Night Fall
Definition
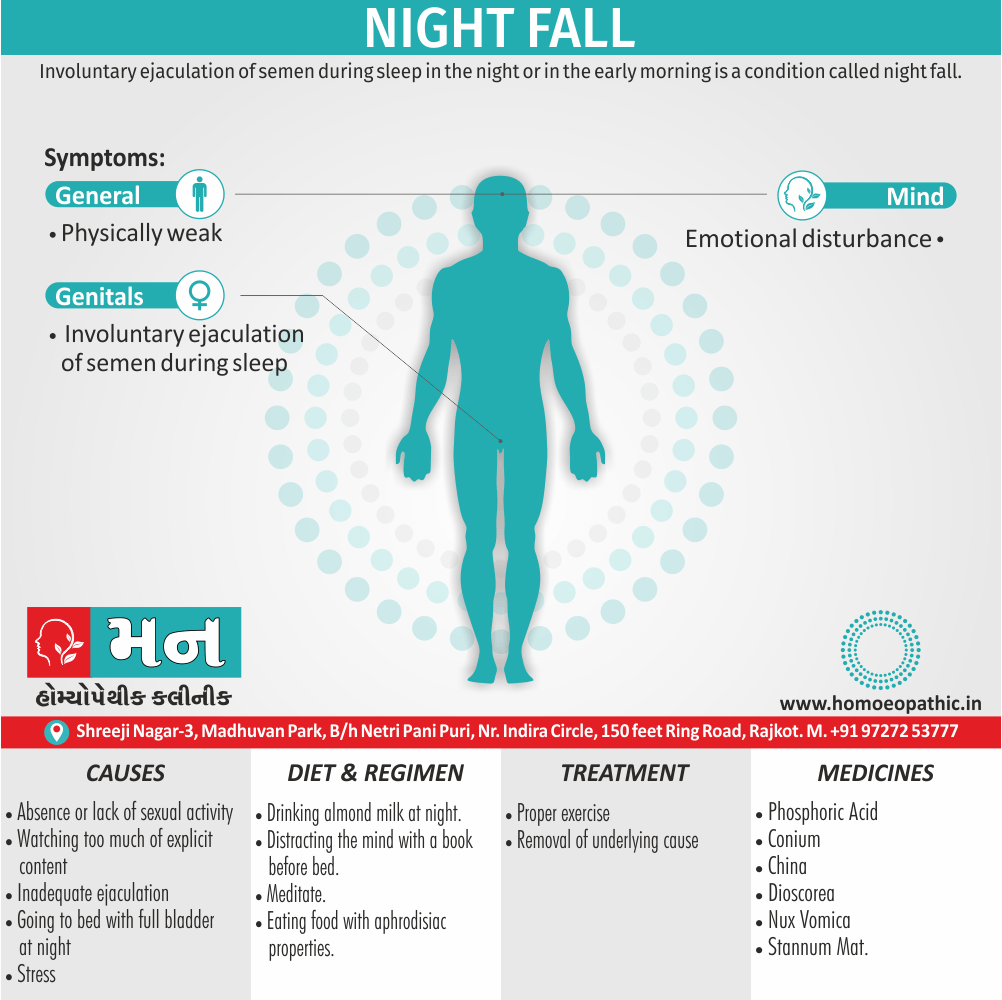
Involuntary ejaculation of semen during sleep in the night or in the early morning is a condition called night fall.
In the medical field, when referring to nighttime bodily functions or conditions, some possible terms you might be thinking of include:
Nocturnal emission: Spontaneous ejaculation during sleep, also known as wet dreams.
Overview
Epidemiology
Causes
Types
Risk Factors
Pathogenesis
Pathophysiology
Clinical Features
Sign & Symptoms
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Complications
Investigations
Treatment
Prevention
Homeopathic Treatment
Diet & Regimen
Do’s and Don'ts
Terminology
References
Also Search As
Overview
Overview of Night Fall
- When a boy reaches adolescence many changes take place in the body.
- One of the main changes is the growth of sex organs and hormone changes in the body.
- As a result of hormone changes in the body a young boy starts to masturbate and has dreams of sex.
- Due to the dreams and masturbation, he can suffer from involuntary ejaculation.
- Doctors call this condition nightfall.
- Though nightfall is a common problem in young boys, men of any age can suffer from this condition.
- Modern life has many distractions like pornography and the internet.
- These distractions provide a wrong angle to sex.
- Young men who watch porn regularly face a lot of problems due to nightfall. [1]
Epidemiology
Epidemiology of Night Fall
Researchers have conducted limited research specifically on the epidemiology of nocturnal emissions (wet dreams) in the Indian population. However, some studies have touched upon the topic as part of broader sexual health research.
One such study is "Profile of sexual disorders in males attending a psychiatric clinic in Mumbai" published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry in 2008. This study found that 50% of the male participants reported experiencing nocturnal emissions. However, it’s important to note that this study had a small sample size and was conducted in a clinical setting, so the results may not be generalizable to the broader Indian population.
Researchers published "A study of sexual dysfunctions in married males" in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry in 2002.While this study doesn’t explicitly focus on nocturnal emissions, it does provide some insights into sexual health patterns among married men in India. [3]
Causes
Causes of Night Fall
Nightfall may occur due to several causes and are usually harmless.
It may usually settle down with age, but if it occurs frequently then it can be a cause of concern.
- Either absence or lack of sexual activity
- Watching too much of explicit content
- Excessive stimulation of genitals
- Inadequate ejaculation
- Going to bed with full bladder at night
- Obesity
- Stress
- Physical inactivity
- Taking of sex hormone supplements
- Weak muscles.[1]
Types
Types of Night Fall
There isn’t a widely recognized classification of nocturnal emissions (wet dreams) into distinct types in the medical literature. However, some sources may discuss variations based on frequency, content of associated dreams, or underlying causes. [4]
Risk Factors
Risk factors of Night fall
While wet dreams are a natural physiological phenomenon, frequent or excessive occurrences might be associated with certain factors. [5]
Possible Risk Factors:
Age: Nightfall is most common during adolescence and young adulthood due to hormonal fluctuations. As men age, the frequency typically decreases.
- Sexual inactivity: Lack of sexual activity or masturbation can lead to a buildup of semen, increasing the likelihood of nocturnal emissions.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional stress can trigger hormonal changes, potentially increasing the frequency of wet dreams.
- Certain medications: Some medications, particularly those affecting hormone levels, might increase the likelihood of nocturnal emissions.
- Spicy food and stimulants: Excessive consumption of spicy foods, caffeine, or other stimulants might irritate the reproductive system and contribute to nightfall
- Tight clothing: Wearing tight undergarments or pants to bed can create friction and stimulate the genitals, potentially leading to wet dreams.
- Underlying medical conditions: In rare cases, frequent nightfall might be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as a hormonal imbalance or neurological disorder.
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of Night fall
Wet dreams are generally considered to be a result of the following factors:
Hormonal Changes: During puberty and adolescence, hormonal fluctuations, particularly testosterone, can lead to increased sexual arousal, even during sleep. This arousal can trigger nocturnal emissions.
Brain Activity: During REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, the brain is highly active, and vivid dreams can occur. These dreams, especially if they are sexually stimulating, can lead to physiological arousal and subsequent ejaculation.
Semen Buildup: In individuals who are sexually inactive or not ejaculating regularly, semen can accumulate in the reproductive system. This buildup can sometimes result in spontaneous release during sleep through nocturnal emissions. [6]
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology of Night fall
The exact pathophysiology of nocturnal emissions (wet dreams) is not fully understood, as it involves a complex interplay of physiological and psychological factors. However, the general understanding of the process is as follows:
Hormonal influence: During puberty and adolescence, testosterone levels increase significantly. This hormone plays a key role in sexual development and function, including the production of sperm and seminal fluid. Elevated testosterone levels can lead to increased sexual arousal, even during sleep.
Brain activity during REM sleep: During the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, the brain is highly active, and vivid dreams often occur. These dreams can be sexually stimulating, triggering physical arousal and leading to ejaculation in some cases.
Spinal reflex mechanisms: Ejaculation is a reflex action controlled by the spinal cord. When sexual arousal reaches a certain threshold, nerve signals from the brain trigger this reflex, resulting in the contraction of muscles involved in ejaculation.
Seminal vesicle filling: In individuals who are sexually inactive or not ejaculating regularly, semen can accumulate in the seminal vesicles. This buildup can sometimes lead to spontaneous release during sleep through nocturnal emissions. [6]
Clinical Features
Clinical Features of Night Fall
- Timing: Nocturnal emissions typically occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, often accompanied by vivid dreams with sexual content.
- Involuntary: The ejaculation is involuntary and happens without conscious awareness or control.
- Sensation: Some individuals may experience a pleasurable sensation during the emission, while others might not feel anything at all.
- Physical evidence: The most common evidence of a nocturnal emission is the presence of semen on bedsheets or nightclothes upon waking.
- Frequency: The frequency of wet dreams varies among individuals and can be influenced by factors like age, sexual activity, and hormonal levels. It’s most common during adolescence and young adulthood, and typically decreases with age. [7]
Sign & Symptoms
Sign & Symptoms of Night Fall
Nightfall can make a person physically, sexually, and mentally weak.
The typical symptoms of a person suffering from nightfall are i.e.:
- Restlessness
- Emotional disturbance
- Difficulty urinating
- Night sweat
- Insomnia
Sometimes a person may face memory-related problems as well.
Clinical Examination
Clinical Examination of Night Fall
Medical History: The doctor will inquire about the frequency and duration of wet dreams, associated symptoms (if any), sexual activity, and overall health status.
Physical Examination: A general physical examination may be performed to assess overall health and rule out any physical abnormalities.
Additional Tests: In rare cases, if an underlying medical condition is suspected, the doctor may recommend additional tests, such as hormone level tests or semen analysis. [8]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Night Fall
- Nightfall is not considered bad for health as it is a sign of healthy sex organs as well as puberty.
- However, frequent occurrences of nightfall may have some negative effect on the body such as it can make a person weak physically, mentally as well as sexually.
- Additionally, it can also cause insomnia, knee pain, dizziness and in severe cases, it can also cause memory-related problems.
- Recurrent nightfall in men is typically associated with a lack of masturbation and low testosterone in the body.
- Nightfall is considered normal if it occurs in a controlled frequency which is about two night fall per week.
- For teen males, the mean frequency of nightfall is approximately 0.36 times a week while for 40-year-old males, the nightfall mean frequency is 0.18 times a week.
- Nightfall in this range displays the healthy functioning of the sexual organs.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Night Fall
- Retrograde Ejaculation: This condition occurs when semen enters the bladder instead of being ejaculated through the penis. It can be caused by certain medications, surgeries, or neurological conditions.
- Premature Ejaculation: This is a common sexual dysfunction characterized by ejaculation occurring sooner than desired during sexual activity. While not directly related to nocturnal emissions, it can sometimes be a concern for individuals experiencing frequent wet dreams.
- Spermatorrhea: This refers to the involuntary discharge of semen without orgasm, which can happen during the day or night. It can be caused by various factors, including stress, weak pelvic muscles, or certain medications.
- Prostatitis: This is an inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, urinary problems, and sometimes, increased frequency of nocturnal emissions. [9]
Complications
Complications of Night Fall
Psychological Distress: While wet dreams are natural, some individuals might experience anxiety, guilt, or embarrassment due to cultural or religious beliefs. This can lead to psychological distress if not addressed.
Relationship Issues: In some cases, frequent nocturnal emissions might cause concern or insecurity in a relationship, particularly if a partner misunderstands the nature of wet dreams. Open communication and education can help alleviate these concerns.
Underlying Medical Conditions: In rare cases, very frequent nocturnal emissions might be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as a hormonal imbalance or neurological disorder. If accompanied by other unusual symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a doctor for evaluation. [10]
Investigations
Investigations of Night Fall
Medical History and Physical Examination: The doctor will inquire about the frequency and duration of wet dreams, associated symptoms (if any), sexual activity, and overall health status. A general physical examination may also be performed to assess overall health and rule out any physical abnormalities.
Semen Analysis: In some cases, a semen analysis might be recommended to assess sperm count, motility, and morphology. This can help rule out any issues with sperm production or quality that might be contributing to frequent wet dreams.
Hormone Level Tests: If a hormonal imbalance is suspected, the doctor may order tests to measure the levels of testosterone and other relevant hormones.
Additional Tests: Depending on the individual’s specific situation and symptoms, other tests like ultrasound or neurological examinations might be considered to rule out any underlying medical conditions. [11]
Treatment
Treatment of Night Fall
- Removal of underlying cause.
- Nightfall is a condition that is caused by stress, anxiety and hectic lifestyle of modern life.
- It can easily be overcome by taking proper exercise and diet and a few changes in lifestyle.
- Yoga and meditation along with a soothing bath to avoid nightfall.
Prevention
Prevention of Night Fall
- Regular Ejaculation: Engaging in sexual activity or masturbation can help reduce the buildup of semen, potentially leading to fewer wet dreams.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can help reduce stress, which might be a contributing factor for some.
- Dietary Changes: Some anecdotal evidence suggests that avoiding spicy foods or excessive caffeine might help, but there is no scientific evidence to support this.
Homeopathic Treatment
Homeopathic Treatment of Night Fall
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Night Fall:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition
The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy, potency and repetition of dose by Homeopathic doctor.
So, here we describe homeopathic medicine only for reference and education purpose. Do not take medicines without consulting registered homeopathic doctor (BHMS or M.D. Homeopath).
Medicines:
Phosphoric Acid:
- It is one of the most prescribed Homeopathic medicines for night fall cases with
- weakness and debility accompanied by involuntary loss of semen during the night.
- Weak, relaxed genitals during sex, which prevents emissions, are also treated well with this medicine.[2]
- China is the most effective Homeopathic medicine for night fall cases where wet dreams are accompanied by loss of vital fluids and followed by weakness.[2]
Dioscorea:
- Dioscorea works best in cases where the wet dreams (without erection) are followed by weakness, especially in the knees. [2]
Conium:
- Conium effectively treats nocturnal emissions with imperfect erections of short duration.
- Conium is also one of the best Homeopathic medicines for nightfall cases with impotency and ill-effects of suppressed sexual desire.[2]
Nux Vomica:
- Nux Vomica is the Homeopathic medicine to prescribe for easily excited desire, especially for bad effects of sexual excesses also wet dreams.
- Besides this; the person cannot even be around women without having emissions in such cases.[2]
Stannum Met:
- Where frequent involuntary discharge of semen also increased sexual desire are not accompanied by dreams
- The genitals start to feel voluptuous in these cases, ending in emission, which leaves the person exhausted.[2]
Diet & Regimen
Diet & Regimen of Night Fall
Nightfall" (nocturnal emissions) is a normal experience, especially for young men. While not usually a medical issue, frequent occurrences can cause worry. Here’s what you can do:
Diet and Lifestyle:
- Eat healthy: Plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Limit stimulants: Cut back on caffeine and spicy foods, especially at night.
- Hydrate: Drink lots of water, but not too much before bed.
- Manage stress: Try relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Exercise: Be active, but avoid intense workouts close to bedtime.
- Sleep well: Stick to a sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and wear comfy clothes.
- Healthy habits: Avoid excessive masturbation or stimulation before bed.
If it’s bothering you:
Talk to a doctor to rule out any medical causes and discuss your concerns. They might suggest:
- Medication review: Some meds can contribute to nocturnal emissions.
- Counseling: If anxiety or stress is a big factor, therapy can help.
For more insights on men’s health and sexuality, check out these books:
- The New Male Sexuality by Bernie Zilbergeld
- Man’s Search for Meaning by Viktor Frankl
Remember:
- Talk to your partner: Open communication can ease any worries.
- Be kind to yourself: Nightfall is natural. Don’t be hard on yourself.
By following these tips and seeking support if needed, you can manage nightfall and any related anxiety.[1]
Do’s and Don'ts
Do’s:
- Educate Yourself: Understand that nocturnal emissions are normal and common. This can help reduce any anxiety or embarrassment you might feel.
- Maintain Hygiene: If you experience a wet dream, simply wash yourself and change your clothes or bedding as needed.
- Open Communication: If you’re in a relationship, talk to your partner about wet dreams. Open communication can help prevent misunderstandings and build trust.
- Manage Stress: If stress seems to trigger more frequent wet dreams, explore relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Consult a Doctor: If wet dreams are excessively frequent, causing distress, or accompanied by other unusual symptoms, consult a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Don’ts:
- Don’t Feel Ashamed: Wet dreams are not a sign of weakness or moral failing. They are a natural bodily function.
- Don’t Try to Suppress Them: Attempts to suppress wet dreams are often unsuccessful and can lead to unnecessary stress and anxiety.
- Don’t Rely on Unproven Remedies: There are no scientifically proven methods to completely prevent wet dreams. Be cautious of products or practices that claim to offer a cure.
- Don’t Isolate Yourself: If you’re feeling embarrassed or anxious, talk to a trusted friend, family member, or therapist. Sharing your concerns can be helpful.
Terminology
References
References
- Man’s Search for Meaning by Viktor Frankl
- https://homeopathica.com/10-best-homeopathic-medicines-for-night
- Profile of sexual disorders in males attending a psychiatric clinic in Mumbai, published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry in 2008
- Wet Dreams, Nightfall, and Nocturnal Emissions Explained: Who Gets Them, Why, and What You Can Do, by Prana Man in 2023
- The Complete Book of Ayurvedic Home Remedies by Dr. Vasant Lad (1998, Three Rivers Press)
- Human Sexuality in a World of Diversity (10th edition)by Spencer A. Rathus, Jeffrey S. Nevid, Lois Fichner-Rathus (2018, Pearson)
- The New Male Sexuality (Revised edition) by Bernie Zilbergeld (2000, Bantam Books)
- Campbell-Walsh Urology (12th Edition) by Alan J. Wein, Louis R. Kavoussi, Andrew C. Novick, Alan W. Partin, Craig A. Peters (2021, Elsevier)
- Smith’s General Urology (18th Edition) Emil A. Tanagho, Jack W. McAninch (2018, McGraw Hill Professional)
- The Male Body: An Owner’s Manual by William J. Cromie (2004, Random House Trade Paperbacks)
- Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations (3rd Edition) H. Kenneth Walker, W. Dallas Hall, J. Willis Hurst, (1990, Butterworths)
- The New Male Sexuality by Bernie Zilbergeld.
Also Search As
Also Search As
There are several ways people can search for homeopathic articles on nightfall or nocturnal emissions:
Online Resources:
- Homeopathic Websites and Blogs: Many websites and blogs are dedicated to homeopathy, offering articles, case studies, and information on remedies. Some popular ones include:
- National Center for Homeopathy (NCH): The NCH website has a resources section with articles and publications on various health topics.
- Homeopathy Plus: This website features articles by homeopathic practitioners and researchers on a wide range of conditions.
- The American Institute of Homeopathy (AIH): The AIH website provides information about homeopathy and links to other resources.
- Online Homeopathic Libraries: Some libraries specialize in homeopathic literature and offer online access to books, journals, and articles. Examples include:
- Hahnemann Digital Library: This library houses a vast collection of homeopathic texts and resources.
- The British Homeopathic Library: This library offers a comprehensive collection of homeopathic materials, including historical texts and contemporary research.
- Search Engines: Utilizing search engines like Google or DuckDuckGo with specific keywords such as "homeopathy nightfall," "homeopathic remedies for wet dreams," or "homeopathic treatment for nocturnal emissions" can yield relevant articles and information.
Offline Resources:
- Homeopathic Books and Journals: Libraries and bookstores often carry books and journals on homeopathy, including materia medica (information on remedies) and repertories (indexes of symptoms and corresponding remedies).
- Homeopathic Clinics and Practitioners: Consulting with a qualified homeopathic practitioner can provide personalized advice and treatment recommendations for nightfall.
There are numerous ways to search for information on nightfall or nocturnal emissions, catering to different preferences and levels of detail.
Online Resources:
- Search Engines (Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo): Using keywords like "nocturnal emission," "wet dreams," "nightfall," along with additional terms like "causes," "treatment," or "home remedies," can yield a wide range of results from medical websites, forums, and blogs.
- Medical Websites (WebMD, Mayo Clinic): These reputable sites offer reliable information on health conditions, including sexual health topics like nocturnal emissions.
- Health Forums and Communities: Online platforms like Reddit or health-specific forums can provide personal experiences and discussions from individuals dealing with nocturnal emissions.
- Educational Websites: Sites like educational institutions or sexual health organizations often have resources on sexual development and related topics.
Offline Resources:
- Books: Libraries and bookstores offer various books on male health, sexual health, or even specific titles on nocturnal emissions. Look for books authored by medical professionals or experts in the field.
- Medical Professionals: Consult a doctor, urologist, or sexual health specialist for personalized advice and information. They can provide a medical perspective and address any concerns.
- Therapists or Counselors: If nocturnal emissions are causing anxiety or distress, seeking guidance from a therapist or counselor can be helpful.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are wet dreams harmful?
No, wet dreams are not harmful and do not pose any health risks. They are a natural bodily function and do not indicate any underlying medical condition in most cases.
Why do wet dreams happen?
Wet dreams are primarily caused by hormonal changes, brain activity during sleep, and the natural buildup of semen. They are not usually a cause for concern and are considered a normal part of male sexual development.
What are nocturnal emissions?
Definition
Nocturnal emissions, also known as wet dreams or nightfall, are involuntary ejaculations of semen that occur during sleep.
They are a normal physiological phenomenon experienced by many males during puberty and adulthood.
How often do wet dreams occur?
The frequency of wet dreams varies among individuals and can be influenced by age, sexual activity, and other factors. They are more common during adolescence and early adulthood and tend to decrease in frequency with age.
Are wet dreams a sign of a sexual problem?
No, wet dreams are not a sign of any sexual dysfunction or problem. They are a normal part of male sexual development and do not indicate any underlying issues in most cases.
Are homeopathic remedies safe?
Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe when prescribed by a qualified practitioner.
They are highly diluted substances and do not typically cause side effects.
How does homeopathy treat wet dreams?
Homeopaths select individualized remedies based on the person’s unique constitution, symptoms, and overall health.
These remedies aim to restore balance and address the root cause of the emissions, rather than just suppressing the symptom.
How long does homeopathic treatment take to show results?
The response time to homeopathic treatment varies depending on individual factors and the severity of the condition.
Some individuals may notice improvement within a few weeks, while others may require longer-term treatment.
Can homeopathy help with nocturnal emissions (wet dreams)?
Yes, homeopathy offers a holistic approach to address nocturnal emissions by considering the individual’s overall health and underlying imbalances. While scientific evidence is limited, many individuals report positive experiences with homeopathic treatment for reducing the frequency and intensity of wet dreams.
What are some common homeopathic remedies for wet dreams?
Homoeopathic Medicines for Night Fall
- Caladium seguinum, China officinalis, Selenium metallicum, and Staphysagria.
- The choice of remedy depends on individual factors and should be determined by a qualified homeopathic practitioner.
