Neoplasm of Esophagus
Definition
Neoplasm of the esophagus is a medical term for a tumor in the esophagus. The esophagus is the muscular tube that connects your throat to your stomach. It moves food you swallow from your mouth down to your stomach for digestion.
Neoplasms of the esophagus can be cancerous or benign. Cancerous neoplasms are more dangerous and can spread to other parts of the body. Benign neoplasms are not cancerous and usually don’t spread.
There are two main types of esophageal cancer:
- Squamous cell carcinoma: This is the most common type of esophageal cancer. It starts in the flat cells that line the inside of the esophagus.
- Adenocarcinoma: This type of cancer starts in the gland cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. This type of cancer is becoming more common in the United States.
Symptoms of esophageal neoplasms can include:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Pain in the chest or upper back
- Weight loss
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Hoarseness
- Cough
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of esophageal neoplasms is important for improving the chances of a cure.
Neoplasm of Esophagus is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue of Esophagus. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor.[1][2]
Neoplasm of the esophagus has several synonyms, depending on whether you want a more general or specific term. Here are some options:
General Synonyms:
- Esophageal tumor
- Esophageal cancer (if it’s malignant)
- Esophageal neoplasms (plural form)
More Specific Synonyms:
- Esophageal carcinoma (focuses on cancerous cells)
- Esophageal cancer, NOS (Not Otherwise Specified) – used when the specific type of cancer isn’t known
Depending on the cell type involved, specific terms like:
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma
Other Options:
- Oesophageal neoplasm (British spelling)
Not Recommended:
- Esophageal mass (less specific, could be cancerous or not)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Overview
Epidemiology
Causes
Types
Risk Factors
Pathogenesis
Pathophysiology
Clinical Features
Sign & Symptoms
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Complications
Investigations
Treatment
Prevention
Homeopathic Treatment
Diet & Regimen
Do’s and Don'ts
Terminology
References
Also Search As
Overview
Overview of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Esophageal cancer occurs when cells in the esophagus develop changes (mutations) in their DNA.
The changes make cells grow and divide out of control.
The accumulating abnormal cells form a tumor in the esophagus that can grow to invade nearby structures and spread to other parts of the body.[5]
Spread of carcinoma
Direct-
- The lesion may fill the lumen and infiltrate the wall of esophagus. It may also spread to the adjoining structures such as the trachea, left bronchus, aorta or pericardium.
- Involvement of the recurrent laryngeal nerves causes aspiration problems.
Lymphatic–
- Depending on the site involved, cervical, mediastinal or coeliac nodes may be involved.
- Cervical and thoracic lesions also spread to supraclavicular nodes.
- “Skip lesions” may also occur due to spread through the submucosal lymphatics.
Blood borne-
- Metastases may develop in the liver, lungs, bone and brain.[1]
Epidemiology
Epidemiology
It is a significant health concern in India, ranking as the fifth most common cancer in males and the sixth in females. According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the age-standardized incidence rate (ASR) is 6.5 per 100,000 for males and 4.2 per 100,000 for females. This translates to approximately 47,000 new cases and 42,000 deaths annually as of 2014.[6]
A study published in Thieme Connect in 2022, titled "Epidemiological Review: Esophagus Squamous Cell Carcinoma in India," revealed that India had 63,180 new cases of esophageal cancer in 2020, with 40,183 males and 22,997 females.[7]
Key Points:
- High Incidence: India has a high incidence of esophageal cancer, particularly in the northeastern region.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): The majority of esophageal cancers in India are of squamous cell histology, unlike Western countries where adenocarcinoma is more prevalent.
- Late Presentation: Esophageal cancer cases in India are often diagnosed at advanced stages (III and IV), leading to higher mortality rates.
- Risk Factors: Tobacco and alcohol consumption are major risk factors for esophageal cancer in India.
Additional Considerations:
- There are regional variations in the incidence of esophageal cancer in India, with some areas reporting higher rates than others.
- Efforts are underway to improve early detection and treatment of esophageal cancer in India.
It is important to note that these figures are estimates, and the actual number of cases may vary. It is also important to consult with healthcare professionals for the most up-to-date information on esophageal cancer in India.
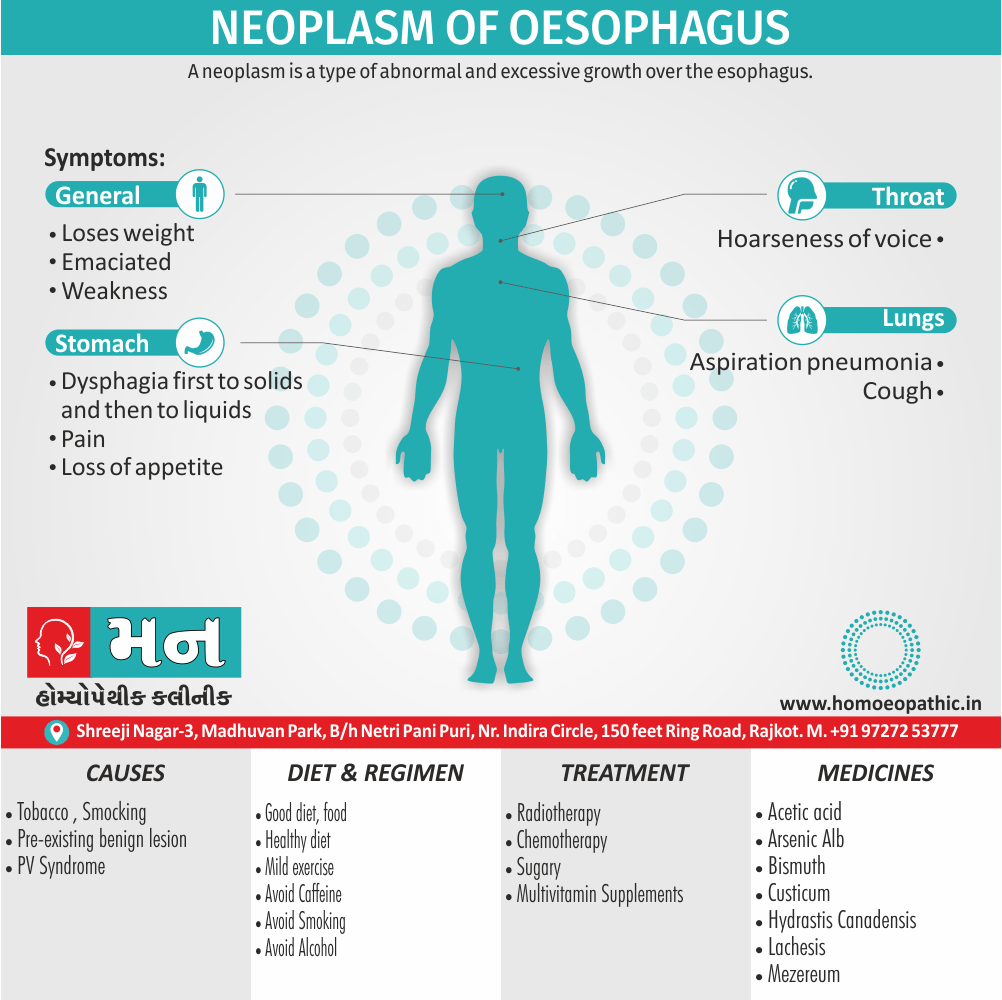
Causes
Causes of Neoplasm of Esophagus
- Smoking and alcohol consumption are high-risk factors and so are some particular dietary habits.
- High incidence is associated with tobacco chewing and smoking.
- About 5% of esophageal cancers arise in the pre-existing pathological lesions, such as benign strictures, hiatus hernia, cardiac achalasia and diverticula.
- Plummer–Vinson syndrome is another predisposing factor.
Types
Classification of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Benign neoplasms:
- Benign neoplasms are rare compared to malignant ones. Leiomyoma is the most common and accounts for two thirds of all the benign neoplasms.
- It arises from the smooth muscle and grows in the wall of esophagus.
- Dysphagia is produced when tumor exceeds the diameter of 5 cm. Barium swallow shows an ovoid filling defect.
- Endoscopy reveals a submucosal swelling. Biopsy should not be taken.
- Treatment is enucleation of the tumor by thoracotomy. Mucosal polyps, lipomas, fibromas and hemangiomas are other benign tumors.
- They are often pedunculated and present in the esophageal lumen. Endoscopic removal is avoided because of the danger of esophageal perforation. Treatment is surgical excision by esophagostomy.
Carcinoma esophagus
- Incidence of esophageal carcinoma is high in China, Japan, USSR and South Africa.
- In India, it constitutes 3.6% of all body cancers in the rich and 9.13% of those in those people who have less income.[1]
Risk Factors
Risk Factors of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Neoplasm of the esophagus, commonly known as esophageal cancer, can be classified into two main types:
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): This type arises from the flat cells lining the esophagus.
- Adenocarcinoma (AC): This type originates in the glandular cells that produce mucus and other fluids.
Each type has distinct risk factors, though some overlap exists.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors:
- Tobacco and Alcohol use: The most significant risk factors, with their combined use dramatically increasing the risk.
- Dietary Factors: Low intake of fruits and vegetables, diets high in processed meats, and consumption of very hot beverages.
- Betel quid chewing: Common in some parts of Asia and strongly associated with SCC.
- Chronic irritation: Conditions like achalasia (a swallowing disorder) or Plummer-Vinson syndrome (iron deficiency anemia and esophageal webs).
- Certain viral infections: Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection has been linked to SCC in some cases.
- Genetic Predisposition: Certain genetic variations may increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Exposures: Occupational exposure to certain chemicals may play a role.
Adenocarcinoma Risk Factors:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic acid reflux can lead to Barrett’s esophagus, a precancerous condition.
- Obesity: Increasingly recognized as a significant risk factor.
- Smoking: While less strongly associated than with SCC, it still increases the risk.
- Dietary Factors: High intake of processed foods and low fiber intake may contribute.
- Hiatal hernia: This condition, where part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm, can exacerbate GERD.
Please note that this is not an exhaustive list, and ongoing research continues to identify new potential risk factors. If you have concerns about your risk, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.[8]
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of Neoplasms of the Esophagus
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Risk Factors: Tobacco use, alcohol consumption, betel quid chewing, chronic esophageal irritation, and certain nutritional deficiencies (e.g., vitamin A, zinc).
- Molecular Changes: Accumulation of genetic alterations in tumor suppressor genes (e.g., TP53) and oncogenes, leading to dysregulated cell growth and proliferation.
- Progression: Chronic inflammation and irritation cause squamous metaplasia, followed by dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, and invasive SCC.
Adenocarcinoma
- Risk Factors: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Barrett’s esophagus, obesity, and smoking.
- Molecular Changes: Similar to SCC, but with additional alterations in growth factor receptors (e.g., HER2) and signaling pathways (e.g., Wnt pathway).
- Progression: GERD leads to Barrett’s esophagus (replacement of normal squamous epithelium with columnar epithelium), which can progress to dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, and invasive adenocarcinoma.[9]
Note: This is a simplified overview of the pathogenesis. The actual process is complex and involves multiple genetic and environmental factors.
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common (93%). Adenocarcinoma (3%) is also seen, but in the lower esophagus, and may be an upward extension of the gastric carcinoma.
Other types are rare..
Clinical Features
Clinical Features
The clinical presentation of esophageal neoplasms (both benign and malignant) is often insidious and nonspecific, leading to delayed diagnosis. The most common symptoms include:
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing): This is the hallmark of esophageal neoplasms and is often the first symptom. It typically starts with difficulty swallowing solids and progresses to liquids as the tumor grows and obstructs the esophagus.
- Odynophagia (painful swallowing): This can occur as the tumor invades the esophageal wall or surrounding structures.
- Weight loss: This is due to a combination of dysphagia, odynophagia, and the metabolic demands of the tumor.
- Regurgitation: This can occur as the tumor obstructs the esophagus, preventing the passage of food and liquids.
- Heartburn and indigestion: These can be caused by acid reflux due to the tumor disrupting the normal function of the lower esophageal sphincter.
- Hoarseness: This can occur if the tumor invades the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which controls the vocal cords.
- Coughing: This can be caused by aspiration of food or liquids due to the tumor obstructing the esophagus.
In advanced cases, patients may also present with:
- Bleeding: This can occur as the tumor erodes into blood vessels.
- Anemia: This can be caused by chronic blood loss or by the tumor interfering with the absorption of nutrients.
- Malnutrition: This can be caused by dysphagia, odynophagia, and the metabolic demands of the tumor.
- Metastasis: This occurs when the tumor spreads to other organs, such as the liver, lungs, or bones.[9]
Please note that this is a simplified overview of the clinical features of esophageal neoplasms. The presentation can vary depending on the type and location of the tumor, as well as the individual patient’s overall health and comorbidities. A thorough medical evaluation, including imaging studies and biopsies, is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.
Sign & Symptoms
Sign & Symptoms of Neoplasm of Esophagus
- Early symptoms. They include substernal discomfort and preference for soft or liquid food.
- Progressive dysphagia and emaciation. Dysphagia first to solids and then to liquids. Patient loses weight and becomes emaciated.
- Pain. Usually signifies extension of tumor beyond the walls of esophagus. It is referred to the back.
- Aspiration problem. Spread of cancer may cause laryngeal paralysis or fistulae formation leading to cough, hoarseness of voice, aspiration pneumonia and mediastinitis.[1]
Clinical Examination
Clinical Examination of Neoplasm of the Esophagus
History:
Presenting complaint:
Past medical history:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Barrett’s esophagus
- Tobacco/alcohol use
- Family history of esophageal cancer
Physical Examination:
General:
- Cachexia (wasting)
- Pallor (due to anemia from chronic blood loss)
Head and Neck:
- Lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) – cervical and supraclavicular
- Hoarseness (recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement)
Chest:
- Wheeze or stridor (tracheal compression)
Abdomen:
- Hepatomegaly (liver enlargement – metastatic disease)
- Ascites (fluid in the abdomen – advanced disease)
Further Investigations:
- Barium swallow: May show narrowing, stricture, or filling defect in the esophagus.
- Upper endoscopy and biopsy: The gold standard for diagnosis. Allows visualization of the tumor and tissue sampling for histological confirmation.
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): Assesses the depth of tumor invasion and lymph node involvement.
- CT scan of chest and abdomen: For staging of the tumor (determining the extent of spread) and to look for distant metastases.
- PET-CT scan: May be used to detect distant metastases not seen on CT.[8]
Please note: This is a general outline of the clinical examination for esophageal cancer. The specific findings may vary depending on the stage and type of tumor.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Barium swallow-
- It shows narrow and irregular esophageal lumen, without proximal dilatation of the esophagus.
Esophagoscopy-
- Useful to see the site of involvement, extent of the lesion and to take biopsy. Flexible fiberoptic oesophagoscope obviates the need for general anesthesia and gives a magnified view.
Bronchoscopy-
- It helps to exclude extension of growth into the trachea and bronchi.
CT scan-
- It is useful to assess the extent of disease and nodal metastases [1]
Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Benign Tumors:
- Leiomyoma (most common)
- Polyps (Inflammatory fibroid polyp, hamartoma, etc.)
- GIST (Gastrointestinal stromal tumor)
- Granular cell tumor
Malignant Tumors:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (most common worldwide)
- Adenocarcinoma (most common in Western countries)
- Small Cell Carcinoma
- Lymphoma
- Melanoma
Non-Neoplastic Conditions:
- Achalasia
- Esophageal Stricture (Peptic, radiation-induced, etc.)
- Esophageal Web (Plummer-Vinson syndrome)
- Esophageal Ring (Schatzki ring)
- Infectious Esophagitis (Candida, Herpes simplex virus, Cytomegalovirus)
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- Barrett’s Esophagus (premalignant condition)
Clinical Approach:
A thorough history and physical examination, along with appropriate diagnostic tests (endoscopy with biopsy, barium swallow, CT scan, endoscopic ultrasound), are essential to accurately diagnose esophageal neoplasms and differentiate them from other conditions. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in patients with esophageal cancer.[8]
Complications
Complications of Neoplasm of the Esophagus
Neoplasms of the esophagus, primarily esophageal cancer, can lead to a variety of complications due to local tumor growth, invasion of surrounding structures, and distant metastasis.
Local Complications:
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing, often the earliest and most common symptom, due to luminal obstruction.
- Odynophagia: Painful swallowing, due to tumor ulceration or inflammation.
- Weight Loss: Due to dysphagia and decreased food intake.
- Hemorrhage: Bleeding from the tumor, which can be mild or severe.
- Obstruction: Complete blockage of the esophagus, preventing the passage of food and liquids.
- Fistula Formation: Abnormal connections between the esophagus and the trachea or bronchi, leading to aspiration pneumonia.
Metastatic Complications:
- Spread to lymph nodes: Common sites of metastasis, leading to further complications.
- Spread to liver: Leading to liver dysfunction and failure.
- Spread to lungs: Causing respiratory symptoms and difficulty breathing.
- Spread to bones: Resulting in bone pain and fractures.[8]
Investigations
Specific Investigations
- Upper Endoscopy and Biopsy: The gold standard for diagnosis. Allows for direct visualization of the tumor, assessment of its extent, and obtaining tissue samples for histological confirmation.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Helps to determine the depth of tumor invasion into the esophageal wall (T-stage) and assess for lymph node involvement (N-stage), which is crucial for staging and treatment planning.
- Barium Swallow: A less invasive test that can show the location and size of the tumor, but it is not as accurate as endoscopy for diagnosis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Used to assess for distant metastasis (M-stage) to organs like the liver, lungs, or lymph nodes.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: Can be used in conjunction with CT to better visualize metabolically active tumor cells and detect metastases.
- Bronchoscopy: May be performed if the tumor is located in the upper esophagus to assess for potential invasion into the airway.
- Laparoscopy: May be performed to assess for peritoneal spread in cases of advanced disease.
- Laboratory Tests: Complete blood count, liver function tests, and tumor markers (e.g., CEA, CA 19-9) may be helpful for staging and monitoring treatment response.[8]
Note: The specific investigations used may vary depending on the individual patient’s presentation and clinical suspicion. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Treatment
Treatment of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Surgery of upper two-thirds of esophagus is difficult due to great vessels and involvement of mediastinal nodes.
Radiotherapy is the treatment of choice.
Surgery is the preferred method of treatment for cancer of lower one-third.
The affected segment, with a wide margin of esophagus proximally and the fundus of stomach distally, can excise with primary reconstruction of the food channel.
Disease of esophagus in advanced lesions, only palliation is possible. An alternative food channel can provide by:
- A by-pass operation.
- Esophageal intubation with Celestin or Mousse au barb in or a similar tube.
- Permanent gastrostomy or a feeding jejunotomy.
- Laser surgery: esophageal growth is burnt with Nd: YAG laser to provide a food channel. Chemotherapy use only as a palliative measure in the locally advanced or disseminated disease.
Prevention
Preventive Measures:
- Avoid Tobacco and Alcohol: Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can significantly reduce your risk.
- Manage GERD: If you have GERD, work with your doctor to manage it effectively. This may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: If you are Higher Weight, losing weight can help reduce your risk.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may help protect against esophageal cancer. Focus on cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage.[10]
Important Note: This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor for personalized recommendations on esophageal cancer prevention.
Homeopathic Treatment
Homeopathic Treatment of Neoplasm of Esophagus
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis.
which includes
- The medical history of the patient,
- Physical and mental constitution,
- Family history,
- Presenting symptoms,
- Underlying pathology,
- Possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions.
What Homoeopathic doctors do?
A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’?.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness also looked for. No a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition.
The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
Homeopathic Medicines for Neoplasm of Esophagus:
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Homoeopathic Approach:
Homeopathy treats the person as a whole. It means that homeopathic treatment focuses on the patient as a person, as well as his pathological condition. The homeopathic medicines are selected after a full individualizing examination and case-analysis, which includes the medical history of the patient, physical and mental constitution, family history, presenting symptoms, underlying pathology, possible causative factors etc.
A miasmatic tendency (predisposition/susceptibility) is also often taken into account for the treatment of chronic conditions. A homeopathy doctor tries to treat more than just the presenting symptoms. The focus is usually on what caused the disease condition? Why ‘this patient’ is sick ‘this way’.
The disease diagnosis is important but in homeopathy, the cause of disease is not just probed to the level of bacteria and viruses. Other factors like mental, emotional and physical stress that could predispose a person to illness are also looked for.
Now a days, even modern medicine also considers a large number of diseases as psychosomatic. The correct homeopathy remedy tries to correct this disease predisposition. The focus is not on curing the disease but to cure the person who is sick, to restore the health. If a disease pathology is not very advanced, homeopathy remedies do give a hope for cure but even in incurable cases, the quality of life can be greatly improved with homeopathic medicines.
The homeopathic remedies (medicines) given below indicate the therapeutic affinity but this is not a complete and definite guide to the homeopathy treatment of this condition. The symptoms listed against each homeopathic remedy may not be directly related to this disease because in homeopathy general symptoms and constitutional indications are also taken into account for selecting a remedy.
Medicines
Acetic Acid
- Scirrhous of pylorus; additionally cancer of stomach, ulcerative gnawing at one spot in stomach, with agony and depression, preventing sleep.
- Moreover, Intense and constant thirst.
- Severe burning pain in stomach also abdomen.
- Vomiting after every meal of yellow, either yeast-like matter, or blood.
- Besides this, Pale, waxen skin.
- Lastly; Tongue pale and flabby; marked debility; copious pale urine.
Arsenic Album
- Basically; Cancer of stomach, with burning pain and excessive thirst, desire for acids.
- Aggravation specifically from cold drinks and cold diet, on the other hand amelioration from hot drinks.
- In detail, Vomiting of all he takes; terrible sensation of weakness and exhaustion with anxiety in region of stomach.
- Uterine cancer with burning pain in uterine region also shooting, stinging pains in upper part of abdomen.
- Thirst and dryness of mouth and throat, worse by motion.
- All in all; Acrid, corroding, burning discharges, often very offensive, light or dark-colored.[3]
Bismuth
- Cancer of stomach with burning, stinging, crampy pains.
- Stomach hangs down to the crest of the ilium; hard lumps between navel and edges of lower ribs, side.
- Vomits only at intervals of days when food has filled the stomach, then vomits large quantities of food during the whole day; vomits all fluids.
Causticum
- Patient cannot bear the pressure of the clothes on the stomach.
- The lightest food or even the smallest quantity causes a violent lancinating pain in the stomach.
- Scirrhous of the lips, with itching and soreness, which when ulcerated has a violent burning pain; pus bloody, or greenish, or corroding, or thin, watery and yellow.
Hydrastis Canadensis
- Cancers hard, adherent, skin mottled, puckered, cutting pain like knives also even after ulcerations sets in, where it may regulate faulty nutrition.
- Epithelioma, cancer to rectum, cancer of stomach vomits everything except water with milk; additionally pain in pit of stomach, emaciation.
Lachesis
- Cancer of stomach, the pit very sensitive to touch, with a gnawing pressure, better by eating, but coming on again in a few hours, and the more violent the emptier the stomach.
- Cancer of breast with lancinating pains and a constant painful feeling of weakness and lameness in left shoulder and arm;[3]
Mezereum
- Cancer of stomach with burning, corroding pains.
- Great emaciation; the muscles of the face are tensely drawn, like strings; additionally internal surface of the gastric mucous membrane feels raw, with sensation as if food remained for a long undigested in the stomach.
- Constant vomiting of chocolate-coloured masses, with great burning in throat.
- Hematemesis; violent retching, accompanied with the agony of death.
- Sleepiness and exhaustion; hard lumps in epigastrium region; hypochondriasis; constipation.
Spigelia
- Cancer of Esophagus, pylorus or rectum, narrowing the lumen of the canal, with constant severe and pressing pains, pressing through to the back and shooting down into the thighs.
- Cancer of uterus, with pressure and pain in the whole pelvic region and shooting down the limbs.
- Burning heat in vagina, with sense of fulness and pressure, worse standing and dislike to move.[3]
Diet & Regimen
Diet & Regimen of Neoplasm of Esophagus
- Eat foods high in calories and protein.
- These include whole, full-fat dairy products, nut products, and meats. For example milkshakes, smoothies with protein powder, peanut butter, beans, eggs, cheese, and yogurt.
- If swallowing is still hard, soften your foods with gravies or sauces. Chop up meat into small pieces. For example scrambled eggs, pasta, custard, pudding, and soups and stews made with ground meat.
- Furthermore; If you’ve had surgery, your stomach may be smaller.
- You may fill up quickly. It may help to eat smaller meals more often. You should also avoid drinking fluids before meals. And keep lots of snacks on hand for between meals.
- You may need to sip fluids while you’re eating. This can help make swallowing easier. It can also help food pass through your esophagus.
- Besides this, Highly acidic or spicy foods, foods with sharp pointed edges, or extremely hot or cold foods.
- Fluids may be irritating, especially during certain types of treatments.
- Overall; Use caution with foods like tough cuts of meat, doughy bread, alcohol, citrus juices or sauces, also piping hot beverages.[4]
Do’s and Don'ts
Do’s & Don’ts
Esophageal cancer (neoplasm of the esophagus) is a serious condition, but there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and improve your chances of early detection if it does occur.
Do’s:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are rich in antioxidants and fiber, which may help protect against esophageal cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Heavy alcohol use is a major risk factor for esophageal cancer.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a leading cause of esophageal cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk.
- Manage GERD: If you have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), work with your doctor to manage it effectively. Chronic GERD can increase your risk of developing esophageal cancer.
- Get Regular Checkups: If you have any risk factors for esophageal cancer, talk to your doctor about getting regular screenings. Early detection can greatly improve your chances of successful treatment.
Don’ts:
- Don’t Smoke: As mentioned earlier, smoking is a major risk factor for esophageal cancer. Avoid smoking or using tobacco products.
- Avoid Drink Excessively: Heavy alcohol use is also a major risk factor. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Don’t Ignore Symptoms: If you experience any symptoms of esophageal cancer, such as difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing, or unintentional weight loss, see your doctor right away. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
- Don’t Eat a Diet High in Processed Foods: Processed foods are often high in fat, sugar, and salt, and low in nutrients. A diet high in processed foods may increase your risk of esophageal cancer.
Remember, these are general recommendations. It’s important to talk to your doctor for personalized advice based on your individual risk factors and medical history.
Terminology
Terminology
Here are some terminologies and their meanings commonly used in articles about neoplasm of the esophagus (esophageal cancer):
- Neoplasm: An abnormal growth of tissue that may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous)
- Oesophagus/Esophagus: The muscular tube that carries food and liquids from your throat to your stomach.
- Adenocarcinoma: A type of cancer that starts in the cells that form glands. In the esophagus, it often develops in the lower part near the stomach.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: A type of cancer that starts in the thin, flat cells lining the esophagus. It often develops in the upper or middle part of the esophagus
- Barrett’s Esophagus: A condition where the normal lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the stomach. It is a precancerous condition that increases the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma
Other Terminologies
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing. This is a common symptom of esophageal cancer.
- Odynophagia: Painful swallowing. This can also be a symptom of esophageal cancer.
- Endoscopy: A procedure where a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera is inserted through the mouth to examine the esophagus.
- Biopsy: The removal of a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope to diagnose cancer.
- Staging: The process of determining the extent of cancer, including its size, location, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body
- Radiotherapy: The use of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: The use of drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Esophagectomy: Surgery to remove all or part of the esophagus
- Palliative care: Care focused on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life for people with serious illnesses like cancer.
Understanding these terms can help you better understand articles and discussions about esophageal cancer, its diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any questions or concerns about your health.
Homoeopathic Terminology Related To Neoplasm Of Oesophagus
- Miasm: A fundamental disturbance or predisposition in the body that underlies disease susceptibility. Homeopaths believe that understanding the miasm is essential for selecting the most appropriate remedy.
- Constitutional Remedy: A homeopathic medicine chosen based on the patient’s overall physical, mental, and emotional characteristics, rather than just their specific symptoms.
- Repertory: A reference book that lists symptoms and the homeopathic remedies associated with them.
- Materia Medica: A collection of descriptions of homeopathic remedies and their effects on the body.
- Potentization: The process of diluting and shaking a homeopathic remedy to increase its therapeutic effect.
- Similimum: The homeopathic remedy that most closely matches the totality of the patient’s symptoms.
- Aggravation: A temporary worsening of symptoms that may occur after taking a homeopathic remedy. This is generally seen as a positive sign that the remedy is working.
- Proving: A systematic study of the effects of a homeopathic remedy on healthy individuals to determine its symptom picture.
- Nosode: A homeopathic remedy prepared from diseased tissue or bodily fluids.
- Organon of Medicine: The foundational text of homeopathy, written by Samuel Hahnemann.
- Vital Force: The energy or life force that animates the body and maintains health. Homeopaths believe that disease arises from a disturbance in the vital force.
- Law of Similars: The principle that a substance that can cause symptoms in a healthy person can cure similar symptoms in a sick person.
- Minimum Dose: The smallest possible dose of a homeopathic remedy needed to stimulate the body’s healing response.
- Individualization: The process of tailoring treatment to the specific needs of each patient, taking into account their unique physical, mental, and emotional characteristics.
References
References use for Article Neoplasm of Esophagus
- Diseases_of_Ear_Nose_and_Throat_6Edition
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=34&ContentID=17970-1
- Homoeopathic Therapeutics by Lilienthal
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=34&ContentID=17970-1#:~:text=Eat%20foods%20high%20in%20calori
- https://www.google.com/search?q=overview+of+neoplssm+of+esophagus&rlz=1C1CHBF_enIN990IN990&oq=overview+of+neoplssm+of+es
- Consensus Document for Management of Esophageal Cancer – Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) (2014).
- Epidemiological Review: Esophagus Squamous Cell Carcinoma in India – Thieme Connect (2022).
- Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 11th Edition, Mark Feldman, Lawrence S. Friedman, Lawrence J. Brandt, 2021, Elsevier Saunders.
- Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (10th Edition), Vinay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, Jon C. Aster, 2021, Elsevier.
- Esophageal Cancer: Prevention, Diagnosis and Therapy Edited by Nabil F. Saba and Bassel F. El-Rayes, published in 2019 by Springer.
Also Search As
Neoplasm Of Oesophagus Also Search As
People can search for homeopathic articles on neoplasm of the esophagus (esophageal cancer) using several methods:
Online Search Engines:
- Keywords: Use specific terms like "homeopathy esophageal cancer," "homeopathic remedies esophagus neoplasm," or "homeopathic treatment esophageal carcinoma." Include variations like "oesophagus" (British spelling) for wider results.
- Platforms: Search on Google Scholar, PubMed (filter for complementary medicine), and general search engines like Google or DuckDuckGo.
Homeopathic Databases and Journals:
- Homeopathic Repertories: These resources list symptoms and associated remedies. Look up symptoms related to esophageal cancer and explore suggested remedies.
- Homeopathic Materia Medica: These texts detail the properties and applications of various homeopathic remedies. Look for remedies known to address cancer or digestive system issues.
- Online Homeopathic Libraries: Websites like Hpathy.com and The American Institute of Homeopathy may offer articles or case studies on esophageal cancer.
Homeopathic Organizations and Practitioners:
- Websites of Homeopathic Organizations: The National Center for Homeopathy (NCH) or similar organizations may have resources or publications on this topic.
- Homeopathic Clinics and Practitioners: Contact local homeopathic clinics or practitioners who specialize in cancer treatment. They may have access to articles, research, or case studies not readily available online.
Social Media Groups and Forums:
- Homeopathic Groups: Search for relevant groups on platforms like Facebook or Reddit. These groups may share articles, discuss case studies, or offer support to individuals with esophageal cancer seeking homeopathic treatment.
Important Considerations:
- Quality of Information: Be critical of the information you find. Look for articles published in reputable homeopathic journals or written by qualified practitioners.
- Consult a Professional: Always consult with a qualified homeopathic practitioner before starting any treatment for esophageal cancer. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure your safety.
- Complementary Approach: Homeopathy can be used as a complementary approach alongside conventional medical treatment. Discuss with your healthcare team to ensure a comprehensive treatment plan.
By combining these search methods and exercising critical judgment, you can find valuable information on homeopathic approaches to esophageal cancer.
What is Neoplasm of Esophagus?
A neoplasm is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. In addition; The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia.
How is esophageal cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves an endoscopy with biopsy, imaging tests like CT scans or PET scans, and sometimes other tests like barium swallow or endoscopic ultrasound.
What causes Neoplasm of Esophagus?
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Tobacco chewing and smoking
- Benign strictures, hiatus hernia, cardiac achalasia and diverticula.
- Plummer–Vinson syndrome
What are the risk factors for esophageal cancer?
Risk factors include smoking, heavy alcohol use, chronic acid reflux (GERD), Barrett’s esophagus, obesity, and a diet low in fruits and vegetables.
What are the symptoms of Neoplasm of Esophagus?
- Substernal discomfort and preference for soft or liquid food
- Progressive dysphagia and emaciation
- Pain
- Aspiration problem
Can homeopathy help with esophageal neoplasms?
Homeopathy is sometimes considered as a complementary approach alongside conventional treatment, but it’s crucial to prioritize medical advice and treatment for this serious condition.
How does homeopathic treatment work in conjunction with conventional cancer care?
Homeopathy might be used alongside conventional treatment to potentially support overall well-being and manage specific symptoms. However, it should never replace necessary medical interventions.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with homeopathic treatment for esophageal neoplasms?
When used correctly, homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe. However, consulting a qualified practitioner is vital to ensure appropriate use and avoid potential interactions.
Homeopathic Medicines used by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of Neoplasm of Esophagus?
- Acetic Acid
- Arsenic Album
- Bismuth
- Causticum
- Hydrastis Canadensis
- Lachesis
- Mezereum
- Spigelia
