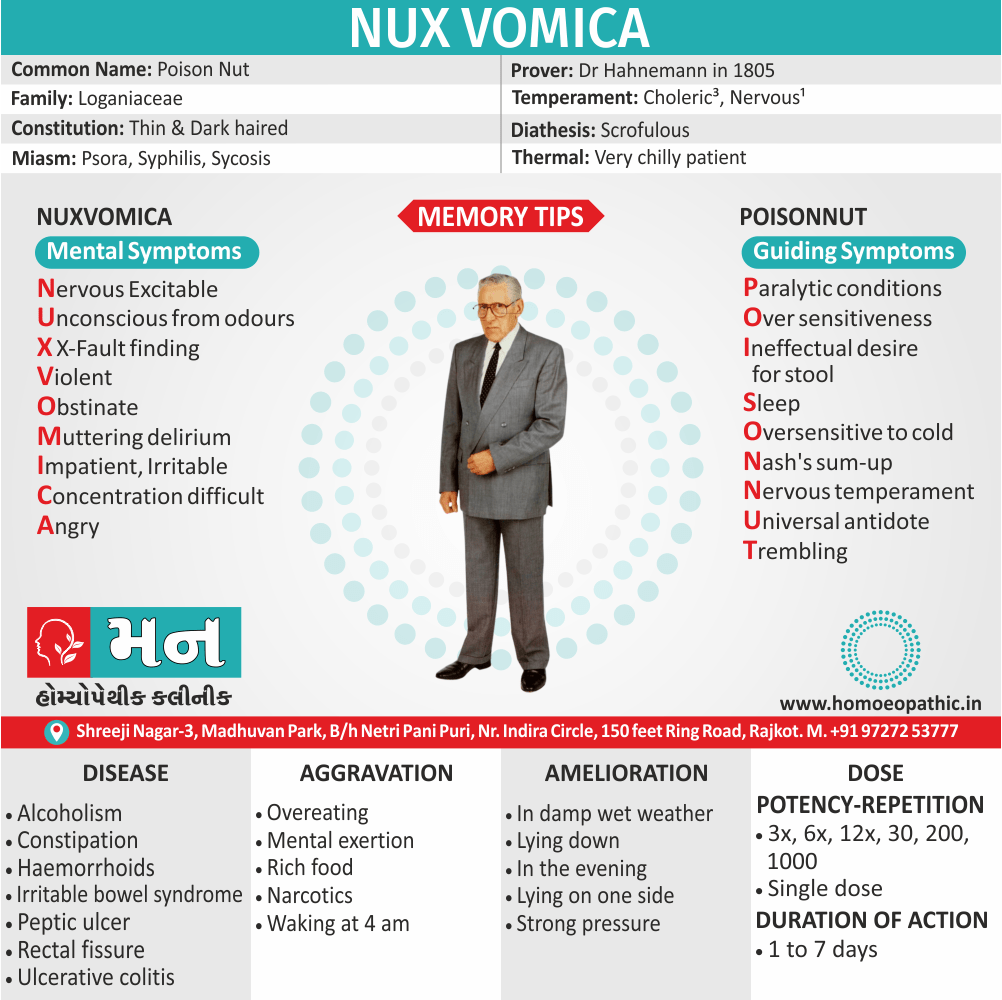
Nux Vomica
Overview
Nux vomica is a homeopathic remedy derived from the seeds of the Strychnos nux-vomica tree. It’s important to note that this substance is actually quite poisonous, and homeopathic nux vomica is highly diluted and should only be taken under the guidance of a licensed homeopathic practitioner.
Here are some lesser-known synonyms for Nux vomica:
- Strychnine tree seed
- Poison nut
- Quaker buttons
- Vomit nut
It’s also important to note that while these are synonyms for the source material, they shouldn’t be used interchangeably with Nux vomica in a homeopathic context.
N
U
X
V
O
M
I
C
A
N
Nervous Excitable:
Nux vomica Nervous anxiety about future; anxiety about business matters, fear of poverty.
U
Unconscious from odours:
Oversensitiveness to external impressions: noise; smells; light and music; or the most trifling ailments are unbearable and affect him much.
Oversensitiveness, every harmless word offends, every little noise frightens, anxious and beside themselves, cannot bear the least, even suitable medicine. (9)
X
‘X’ Fault Finding:
Very much inclined to violently reproach others for their faults.
He quarrels, reproaches, scolds, insults from jealousy, mingled with unchaste expressions; soon afterwards howls and sweeps aloud.
Quarrelsome, even to violence. She cannot tolerate the slightest contradiction or the most gentle persuasions to do differently, which make her beside herself. (8)
V
Violent:
Violent. Ugly; suicidal, homicidal impulses. (9)
O
Obstinate:
Headstrong, self-willed. Obstinately resists wishes of others. (11)
M
I
Impatient, irritable:
Intolerable anxiety.Unable to think correctly.
He has no patience for work. (8)
Impatient when spoken to, gets angry and violent without any provocation.
Spiteful. Cursing. Ugly, malicious. (11)
C
Concentration difficult:
Concentration difficult, while calculating (10)
Easily makes mistakes. Confusion of mind after vexation (11).
Defective memory; manner shy and awkward.
Can’t read or calculate, for she loses the connection of ideas; thinks she will lose her reason. (9)
A
Angry:
Anger with habitual malicious, spiteful disposition. (9)
Angry when consoled. Reproaches others. (11)
P
O
I
S
O
N
N
U
T
P
Paralytic conditions:
Master Kent said, Nux Vom. is full of paralytic conditions.
The bowels are in a state of excitement but this passes away and the time comes when the faeces remain in the rectum with no warning, this extends to the bladder, so that it becomes full of urine which can’t be voided, or dribbling of urine; paralysis of the extremities, of the face, of single muscles: with characteristic sticking pains.
Nux cures such cases, provided totality corroborates.
O
Over sensitiveness:
1. Mentally:
is oversensitive mentally (Ref: Kent), irritable, touchy, sensitive conditions, the woman has impulses to destroy her husband, to throw her child into the fires.
cannot be contradicted-such an over sensitiveness; over sensitive to music (Nux Mos.); trifling ailments are unbearable.
Harmless word offends.
Such a mental over sensitiveness finds its similimum in Nux Vom.
2. Physically:
Oversensitive to external impressions, to light, noise, odours, touch.
is extremely touchy in regard to his food and our Master Kent said oversensitive to medicines, oversensitive to stimulants.
Tendency to faint from odours, after eating, after every labour pain (Ref. Allen).
I
Ineffectual desire for stool and urine-the general concomitant:
‘Frequent and ineffectual desire to defecate but small quantities of faeces at each attempt’-this symptom as Dr. E. B. Nash said, is pure gold.
There are a few other remedies that have it, but none so positively and persistently.
It may be coined, that the frequent and in-effectual desire for stool and urine is a general concomitant symptom.
S
Sleep:
Sleep is a characteristic indication of Nux Vom. Dr. N. M. Chowdhury emphasized that the most important point to remember in this remedy is that the patients are always worse after a disturbed sleep.
There is irresistible desire to sleep in the evening, cannot keep from falling asleep in the evening while sitting or reading, hours before bed time and consequently pt. is compelled to retire and sleep.
He wakes up at about 3 A.M. (Ref. Allen) and then falls into a dreamy sleep early in the morning from which he is hard to arouse, if aroused, he feels tired and weak.
Dr. N. M Chowdhury says
Reported, pt. find it difficult to sleep again in the early morning, ideas keep on crowding upon them till at last out of sheer exhaustion, he falls asleep again, tried and irritable (-Puls, point of similarity with Nux Vom. wide awake in the evening, does not want to go to bed).
O
Oversensitive to cold:
E. B. Nash said, chilliness of Nux Vom. is a characteristic.
Great tendency to take cold and aversion or repugnance to cold air. Pt. is compelled to close the doors and windows and cover-up the body.
Chilly on least movement. from being uncovered, must be covered from head to feet in every stage of fever.
Master Kent said, over-sensitive to open air, to a draft of air always chilly, always taking cold, cold air aggravates (Master Kent in his Repertory graded Nux Vom. in first grade under the sub-rubric, cold air aggravates. Ars1. Baryta1. Calc.C1., Caust1. Dulc.1 Hell1., Hep1., Lyco1., N.V1., Rhus Tox1., Psor1., Rumex1, Sep1., Sil1.) (-cold air, ameliorates lod., Lyco1., Puls1.) (Tendency to take cold, Acon1., Baryta1., Bry1, Cale1: Phos1., Chamo1., Dulc1., Hep1., Lyco1. Merc1., Nat. Mur1. Nit. Ac1., Nux Vom1., Psor1., Rumex1., Sil.1)
N
Nash’s sum-up
E. B. Nash aptly sum-up the essence of Nux Vom. through sensitiveness, nervousness and chilliness-three general characteristic of Nux Vom.
N
Nervous temperament:
Nash said Nux. Vom. bears nervous temperament and can be classed with Chamo., Ign., Staph. Nervous, Hyper impressionable, thin, spare subjects (Ref. Farrington).
In this temperamental concern we must know the verdict of our immortal Master Samuel Hahnemann, that prodigious personality has reported. "Nux is chiefly successful with persons of an ardent character, of an irritable, impatient temperament. disposed to anger, spite or deception."
U
Universal antidote:
Our Nux Vom. is one of the best remedies with which to commence treatment of cases that have been drugged by mixtures, bitters, vegetable pills. nostrum or quack remedies, esp., aromatic or hot medicines.
Master Kent said,
over drugged by the old-school, -Nux Vom. acts as a universal antidote.
Master Kent said when a patient comes from the old school and bad prescribing, having had stimulants and tonics to brace him up.
Wine and stimulants of all sorts, it is sometimes impossible to get reliable symptoms; to get the pt. settled down, we give Nux as an antidote.
Note:
Dr. E. Nash said, it would be true if said that Nux Vomica will often benefit such cases.
The facts are the use of such drugs, aromatics, pills etc. has brought about a condition that, it will benefit those cases in which that stimulates the symptoms produced in the proving of Nux Vomica, or in cases to which it is. homoeopathic, and no others.
T
Trembling:
Master Kent said trembling of parts, -spasm is another characteristic of Nux Vom.
E. B. Nash also emphasized that spasm is a characteristic feature, spasm from simple twitching to clonic form; convulsions with consciousness characterizes the remedy.
Harvey Farrington said, Nux. produces twitching and jerking of muscles in all parts of the body, strabismus, cramps in the extremities; the convulsions may at times characterized by protruding eyes, blueness of the lips, tossing and rolling about, sudden drawing up of the limbs and thrusting them out again. (4)
Introduction
Constitution
Clinical
Mental Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms
Characteristic
Therapeutic Value
Modality
Remedy Relationship
Dose
Terminology
Reference
Also Search As
Introduction
Introduction of Nux vomica
Common name
- Poison Nut
Synonyms
- Strychnos nux vomica, Poison nut, Kuchla
Family / Group / Class / Order
- Loganiaceae
Habit and habitat / Description
- It is native of east Indies. It is also found in Ceylon and on the Malabar coast in India.
- It grows in the forests.
- The stem is short and crooked.
- The wood is white and tough.
- The leaves are oval and shiny.
- The branches have a disagreeable smell.
- Flowers are terminated, small and greenish-white in colour.
- The official Nux vomica means the seeds of Nux vomica plant.
- The covering of the seeds is very tough and cannot be broken easily.
Name of prover
- Dr Hahnemann in 1805
Introduction and history
- This is the king of our polychrest remedies.
- This remedy is a unique gift from the vegetable kingdom.
- It is the best remedy to commence treatment of cases that have been drugged by different pathies, especially after much dosing with allopathic drugs.
- It is a very suitable remedy for people of every sex and age.
- This remedy is called as the male counterpart of pulsatilla and ignatia.
- It is truly Hahnemann’s greatest polychrest remedy because its dominion is vast.
- It’s sphere of action extends from pole to pole and it encompasses a perplexity of character that is truly astonishing.
- It is useful for people of all occupations.
- The word has been taken from Latin ‘nux’ meaning ‘nut’ and ‘vomicine’ meaning ‘smell’ because of the peculiar property of the nut.
- It was introduced into medicine by the Arabians.
Parts used
- Tincture is prepared from seeds with alcohol.
Active principles of Nux vomica:
- The chief constituents of this drug are strychnine and brucin which are alkaloids. Vomicine and others are linked with chlorogenic acid.
Preparation of Nux vomica:
- Tincture is prepared from seeds with alcohol. (1)
Constitution
Constitution of Nux vomica
Physical make up
- Especially suited to people who are thin, nervous and extremely susceptible to external impressions. They are dark haired, debauched and lead a sedentary life. Indicated in jealous, hypochondriacal males.
Temperament
- Nervous, spiteful, malicious, irritable, sanguine
Diathesis
- Scrofulous
Relation with heat & cold
- Very chilly patient
Miasm
- Psora, syphilis, sycosis (1)
Clinical
Clinical conditions of Nux vomica
In Homeopathy Nux Vomica medicine use by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of following Disease Conditions
- Alcoholism, Angina, Arrhythmia, Arthritis, Asthma, Behaviour disorder, Chronic fatigue syndrome, Colds, Colic, Constipation, Crohn’s disease, Cystitis, Endometriosis, Fibrositis, Headaches, Haemorrhoids, Hypertension, Inflammatory bowel disease, Influenza, Insomnia, Irritable bowel syndrome, Lumbago, Multiple sclerosis, Neuralgia, Peptic ulcer, Premenstrual syndrome, Prostates, Pyelonephritis, Rectal fissure, Renal calculi, Sciatica, Ulcerative colitis. (3)
Sites of action / Pharmacodynamics of Nux vomica
- The main action of this drug is upon the gastrointestinal tract. It also acts upon muscles, central nervous system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, mind, nerves (1)
Causation (Causes / Ailments from) of Nux vomica:
- Anger, coffee, alcohol, masturbation, sexual excesses, injuries, hot medicines, rich food, sedentary habits, night keeping, mental exertion, sitting on cold stones, stress and strain of modern life. (1)
Physiological action of Nux vomica:
- The physiological action of Nux vomica and Strychnine are so nearly alike that they are commonly considered to be identical.
- In small doses, Nux vomica stimulates the entire digestive system, promoting gastric, pancreatic and biliary secretions. But, like other bitter tonics, when used over a long period of time, it deranges digestion and produces constipation.
- In larger doses, the most marked feature of its action is increased reflex excitability of the spinal cord and other reflex centres, especially the vasomotor and respiratory.
- In full doses the pupils are dilated, the limbs jerk, respiration becomes spasmodic and the jaws stiffen; shuddering and anxiety soon follow.
- Toxic doses induce powerful contractions of tetanic character with dyspnoea, suffocation, cyanosis and opisthotonos, although consciousness persists until death occurs from carbon dioxide asphyxia (1)
Patho-physiological changes / Pathogenesis of Nux vomica:
- The chief action of this drug is of a stimulating nature. It produces tetanic convulsions, causing death from asphyxia.
- It stimulates the vasomotor center and thus increases blood pressure and the pressure of arterioles. It causes vasomotor spasms, constipation and piles.
- Acts pre-eminently upon the spinal cord including the motor and sensory centres at the base of the brain affecting specially the region of reflex function. The condition produced is one of excessive irritability and excitability giving rise to paralysis.
- Acts profoundly on the organs and functions of nutrition, the secretions being altered, the functions perverted and the organic substance changed.
- It acts upon the mucous membrane of the alimentary tract, giving rise to dyspeptic symptoms and constipation.
- It acts on the respiratory system producing a dry catarrhal condition obstructing the nasal passages. Also produces dry cough (1)
Mental Symptoms
Characteristic Mental Symptoms (psychology) of Nux vomica:
- Patient is inclined to suicide but is afraid to die.
- Ill-humoured, finds faults and scolds.
- Irritable, careful, jealous people inclined to get excited and angry
- Over sensitiveness to external impressions; cannot tolerate noise, music, talking, strong odours and bright light.
- Hypochondriacal, after eating, affected by the slightest thing.
- Defective memory; manner shy and awkward.
- Disinclined to work and great lassitude or weakness in the morning, loss of energy.
- Time passes too slowly.
- Hypochondriacal mood, especially in people having sedentary habits with abdominal complaints and constipation.
- Great laziness and aversion to work.
- Muttering delirium, cannot think correctly; mental derangement in drunkards.
- Gets angry easily and loses temper even at trifles.
- Cannot bear the least contradiction. (1)
Guiding Symptoms
Guiding symptoms of Nux Vomica:
The common name of Nux Vomica is ‘Poison Nut’-and thus allow me to impress you the totality through its common name.
- P-Persons who are very particular.
- O-Oversensitive to external impressions.
- I-Ineffectual desire for stool and urine: the general concomitant.
- S-Sleep: cat-nap: awakes tired.
- O-One of the best remedies with which to commence treatment: after much drugging.
- N-Nervous temperament. (Ref. Nash)
- N-Nausea if I could vomit, I would feel better,
- U-Universal antidote.
- T-Tendency to faint from odours; after labor pains (7)
1. Generalities
- Nux-v. is an everyday remedy. – It corresponds to many diseased conditions to which a modern man is prone to.
- It is useful to those persons who lead a sedentary life, doing much mental work; or to those who remain under stress and strain of prolonged office work, business cares and worries.
- Such persons in order to forget their worries are apt to indulge in wine, women, rich stimulant food and sedative drugs; and ill effects from which they are apt to suffer.
The typical Nux.
- patient is rather thin, spare, quick, active, nervous and irritable.
- It affects the nerves, causing hyper-sensitiveness, and over-impressionability, mentally and physically.
- Produces Digestive Disturbances; partial congestion and hypochondriacal states.
- Dyspeptic persons who always select their food for experimenting, that is digested little.
- He is subject to spasms, convulsions, and fainting.
- The patient seems to be always out of tune; The Action is Violent, often irregularly fitful or inefficient.
- Fainting, after stools, vomiting; after labour pains etc.
2. Head
- Vertigo; brain and other objects turn in circle; with momentary loss of consciousness; with black spell; on empty stomach.
- Bruised sensation of the brain.
- Dizzy and faint in a crowd or where many lights are burning.
- Headache in the sunshine.
- Sensitive scalp.
- Swelled forehead.
- Head seems larger than body.
- Takes cold amel. wrapping head warmly.
- Frontal head ache with desire to lean it on something.
3. Eye
- Bloodshot.
- Lachrymation from affected side.
- Atrophy of the optic nerve. – Photophobia.
- Paresis of ocular muscles.
- Lower eyeballs yellow.
- Loss of vision due to alcohol and tobacco.
- Exudation of blood from eyes.
- Spring conjunctivitis.
4. Ears
- Itching in ear through Eustachian tubes.
- External meatus dry and sensitive.
- Pain; stitching when swallowing.
- Loud sounds are painful.
5. Nose
- Oversensitive to strong odours; even fainting.
- Nose stopped, but runs water; on one side.
- Snuffles; of the new born.
- Nose bleed during sleep; from suppressed flow of piles, from coughing.
- Sneezing violent, abortive; from intense crawling in nostrils (left).
- Coryza, fluent by day, and in open air, dry at night.
6. Face
- Red, turgid or yellowish agg. about nose and mouth.
- Left angle of the mouth drops.
- Infra-orbital neuralgia; with swelling of cheek, intermittent; amel. when lying in bed.
- Jaws, snap shut; stiff.
- Acne from eating cheese.
- Pimples from excessive use of liquors.
- Child passes its hand constantly over face (brain disease).
7. Mouth
- Teeth chatter.
- Toothache amel. warm drinks.
- Foetor orris; sour.
- Small aphthous ulcers in the mouth.
- Taste; bitter; sour, bad in a.m. low down in throat.
- Itching palate; eustachian tube.
- Gums; swollen white, and bleeding.
- Needles at edges of tongue agg. after eating; washing face in cold water.
8. Throat
- Rough, raw; as if scraped.
- Putrid taste in; on coughing.
- Small ulcers in the throat; pain agg. during empty swallowing.
- Stitches into ears.
9. Stomach
- Craves piquant food; beer; fat food, chalk; stimulants.
- Hiccough: From over eating; from cold or hot drinks.
- Violent retching agg. hawking.
- Eructations, sour.
- Heart burn.
- Water brash.
- Nausea; amel. if he can only vomit.
- Violent Vomiting; bilious, sour, wants to vomit but cannot.
- Food lies like a heavy knot in stomach.
- Gastralgia; pain go into back and chest; amel. vomiting and hot drinks, agg. from food.
- Hunger; yet aversion to food.
- Eructations; difficult; sour; bitter.
- Severe pain in stomach from injury, agg. least food.
10. Abdomen
- As of a hand about waist, clothes oppress it.
- Bruised soreness of abdominal wall.
- Liver sore, enlarged; sticking pain.
11. Rectum & Anus
- Rectum; spasms of; flatus retained in; constant uneasiness in.
- Piles itching, blind, bleeding, amel. cool bathing.
- Dysentery; stools amel. pains for a time.
- Diarrhoea; with jaundice; after debauch during fevers.
- Colic in nursing infants from stimulating food taken by the mother.
- Colic from suppressed haemorrhoidal flow.
- Prolapse of rectum from diarrhoea.
12. Stool
- Strains hard at stools; feeling as if part remained unexpelled; passes small quantity at each attempt.
- First part of stool soft, last hard.
13. Urinary Organ
- Renal colic (right), extending to genitals and legs; with dribbling urine; amel. lying on back.
- Painful ineffectual urging to urinate.
- Spasmodic strangury.
- Haematuria from suppressed haemorrhoidal flow or menses.
- Spasmodic urethral stricture.
- Paralysis of bladder; urine dribble; in old men, with enlarged prostate or gonorrhoea.
- Involuntary urination when laughing, coughing, sneezing.
14. Sexual Organ
- Desire easily excited.
- Penis becomes relaxed during an embrace.
- Bad effects of onanism; sexual excess.
- Premature ejaculation.
- Cannot be in female society without having emission.
- Desire too strong; with burning in vulva.
- Menses; profuse, early and prolonged; intermittent; of dark lumpy bloody; irregular; with fainting spells.
- Dysmenorrhoea; cramps extend to the whole body; with constant urging to stool.
- Leucorrhoea; foetid; staining yellow.
- Inefficient labour pains; faints at every labour pain.
- Profuse bleeding after abortion.
- Prolapse of uterus; from straining or lifting.
- All the old symptoms are agg. after menses.
15. Respiratory System
- Cough; violent; throwing the patient down; paroxysmal; whooping; with splitting headache; has to hold his head.
- Shallow respiration.
- Oppressed breathing.
- Asthma: from disordered stomach; with fulness of stomach.
- Hoarseness, with painful roughness in larynx and chest.
- Cough; with sensation as if something torn loose in the chest.
- Intercostal neuralgia agg. lying on painful side.
- Asthma; with feeling as if clothing were too tight, amel. belching.
- Desire to eat during cough.
16. Heart & Pulse
- Palpitation on lying down.
- Heart feels tired.
- Angina pectoris; patient lies on knee with body leant backwards
17. Neck & Back
- Cervico-brachial neuralgia; painfully stiff neck; pains down shoulder (right) agg. touch.
- Wry neck from cold or nervous shock.
- Lumbar ache, as if breaking; must sit up in order to turn in bed.
- Crawling along spine.
- Acute lumbago.
- Sacral region as if unimpressive; after parturition
18. Extremities
- Arms go to sleep, numb, stiff feeling.
- Tense cramp in calves and soles, must stretch feet; or stand still while walking.
- Feet feel clubby and raw.
- Shooting from toes to thighs; agg. after stool.
- Drags his feet while walking, (chorea); legs tremble; unsteady gait.
- Knee joints as if dry; cracking during motion.
- Paralysis of lower limbs from over exertion or from being soaked.
- Automatic motions of hand (R) towards mouth (Apoplexy).
- Legs stiff.
19. Skin
- Goose skin.
- Skin red and blotchy.
- Urticaria with gastric derangement.
- Bluish spots
20. Sleep
- Sleepy in the evening or sleepless from rush of ideas.
- Awakes too early, cannot go to sleep again; finally sleeps but on waking feels wretched.
- Better after a short sleep, unless aroused.
- Nightmares.
21. Fever
- Chill with thirst, and heat without thirst.
- Easily Chilled, Can Not Uncover, agg. motion; drinking even during the heat.
- Body burning hot esp. face, but unable to move or uncover without feeling chilly. – Excessive rigor with blue finger nails.
- Sweat sour; one sided; warm, on upper most side, en lying down. (3)
Characteristic
Characteristics of Nux vomica
Keynotes / Redline symptoms:
- Extremely chilly – sensitive to cold air.
- Frequent, ineffectual desire for stools.
- Convulsions with consciousness.
- Snuffles of infants > Open air.
- Inclination to vomit, feels " If I could vomit, I would feel better".
- Stools ameliorates complaints for some time.
- Asthma gastric in origin.
- Sleep- early in evening, awakes 3-4 a.m., falls into dreamy sleep at day break which is hard to arouse.
- Must be covered in every stage of fever.
- Backache must sit up to turn in bed. (2)
Guiding symptoms:
- Patients who are chilly; always taking cold.
- One of best remedy to commence treatment in cases who are drugged by strong allopathic treatment. Oversensitive to all external impressions.
- Fainting tendency from odours, after eating, after labour, with pain.
- Convulsions with consciousness, by anger or emotion.
- Violent pains – lighting like, twisting, jerking.
- Bruised soreness in abdomen, brain, larynx, throat.
- Head-Gastric headaches.
- Sensation as if nail were driven into head.
- Sensation as if head was beaten with axe > pressure.
- Drunken confusion in head.
- Constipation with constant, ineffectual urging for stool.
- Ineffectual urging for stools, as if part remained unexpelled (Caust).
- Passes small quantities of stools at each attempt.
- Sleep-Sleeps before bed time, awakes 3-4 a.m., falls into a dreamy sleep at day break, from which is hard to arouse.
- Short sleep ameliorates. (2)
PQRS symptoms:
- Inclination to died by suicide, but lack of courage.
- Convulsions with consciousness (Strych.).
- Cannot keep from falling asleep in the evening while sitting or reading hours before bed time.
- Catarrh<in warm room and relieved in cold air (though a chilly pt.).
- Labor pains: violent, spasmodic pain <in back.
- Fever: great heat whole body burning hot (Acon.), face red and hot (Bell.), yet the patient cannot move or uncover without being chilly. (5)
Confirmatory symptoms:
- Anger, irritability and violent anger.
- Oversensitive to all impressions, like noise, touch, etc.
- Ineffectual desire for stools > temporarily after stools.
- Convulsions with consciousness.
- Inclination to vomit, sensation as "If I could vomit, I would feel better".
- Sleeps early in evening, awakes 3-4 a.m.
- Must he cover in every stage of fever. (2)
Nucleus symptoms:
- It is suited to persons who are quarrelsome, spiteful, malicious, addicted to wine, narcotics, coffee, highly rich food, living a sedentary life.
- Mentally overworked, over sensitive individuals, suffering from gastric complaints or have been drugged by allopathic or other non-homoeopathic drugs.
- The nerves are in a state of irritation, with over sensitiveness, over impressionability.
- This produces a tendency to twitching, cramps, convulsions, causing a constant urge for stool. (2)
Therapeutic Value
Therapeutic Value of Nux vomica
- Angina pectoris, Apoplexy, Asthma, Cirrhosis of liver, Conjunctivitis, Constipation, Coryza, Diarrhoea, Dysentery, Dyspepsia, Gastralgia, Gastritis, Gonorrhoea, Haemorrhoids, Hernia, Hyperaemia of the liver, Jaundice, Mental strain, Metrorrhagia, Morning sickness, Neuralgia, Renal colic, Rheumatism, Torticollis, Venereal ulcers, Whooping cough. (1)
Modality
Modality of Nux vomica
Aggravation:
- Overeating, mental exertion, anger, rich food, narcotics, after eating, touch, noise, odours, bright light, spices, dry weather, cold air, in the morning, waking at 4 am.
Amelioration:
- In damp wet weather, lying down, while at rest, in the evening, lying on one side, strong pressure. (1)
Remedy Relationship
Remedy Relationship of Nux vomica
Complimentary
- Sep, Sulph, Kali-c.
Follows Well
- Sep, Sulph, Phos, Ip, Ars, Bry, Bell, Cact, Hyos, Lyc
Inimical
- Zinc, Ign, Acet-ac.
Antidoted By
- Acon, Bell, Camph, Cham, Cocc, Mez, Op, Pal, Plat, Puls, Stram, Thuj
It Antidotes
- Acon, Ars, Bell, Op, Puls, Thuj.
Comparison
- Acon, Aesc, Agn, Ambr, Apis, Ars, Asar, Bell, Bism, Calc, Camph, Carb-an, Carb-v, Cast-eq, Cham, Chel, Chic, Cic, Cob, Cocc, Coloc, Con, Cur, Dig, Hep, Hydr-ac, Ign, Kali-c, Kreos, Lyc, Mag-m, Mosch, Nat-m, Nat-s, Nit-ac, Nux m, Nux-m, Oci, Op, Phys, Phyt, Pic-ac, Prun, Puls, Sep, Sulph, Tab, Thuj, Zing (1)
Dose
Dose of Nux vomica:
- Single dose, maybe repeated when the symptoms call for it.
Potency
- 3x, 6x, 12x, 30, 200, 1000
Duration of action
- 1 to 7 days (1)
Terminology
Terminology of Nux vomica
Key Terms
- Oversensitiveness: Increased sensitivity to external stimuli like noise, light, odors, and touch.
- Ineffectual Urging: Frequent, unsuccessful urges to defecate or urinate.
- Spasms: Involuntary muscle contractions.
- Hypochondriacal: Excessively worried about health.
- Chilliness: A heightened sensitivity to cold.
Mental Symptoms
- Irritability and Anger: Easily angered, impatient, and prone to outbursts.
- Anxiety: Worried about the future, especially regarding business and finances.
- Fault-Finding: Critical of others and their shortcomings.
- Concentration Difficulties: Struggles to focus and easily makes mistakes.
Guiding Symptoms
- Oversensitiveness: Both mentally and physically oversensitive.
- Ineffectual Urging for Stool and Urine: A hallmark symptom of Nux Vomica.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty sleeping, often waking around 3 a.m.
- Chilly: Very sensitive to cold and easily chilled.
General Information
- Constitution: Suitable for thin, nervous individuals with sedentary lifestyles.
- Causation: Can be triggered by stress, overindulgence in food or stimulants, and overwork.
- Aggravation: Symptoms worsen in the morning, after eating, and with mental exertion.
- Amelioration: Symptoms improve in the evening, with rest, and in damp weather.
Reference
References
- Textbook of homoeopathic materia medica by Dr. J.D. Patil 2013, Section II, chap Nux vomica
- Zomoeo Lite chap Nux vomica
- Phatak materia medica chap Nux vomica
- Synoptic memorizer MM by Dr. S.K.Banerjea Vol- 1, Chap- 2,> Nux vomica
- Synoptic memorizer MM by Dr. S.K.Banerjea Vol- 1, Chap- 3,> Nux vomica
- Synoptic memorizer MM by Dr. S.K.Banerjea Vol- 2, Part-1 ,> Nux vomica
- Synoptic memorizer MM by Dr. S.K.Banerjea Vol- 2, Part-2 ,> Nux vomica
Also Search As
Also Search As
People can search for homeopathic articles on Nux Vomica using various methods and keywords:
Search Engines:
- Broad terms: "Nux Vomica homeopathy," "Homeopathic remedy Nux Vomica," "Nux Vomica uses in homeopathy"
- Specific symptoms: "Nux Vomica for indigestion," "Nux Vomica for irritability," "Nux Vomica for constipation"
- Alternative names: "Poison Nut homeopathy," "Kuchla homeopathic remedy"
- Questions: "What is Nux Vomica used for in homeopathy?" "Is Nux Vomica safe?"
Homeopathic Websites and Forums:
- Reputable homeopathic websites often have sections on remedies, where you can search for Nux Vomica specifically.
- Online homeopathic forums can be a good place to ask questions and find information from experienced practitioners and users.
Homeopathic Materia Medica:
- This is a comprehensive reference book listing all homeopathic remedies and their associated symptoms. You can find detailed information about Nux Vomica here.
Consulting a Homeopath:
- If you are considering using Nux Vomica for a specific health concern, it’s always best to consult a qualified homeopathic practitioner. They can assess your individual needs and recommend the appropriate remedy and dosage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Mention Banerjea’s reference for irritable family.
An irritable family:
Father:
Mr. Nux Vomica.
Mother:
Mrs. Natrum Mur.
Three children
i) Firstly, Master Chamomilla. ii) Secondly, Master Cina. iii) Thirdly, Master Antim Crud.
The maid-servant of the family
i) Mr. Bryonia.
Thus, a classical composition of a horrible family.
Bilious temperament’ – what does it indicate, compare in reference to other temperaments? State what do we mean by temperament?
Temperament
- Firstly, The psychological-physical organization, peculiar to the individual.
- Secondly, In influences the metabolic processes, manner of thought and action, and general views of life.
Patient have suicidal impulses-mention three medicines.
Literary, studious persons’-mention three medicines?
i) Firstly, Lycopodium. ii) Secondly, Nux Vomica. iii) Thirdly, Sulphur.
‘Over sensitiveness’-mention some medicines with indications?
Oversensitive
i) Arnica Montana i.e.:
a) Firstly, Nervous, cannot bear pain. b) Secondly, Whole body oversensitive.
ii) Apis Mel. i.e.:
a) Extreme sensitiveness to touch.
iii) Belladonna i.e.:
a) Firstly, Women and children of delicate skin, sensitive nature. b) Secondly, Sensitive to drafts of air. c) Thirdly, Skin is oversensitive; extreme sensitiveness to touch.
iv) Hepar Sulph i.e.:
a) Firstly, Oversensitive, physically and mentally.
b) Secondly, Extreme sensitive to cold air, imagines he can feel the air if a door is opened in the next room.
v) Lachesis i.e.:
a) Firstly, Great sensitiveness to touch.
b) Secondly, Cannot bear bed-clothes or night dress to touch throat or abdomen, not because sore or tender as in Apis and Belladonna, but clothes cause an uneasiness, makes her nervous.
vi) Nux Vomica i.e.:
a) Oversensitive to external impressions; to noise, odours, light or music.
vii) Phosphorus i.e.:
a) Over sensitiveness of all senses. b) Secondly, To external impressions: light, noise, odour, touch.
State the particular symptom where Nux Vom. has reverse modality?
Introduction i.e.
Though Nux Vom. is awfully chilly patient, yet then, in coryza and catarrh, it has reverse modality.
Catarrh and Coryza i.e.
Agg. in warm room.
Amel. in cold air.
Alternate constipation and diarrhoea-mention three medicines.
1) Firstly, Antim Crud 2) Secondly, Nux Vomica 3) Thirdly, Sulphur.
State the labor pain of Nux Vomica.
i) Firstly, Violent labor pain.
ii) Secondly, Spasmodic
iii)Thirdly, Causes urging to stool or to urinate.
iv) Fourthly, Labor pain especially felt in the back; Agg. in back
v) After that, Patient prefers a warm room.
vi) Lastly, Pains are sticking, tingling, aching; worse from motion and contact. vii) Tendency to faint after every labor pain.
What is the best time for Nux Vomica dosing?
i)Firstly, Nux Vomica should be best given on retiring.
ii) Secondly, But what is better, several hours before going to bed.
iii) Thirdly, It acts best during repose of mind and body.
iv) Fourthly, Dr. Boericke says. Nux is said to act best given in the evening.
State the mental symptoms of Nux Vomica.
Mental Symptoms
1) Irritability i.e.
i) Very much irritable, quarrelsome, spiteful, malicious persons, Master Hahnemann says, Nux is chiefly successful with the persons of an ardent character; of an irritable, impatient temperament, disposed to anger, spite or deception’.
2) Anxiety i.e.
i) Firstly, Anxiety with irritability.
ii) Secondly, Nervous, melancholic.
3) Suicidal tendency i.e.
i) Inclination to died by suicide, but is afraid to die.
4) Over sensitiveness i.e.
i) Oversensitive to external impressions: to noise, odour, light, or music, or from touch,
6) Ill-humoured i.e.
i) Firstly, Trifling ailments unbearable.
ii) Secondly, Every harmless word offends.
iii) Thirdly, ill-humoured, finds slightest fault of every body and scolds them,
7) Mood i.e.
i)Firstly, Hypochondriac mood, wants to be alone.
ii) Secondly, Incapacity to literary work.
iii) Thirdly, Hypochondriac.
State the gastric symptoms of Nux Vomica.
a) Causations i.e.
i) Firstly, From the bad-effects of taking coffee, tobacco, alcohol etc.
ii) Secondly, From highly spiced, seasoned foods.
iii) Thirdly, From over-eating, irregular diets.
iv) Fourthly, From aromatic, patent or purgative medicines nostrums etc.
v) After that, From mental over-exertion.
vi) Lastly, From night watching, sexual sedentary habits, etc.
b) Character of Symptoms
1) Nausea and vomiting i.e.
i) Firstly, Sour taste, constant nausea in the morning after eating.
ii) Secondly, Vomiting especially in the morning, patient feels, ‘If I could only vomit, I would be so much better’,
iii) Thirdly, Ineffectual urging for vomiting.
iv) Fourthly, Vomiting gives relief, so wants to vomit by inducing the finger into the mouth
v) Lastly, Wants to vomit, but cannot, so induces the finger.
2) Hungry i.e.
Very hungry: ravenous hunger, especially about a day before an attack of dyspepsia. (Ref. Boericke).
3) Desire i.e.
i) Firstly, Loves fat and tolerates them well. (Ref. Boericke).
ii) Secondly, Stimulants, bitter things, alcohol etc.
4) Aversion i.e.
i) Firstly, Aversion to foods.
ii) Secondly, Dyspepsia from drinking strong coffee.
5) Sensation i.e.
After two and three hours of eating sensation of a pressure appears in the stomach, as from stone; with tightness.
6) Mouth i.e.
i) Firstly, Foetid odour and sour taste, especially in the morning.
ii) Secondly, Small aphthous ulcers, with bloody saliva.
7) Tongue i.e.
Anterior half clean; posterior half slightly coated, with deep fur, white, yellow cracked edges.
8) Liver i.e.
i) Firstly, Non-functioning liver in beer and alcoholic drinkers.
ii) Secondly, Enlarged liver, chronic hepatitis with stitches and colic.
iii) Thirdly, Bruised soreness of abdominal walls; with upward pressure, causing short breath and desire for stool.
9) Abdomen i.e.
i) Firstly, Bruised soreness of the abdomen walls.
ii) Secondly, Weakness of abdominal ring region, strangulated hernia.
iii) Thirdly, Umbilical hernia of infants.
c) Modalities i.e.
Agg. In the morning, after eating.
Amel. In the evening, while in rest.
d) Concomitants i.e.
i) Firstly, Ineffectual urging for stool and urination which gives temporary relief.
ii) Secondly, Mentally very irritable and oversensitive.
Describe the abdominal colic of Nux Vomica.
Abdominal Colic
a) Causation i.e.
i) Firstly, From the bad-effects of taking coffee. tobacco, alcohol, beer.
ii) Secondly, From highly spiced, seasoned foods
iii) Thirdly, From over eating, irregular diets.
iv) Fourthly, From purgatives, patent, aromatic medicines.
v) Lastly, From mental over-exertion, night watching, sedentary habit etc.
b) Character of pain i.e.
i) Firstly, Sensation of weight, as from a stone with pain in the stomach, an hour or two after eating.
ii) Secondly, Colic from indigestion, pain around the umbilicus.
iii) Thirdly, Very much over sensitiveness to the pain.
iv) Fourthly, There is tightness in the abdomen; must loosen the clothing.
v) After that, Cannot use mind for two or three hours after a meal; sleepy after dinner,
vi) Then, Region of stomach is very sensitive to pressure.
vii) Lastly, Flatulent distension, with spasmodic colic, colic from uncovering. (Ref. Boericke)
c) Modalities i.e.
Agg. Immediately after eating, in morning, before stool.
Amel. At bed time, during rest, after, stool.
d) Concomitants i.e.
i) Firstly, Ineffectual urging for stool, but passes little with temporary relief of suffering and pains.
ii) Secondly, Tendency to vomit, which gives relief, so wants to vomit by inducing the finger inside the mouth. Patient says, ‘if I could vomit, I would remain better."
State the constipation of Nux Vomica.
Constipation
a) Causations i.e.
i) Firstly, From the bad-effects of tea, coffee, tobacco etc.
ii) Secondly, From beer, alcohol, brandy.
iii) Thirdly, From highly-spiced, seasoned foods etc.
iv) Fourthly, From irregular diet, over-eating.
v) After that, From mental exertion, night watching.
vi) Lastly, From aromatic, parent, purgative medicines, hot medicines, nostrums etc.
b) Character of stool i.e.
i) Firstly, Large, hard, difficult stool.
ii) Secondly, Scanty small amount of stool passes at each time
iii) Thirdly, Constant ineffectual urging; incomplete and unsatisfactory.
c) Sensation i.e.
i) Firstly, Sensation as if not finished.
ii) Secondly, Feeling as if part remained unexpelled.
iii) Thirdly, Constriction of rectum with irregular, peristaltic action, hence frequent ineffectual desire, or passing but small quantities at each attempt.
iv) Fourthly, Constipation: Desire felt at rectum.
d) Modalities i.e.
Agg. i) Firstly, In the morning after rising.
ii) Secondly, After mental exertion etc
Amel. i) After every stool, with temporary satisfaction.
e) Concomitants i.e.
i) Firstly, Alternate diarrhoea and constipation.
ii) Secondly, Blind piles may protrude.
Note: -Dr. Boericke says, ‘absence of all desire for defecation is a contraindication’.
State the piles of Nux Vomica.
Piles
a) Types i.e.
Blind piles those are chronic in nature.
b) Causation i.e.
i) Firstly, Due to bad-effects of over-use of purgatives.
ii) Secondly, From bad-effects of aromatic, medicines etc.
c) Character of haemorrhoids i.e.
i) Firstly, Stitching, burning pain.
ii) Secondly, Itching in the anus.
iii) Thirdly, Cutting, aching smarting pain.
iv) Fourthly, Constant uneasiness in the rectum (Ref. Boericke).
d) Modalities i.e.
Agg. i) Firstly, Before stool. ii) Secondly, In morning. iii) Thirdly, After taking purgatives, drastic drug (Ref. Dr. Boericke).
Amel. After stool.
e) Concomitant i.e.
i) Ineffectual urging for stool is a common concomitant.
State the morning diarrhoea of Nux Vomica.
Morning Diarrhoea
Causation i.e.
Debauchery, abuse of alcohol, spirit, from night watching, spoiled seasoned foods, excessive mental and physical exertion, using aromatic patent medicines, irregular diet, etc.
Time i.e.
Urging for stool in the morning, after rising. Nash says, after having some foods.
Sensation i.e.
‘As if not finished sensation’.
Quantity i.e.
Scanty stool with mucus.
Character i.e.
Stool is watery and offensive, passes little quantity at a time with temporary satisfaction. Diarrhoea of dark colour; stool with blood (+). mucus (++++).
Before stool
Gripping pain and tenesmus in abdomen.
During stool i.e.
Great tenesmus (++).
Modality i.e.
Agg. in the morning at 5 a.m. Amel. (temporary) after evacuation.
Concomitant i.e.
i) Firstly, Mental irritability.
ii) Secondly, Dyspepsia with inclination to vomit.
iii) Thirdly, Ineffectual desire for stool and urine: is a general concomitant.
State the urinary symptoms of Nux Vomica.
Urinary Symptoms
a) Character of urine i.e.
i) Firstly, Frequent dribbling.
ii) Secondly, Dirty, yellow sediment in the morning.
iii) Thirdly, Haematuria: bloody urine.
b) Before urination i.e.
i) Firstly, Ineffectual urging for urination, spasmodic and strangury.
ii) Secondly, Dr. Tyler refers, patient says, that he would be better if he could pass water.
iii) Thirdly, Renal colic extends up to genitals.
c) During urination i.e.
i) Firstly, Pain in the neck of bladder, violent straining without being able to pass a single drop.
ii) Secondly, Itching in urethra.
iii) Thirdly, Irritable bladder, from spasmodic sphincter.
d) After urination i.e.
i) Firstly, Pain in bladder is ameliorated by passing of urine.
Describe the menstrual symptoms of Nux Vomica.
Menstrual symptoms
1) Time i.e.:
i) Firstly, Too early; irregular, never at right time.
ii) Secondly, Flow occurs every two weeks interval.
2) Chilliness i.e.:
i) Firstly, Repugnance to cold or cold air.
ii) Secondly, Very much chilly, always wants to cover up; due to chilliness.
iii) Thirdly, Wants to cover up at every stage of fever, cannot move or uncover without being chilly.
iv) Fourthly, Chilly on least movement.
3) Over sensitiveness i.e.:
Oversensitive to external impressions; to noise, odours, light, music, etc.
4) Ineffectual desire i.e.
Frequent and ineffectual desire for stool and urine is a general concomitant of Nux Vomica; as it accompanies with almost all symptoms thus it is regarded as a characteristic indication. Dr. Boericke refers, ‘absence of all desires for defaecation is a contraindication’ of Nux Vomica.
5) Mind i.e.
Very much irritable, quarrel-some, zealous, spiteful, malicious, and nervous disposition.
6) Sleep i.e.
i) Firstly, Cannot keep from falling asleep in the evening, while sitting or reading hours before bed time.
ii) Secondly, Awakes at 3 to 4 A.M. and again falls into as dreamy sleep at day-break,
iii) Thirdly, It is hard to arouse and then feels tired and weak.
iv) Fourthly, Cat-nap sleep; better from a nap if allowed to finish (Ref. Boericke).
7) Ailments from i.e.
i) Firstly, High living.
ii) Secondly, Night watching.
iii) Thirdly, From anxiety, worry.
Duration i.e.
Long lasting, lasts for several days.
Quantity i.e.
Profuse.
d) Character of blood i.e.
i) Firstly, Dark, black, offensive.
ii) Secondly, Intermittent flow stops and starts again.
e) Before menstruation i.e.
i) Firstly, Excessive sensitiveness to external impressions: oversensitive to light, odour, noise, music.
ii) Secondly, Anxious, excited, irritable disposition.
f) During menstruation i.e.
i) Firstly, Irritable and quarrel-some mood.
ii) Secondly, Dysmenorrhea with pain in sacrum, and constant urging to stool. (Ref. Boericke) g) Modalities Agg. All complaints aggravate during and after menstruation. Old symptoms reappear.
h) Concomitants i.e.
i) Firstly, Anxious, taciturn, angry.
ii) Secondly, Wants to be alone.
iii) Thirdly, Constant ineffectual desire for stool and urine.
iv) Fourthly, Dr. Tyler refers, cramps in abdomen with nausea in the morning, accompanying with chilliness and attacks of fainting.
State the characteristic symptoms of Nux Vomica.
1) Universal antidote i.e.
"One of the best remedies with which to commence treatment of cases that have been drugged by mixtures, bitters, nostrums, quack remedies especially aromatic and hot remedies, but only if symptoms correspond.
2)Modalities i.e.
Agg. In the morning, waking at 4 A.M., after mental exertion, after taking spiced foods, after over eating, dry weather; in cold air, in clear fine weather. Amel In evening, while at rest; in damp wet weather.
Note: Dr. E.B. Nash’s sum up i.e.:
Spasm, nervous sensitive ness and chilliness are the three general characters of Nux Vomica. (6)
