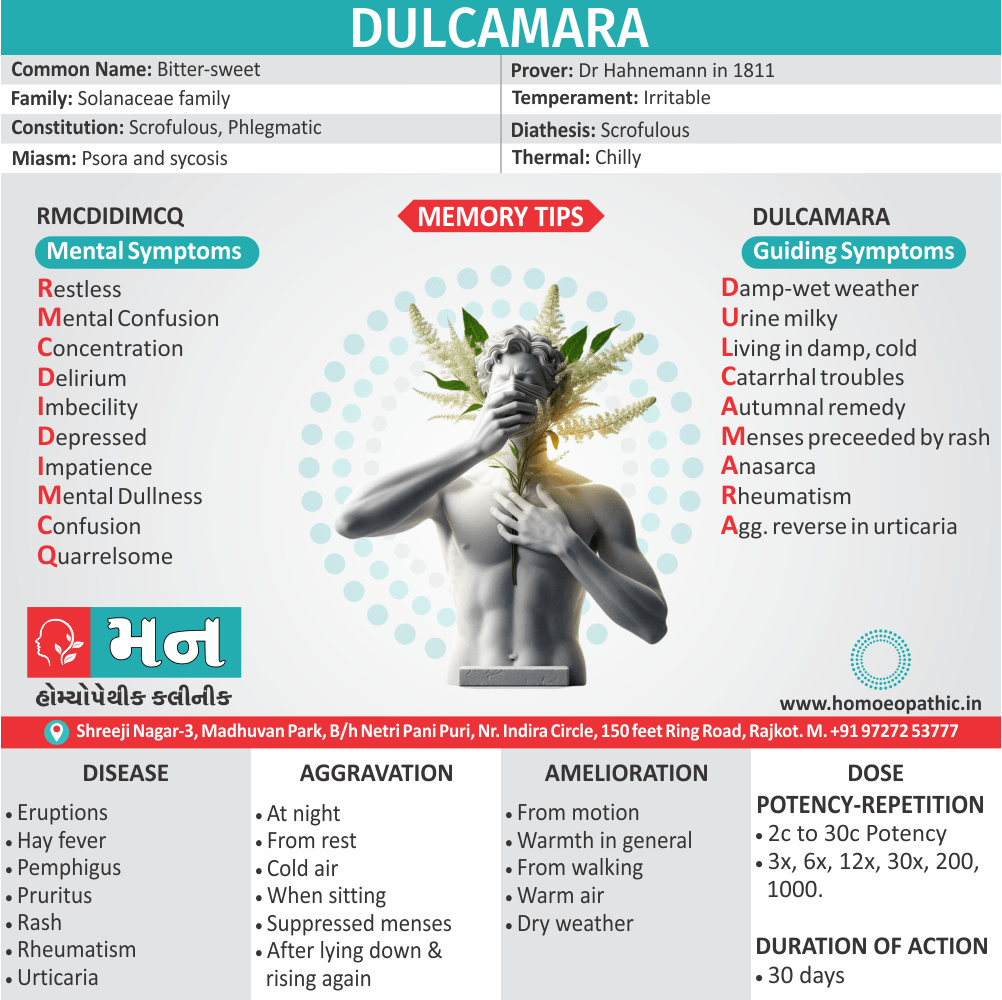
Dulcamara
Dulcamara has synonyms depending on whether you’re referring to the plant itself or its other uses:
For the Plant:
- Common names:
- Bittersweet
- Bittersweet nightshade
- Woody nightshade
- Climbing nightshade
- Violet bloom (referencing the flowers)
- (and many others)
Important Note: Dulcamara is poisonous, so these common names should be used with caution, especially if there’s a risk of someone confusing it with a safe plant.
For other uses:
- Dulcamara itself means "bittersweet" (literally "sweet-bitter") – This refers to the taste of the plant.
D
U
L
C
A
M
A
R
A
D
Damp-wet weather remedy:
Dr. E. B. Nash said Dulcamara is a ‘wet-cold weather remedy (Natrum Sulph.).
Dr. Clarke said, the leading indication for the homoeopathic use of Dulcamara is found in its modality aggravation from cold and damp.
Any condition which has this feature may find its remedy in Dulcamara.
U
Urine milky:
In Dulc. we find, milky urine from wading with bare feet in cold water, esp. in children.
Urine also escapes involuntarily So, the frequency of urination is increased.
Master Kent said, pt. says, ‘Doctor, if I get chilled, I must hurry to urinate."
L
Living in damp, cold basement:
- Dr. Clarke said, effects of lying on damp ground for,e.g., paralysis-condition which are esp. if sudden, So Dulc. rescues such cases.
- Dr. Allen expressed that pt. living or working in a damp, cold basement, or a milk dairy (Aran., Ars., Nat.S.), diarrhoea from taking cold in damp places etc.-Dulc. will be the drug of choice, provided other symptoms corroborate.
C
Catarrhal troubles:
Master Kent said Dulc. produces a marked catarrhal state.
Catarrhal condition from the eyes, nose, catarrh of the stomach, intestines, -characterized by increase or profuse secretion from mucous membranes, Dulc. finds similimum in such cases.
A
Autumnal remedy:
Our lamented Kent said, Dulc. is markedly an autumnal remedy.
The Dulc. patients go through the summer very comfortably, their catarrhal conditions to a great extent pass away, but as soon as the cold nights come on, and the cold rains come, all their difficulties return.
M
Menses preceeded by rash:
Master Kent discussed it as, ‘rash comes out upon face before the menses. (Conium., -during menses, Bellis, Bell., Calc., Eug.. Graph., Psor., Sang C., Sars.).
This symptom comes as forerunner of catamenia, with extraordinary sexual excitement.
A
Anasarca:
Anasarca, after ague, rheumatism or scarlet fever; dropsical condition results after suppressed sweat, suppressed eruptions, exposure to cold.
Master Kent said if the pt. has taken cold, or from sudden change of weather, damp and the cold, the feet commence to swell, there is albumin in the urine, the limbs are waxy, the face becomes waxy and sallow.
R
Rheumatism:
Catarrhal rheumatism brought on or aggravated by exposure to cold, damp, rainy weather, or sudden changes in hot weather.
Dr. E. B. Nash said all kinds of inflammatory and rheumatic diseases may spring from change of weather, from warm to cold.
Master Kent said, Dulc. is full of rheumatism, full of rheumatic pains and aches, sore and bruise all over, the joints are inflamed, become red, sensitive to touch and are swollen; inflammatory rheumatism due to suppressed perspiration, –Dulc. will be the drug of choice, ‘provided other symptoms corroborate’.
A
Aggravation reverse in urticaria:
Urticaria, over whole body, no fever; itching burns after scratching; aggravation in warmth and amelioration in cold.
The modalities reverse of general modality. (3)
R
M
C
D
I
D
I
M
C
Q
R
Restless
Restlessness of mind.
Screaming, as in hydrocephalus
M
Mental
Confusion Mental confusion, cannot concentrate his thoughts.
C
Concentration
Cannot find the right word, cannot concentrate his thoughts
I
Imbecility
Imbecility more frequent than insanity.
Asks for one thing or another, rejecting it when proffered.
D
Depressed
Depressed; solicitude concerning the future.
I
Impatience
Quarrelsome, irritable mood; easily angered.
M
Mental Dullness
Dullness of mind
C
Confusion
Confusion, cannot find the right word.
Q
Quarrelsome
Quarrelsome disposition, in the afternoon, without being angry.
Introduction
Constitution
Clinical
Mental Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms
Characteristic
Therapeutic Value
Modality
Remedy Relationship
Dose
Reference
Terminology
Also Search As
Introduction
Introduction
Common name:
- Bitter-sweet, Woody night shade (3)
Synonyms:
- Fellon wood, Garden night shade, scarlet berry, Violent bloom,
- Latin-Amara dulcis (3)
Family / Group / Class / Order:
- Vegetable kingdom, Solanaceae family
Habit and habitat / Description:
- It is widely distributed in Europe, Asia and Africa and now naturalised in America.
- It is a deciduous and climbing plant.
- The stem grows up to 10 feet in height.
- Leaves are alternate with two ear-like lobes at the base.
- When the leaves are chewed, it is first sweet But then bitter.
- Flowers are purple in colour.
- They bloom from May to September. (1)
Name of prover:
- Dr Hahnemann in 1811
Introduction and history:
- Dulcamara is a very good medicine in homeopathy.
- It is well known to the world since a very long time and was used to make ointments for smarting wounds.
- Dulcamara is one of those medicines which can combat suppressed conditions.
- The name Dulcamara is from Latin word ‘dulces’ meaning sweet and ‘amarus’ bitter, since the taste is first sweet and then bitter.
- Dulcamara was used as a medicine as early as the thirteenth century.
Active principles:
- The chief alkaloid is solnin.
Preparation & Parts used:
- Mother tincture is prepared from the fresh green stems gathered before flowering. (1)
Constitution
Constitution
Physical make up:
- It is specially adapted to people who take cold from a slight change of weather.
- They have a scrofulous and phlegmatic constitution with slow perception.
Temperament
- Irritable
Diathesis:
- Scrofulous
Relation with heat & cold:
- Chilly
Miasm:
- Psora and sycosis (1)
Clinical
Clinical conditions
- Adenitis, Asthma, Diarrhoea, Eruptions, Facial neuralgia, Hay fever, Headache, Herpes zoster, Middle ear catarrh, Paralysis, Pemphigus, Pruritus, Rash, Rheumatism, Rhinitis, Scald head, Umbilical colic, Urticaria, Warts, Whooping cough. (2)
Sites of action / Pharmacodynamics:
- Mucous membrane of eyes, bronchi, bladder, back, skin, loin muscles, etc. (1)
Causation (Causes / Ailments from):
- Damp with cold, checked eruptions, injuries, checked perspiration, getting wet in rain, exposure to cold. (1)
Physiological action of Dulcamara
- The agent in toxic doses causes dyspnoea, tremor, muscular contractions, nausea, vomiting, with pain in the joints, a purplish colour of the hands and face, and a general catarrhal inflammation.
- It produces enlargement of the lymphatic glands and an erythematous eruption upon the skin. (5)
Patho-physiological changes / Pathogenesis:
- It has a great action on the vagus nerve; it depresses, paralyses the respiratory system causing slowing of respiration with dyspnoea.
- Acts specially upon the mucous membranes and muscular tissues giving rise to catarrhal conditions.
- It acts on lungs and produces an emphysematous condition.
- It acts on serous membranes producing inflammation of joints resulting in rheumatism.
- It acts upon the lymphatics and skin producing glandular enlargements, cellular effusions and eruptions. (1)
Mental Symptoms
Characteristic Mental Symptoms (psychology)
- Mental confusion, cannot concentrate his thoughts.
- Inclination to scold without being angry.
- Patient is very restless, depressed and quarrelsome.
- Delirium at night with pain.
- Cannot find the right word due to mental confusion.
- Ask for one or another thing, rejecting it when offered.
- Great impatience with restlessness; combative disposition, without anger. (1)
Guiding Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms Of Dulcamara
1. Generalities:
- Rheumatic-like pains in the muscles, (<) cold, wet weather.
- General catarrhal symptoms, with free secretions, (<) cold, wet weather.
2. Head:
- Stupefying headache; with heaviness; unpleasant sensation of chilliness in the cerebellum and over the back
- Sensation as if the hair were standing on end; returning every day in the evening; better when talking; when lying quiet; worse before midnight.
- Digging pain in the cerebellum with the sensation as if the brain were enlarged.
Vertigo
- with darkness before the eyes when rising from bed.
- Severe headache with dry nose; worse after cold, damp spell or getting overheated with too much clothing.
- Scald head, thick brown crusts with reddish borders, on forehead, temples and chin; bleeding when scratched.
3. Eye:
- Dim-sightedness; he sees everything as through a gauze; sparks before the eyes. (Primary amaurosis).
- Thick yellow discharge; granular lids.
4. Ears:
- Stitches and tingling in the ears.
5. Nose:
- DRY coryza with headache; better by motion; worse during rest; in cold air; in open air; (Nux v. better in open air); renewed by the slightest exposure.
- Profuse discharge of WATER from nose and eyes; worse in open air; THICK, YELLOW mucus, with BLOODY CRUSTS IN NOSTRILS.
Nose STUFFED UP;
- unable to breathe through them with characteristic headache; constant sneezing and desire to keep the nose WARM because heat relieves the stuffing up of the nose.
- Colds with sluggish circulation in brain, with trembling and chilliness; cold feeling, as if in the bones.
- Bleeding from the nose; the blood is bright red, very warm; with pressure over the nose.
6. Face:
- Pale with red spots on the cheeks.
- THICK HERPETIC CRUSTS; brown or yellow crusts, on the face, forehead, chin and cheeks; warts; eruptions.
- Tearing in cheeks extending to ears, orbits and jaw, preceded by coldness of the parts, and attended by canine hunger; worse by change of weather to wet, cold damp.
7. Mouth:
Ulceration of the mouth, even gangrene, with great swelling of mucous membranes, raw spots, heavily coated tongue, great flow of saliva of putrid odor; saliva tenacious; soap-like.
Constant hawking up of very tough saliva, with much rawness in the fauces.
8. Stomach:
- Unquenchable thirst; strong desire for cold drinks, with dryness of tongue and increased saliva.
- Nausea, vomiting of tenacious mucus of blackish green liquid.
9. Abdomen:
- Colic with rumbling before and after stool, as after taking cold, with pain in small of back, sticking in umbilical region.
10. Stool:
- Mucus; green; changeable in color; of sour odor and with general dry heat of the skin.
- Yellow; watery diarrhoea, with tearing and cutting before stool; worse AFTER TAKING COLD; or when hot day is followed by a cool and damp night.
- Constipation with infrequent, sluggish, hard, difficult stool.
11. Urinary Organ:
- MUST URINATE WHEN GETTING CHILLED AND MUST HURRY TO PASS WATER.
- Albumin in the urine with oedematous feet, waxy limbs, face waxy and sallow, constant urging to urinate.
12. Sexual Organ:
- Female: Mammae ENGORGED, HARD, SORE, PAINFUL.
- Herpetic eruptions on the face before the menses with unusual sexual excitement.
- Male:
- Impotence.
- Herpes on genitals.
13. Respiratory System:
- Bronchial catarrh with free, greenish expectoration.
Asthma,
- after disappearance of tetters in the face
- loose, rattling cough with dyspnoea.
Cough,
Caused by constant tickling in larynx; which is worse after physical exertion.
Expectoration tough; greenish; dry; hoarse; spasmodic; worse after change of weather to cold and wet.
14. Neck & Back:
- Pain in small of back as after long stooping.
- Stiffness ; Lousyness of the neck; induration of cervical glands after taking cold.
- Neck stiff, back painful, loins corny, after taking cold (Cimic
15. Extremities:
- Paralysis of the arms, ARMS ICY-COLD.
- SORE, BRUISED feeling all over the body.
16. Skin:
- HUMID eruptions on face, genitals, hands, etc.
- WARTS ON face, hands and fingers; fleshy warts.
- Violent itching when undressing and exposed to cold damp air; especially when caused by sour stomach; extreme soreness; scratches until the skin bleeds and becomes raw.
- Colic and diarrhoea after suppression of eruption; after sudden exposure to cold.
THICK CRUSTS
- all over the body.
- Herpes suppurating; pale, oozing water when scratched; small, round, yellowish-brown tetters; they bleed when scratched.
- Very sensitive, bleeding ulcers with false granulations; phagedenic ulcers.
- URTICARIA; stinging, itching, burning when rubbed.
- Cold sores upon lips and genitals.
17. Sleep:
- Uneasy sleep, with frequent sweat.
- Sleeplessness.
18. Fever:
Fetid perspiration at night, and in the morning, over the whole body; during the day more on the back, in the armpits and hands. (6)
Characteristic
Important characteristic features Of Dulcamara
Keynotes / Redline:
- Skin rash < before menses.
- Nose stopped up every time there is a cold rain.
- Every cold settle in the eyes. (2)
Guiding:
Mucous secretions:
- Coryza in damp rainy weather with sneezing followed by thick, yellow discharge.
- Dry coryza stuffs up when there is cold rain, complete stoppage of nose.
Skin:
- Skin eruptions, itching in scabies and urticaria, red spots on skin.
- Skin is very delicate and sensitive to cold.
- Before menses, rash appears on the skin.
Glands:
- Induration and swelling of glands.
- Mammae hard, sore and painful.
- Enlarged testes with griping pain.
- Diarrhoea: Diarrhoea from taking cold, in damp places, in foggy weather, change from warm to cold weather.
- Dropsy: Dropsy after suppressed sweat, exposure to cold, suppressed eruptions.
- Urticaria: Urticaria all over the body. Itching burning after scratching, no fever.
Rheumatism:
Shooting pain occurs again and again; catarrhal rheumatism, aggravated by exposure to cold, damp, rainy weather. (1)
PQRS:
- Bad effects of damp weather, in hot days and cold nights, towards the close of summer.
- Results from sitting on cold, damp ground.
- Patients living or working in damp, cold basements.
- Headache > by conversations.
- Nose stuffs up when there is a cold rain.
- Burning thirst for cold drinks.
- Cutting pain about navel, with slimy bloody mucous stools in summer.
- Must urinate when getting chilled.
- Rash on skin before menses.
- Cough after physical exertion. (2)
Confirmatory:
- Complaints caused by exposure to cold damp, rainy weather or sudden change of weather.
- Patients living or working in damp, cold basements. (2)
Nucleus symptoms:
- Catarrhal, rheumatism and herpetic affections.
- Caused by exposure to cold, damp, rainy weather; sudden change from hot to cold.
- Symptom caused by suppressed eruptions, perspiration, menses.
- Paralytic effect of single parts, vocal cords, tongue, etc. (2)
Therapeutic Value
Modality
Modality Of Dulcamara
Aggravation Of Dulcamara
- At night, from rest, from cold air, when sitting, from suppressed menses, in wet cold weather, after lying down and rising again.
Amelioration Of Dulcamara
- From motion, warmth in general, from walking, warm air, dry weather. (1)
Remedy Relationship
Remedy Relationship Of Dulcamara
Complimentary To Dulcamara :
- Bar-c
Follows Well Of Dulcamara :
- Bell, Bry, Lyc, Sep, Calc, Rhus-t.
Inimical To Dulcamara :
- Bell, Lach
Antidoted By:
- Camph, Cupr, Ip, Kali-c, Merc
It Antidotes:
- Cupr, Merc
Comparison Of Dulcamara :
- Acon, Ars, Bry, Calc, Cham, Croton-t, Hell, Nit-ac, Nux-m, Puls, Staph, Sulph, Verat. (2)
Dose
Dose Of Dulcamara
- 2c to 30c potency
Potency of Dulcamara:
- 3x, 6x, 12x, 30, 200, 1000.
Duration of Action Of Dulcamara :
- 30 days
Repetition Of Dulcamara :
- Maybe repeated in lower potencies.
- Single dose of higher potency – 200 to CM. (1)
Reference
Reference Of Dulcamara
1. MM by J.D. Patil 2013, Section-II, Chap> Dulcamara
2. Zomeo lane Chap> Dulcamara
3. Synoptic Memorizer of MM by Dr.S.K.Banerjea Vol-I, Section-2,Chap > Dulcamara
4. Synoptic Memorizer of MM by Dr.S.K.Banerjea Vol-II, Part-1,Chap > Dulcamara
5. Manual of MM and Therapeutic, Pharmacology by Blackwood, Alexander leslie
6. MM by W.Borieke
Terminology
Terminology
Plant-Related Terms:
- Synonyms: Different names for the same plant (Bittersweet, Woody Nightshade).
- Common Names: Everyday names used for the plant, which can vary regionally.
- Latin Name: The scientific name for the plant (Amara dulcis). This is universally recognized.
Homeopathic Terms:
- Guiding Symptoms: Specific physical or mental symptoms that suggest a particular remedy might be helpful for a patient.
- Modalities: Factors that make symptoms better or worse (e.g., Dulcamara symptoms often worsen in damp, cold weather).
- Miasm: A predisposition to certain types of illnesses, believed to be inherited. Dulcamara is associated with psora and sycosis.
- Prover: A healthy person who takes a substance to record its effects, helping to understand the substance’s potential as a homeopathic remedy.
- Mother Tincture: The original, undiluted preparation of a homeopathic remedy made from the source material (in this case, the Dulcamara plant).
- Potency: The number of times a homeopathic remedy has been diluted and succussed (shaken). Higher potencies are considered more dilute and potentially stronger.
- Repertory: A book that lists symptoms and the remedies associated with them, helping homeopaths find the most appropriate remedy for a patient.
- Rubric: A category of symptoms within a repertory.
Additional Terms:
- Catarrhal: Relating to inflammation of mucous membranes, often with increased secretions (e.g., runny nose, cough).
- Ague: An old term for malaria or other illnesses with fever and chills.
- Anasarca: Severe generalized edema (swelling) of the body.
- Umbilical Colic: Colicky pain around the belly button.
- Herpes Zoster: Shingles, a painful rash caused by the varicella-zoster virus.
Also Search As
Also Search As
- Dulcamara homeopathy
- Homeopathic uses of Dulcamara
- Dulcamara remedy guide
- Dulcamara Materia Medica (This is the formal term for a detailed description of a homeopathic remedy)
- Bittersweet Nightshade in homeopathy
- Symptoms and treatment with Dulcamara
Online:
Search Engines: Use search engines like Google, DuckDuckGo, or Bing. You can use a combination of keywords like "Dulcamara homeopathy," "Homeopathic uses of Dulcamara," or "Dulcamara remedy guide."
Homeopathic Websites and Forums: Many websites and online forums are dedicated to homeopathy. These platforms often have sections where practitioners and enthusiasts share information and articles about specific remedies like Dulcamara.
Offline:
Homeopathic Books and Materia Medica: Look for books on homeopathy, especially Materia Medica texts, which are detailed references about homeopathic remedies. Libraries or bookstores specializing in alternative medicine might have these resources.
Homeopathic Practitioners: Consult a homeopathic practitioner. They are knowledgeable about remedies and their uses and can provide you with information or direct you to relevant resources.
1. Directly Searching for the Article:
- If it’s online: Use the exact title of the article in quotation marks in a search engine.
- If it’s in a book or journal: Look up the publication in a library catalog or online database and use the title or author to find the specific article.
2. Searching Using Keywords:
- General terms:
- Dulcamara
- Homeopathy
- Materia Medica
- Remedy
- Specific symptoms or conditions:
- Skin rash before menses
- Colds in damp weather
- Urticaria (hives)
- Rheumatism
- Combinations: Try different combinations of the above keywords to narrow down your search. For example, "Dulcamara skin rash" or "Dulcamara cold remedy."
3. Searching in Specific Places:
- Homeopathic websites and forums: Many websites and forums dedicated to homeopathy host articles or discussions about remedies. Search within these sites using keywords.
- Homeopathic repertories and Materia Medica: These reference books list symptoms and corresponding remedies. Look up Dulcamara in the repertory or Materia Medica to find information about its uses.
- Online databases: Some online databases, like PubMed for biomedical literature, may contain articles or abstracts related to homeopathic remedies.
4. Asking for Help:
Homeopathic practitioners: They can provide information about Dulcamara or direct you to relevant resources.
Librarians: They can help you search library catalogs and databases to find the article or related information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How is Dulcamara taken?
Dulcamara is available in various potencies (dilutions). The appropriate potency and dosage will be determined by a homeopathic practitioner based on the individual’s specific symptoms and health history.
State the effects of cold in Dulcamara.
Dulcamara Effect In Cold
- Catarrhal rheumatism which is brought on or aggravated by exposure to cold, damp, rainy weather or sudden changes in hot weather.
- Skin is delicate, sensitive to cold, liable to eruptions, especially urticaria; every time patient takes cold or is long exposed to cold.
- Increased secretion of mucous membranes; perspiration being suppressed from cold.
- Dropsy: after suppresses sweat; exposure to cold.
- Catarrhal ischuria in grown-up children, with milky urine; from wading with bare-feet in cold water.
- Diarrhoea : from taking cold in damp places, or during damp, foggy weather; change from warm to cold weather
- Aggravation from cold in general, cold air, cold wet weather.
State the skin symptoms of Dulcamara.
Skin Symptoms Of Dulcamara
- The affections of skin are brought on or aggravated by expo sure to cold, damp, rainy weather, or sudden changes in hot weather.
- Skin is delicate, sensitive to cold, liable to eruptions, especially urticaria; every time patient takes cold or is long exposed to cold.
- Rash before the menses.
- Urticaria over whole body, no fever; itching, burns after scratching. Agg. from warmth. Amel. from cold.
- Thick brown-yellow crusts on scalp, face, forehead, temples, chin, with reddish borders, bleeding when scratched. ben
Warts: fleshy, large, smooth; on face or back of hands and fingers.
Who is a good candidate for Dulcamara?
Individuals prone to catching colds in damp conditions, experiencing skin problems during cold weather, or suffering from joint pain aggravated by dampness are often good candidates for Dulcamara. It’s also used for specific complaints like urinary issues and colic triggered by cold exposure.
State the febrile symptoms of Dulcamara.
Febrile Symptoms Of Dulcamara
a) Causation
i) From exposure to damp cold air.
ii) From wet or rainy weather.
iii) From drenching in rain.
b) Types of fever
i) Influenza or other types of pyrexia.
c) Onset
i)Very slow or insidious.
d) Symptoms
1) Catarrhal discharge
i.) Profuse, watery discharge from the nose
ii.) Discharges are thick and yellowish.
2) Heat
- Dry, burning heat all over the body.
3) Pain
- Aching pain all over the body.
4) Tongue
- Presents imprint of teeth with profuse salivation.
5) Cough
6) Stool
- Loose stool, from taking cold in damp places.
e) Modalities
Agg
- i) From cold.
- ii) From damp.
- iii) From rainy weather.
- iv) From cold drink. (Ref. Clarks)
- v) In the evening and night
- vi) From rest.
Amel.
- i) By warm food and warm dress
- ii) From motion.
- iii) From pressure.
f) Concomitants
- i) Thick brown-yellow crusts on promise scalp, face, forehead, temples and chin; with reddish borders, bleeding when scratched.
- ii) Anasarca after ague, scarlet
- iii) Increased secretion of mucous membranes.
- iv) Headache better by conversation.
State the urinary symptoms of Dulcamara.
Urinary Symptoms Of Dulcamara
a) Causation:
Urinary trouble occurs from:
- i) Cold, damp, wet weather.
- ii) From wading with bare-foot in cold water.
b) Character of urine
i) Thick, milky urine passes involuntarily, due to paralysis of the bladder.
ii) Thick mucus, purulent sediment.
iii) Offensive odour.
c) Before urination
Burning pain in the bladder.
d) During urination
- i) Burning in the urinary meatus.
- ii) Urine drops vertically without force.
- iii) Cannot empty the bladder thoroughly.
e) After urination
- Slimy sediment, deposits in the
f) Modalities
- i) From cold.
- ii) From damp wet weather, etc.
g) Concomitants
- i) Catarrhal ischuria in grown up
- ii) Flabby moist tongue with profuse (4)
What are the key symptoms of Dulcamara?
Key Symptoms
Key symptoms include a stuffy nose that worsens in cold rain, thick yellowish nasal discharge, skin rashes before menstruation, urticaria (hives), and a strong desire for cold drinks. Additionally, any condition aggravated by damp, cold weather may indicate Dulcamara.
How does Dulcamara affect the respiratory system?
Dulcamara is known to cause and exacerbate respiratory issues, especially when triggered by cold and damp conditions. Common symptoms include:
- Thick, yellow nasal discharge
- Stuffy nose, worse in cold air
- Dry or loose cough, often with rattling
- Asthma, especially after suppressed skin eruptions
- Bronchial catarrh with greenish expectoration
Correlation: These respiratory symptoms are often accompanied by Dulcamara’s characteristic skin eruptions, muscle aches, and overall sensitivity to cold and dampness.
Differentiation: Dulcamara is differentiated from other remedies like Bryonia (dry cough, worse with motion) and Rhus tox (rheumatic pains, restlessness) by its distinct modality of aggravation from dampness and cold.
What skin problems are associated with Dulcamara?
Dulcamara is a prime remedy for various skin issues, including:
- Urticaria (hives) that worsen with warmth and improve with cold
- Skin rashes, especially before menstruation
- Warts, particularly on the face and hands
- Thick, crusty eruptions on the scalp, face, and body
- Intense itching, especially when undressing in cold air
Correlation: Skin issues often coincide with respiratory problems, muscle aches, and diarrhea.
Differentiation: Dulcamara’s urticaria that worsens with warmth is a key differentiator. Rhus tox urticaria typically improves with warmth, while Apis is indicated for stinging, burning hives.
How does Dulcamara affect the musculoskeletal system?
Dulcamara is known for its effect on muscles and joints, causing:
Rheumatic pains and stiffness, worse in damp weather
Muscle aches, often with a bruised feeling
Soreness and swelling of joints
Paralysis of the arms, especially when cold
