Factitious Disorder
Definition
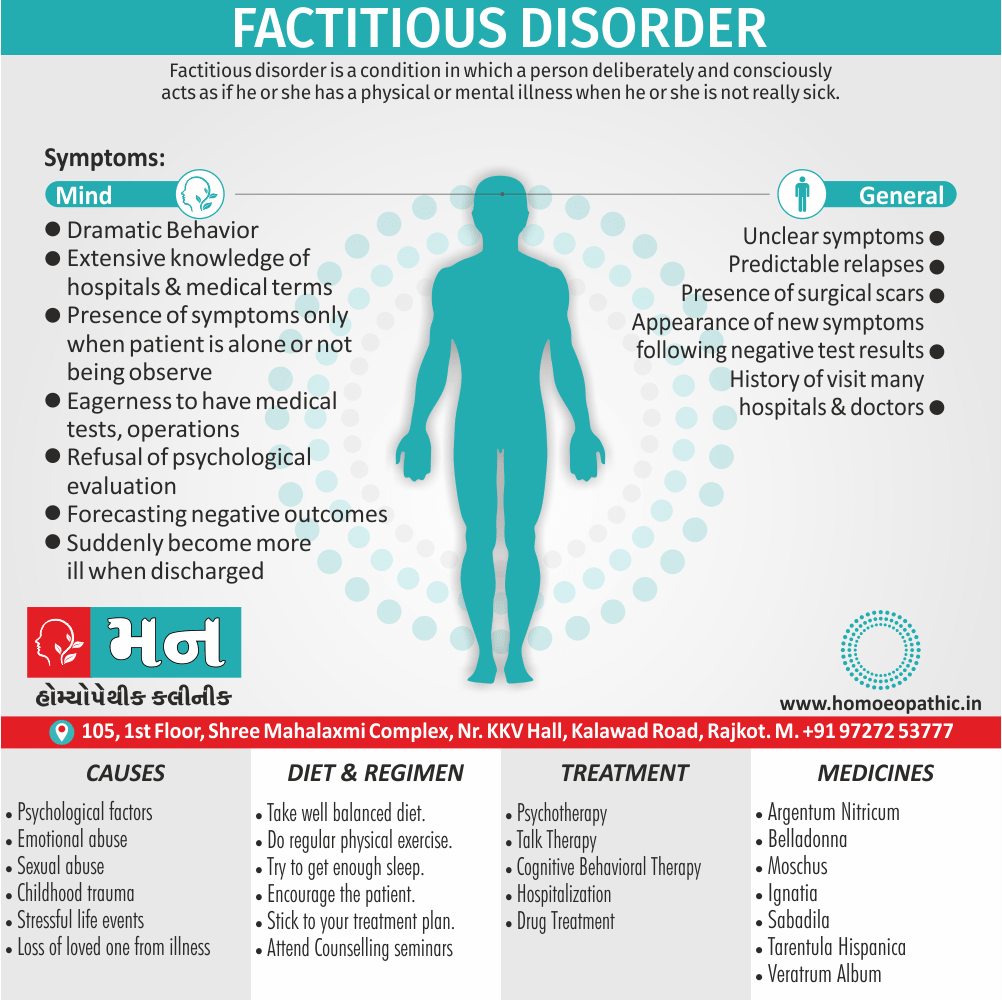
Factitious disorder is a condition in which a person deliberately and consciously acts as if the person has a physical or mental illness when the person is not really sick. [4]
Here are some synonyms for "factitious disorder":
- Munchausen syndrome (for factitious disorder imposed on self): This is the older and more widely recognized term for when someone falsifies illness in themselves.
- Factitious illness: This term emphasizes the act of creating or exaggerating illness.
- Fictitious illness: Similar to factitious illness, but "fictitious" implies a more deliberate fabrication.
- Simulated illness: This term highlights the act of imitating symptoms of a real illness.
- Fabricated illness: Similar to fictitious illness, but emphasizes the creation of a false illness.
Note: It’s important to use the specific term that best describes the situation.
- Factitious disorder imposed on another, also known as Munchausen syndrome by proxy, requires a separate term.
Overview
Epidemiology
Causes
Types
Risk Factors
Pathogenesis
Pathophysiology
Clinical Features
Sign & Symptoms
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Complications
Investigations
Treatment
Prevention
Homeopathic Treatment
Diet & Regimen
Do’s and Don'ts
Terminology
References
Also Search As
Overview
Overview
- The term factitious disorder refers to the intentional production of physical pathology or the feigning of physical or psychological symptoms, with the apparent aim of being diagnose as ill. [1]
- It is a serious mental disorder in which someone deceives others by appearing sick, by purposely getting sick or by self-injury.
- Factitious disorder also can happen when family members or caregivers falsely present others, such as children, as being ill, injure or impair.
- Factitious disorder symptoms can range from mild (slight exaggeration of symptoms) to severe (previously called Munchausen syndrome).
Other key points
- The person may make up symptoms or even tamper with medical tests to convince others that treatment, such as high-risk surgery, is need.
- Although people with factitious disorder know they are causing their symptoms or illnesses, they may not understand the reasons for their behaviors or recognize themselves as having a problem.
- Factitious disorder is challenging to identify and hard to treat. However, medical and psychiatric help are critical for preventing serious injury and even death cause by the self-harm typical of this disorder. [2]
- Factitious disorder differs from malingering in that it does not bring any external reward such as avoidance of military or other occupational duties, or financial compensation. [1]
Epidemiology
Epidemiology
Dahale et al. (2014) conducted a retrospective review of cases diagnosed with FD at a neuropsychiatric center in Southern India over a 10-year period (2001-2010). Out of 81,176 patients, only 8 received a diagnosis of FD, indicating a prevalence of 0.985 per 10,000 patients in this specific sample. This suggests potential underdiagnosis in general psychiatric settings in India.
A study by Chauhan et al. (2023) explored the clinical profile of FD patients in India. They found that physical symptoms were more common than psychological ones, with frequent hospitalizations and a history of multiple surgeries being notable features.
Possible Contributing Factors:
- Cultural Factors: Certain cultural beliefs and practices in India might influence the presentation and recognition of FD. For example, the emphasis on physical symptoms and somatic expressions of distress could lead to FD manifesting primarily through physical complaints.
- Doctor-Patient Relationships: The traditional hierarchical doctor-patient relationship in India, where patients may be less likely to question authority, could potentially create an environment where FD goes undetected.
Emerging Trends:
- Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another (FDIA): While research is limited, there’s a growing awareness of FDIA (formerly Munchausen syndrome by proxy) in India, where a caregiver fabricates or induces illness in another person (often a child) under their care. This raises concerns about potential abuse and highlights the need for increased vigilance and protection of vulnerable individuals.
- Internet and Social Media: The rise of the internet and social media may be influencing the presentation of FD, with individuals potentially using online platforms to seek attention and validation for their fabricated illnesses. This adds another layer of complexity to understanding and addressing FD in the digital age.
Causes
Causes
Biological Factors:
- Brain Function: Some research suggests possible differences in brain structure and function in individuals with factitious disorder, particularly in areas related to emotional regulation and decision-making.
- Genetic Predisposition: While no specific genes have been identified, there may be a genetic vulnerability to developing factitious disorder, especially in families with a history of mental health conditions.
Psychological Factors:
- Early Trauma or Abuse: A history of childhood trauma, abuse, or neglect is often reported in individuals with factitious disorder. These experiences may contribute to difficulties with emotional regulation, self-esteem, and interpersonal relationships.
- Personality Disorders: Factitious disorder can co-occur with personality disorders, particularly borderline personality disorder and narcissistic personality disorder.
- Cognitive Distortions: Individuals with factitious disorder may have distorted thinking patterns that contribute to their deceptive behaviors, such as a need for attention or a belief that they are not worthy of love unless they are sick.
Social Factors:
- Reinforcement of Sick Role: Receiving attention and sympathy when sick can inadvertently reinforce factitious behaviors.
- Healthcare Exposure: Individuals with extensive healthcare knowledge or experience may be more likely to develop factitious disorder, as they have a greater understanding of medical conditions and procedures.
Types
Types of Factitious Disorder (According to DSM-5-TR)
Factitious Disorder Imposed on Self: This is the most common type, where individuals feign or induce illness in themselves. They may:
- Exaggerate existing symptoms
- Fabricate symptoms entirely
- Tamper with medical tests (e.g., contaminating urine samples)
- Self-induce illness (e.g., ingesting toxins)
Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another (FDIA): Previously known as Munchausen syndrome by proxy, this involves a caregiver (usually a parent) fabricating or inducing illness in another person under their care (often a child). This is considered a form of abuse and can have serious consequences for the victim.
Subtypes Based on Symptom Presentation:
While not explicitly categorized in the DSM-5-TR, factitious disorder can also be classified based on the types of symptoms presented:
Predominantly Physical Symptoms: Individuals focus on fabricating or inducing physical symptoms, often leading to repeated hospitalizations and unnecessary medical procedures.
Predominantly Psychological Symptoms: Individuals feign or induce psychological symptoms, such as depression, anxiety, or hallucinations.
Combined Physical and Psychological Symptoms: Individuals present with a combination of fabricated or induced physical and psychological symptoms.
Risk Factors
Risk factors:
Several factors may increase the risk of developing factitious disorder, including:
- Childhood trauma, such as emotional, physical or sexual abuse
- A serious illness during childhood
- Loss of a loved one through death, illness or abandonment
- Past experiences during a time of sickness and the attention it brought
- A poor sense of identity or self-esteem
- Personality disorders
- Depression
- Desire to be associated with doctors or medical centers
- Work in the healthcare field
Factitious disorder is consider rare, but it’s not known how many people have the disorder.
Some people use fake names to avoid detection, some visit many different hospitals and doctors, also some are never identify all of which make it difficult to get a reliable estimate. [2]
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis
Factitious disorder is a challenging condition to understand, not only due to its deceptive nature but also because its underlying causes remain somewhat elusive. While a definitive "pathogenesis" (the biological mechanism that leads to a disease) hasn’t been fully established, we can explore the intricate interplay of factors that contribute to its development.
Factors Contributing to the Development of Factitious Disorder
It’s important to view factitious disorder through a biopsychosocial lens, acknowledging the interconnectedness of biological, psychological, and social factors.
Biological Factors:
- Neurobiological Abnormalities: Research suggests potential alterations in brain function, particularly in regions associated with emotional regulation, reward processing, and decision-making. However, more studies are needed to confirm these findings.
- Genetic Vulnerability: While no specific genes have been directly linked to factitious disorder, a family history of mental health conditions, including personality disorders, may increase the risk.
Psychological Factors:
- Early Trauma and Attachment: Adverse childhood experiences, such as abuse, neglect, or insecure attachment, can significantly impact emotional development and increase vulnerability to factitious disorder. These experiences may lead to difficulties with self-regulation, identity formation, and interpersonal relationships.
- Personality Dynamics: Factitious disorder often co-occurs with personality disorders, particularly borderline personality disorder and narcissistic personality disorder. These disorders involve challenges with emotional regulation, impulsivity, and interpersonal relationships, which may contribute to the development and maintenance of factitious behaviors.
- Cognitive Distortions: Individuals with factitious disorder may exhibit distorted thinking patterns, such as a need for attention and validation, a belief that they are only worthy of love when sick, or a difficulty distinguishing between internal needs and external validation.
Social Factors:
- Reinforcement of the Sick Role: Receiving attention, sympathy, and care when presenting as ill can inadvertently reinforce factitious behaviors. This can create a cycle where the individual continues to fabricate or induce illness to meet their emotional needs.
- Healthcare Environment: Exposure to the healthcare system, either through personal experience or through employment in a healthcare setting, may provide individuals with the knowledge and opportunity to deceive others effectively.
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
Neurobiological Factors
Brain Structure and Function: Neuroimaging studies have suggested possible differences in brain structure and function in individuals with factitious disorder compared to healthy controls. These differences may involve:
- Prefrontal Cortex: This area is involved in decision-making, planning, and impulse control. Abnormalities in this region could contribute to the impulsive and deceptive behaviors seen in factitious disorder.
- Amygdala and Limbic System: These areas are involved in emotional processing and regulation. Dysfunction in these regions may contribute to difficulties with emotional regulation and increased sensitivity to stress, potentially leading to factitious behaviors as a coping mechanism.
- Reward System: The brain’s reward system, involving dopamine pathways, may be implicated in factitious disorder. The attention and sympathy received when presenting as ill could activate reward circuits, reinforcing the deceptive behaviors.
- Prefrontal Cortex: This area is involved in decision-making, planning, and impulse control. Abnormalities in this region could contribute to the impulsive and deceptive behaviors seen in factitious disorder.
Neurotransmitters and Hormones:
- Dopamine: Dysregulation of dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in reward and motivation, may contribute to the compulsive nature of factitious behaviors.
- Cortisol: Individuals with factitious disorder may exhibit altered cortisol levels, indicating dysregulation of the stress response system. This could contribute to emotional instability and increased vulnerability to stress.
Genetic and Epigenetic Factors
- Genetic Predisposition: While no specific genes have been definitively linked to factitious disorder, there may be a genetic vulnerability to developing the condition, especially in families with a history of mental health disorders, including personality disorders.
- Epigenetic Modifications: Environmental factors, such as early trauma or stress, can influence gene expression through epigenetic modifications. These modifications could potentially contribute to the development of factitious disorder.
Clinical Features
Clinical Features
Deliberate Fabrication or Induction of Symptoms: This is the hallmark of factitious disorder. Individuals may:
- Exaggerate existing symptoms: Making a minor illness seem more severe.
- Fabricate symptoms entirely: Reporting symptoms that don’t exist.
- Tamper with medical tests: Altering samples or manipulating devices to produce abnormal results.
- Self-induce illness: Ingesting toxins, injuring themselves, or interfering with wound healing.
Predominantly Physical or Psychological Symptoms:
- Physical: Focus on physical complaints, often leading to numerous medical investigations and procedures.
- Psychological: Feigning psychological symptoms like depression, anxiety, or PTSD.
- Combined: Presenting with both physical and psychological symptoms.
Extensive Medical Knowledge: Individuals with factitious disorder often have a surprising depth of medical knowledge, acquired through personal experience, research, or even employment in a healthcare setting.
Dramatic Presentation and Seeking Attention: They may present their symptoms in a dramatic or exaggerated manner, often seeking attention and sympathy from healthcare providers.
Pseudologia Fantastica: A tendency to tell elaborate and fantastical stories about their medical history or personal life.
History of Multiple Hospitalizations and Procedures: Individuals with factitious disorder often have a history of frequent hospitalizations, surgeries, and invasive procedures, despite a lack of clear medical explanations.
Acceptance of Invasive Procedures: They may readily agree to painful or risky procedures, even when the potential benefits are questionable.
Lack of Cooperation with Treatment: Individuals may be reluctant to comply with treatment recommendations or follow-up appointments, especially when their deception is challenged.
Reference: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). American Psychiatric Association,
Sign & Symptoms
Sign & Symptoms
- Dramatic but inconsistent medical history
- Unclear symptoms that are not controllable, become more severe, or change once treatment has begun
- Predictable relapses following improvement in the condition
- Extensive knowledge of hospitals and/or medical terminology, as well as the textbook descriptions of illness
- Presence of many surgical scars
- Appearance of new or additional symptoms following negative test results
- Presence of symptoms only when the patient is alone or not being observe
- Willingness or eagerness to have medical tests, operations, or other procedures
- History of seeking treatment at many hospitals, clinics, and doctors’ offices, possibly even in different cities
Other symptoms:
- Reluctance by the patient to allow healthcare professionals to meet with or talk to family members, friends, and prior healthcare providers
- Refusal of psychiatric or psychological evaluation
- Forecasting negative medical outcomes despite no evidence of this
- Sabotaging discharge plans or suddenly becoming more ill as one is about to be discharged from the hospital setting [3]
Clinical Examination
Clinical Examination
While a definitive diagnosis of factitious disorder relies on identifying deliberate deception, the clinical examination plays a crucial role in gathering information and assessing for inconsistencies.
- Thorough Medical History: Obtain a detailed medical history, including past hospitalizations, surgeries, and medications. Pay close attention to any inconsistencies or gaps in the narrative.
- Comprehensive Physical Examination: Conduct a thorough physical examination, looking for any objective signs of illness or injury. Note any discrepancies between the reported symptoms and the physical findings.
- Targeted Investigations: Order relevant investigations to rule out any underlying medical conditions. Be mindful of the potential for manipulation of samples or results.
- Collateral Information: With the patient’s consent, gather information from family members, previous healthcare providers, and medical records. This can help identify patterns of deceptive behavior or inconsistencies in the patient’s history.
- Observation and Documentation: Carefully observe the patient’s behavior and interactions with healthcare staff. Document any unusual findings or inconsistencies in the medical record.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
Generally, Diagnosing factitious disorder is often extremely difficult.
In detai; People with factitious disorder are experts at faking many different diseases and conditions.
And often they do have real and even life-threatening medical conditions, even though these conditions may be self-inflicted.
The person’s use of multiple doctors and hospitals, the use of a fake name, and privacy and confidentiality regulations may make gathering information about previous medical experiences difficult or even impossible.
Diagnosis is based on objectively identifying symptoms that are made up, rather than the person’s intent or motivation for doing so.
A doctor may suspect factitious disorder when:
- The person’s medical history doesn’t make sense
- No believable reason exists for an illness or injury
- The illness does not follow the usual course
- There is a lack of healing for no apparent reason, despite appropriate treatment
- There are contradictory or inconsistent symptoms or lab test results
- The person resists getting information from previous medical records, other health care professionals or family members
- The person is caught in the act of lying or causing an injury
Physician may use the criteria for factitious disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), published by the American Psychiatric Association. [2]
Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Factitious disorder, with its intricate tapestry of fabricated or induced symptoms, often poses a significant diagnostic challenge. Distinguishing it from other conditions with similar presentations is crucial for ensuring appropriate care and avoiding unnecessary medical interventions.
Key Conditions to Consider in the Differential Diagnosis
- Malingering: While both involve intentional deception, malingering is motivated by external incentives, such as financial gain, avoiding work, or obtaining drugs. In contrast, factitious disorder is driven by an internal need to assume the sick role.
- Somatic Symptom Disorder: Individuals with somatic symptom disorder experience genuine physical symptoms, but their distress and preoccupation with these symptoms are excessive and disproportionate to the objective medical findings. Unlike factitious disorder, there is no intentional deception.
- Conversion Disorder (Functional Neurological Symptom Disorder): Conversion disorder involves neurological symptoms (e.g., paralysis, blindness) that cannot be explained by any known medical condition. While the symptoms are real, they are thought to be caused by psychological factors. Differentiating conversion disorder from factitious disorder can be challenging, as both may involve a lack of conscious awareness of the underlying psychological motivations.
- Medical Conditions: It’s crucial to thoroughly rule out any underlying medical conditions that could explain the presented symptoms. This may involve extensive investigations and consultations with specialists. Some medical conditions with complex or atypical presentations that might mimic factitious disorder include:
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus)
- Rare genetic disorders
- Neurological conditions
- Endocrine disorders
Complications
Complication
Factitious disorder, characterized by the deliberate fabrication or induction of illness, can have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the initial deception. The pursuit of the sick role, often driven by complex psychological needs, can lead to a cascade of complications that affect physical health, psychological well-being, and social relationships.
Physical Complications
- Iatrogenic Harm: Perhaps the most significant risk is iatrogenic harm, which refers to complications arising from unnecessary medical interventions. Individuals with factitious disorder may undergo numerous invasive procedures, surgeries, and medications, all of which carry risks of complications, infections, and even death.
- Substance Abuse: Some individuals with factitious disorder may abuse substances, such as prescription medications or illicit drugs, to induce or mimic symptoms. This can lead to addiction, overdose, and other health problems.
- Self-Harm: The methods used to induce illness can range from subtle manipulations to severe self-harm, including poisoning, self-inflicted wounds, and interference with wound healing. These actions can lead to significant physical damage and even disability.
- Chronic Pain: Repeated self-induced injuries or the long-term effects of unnecessary medical treatments can lead to chronic pain syndromes.
Psychological Complications
- Comorbid Mental Health Disorders: Factitious disorder frequently co-occurs with other mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, personality disorders, and substance use disorders. These conditions can exacerbate the challenges of managing factitious disorder and increase the risk of suicide.
- Impaired Social Functioning: Deceptive behaviors and the constant need for medical attention can strain relationships with family, friends, and healthcare providers. Individuals with factitious disorder may experience social isolation and difficulty maintaining employment.
- Decreased Quality of Life: The preoccupation with illness and the pursuit of medical care can significantly impair an individual’s quality of life, leading to reduced enjoyment of activities, social withdrawal, and financial difficulties.
Complications of Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another (FDIA)
- Abuse and Neglect: FDIA, where a caregiver fabricates or induces illness in another person (often a child), is a form of abuse and neglect. The victim may suffer significant physical and psychological harm, including unnecessary medical procedures, emotional trauma, and even death.
- Legal Consequences: Perpetrators of FDIA may face legal charges, including child abuse, medical neglect, and assault.
Investigations
Investigations
Factitious disorder, characterized by the deliberate fabrication or induction of illness, presents a unique challenge in medical investigation. The pursuit of the sick role, often driven by complex psychological needs, can lead individuals to undergo a myriad of tests and procedures, many of which are unnecessary and potentially harmful. Therefore, the investigation of suspected factitious disorder requires a careful and ethical approach, balancing the need to rule out genuine medical conditions with the recognition of potential deception.
Challenges in the Investigative Process
- The Paradox of Investigation: The very act of investigating factitious disorder can inadvertently reinforce the patient’s deceptive behaviors. Each test or procedure, even if it yields negative results, can be seen as validation of their illness and perpetuate the cycle of seeking medical attention.
- Maintaining Objectivity: It can be challenging for healthcare professionals to remain objective when faced with a patient who appears genuinely distressed and eager for medical intervention. However, it’s crucial to avoid being swayed by emotional appeals and to maintain a critical eye when evaluating the evidence.
- Ethical Considerations: The investigation of factitious disorder must be conducted ethically, respecting the patient’s autonomy and dignity. Covert surveillance or deceptive techniques should be avoided, as they can erode trust and damage the therapeutic relationship.
Key Components of the Investigation
- Thorough Medical History: Obtain a detailed medical history, including past hospitalizations, surgeries, and medications. Pay close attention to any inconsistencies, gaps in the narrative, or evidence of "doctor shopping" (seeking care from multiple providers).
- Comprehensive Physical Examination: Conduct a thorough physical examination, documenting any objective findings. Note any discrepancies between the reported symptoms and the physical examination.
- Targeted Investigations: Order relevant investigations to rule out any underlying medical conditions. Be mindful of the potential for manipulation of samples or results. Consider repeating tests at different laboratories or under close observation if tampering is suspected.
- Review of Medical Records: Obtain and review medical records from previous healthcare providers, with the patient’s consent. This can help identify patterns of deceptive behavior or inconsistencies in the patient’s history.
- Collateral Information: Gather information from family members, friends, or other individuals who may have relevant insights into the patient’s behavior and medical history.
- Psychological Assessment: Consider a referral for a psychological evaluation to assess for underlying mental health conditions, including personality disorders, that may contribute to factitious behaviors.
Treatment
Treatment
Having a primary care doctor i.e.:
- Using one doctor or gatekeeper to oversee medical care can help manage needed care and the treatment plan and reduce or eliminate visits to numerous doctors, specialists and surgeons.
Psychotherapy i.e.:
- Talk therapy (psychotherapy) and behavior therapy may help control stress and develop coping skills.
- If possible, family therapy also may be suggested.
- Other mental health disorders, such as depression, also may be addressed.
Medication i.e.:
- Medications may be used to treat additional mental health disorders, such as depression or anxiety.
Hospitalization i.e.:
- In severe cases, a temporary stay in a psychiatric hospital may be necessary for safety and treatment.
Connect with someone i.e.:
- Many people with factitious disorder lack friendships and other relationships.
- Try to find someone you’re able to confide in, share enjoyable times with and offer your own support to.
Treatment may not be accepted or may not be helpful, especially for people with severe factitious disorder.
In cases where the factitious disorder is imposed on others, the doctor assesses for abuse also reports the abuse to the appropriate authorities, if indicated. [2]
Prevention
Prevention
Unfortunately, there’s no known way to prevent factitious disorder.
This is because the exact causes of factitious disorder are still not fully understood. It’s believed to be a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Underlying psychological issues: Possible contributors include childhood trauma, personality disorders, or having a serious illness as a child.
- Biological factors: There might be some biological predisposition to the disorder, though research is ongoing.
- Environmental factors: Stressful life events or a history of frequent illnesses in the family could play a role.
Homeopathic Treatment
Remedies for Factitious Disorder:
Tarentula Hispanica:
- It is one of the most important remedy for factitious disorder.
- It has fearfulness, especially when out of her usual surrounding of impending calamity.
- Because of this fear it develops the symptoms of pretending and seek attention.
- Pretends to be sick.
- Faints in front of everyone.
- Fear of being assaulted.
- Profound grief and anxiety, anguish, melancholy profound with quick change of mood and becomes cheerful.
Veratrum album:
- Melancholy, with stupor and mania.
- Always wants to escape from work.
- Aimless wandering at home.
- It is one of the strongest remedies for malingering.
- Puerperal mania.
- Pretends to be pregnant.
- Delusions of impending misfortune.
- Frenzy of excitement and curses everyone.
- Attacks of pain, with delirium driving to madness.
- Cursing howling at night.
Other indicated remedies are:
- Moschus
- Silica
- Argentum Nitricum
- Belladonna
- Ignatia
- Plumbum
- Sabadilla [5]
Diet & Regimen
Diet and Regimen
It’s important to understand that factitious disorder is a mental health condition, not a physical one. Therefore, there isn’t a specific diet or regimen that can cure or treat it.
Think of it this way: someone with factitious disorder may fake a stomach ache, but their real issue isn’t their stomach, it’s a psychological need for attention and care. Focusing on physical treatments like diets might even unintentionally reinforce their behavior.
Here’s what DOES help:
- Psychotherapy: This is the core treatment. Therapy helps address the root causes of the disorder, such as past trauma or personality difficulties. It also teaches coping skills and helps change harmful thought patterns.
- Medication: Sometimes medication is used to treat conditions that occur alongside factitious disorder, like depression or anxiety. However, medication doesn’t directly treat the factitious disorder itself.
A healthy lifestyle is important for everyone, including people with factitious disorder:
- Balanced diet: Eating nutritious foods supports overall well-being, but it won’t directly address the factitious disorder.
- Regular exercise: Exercise can help reduce stress and improve mood, which can be beneficial, but it’s not a cure.
- Stress management: Learning to manage stress can be helpful, as stress can sometimes trigger factitious disorder behaviors.
The key takeaway: Factitious disorder requires professional mental health treatment to address the underlying psychological needs driving the behavior. While a healthy lifestyle is always a good idea, it’s not a substitute for therapy and addressing the root causes of this complex condition.
Do’s and Don'ts
Do’s & Don’ts
Factitious disease do’s & don’ts
Do:
- Express concern and offer support: Focus on your concern for their well-being, not on accusing them of faking.
- Encourage them to seek professional help: Gently suggest they talk to a mental health professional, emphasizing that help is available.
- Set boundaries: Don’t play along with their fabricated illnesses or enable their behavior.
- Protect yourself: If you’re dealing with someone with Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another (FDIA), prioritize the safety and well-being of the potential victim.
- Educate yourself: Learn about factitious disorder to better understand the condition and how to respond.
Don’t:
- Confront them angrily or accuse them of lying: This is likely to make them defensive and less receptive to help.
- Enable their behavior: Avoid giving them the attention and sympathy they may be seeking through their fabricated illnesses.
- Ignore the situation: Factitious disorder is a serious condition that requires professional help.
- Try to diagnose them yourself: Leave the diagnosis to qualified mental health professionals.
If you think you might have factitious disorder:
Do:
- Seek professional help: A therapist can help you understand the underlying causes of your behavior and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Be honest with yourself: Acknowledge the challenges you’re facing and the impact your actions have on yourself and others.
- Focus on your mental health: Prioritize your psychological well-being and engage in healthy coping strategies.
Don’t:
- Be ashamed or embarrassed: Factitious disorder is a mental health condition, not a character flaw.
- Ignore the problem: The longer you wait to seek help, the more difficult it can be to address the underlying issues.
- Give up: Recovery is possible with the right support and treatment.
Terminology
Terminology
- Factitious Disorder Imposed on Self (FDIS): Faking illness in yourself. Formerly known as Munchausen syndrome.
- Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another (FDIA): Making someone else appear sick, often a child. Formerly Munchausen syndrome by proxy.
- Malingering: Faking illness for external gain (like money or time off). Different from factitious disorder, where the motivation is internal.
- Peregrination: Going to different hospitals with fake identities and stories.
Pseudologia fantastica: Habit of elaborate lying, often seen in factitious disorder.
- Pathological Lying:
- Meaning: This goes beyond typical lying. It’s a persistent pattern of deception, often without clear external motivation. People with factitious disorder may engage in pathological lying to support their fabricated illnesses.
- Ganser Syndrome:
- Meaning: A rare condition where someone gives approximate answers to questions, even when they know the correct answer. Sometimes seen in people with factitious disorder or other mental health conditions.
- Munchausen by Internet:
- Meaning: This is a newer term for when someone uses online platforms (social media, forums) to fabricate illnesses and gain attention and sympathy.
- Hospital Addiction:
- Meaning: Some individuals with factitious disorder develop a strong attachment to the hospital environment and become dependent on the care and attention they receive there.
- 5. Factitious Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (NOS):
- Meaning: This was a category used in older versions of diagnostic manuals (like DSM-IV) for cases that didn’t perfectly fit the criteria for FDIS or FDIA, but still had features of factitious disorder.
Other terminologies
1. "Susceptibility":
- Meaning in Homeopathy: This refers to an individual’s predisposition to illness or imbalance.
- Relevance to Factitious Disorder: A homeopath might explore whether the person has an increased susceptibility to emotional distress or a heightened need for attention, which could contribute to factitious behaviors.
2. "Disharmony":
- Meaning in Homeopathy: An imbalance or disturbance in the vital force, leading to ill health.
- Relevance to Factitious Disorder: Factitious disorder might be seen as a manifestation of a deeper disharmony within the individual, a misdirected attempt to seek healing or balance.
3. "Mental/Emotional Remedies":
- Meaning in Homeopathy: Substances that specifically target mental and emotional symptoms.
- Relevance to Factitious Disorder: While not directly treating the disorder, these remedies might be used to address underlying anxiety, depression, or trauma that could contribute to factitious behaviors.
4. "Constitutional Type":
- Meaning in Homeopathy: The individual’s overall physical, mental, and emotional makeup.
- Relevance to Factitious Disorder: Understanding the person’s constitutional type could help identify underlying vulnerabilities and tailor homeopathic support.
5. "Aggravating/Ameliorating Factors":
- Meaning in Homeopathy: Factors that worsen or improve symptoms.
- Relevance to Factitious Disorder: Observing what triggers factitious behaviors could provide valuable insights for homeopathic treatment and management.
References
References
- Psychiatry, Fourth Edition- Oxford Medical Publications – SRG- by Geddes, Jonathan Price, Rebecca McKnight / Ch 25.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/factitious-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20356028
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9832-an-overview-of-factitious-disorders
- https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/factitious-disorders#1
- Homeopathy in treatment of Psychological Disorders by Shilpa Harwani / Ch 10.
Also Search As
Also Search As
1. Broaden your search terms:
- Use synonyms for "factitious disorder" like:
- Munchausen syndrome
- Hysteria (older term)
- Deception syndrome
- Include related concepts:
- Attention-seeking behavior
- Pathological lying
- Emotional dependency
- Focus on specific symptoms:
- If you know the person’s specific complaints (e.g., fabricated abdominal pain), search for homeopathic approaches to those symptoms.
2. Explore homeopathic resources:
- Homeopathic journals: Search journals like "The American Homeopath," "Homeopathy," or "The British Homeopathic Journal" using the keywords mentioned above.
- Homeopathic databases: Utilize online databases like "Hompath" or "ReferenceWorks" to search for relevant cases or remedies.
- Homeopathic websites: Explore reputable websites like the National Center for Homeopathy or the Homeopathic Educational Services for articles or case studies.
3. Consult with a homeopath:
- A qualified homeopath can offer insights into how homeopathy might approach cases with similar presentations to factitious disorder, even if they don’t use that specific term. They can also help you understand relevant homeopathic principles and remedies.
4. Be patient and persistent:
- Finding relevant information may take time and effort. Be prepared to explore different resources and refine your search strategy as needed.
Other ways
By Specific Names/Types:
- Factitious Disorder Imposed on Self (FDIS): The most common and accepted term currently.
- Factitious Disorder Imposed on Another (FDIA): Crucial when researching cases involving caregivers, replacing the outdated "Munchausen by Proxy."
- Munchausen Syndrome: Though outdated, it’s still relevant for finding older research and resources.
2. By Related Symptoms/Behaviors:
- Pseudologia Fantastica: For articles focusing on the compulsive lying aspect often associated with the disorder.
- Peregrination: Useful when researching patients who travel between hospitals and assume new identities.
- Self-harm: Important to include if this is a specific area of interest within factitious disorder.
3. By Underlying Psychological Aspects:
- Attention-seeking behavior: This can lead to research on the motivations behind factitious disorder.
- Histrionic Personality Disorder: Exploring potential connections and overlapping traits can be insightful.
- Trauma/Abuse: Searching for these as risk factors can uncover information on vulnerability to the disorder.
4. By Medical/Diagnostic Focus:
- Conversion Disorder: Essential for distinguishing factitious disorder from conditions with genuine, but psychologically-influenced, neurological symptoms.
- Somatic Symptom Disorder: Helps differentiate from cases where physical symptoms are present but not intentionally produced.
- Differential Diagnosis: This focuses on how healthcare professionals accurately identify factitious disorder.
5. By Resource Type:
- Medical Journals: PubMed, JAMA, etc., for clinical studies and professional articles.
- Psychology Databases: PsycINFO, Google Scholar, for research on the psychological aspects.
- Patient Advocacy Sites: Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, for accessible information and personal stories.
- Books: Search library catalogs or online retailers using the terms above.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Factitious Disorder?
Factitious disorder is a condition in which a person deliberately and consciously acts as if the person has a physical or mental illness when the person is not really sick
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Factitious Disorder?
- Tarentula Hispanica
- Veratrum album
- Moschus
- Silica
- Argentum Nitricum
- Belladonna
- Ignatia
- Plumbum
What causes Factitious Disorder?
- Childhood trauma
- A serious illness during childhood
- Loss of a loved one through death, illness or abandonment
- Past experiences during a time of sickness and the attention it brought
- A poor sense of identity or self-esteem
- Personality disorders
- Depression
- Desire to be associated with doctors or medical centers
- Work in the healthcare field
What are the symptoms of Factitious Disorder?
- Dramatic but inconsistent medical history
- Unclear symptoms
- Predictable relapses
- Extensive knowledge of hospitals and/or medical terminology
- Presence of many surgical scars
- Presence of symptoms only when the patient is alone or not being observe
