. Constitutional Remedy
- It is a remedy that matches the overall physical, mental, and emotional characteristics of an individual.
- Silicea is often considered a constitutional remedy for people with certain personality traits, such as being sensitive, timid, and easily exhausted.
4. Miasm
- It is a theoretical concept in homeopathy that refers to an inherited predisposition to certain diseases.
- Silicea is associated with the psoric miasm, which is characterized by functional disturbances and a tendency to develop chronic diseases.
5. Materia Medica
- It is a reference book that describes the symptoms and characteristics associated with different homeopathic remedies.
- The Materia Medica of Silicea includes a detailed list of physical and mental symptoms that may be relieved by this remedy.
6. Repertory
- It is an index of symptoms and the remedies that are associated with them.
- Homeopaths use repertories to help them select the most appropriate remedy for a patient based on their presenting symptoms.
7. Proving
- It is a process in which healthy volunteers take a homeopathic remedy and record the symptoms they experience.
- The symptoms collected from provings are used to create the Materia Medica for that remedy.
8. Aggravation
- It is a temporary worsening of symptoms that may occur after taking a homeopathic remedy.
- It is considered a sign that the remedy is working and stimulating the body’s healing process.
9. Amelioration
- It refers to an improvement in symptoms after taking a homeopathic remedy.
10. Keynotes
- They are the most characteristic and distinctive symptoms of a remedy.
- Keynotes of Silicea include:
- Sensitivity to cold
- Tendency to suppuration (pus formation)
- Weakness and lack of stamina
- Slow development in children
- Brittle nails and hair
Remember: It is important to consult a qualified homeopath before taking any homeopathic remedy, including Silicea. They can help you determine the appropriate remedy and potency for your individual needs.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Homeopathy is a complementary therapy and should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment.
Also Search As
Also Search As
People can search for homeopathic articles on Silicea through various online and offline resources. Here are some ways:
Online
Search Engines: Use search engines like Google, DuckDuckGo, etc., with relevant keywords like:
- "homeopathic article Silicea"
- "Silicea remedy benefits"
- "Silicea materia medica"
- "Silicea homeopathy uses"
- Be specific if you’re looking for something particular, like "Silicea for skin conditions"
Homeopathic Websites and Databases:
- Reputable homeopathic organizations often have articles and resources on their websites:
- The National Center for Homeopathy (NCH)
- The British Homeopathic Association (BHA)
- The North American Society of Homeopaths (NASH)
- Online Materia Medica databases:
- Reference Works
- RadarOpus
- Hompath
- Reputable homeopathic organizations often have articles and resources on their websites:
Social Media and Forums:
- Homeopathic groups and forums on platforms like Facebook and Reddit can be a source of information and discussions.
- Be sure to evaluate the credibility of the information and the source before relying on it.
Online Journals and Publications:
- Search for homeopathic journals and publications that may have research articles or case studies related to Silicea.
- Some examples include:
- The Homeopathy Journal
- Homeopathy
- The International Journal of High Dilution Research
Offline
Libraries:
- Public and university libraries often have a collection of homeopathic books and journals.
- Consult the library catalog or ask a librarian for assistance.
Homeopathic Clinics and Practitioners:
- Homeopathic practitioners often have brochures, pamphlets, or books on specific remedies like Silicea that they can share with patients.
Homeopathic Bookstores:
- Dedicated homeopathic bookstores often carry a wide selection of books and materials on homeopathy, including information on Silicea.
Tips for Effective Searching
- Use a variety of keywords and search terms.
- Be specific in your search if you’re looking for information on a particular aspect of Silicea, like its use for a specific condition or its mental and emotional symptoms.
- Evaluate the credibility of the source before relying on the information. Look for articles written by qualified homeopaths or published in reputable homeopathic journals.
- Cross-reference information from multiple sources to get a well-rounded understanding of Silicea.
Remember: While online and offline resources provide a wealth of information, it is always best to consult a qualified homeopath for personalized advice and treatment recommendations regarding Silicea or any other homeopathic remedy.
Here are different ways to search specifically for the homeopathic remedy Silicea, both online and offline:
Online
Search Engines: Use precise search terms like:
- "Silicea homeopathic remedy"
- "Silicea 30C uses"
- "Silicea materia medica online"
- "Silicea for hair loss"
Homeopathic Websites and Databases:
- Search directly within these resources using "Silicea" as the keyword.
- Filter your search by potency, symptoms, or use case if applicable.
Online Homeopathic Pharmacies:
- Many online pharmacies specializing in homeopathic remedies allow you to search for specific remedies like Silicea.
- These sites often provide detailed product information and indications.
YouTube and Video Platforms:
- Search for videos on "Silicea homeopathy" or related terms.
- These videos might offer explanations, case studies, or testimonials about the remedy.
Offline
Homeopathic Pharmacies:
- Visit a local homeopathic pharmacy and ask the pharmacist about Silicea.
- They can provide information on its uses, potencies, and any specific instructions.
Homeopathic Clinics and Practitioners:
- Consult a homeopathic practitioner and inquire about Silicea specifically.
- They can assess your individual case and determine if Silicea is suitable for you.
Homeopathic Books and Materia Medicas:
- Look for dedicated books on homeopathic remedies or materia medicas in libraries or bookstores.
- These resources will contain detailed information on Silicea, including its key symptoms and indications.
Additional Tips:
- Use synonyms: Search for "Silica" or "Silica terra" as these are alternative names for the same remedy.
- Specify the condition: If you’re looking for information on Silicea for a particular health concern, include that in your search terms. For example, "Silicea for eczema" or "Silicea for anxiety."
- Consider the potency: If you’re already familiar with homeopathy, include the desired potency in your search, like "Silicea 30C."
Remember: While online and offline resources can provide a wealth of information on Silicea, it’s crucial to consult a qualified homeopath for personalized advice and treatment. They can properly assess your individual needs and recommend the most appropriate remedy and potency for you.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Homeopathy is a complementary therapy and should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Silicon is derived from sand: thus, deficiency of It causes lack of grit mental and physical-elaborate?
Lack of grit-Physical debility:
i) Persons of light complexion, pale face; weakly, with lax muscles.
ii) Constitutions which suffer from deficient nutrition, not because food is lacking in quantity or in quality, but from imperfect assimilation.
iii) Scrofulous, rachitic children; weak ankles, slow in learning to walk.
iv) Great weariness and debility: wants to lie down.
Lack of grit – Mental debility:
i) Adapted to persons of nervous, sanguine temperament,
ii) Oversensitive mentally.
iii) Nervous debility; exhaustion and erethism may be overcome by force or will.
iv) Restless, fidgety, starts at least noise.
v) Anxious, yielding, faint-hearted.
vi) Mental labor very difficult: reading and writing fatigues: cannot bear to think.
vii) Master Kent says, dread of failure, but when forces himself into the harness, he can go on with ease, his usual self-command returns to him and he does well: he does his work with promptness, fullness and accuracy. (Ref. Kent)
Note: – Master Kent says. Lycopodium is foolish, the dread of undertaking anything is from a general knowledge of inability, but in Silicea it is imaginary.
Mention four medicines for ailments from suppressed foot sweat.
i) Baryta Carb
ii) Graphites
iii) Pulsatilla
iv) Silicea
Mention three medicines for bad effects of vaccianation.
Medicines
i) Antim Tart
ii) Thuja
iii) Silicea
State the chest symptoms of Silicea.
i) Chest complaints of stone-cutters with total loss of strength.
ii) Fistula in ano, alternates with chest symptoms.
State the eye symptoms of Silicea.
State the headache of Silicea.
Headache
1.Causation
i) Chronic-sick headache since some severe diseases of youth (Psor.)
ii) Headache when overheated. (Ref. Clarke)
iii) Headache from fasting.
2.Type
Headache of nervous character.
3.Location
Headache arises from nape of the neck ascends to the vertex and finally settles over the right eye. Generally, right sided headache.
4.Sensation
Sensation of roaring or shattering in brain.
5.Character of pain
i) Pressing, bursting headache, as if eyes and brain were forced out.
ii) Violent tearing headache with pressive pain in the morning
iii) Jerking headache, extending to brain
iv) Tearing in vertex, as if it would burst.
v) Headache with bruished pain above the eyes so that patient can scarcely open them. lancinating pain in head.
6.Criteria
I)Violent headache with confusion of mind.
ii) Headache with shivering and lassitude necessary to lie down.
iii) Tension and pressure in the head, as if it were about to burst.
7.Vertigo
i) Vertigo from looking up.
ii) Vertigo especially in the morning, when riding in a carriage.
iii) Vertigo with nausea vertigo causes to fall backwards or forwards.
iv) Vertigo ascending from dorsal region.
8.Modality
a) Aggravation: Agg. by light, Agg. by mental exertion, noise, motion, jerking light stooping, cold air, Agg. by uncovering draught of air. Agg. from evening till night,Agg. from stepping hard. Agg. if head becomes cold in open air (Ref. Clarke). Agg.
b) Amelioration: lying on left-side. Amel. by profuse urination(, Ign.).by stooping, jar. Amel. by binding head tightly (Ref. Nash), Amel. in warm room, wrapping up the head warmly. Amel., by hot compress.
9.Concomitants
i) Clouded sight.
ii) Difficulty in holding up the head.
iii) Headache causes chilliness and nausea.
iv) Scalp in very sensitive to touch.
v) Chilly with low vitality.
vi) Usually constipated.
State the constipation of Silicea.
Constipation
a) Causation
Before and during menses.
b) Character of stool
i) Stool, large, hard lumps.
ii) Passing of stool is difficult as from inactivity of rectum; with great straining.
iii) Stool partly expelled but recedes again.
iv) Faeces remains a long time in the rectum.
c) Sensation
i) As from inactivity of rectum.
ii) As if rectum is paralyzed.
iii) Great straining, rectum stings; closes upon stool, (Ref. Boericke)
d) Concomitants
i) Fistula in ano.
ii) Fissures and haemorrhoids, painful with spasm of sphincter.
State the skin symptoms of Silicea.
Skin Symptoms
Introduction
It has a wonderful control over the suppurative process soft tissue, periosteum or bone, maturing abscess when desired or reducing excessive suppuration.
Causation
I) Bad-effects of vaccination especially when abscess results.
II) Bad-effects of suppressed foot-sweat.
III)Character –
- Unhealthy ;Every little injury suppurates.
- Clinical – Abscesses, boils, old fistulous ulcers (Ref. Boericke), blood boils, carbuncles, ulcers of all kinds.
- Cracks – At the end of fingers.
- Scar – Which suddenly becomes painful.
- Eruptions – Itch only in daytime and evening.
- Keloid – growths When tends to suppurate.
- Nails –
a) Brittle nails.
b) Ingrowing toe-nails.
a) Fistula lachrymalis.
b) Fistula: painful, offensive, high spongy edges, proud flesh in them
c) Fissura ani, great pain after stool.
- Suppurative diathesis
a) Promotes expulsion of foreign bodies from the tissues: fish-bone, needles, bone-splinters. Silicea promotes suppur- ation: causing focal local necrosis of the area-sloughing out of the part- expulsion of foreign-body results.
b) The leader of the suppurative medicines: In advanced pyogenic condition i.e., full of pus on the verge of rupturing or already ruptured; thence thin, bloody, ichorous, pus, offensive smell, and moreover Nash points out to find the similimum in regard of constitution, weakly. fine skin with pale face, lax muscles with lack of grit. Agg. from washing, cold uncovering and Amel, from heat.
Describe a Silicea baby?
Constitution
a) Physical make up- A constitutional tendency which suffer from deficient nutrition, malnutrition, not because of the food is lacking in quantity or quality. but because the system does not assimilate the food materials properly, ie. imperfect assimilation.
Baby having large head, open fontanalles and sutures, potbellied abdomen, with pale face, lean and thin body, sickly appearance.
b) Temperament- Nervous, irritable and sanguine temperament.
c) Miasm- Covers all the three miasms; still predominantly antipsoric.
d) Diathesis- Scrofulous diathesis (++) and tubercular diathesis.
e) Heat and cold Relation.- Highly chilly patient (+++); lack of vital heat, wraps up with warm clothing even in hot summer
Mile-stones
a) Dentition.
b) Learning to read.
c) Learning to walk etc.-The baby is very slow in learning to walk due to weak ankles resulting in retardation of walking as because of malnutrition and defective assimilation of food.
Mental criteria.
i) The baby is head-strong and obstinate, who cries when kindly spoken to.
ii) Baby is very nervous and excitable; patient is sensitive to all external impressions.
iii) Baby may have fixed ideas: -like pin mania. The baby thinks nothing except pins, the baby fears them, still searches them, counts and preserves them with great care (in case of 5-6 years old child).
iv) Night-walking baby gets up while asleep walks about and lies down again all quite unconsciously.
v) Child desires to be magnetized.
Aversions
Aversions :-Child has got aversion to mother’s milk,
Sweat
i) Baby has very offensive foot sweat, further more the sweat in axilla and in hands is also offensive (+++).
ii) Intolerable, sour, carrion like odour of the feet, without perspiration every
iii )Sweat behind the neck, in the region of head and occiput.
GI Symptoms
i) In child the constipation may also observed
ii) Stool is difficult to evacuate from the rectum due to its
iii) The stool partly comes out and then recedes back, consequently stool has to removed mechanically.
Skin
i) The baby suffers from various kinds of skin troubles caused by bad effects of vaccination.
ii) Every little injury suppurates: swelling and abscess formation after vaccination.
Causative factors
i) Constitution which suffers from deficient nutrition from defective assimilation.
ii) Bad effects of vaccination.
iii) Exposure to draught of air.
Modalities
Agg. in new moon and full moon, cold and uncovering especially the head, Agg. from draught. (Ref. Lippe).
Amel. by warmth, wrapping up the head.
State the characteristic symptoms of Silicea.
Characteristics Symptoms
Chilly patient
i) Extreme chilliness.
ii) Lack of vital heat.
iii) Always chilly, even when taking active exercise.
Debiliated constitution
i) Constitutions which suffer from deficient nutrition; not because food is lacking in quality or in quantity but from imperfect assimilation.
ii) Great weariness and debility; wants to lie down.
iii) Nervous debility, exhaustion with erethism.
iv) Lack of grit moral and physical-is very well marked.
Bad effects of
The bad effects of vaccination, especially when abscesses convulsion results.
Suppurative diathesis
i) Has a wonderful control over the suppurative process, soft tissue, periosteum or bone, maturing abscesses when desired or reducing excessive suppuration.
ii)Every little injury suppurates.
Oversensitiveness
i) Persons oversensitive: physically and
ii) Restless, fidgety, starts at least noise.
iii) Anxious, yielding, fainthearted.
Desire and Aversion
i) Desire for cold food, cold drink, ice-cream.
ii) Desire to be magnetised, which ameliorates.
iii) Child has an aversion to mother’s milk.
Sweat
i) Sweat of hands, toes, feet and axillae, are very offensive
ii) Intolerable, sour, carrion like odour of the sweat.
iii) Without perspiration, every evening. (2)
