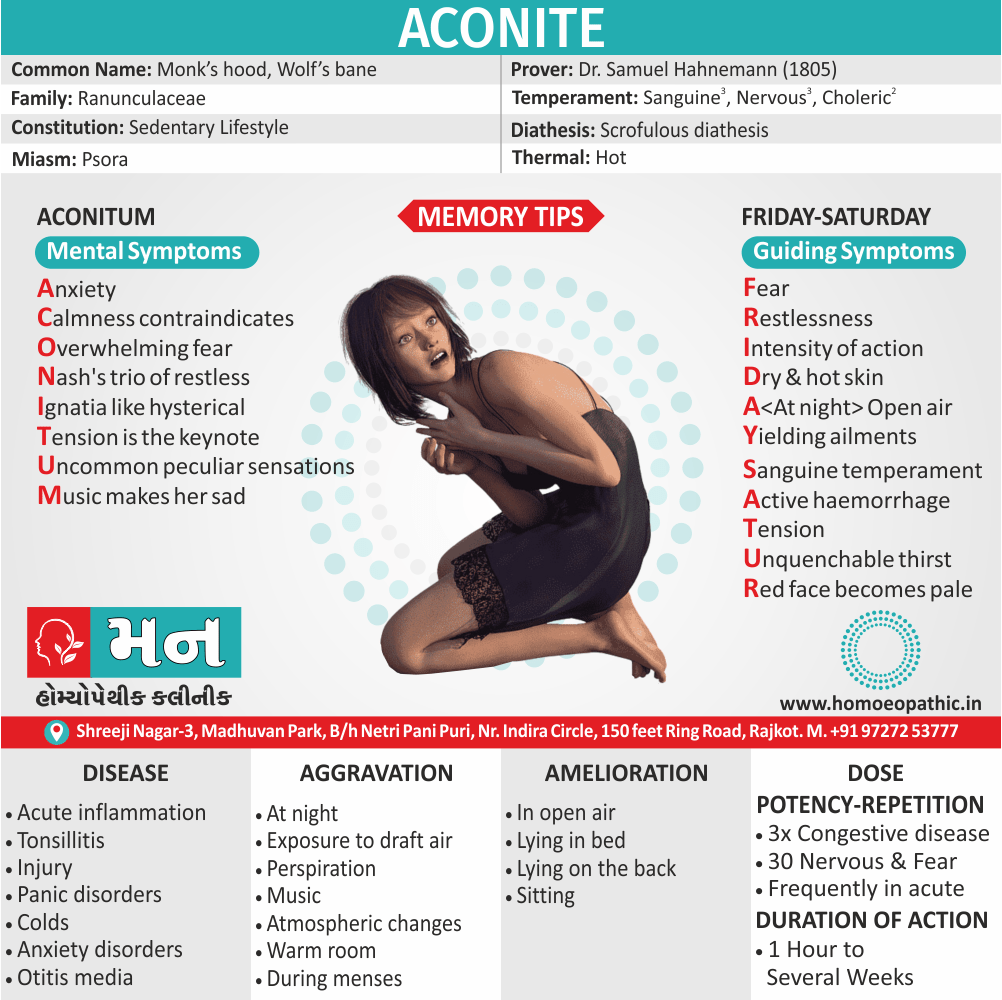
Aconitum Napellus
Overview
Aconitum napellus, commonly known by various names such as Aconite, Monkshood, and Wolf’s bane, is a beautiful but deadly flowering plant. Its hood-shaped flowers, resembling a monk’s cowl or a helmet, give it its distinct names.
- Aconite: This name is derived from the Greek word "akoniton," meaning "without dust" or "without struggle," perhaps referencing its rapid and potent effects.
- Monkshood: This name is inspired by the resemblance of the flower’s upper sepal to a monk’s hood.
- Wolf’s bane: This name refers to the plant’s historical use as a poison for wolves and other large predators.
- Angustifolium: This is a botanical term meaning "narrow-leaved," referring to the shape of the plant’s leaves.
- Friar’s Cap: Similar to Monkshood, this name refers to the flower’s resemblance to a friar’s headwear.
- Helmet flower: Also referencing the flower’s shape, this name highlights the protective helmet-like structure.
- Leopard’s bane: This name refers to the plant’s use as a poison for leopards in some regions.
- Devil’s helmet: This name reflects the plant’s toxicity and potential danger.
- Blue rocket: This name is given to certain cultivars of Aconitum napellus with blue flowers due to their tall, upright growth and striking blue color.
All parts of Aconitum napellus are highly poisonous due to the presence of alkaloids, particularly aconitine. Despite its toxicity, it has been used in traditional medicine for various purposes, and in homeopathy, a highly diluted preparation of Aconitum napellus is used as a remedy for various ailments.
A
C
O
N
I
T
U
M
A
Anxiety of mind and Anxiety of body
- The anxiety of Aconite pt.is due to the internal turmoil and hence the pt. is
- This anxiousness of the mind is evidenced by her intellectual tension which is reflected as great acuteness of all her senses.
- In the mental sphere this hyperactivity is specially evidenced as she gets vexed at trifles.
- In the physical sphere it is evidenced as slight bearable pain to her becomes unbearable she jumps in agony, a state of hyperesthesia. Dr. Hering said due to this mental anxiety he is agonized and tossing about.
Note:
Fear of future and forebodings also characterizes this anxiety. [1]
C
Calmness contraindicates Aconite
- Guernsey said, ‘Mental calmness contraindicates Aconite. (Chamo. -indicates, Puls.).
- Thus, whenever Aconite will be the drug of choice, there must be the mental uneasiness, mental restlessness, worry, anxiety and great fear, otherwise it is contraindicated. [1]
O
Overwhelming fear:
- It is leading remedies having characteristic types of fear.
- It has got not that type of fear viz., fear of poverty like Bryonia. fear of thunder like Phos.; fear of dogs like Bell: fear of approach like Arnica. fear of being alone like Ars. Arg Nit.; but it has got characteristic fear, fear of death with prediction of day and time of death.
- Tyler said, fear of death may be so great, that people have actually killed themselves for fear of dying.
- Hence Aconite. has got fear of death (Ars.’, Calc. Carb.’, Cimicifuga, Gels.’, Lac Can.’, Nit. Ac.’, Phos., Platina¹) (Ref. Kent’s Repertory) but the characteristic is pt. predicts the day: even the time of death, i. e., the clairvoyance.
Master Kent said,
- many times the pt. actually predicts the moment or hour of death; if a clock is in the pt.’s room, she may say, that when the hour hand reaches a certain point, she will be a corpse. Dr. Tyler said, it is Aconite pt. who calls her friends around her and takes leave of them. Fear of death is such an important feature. Dr. Farrington said that prediction of hour of the death esp. in childbed is also found in it and can be bracketed with Argentum Nit. and Coffea.
Besides this:
- (a) fear of darkness (Can. Ind.1, Stramo1, Acon 2., Calc. C 2., Camph.2, Carb. An2, Carb. Veg2, Caust2, Cup 2, Lyco 2, Phos 2, Puls 2.)
- (b) fear of bed (Acon 2, Ars 2, Caust 2, Cup 2, Lach 2)
- (c) fear of ghost (Acon 2, Ars 2, C.V2, Caust 2, Lyco 2, Phos 2, Puls 2, Sulph 2.)
- (d) fear of going out, fear of crowd (Acon. 1, Arg. N 2, Lyco 2, Nat. Mur 2, Nux Vom 2, Puls 2).
Note:
Dr. Nash said, ‘fear to go into society- Anthropophobia.
- (e) fear of death in pregnancy (Acon.3).
- (f) fear of approaching death (Arg. Nit., Ars., Cimic., Nit. Ac. Secale Cor.) (Ref. Cowperthwaite).
- (g) fears the loss of reason-leading to mental prostration with weakness of memory, cannot remember dates. (Ref.Dr. Talcott’s Mental diseases). [1]
N
Nash’s trio of restless and Nash’s trio of pain- killers.
- Aconite is one of the Nash’s trios of restless medicines.
- Aconite is mentally restless, whereas Rhus Tox. Is physically restless and Arsenic is restless both mentally and physically thus the trio: Acon., Ars. Alb., and Rhus Tox.
- E. B. Nash said, fear, as much as the pain that makes the pt. so full of that agonized restlessness.
- N. M. Chowdhury said, the impatience and anxiety makes the pt. restless. She throws herself about and cons tantly changes the position. The true reason of this restless ness is to be found in a state of internal turmoil and anxiety and agony. She moans and laments, screams and shouts, not knowing what to do and how to find consolation.
- In such a case of mental restlessness, Aconite will be the drug of choice-give her drug-it will cure. [1]
I
Ignatia like:
- Aconite patient is also inclined to be Chaotic. (Caust¹, Gels 1, Ign 1, Lach 1, Nat Mur 1, Nit. Ac 1, Nux Vom’, Puls.’, Sep., Sil¹).
- N. M. Chowdhury said, great variation of mood and temperament. She is cheerful this minute, weeps the next. She is sad and taciturn now but gay and loquacious the next moment.
- Master Kent said, sometimes Aconite pt. loses all her affection, which leads to a state of indifference-this state is also characterized by Vehemental mood.
- Talcott said pt. moves from dry anguish to exuberant tears. [1]
T
Tension is the key-note
Dr. Huge said, tension is the key note of Aconite pt.(-Congestion is the keynote of Bell.).
This tension is mentally evidence by intense restlessness, inconsolable anxiety, acute imagination and fears. [1]
U
Uncommon peculiar sensations
It has got some peculiar sensations. viz.,
a) All the intellectual functions are going on in the region of the stomach.
b) Some parts of the body are deformed e.g., a limb is displaced, lips are too thick. (Ref. Farrington). [1]
M
Music makes her sad
- Music is unbearable for Aconite pt.; it makes her sad (Acon 2, Graph 2, Dig 2, Kreos 2, Nat.C 2, Thuja 2)
- (-music > Aurum 1, Tarent. ¹).
Note. 1:
Countenance:
Master Kent has pointed to note the countenance of Aconite, which is expressive of fear. Fear is depicted upon her countenance.
Note. 2:
- Kent reported that every mental condition is marked by intensity. If it is a delirium, thence it is intense; – thus
- Dr. Farrington said the intensity of these symptoms denotes overexcitement of brain, common enough to intense patients.
Note. 3:
Master Kent said, this type of mental picture is always present in pneumonia, inflammatory conditions of any part, or kidney, liver, bowels etc.
Note. 4:
In case of female’s amenorrhoea in plethoric young girls after fright is a marked feature.
Note. 5:
Our immortal Master Hahnemann said ‘whenever Aconite is chosen homeopathically, you must above all, observe the moral symptoms, and be careful that it closely resembles them; the anguish of mind and body: the restlessness: the disquiet not to be allayed’.
Note. 6:
Master Kent said even congestion of parts as a result of fear. A turmoil affecting the whole sensorium. [1]
F
R
I
D
A
Y
S
A
T
U
R
F
Fear
- Great fear and anxiety of mind with great nervous excitability is the characteristic of Acon. patient.
- Afraid to go out, to go into a crowd where there is any excitement of many people.
It has got fear of death in acute disease, fear of darkness (Caust.), fear of ghost, fear to cross the street (Arg. Nit.), fear to cross a bridge, fear of death in pregnancy. Fear of future. Fear of the fright remains (Op. Stramo.).
- Life is rendered miserable for Acon. patient due to fear.
- He is sure his disease will prove fatal, predicts the day and moment of death. [1]
R
Restlessness of Aconitum Napellus:
- Patient is restless, anxious, does everything in a great haste, must change position often, everything startles him.
- It is one of the Nash’s trios of restless medicines (others being Arsenic & Rhus tox).
- is restless mentally
- (-Rhus Tox. is restless physically. Arsenic is restless both physically & mentally).
- patient is impatient and his impatience makes him restless (Ref. Dr. N. M. Chowdhury).
- Aconite pains are intolerable. It is also one of the Nash’s trio of greatest pain remedy (others are Chamomilla and Coffea).
- They drive him reckless, patient becomes restless at night, due to this pain, with agony and mental anxiety. Our immortal Master Hahnemann says, "Whenever Aconite is chosen homeopathically you must, above all, observe the moral symptoms, and be careful that it closely resembles them, the anguish of mind and body, the rest less ness, the disquiet not to be allayed."
Note:
It is interesting to note that Master Kent in his Repertory classed Acon. in first grade, under sub-rubric, aversion to motion (Acon.’, Ars.’, Bell.’, Bry.’, Calc.¹, Lach. ¹, Nux Vom.’, Ruta.’, Sil.’, Sulph.’, Baryta 2, CarboVeg 2, China 2 Gels 2, Graph 2, Lyco 2, Nat. Mur 2, Thuja.2). [1]
I
Intensity of action:
- is indicated in the first stage of any acute disease which starts suddenly and violently like a storm.
- Kent says that the patient seems to be threatened with a sudden and violent death, but recovery is quick. So, as was observed by Dr. Dunhum, it is like a great storm. Dunham’s discussion of this remedy in his Materia Media is very poetical. It has got no periodicity, nor any wave (Ref. Tyler).
Note 1
Acon. is the acute of Sulphur and both precedes and follows it in acute inflammatory conditions.
Note 2
Acon. is the drug for the congestive stage of inflammation before localization takes place (Ref. Nash). [1]
D
Dry and hot Skin
- Dry and hot skin with rare sweat (Nash).
- There is drenching sweat, especially on parts laid on. (Master Kent in his Repertory classed, ‘perspiration on the affected parts. Ambra.’, Ant. T 1, Merc.’, Rhus Tox. ¹). which relieves (Boericke) (Nat.Mur, Psor.), (Master Kent in his Repertory said, symptoms ameliorate while sweating. Bry., Cup.’, Gels.’, Nat. Mur 1, Rhus Tox 1, Acon 2, Ars 2, Chamo 2, Graph 2, Lach 2, Hep 2, Thuja 2, Verat 2).
Note:
Cold sweat, icy coldness of face may be observed in Acon. patient. It is mostly found in febrile condition. [1]
A
Aggravation & Amelioration
- <in the evening.
- <at night.
- <in the warm room
- >by uncovering
- >in the open air. (Alum., Mag.C., Puls., Sab.). [1]
Y
Yielding ailments
- Acon. diseases caused by exposure to dry cold air (Ars. Chamo., Camph., Caust., Rumex., Sil., Hepar., Psor., China.), dry north or west wind or exposure to draught of cold air, bad effects of checked perspiration (Bellis., Dulc., Rhus Tox., Baryta Carb.), fear, fright, shock, heat of the sun, excitement, injury, surgical operation etc. [1]
Note. 1
Paralysis from exposure to dry cold wind (acute effect) (-chronic effect, Caust.).
Note. 2
Master Kent said, complaints come on suddenly from the very cold weather of winter or from the intense hot weather of summer.
S
Sanguine temperament with sedentary life
It is generally indicated in acute or recent cases occurring in young persons, especially girls of a full, plethoric habit who lead a sedentary life; persons easily affected by atmospheric changes, dark hair and eyes, rigid muscular fibre and of sanguine temperament (quick in action and perception). [1]
A
Active hemorrhage
- It has got active hemorrhage from any part of the body both internal and external; uterus or other places in stout plethoric patients.
- The character of the blood is pure, and bright red, accompanied by fear of death and nervous excitability. [1]
(Master Kent classed Acon. under second grade, in the rubric, hemorrhage under generalities, Acon 2, Bell 1, Calc1, Carbo Veg 1, China 1, Crot 1, Fer 1, Ham 1, Ipec 1, Lach1, Merc Cor 1, Mill 1, Nat. Mu 1., Nit. Ac 1, Nux Vom 1, Phos 1, Puls 1, Sabina 1, Sec 1, Sulph 1, Apis 2, Arg. N 2, Bry 2, Chamo 2, Dulc2, Graph 2, Psor 2, Rhus Tox 2, Sil 2, Tril 2).
T
Tension
- Huge says "Tension" is the key-note of Aconite patient (-key-note of Belladonna is congestion).
- Due to irritation of mind and affection of circulation, tension always prevails in Acon. patient.
N. B. Aconite causes turmoil in circulation, Belladonna causes turmoil in brain and Chamomilla cause turmoil in temperament. These three are the Dr. CLARKE’S A.B.C. of nurseries.
U
Unquenchable thirst
Unquenchable thirst for large quantity of cold water is the characteristic symptom of Acon.
Everything tastes bitter except water (Kent) (Stan.).
N.B. Desire for bitter things (Dig., Nat.M., Tereb.) (Ref. Lippe). [1]
R
Red face becomes pale
- The face of Aconite is red or red and pale alternately anxious & frightened expression.
- Sensation of face growing or swelling on rising from a recumbent position, the red face becomes deathly pale or he becomes faint or giddy and falls, and he fears to rise again, often accompanied by vanishing of sight and unconsciousness. It is mostly found in febrile condition. (1)
Introduction
Constitution
Clinical
Mental Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms
Characteristic
Therapeutic Value
Modality
Remedy Relationship
Dose
Terminology
Reference
Also search as
Introduction
Introduction of Aconitum Napellus
Common name:
- Monkshood
- Wolf’s Bane
Synonyms
- Latin: Aconitum, Angustifolium
- English: Friar’s Cap, Helmet flower
Family / Group / Class / Order
- Ranunculaceae family
- Vegetable Kingdom
Habit and habitat / Description
- Europe
- It is usually known by its characteristics, benumbing taste, due to its alkaloid ACONITINE; this is, however, less noticeable in the tincture prepared from the fresh green plant than in that prepared from the dried root. (2)
Name of prover :
Samuel Hahnemann (1805)
Introduction and history of Aconite :
- The name Aconitum is derived from Greek word, meaning ‘without soil’
- Napellus is Latin word, meaning a little turnip.
- It is also called Monk’s hood because of shape of its flowers, which turn over and give appearance of hood thrown over head.
- In 1762, Baron Stoerck, a Viennese physician introduced Aconite to medicine.
- In 1805, Dr. Hahnemann introduced it to homeopathy. It belongs to the cardiac irritant group.
- It is acute, short acting remedy.
- All complaints come suddenly,violently and go away in the same manner.
- It is 1st remedy to be thought in inflammation.
- Dr Clarke mentioned ‘If Cinchona was the Newton’s apple of homeopathic discovery, Aconite is remedy by which Dr Hahnemann cured conditions which were were treated by bloodletting.
- This poisonous drug affects every system and the organs of the body.
- This drug causes functional disturbance.
- This drug covers acute and chronic complaints relating to the CVS.(5)
Doctrine of signature
- Doctrine of Signature of Aconite is ‘ailments from cold wind’.
- It is go-to remedy for 1st sign of any inflammation, but if symptom arose due to exposure to cold wind, you can give Aconite.
- Take a look at picture of Monkshood flower and observe how the purple ‘hood’ of petals surround and look as if they are protecting the center of the flower.
- Imagine yourself outside on a cold night, with wind whipping about your head.
- This is the Doctrine of Signatures – Mother Nature ‘shows’ us, with her beautiful, awe-inspiring design, the medicinal purpose for several of the members of her floral pharmacy.(6)
Parts used :
Fresh root, flowers and leaves.
Active principles :
- This drug contains acotinine, neopelline, aconine, ephedrine, aconitic and succinic acid.
- The main alkaloid is ‘aconitine’.
- The properties of aconite are mainly those of aconitine – extremely poisonous and narcotic.
- It also contains calcium and plenty of starch,
- Hypaconitine, mesaconitine and neoline.
Preparation :
- Mother tincture from the entire plant except the root, and dilutions. U.S.P., Extractum Aconiti. Fluid extractum Aconiti.(5)
Constitution
Constitution of Aconitum Napellus
Physical make up :
- It is a short acting remedy; suits people leading a sedentary life.
- Suits persons who are strong, robust, plethoric, sanguine, have dark hair and eyes and are with rigid muscular fibre.(5)
Temperament :
- Sanguine Temperament (5), Nervous, Choleric (9)
Diathesis :
- Scrofulous diathesis (5)
Relation with heat & cold :
- Neither chilly nor hot, but seems to be hot (5)
Miasm :
- Psoric (5)
Clinical
Clinical conditions of Aconitum Napellus
In Homeopathy Aconite Napellus medicine use by Homeopathic Doctors in treatment of following Disease Conditions
- Angina pectoris, Anxiety disorders, Bell’s palsy, Cerebral accidents, Colds, Conjunctivitis, Cystitis, Facial neuralgia, Gastritis, Influenza, Injury, Labour, Myocardial infarction, Orchitis, Otitis media, Panic disorders, Pneumonia, Shock, Tonsillitis, Toothache, Urinary retention or hemorrhage.
- Aconite is the acute of Sulphur – both precedes, follows it well in acute inflammatory conditions. (4)
Sites of action / Pharmacodynamics
Mind, brain, cerebrospinal nervous system, mucous and serous membranes, heart, cardiovascular system and blood. (5)
Causation (Causes / Ailments from)
A/F; Cause: Fear, fright, shock, Chill, dry cold weather, -Heat especially of sun, Injury, surgical shock, Draught of cold air, Checked perspiration, very hot weather (G.I.T.)(4)
Physiological action
i)Heart: a) Inhibitory paralysis, b) Blood pressure lessened.
ii) Circulation: Vaso-motor paralysis.
iii) Temperature: Depressed with diaphoresis.
iv) C. N. S.: Motor paralysis.
v) Mucous Membranes: Asthenic inflammation.
vi) Stomach: a) Emesis. b) Congestion, c) Neuralgia
vii) Lungs: a) Centric vagi paralysis, b) Congestion, c) Inflammation.
viii) Tendons and fibrous tissues: Rheumatoid inflammation.
ix) Serous membranes: Plastic inflammation.(4)
Patho-physiological changes / Pathogenesis:
- It is an antipyretic, diaphoretic and diuretic.
- The principal action of this drug is through cerebrospinal nervous system.
- The drug produces inhibitory paralysis of the heart resulting in reduction of blood pressure.
- The arterioles are contracted.
- Aconite is depressant to the heart and cerebrospinal nervous system when taken in higher physiological doses.
- It on the cardiovascular system.
- Pulse becomes very slow and death may occur due to respiratory failure. Heart’s action initially slows down, but later it becomes rapid and weak.
- It acts on nerves and skin. Firstly it causes a burning and tingling sensation on the entire body along with a feeling of coldness, as if ice water circulated instead of blood.
- It causes vasomotor paralysis, lowers temperature of body and causes diaphoresis.
- It acts on cerebrospinal nervous system, producing numbness and complete motor paralysis.
- Due to paralysis of capillaries, it leads to congestion, tension ,then inflammation. (5)
Mental Symptoms
Characteristic mental symptoms (psychology) of Aconitum Napellus
- GREAT FEAR, ANXIETY, and worry accompany every ailment, however trivial.
- Delirium is characterized by unhappiness, worry, fear, raving, rarely unconsciousness.
- FOREBODINGS AND FEARS. FEARS DEATH but believes that he will soon die; predicts the day. FEARS THE FUTURE, a crowd, crossing the street.
- RESTLESSNESS, tossing about.
- Tendency to start.
- Imagination acute, clairvoyance.
- Pains are intolerable; they drive him reckless.
- Music is unbearable; makes her sad. [Ambra.]
- Thinks his thoughts come from the stomach that parts of his body are abnormally thick. Feels as if what had just been done was a dream. (4)
Guiding Symptoms
Guiding Symptoms of Aconitum Napellus
A-Anguish of mind, Anguish of body (Ref. Master Hahnemann).
C-Calmness contra-indicates Aconite.
O-Onset is sudden and violent.
N-Nash’s trio of restless medicines, Nash’s trio of pain killers.
I-Inter-action of Anxiety, Worry, Fear (Those accompanies the most trivial ailments.)
T-Thirst for large quantities of cold water.
E-Exposure to dry cold air.
Exposure to dry north or west winds.
Exposure to draughts of cold air, while in a perspiration.(8)
1. Generalities
- Malaise, feebleness, muscular prostration.
- Twitching and convulsions over whole body.
- Heaviness as of lead all over body.
2. Head
- Vertigo and confusion, with ringing in ears, falls almost immediately.
- With giddiness, dimness of vision, and muscular weakness, Fullness in the head, with noises in the ears.
- Head and face ache, often darting pains in face, sometimes accompanied by vomiting, (Hemicrania cured).
- Weight about head, unable to hold it up.
3. Eye
- Strained feeling in eyes.
- Pupils dilated (both from internal and external use).
- Complete blindness, accompanying dilatation of pupils, sight returning when pupils contract.
- Vision hazy, with giddiness and nausea, Pupils insensible to light.
4. Ears
- Sense of pressure in ears, Roaring in ears.
- Complete deafness.
5. Nose
- SMELL ACUTELY SENSITIVE.
- PAIN AT ROOT OF NOSE.
- Coryza; much sneezing; throbbing in nostrils Haemorrhages of bright red blood.
- MUCOUS MEMBRANE DRY, NOSE STOPPED UP; DRY OR WITH BUT SCANTY WATERY CORYZA.
6. Face
- Aconite can cause a range of sensations in the face, starting with fullness in the cheeks and temples that gradually transforms into a painful tension, tingling, and prickling. The face becomes tense and swollen, with a creeping sensation that may also extend to the forearms.
- Furthermore, a distinctive drawing, stretching, and pressing sensation develops in the cheeks, upper jaws, and forehead—essentially, throughout the entire trigeminal nerve pathway. This sensation intensifies gradually, alternating with actual pain. Initially, this pain is occasional and fleeting, but it eventually becomes constant and severe, particularly at the temples and along the supraorbital nerve.
- In severe cases, darting facial pains may be accompanied by vomiting. Tonic contractions, starting in the fingers and then spreading to the face, can lead to trismus (lockjaw). After a while, clonic convulsions may occur throughout the body. The eyes may become closed, the lips dry and cracked, and the tongue stiff. The individual may feel chilly and experience a sense of impending doom. Breathing becomes rattling and rapid, accompanied by moaning. The facial expression may even take on a Hippocratic appearance, indicative of approaching death.
7. Mouth
- Burning on tip of tongue and lips.
- Burning, constricting, acrid, dry sensation in mouth and fauces. Tongue stiff.
- Taste disagreeable and disgustingly bitter.
- Taste completely lost. Taste impaired, teeth more sensitive when biting. Salivation.
8. Throat
- Aconite can cause a range of sensations in the throat and esophagus, including a burning anguish and a feeling of constriction and burning that extends from the mouth to the stomach. Each attempt to swallow triggers spasms reminiscent of hydrophobia, though unlike hydrophobia, these spasms are not exacerbated by the sight of water. Swallowing becomes difficult, and pain develops in the back of the neck, behind the jaws, and in the parotid region. This pain is so severe that the individual may need to support the back of their neck with their hand while eating. They may also describe a burning sensation in the esophagus, as if a hot coal were lodged there.
9. Stomach
- Eructation immediately.
- Severe vomiting, which recurred every two or three minutes and was performed by a sudden, jerking action of abdominal muscles accompanied by a loud shout.
- Nausea induced by erect position.
- Vomiting relieves all symptoms. Warmth most marked in region of stomach.
10. Abdomen
- Rumbling in bowels (immediately in one case, two hours after dose in another).
- Sudden contraction of diaphragm. Liver and spleen greatly enlarged.
11. Rectum & Anus
- Pain with nightly itching and stitching in anus.
- Choleraic discharge with collapse, anxiety and restlessness. Bleeding haemorrhoids. [Hamam]
- Watery diarrhoea in children. They cry and complain much, are sleepless and restless.
12. Stool
- Frequent scanty stool, with tenesmus.
- Green, watery stools, like chopped spinach. White stools, with dark red urine.
13. Urinary Organ
- Copious diuresis.
- Difficulty in voiding urine.
- Dysuria also occasionally retention with hypogastric pain.
- Scanty, red, hot urine, without sediment.
14. Sexual Organ
- Male: Nocturnal pollutions (unusual to prover).
- Female: Menses too profuse and too protracted, especially in young plethoric women. Suppression of the menses from fright or cold. Too scanty or suppressed lochia. Rigidity of the os uteri. Frenzy on the appearance of the menses. Ovaries congested also painful. Sharp shooting pains in womb.
15. Respiratory System
- Respiration difficult.
- Oppressive anguish in precordial region. Sighing breathing.
16. Heart & Pulse
- Pulse at first, on entering a warm room, more frequent then sinks far below normal, small, weak, intermittent.
- Sounds of heart only heard at apex.
17. Neck & Back
- Numb, stiff, painful. Crawling and tingling, as if bruised.
- Stiffness in nape of neck. Bruised pain between scapulae.
18. Extremities
- Weakness, trembling, burning, creeping, tingling, numbness of limbs.
19. Skin
- General formication.
20. Sleep
- Sleep disturbed, Throws himself continually around in bed.
- Somnolence.
21. Fever
- Surface cold, sweating, and quite pale.
- Intense coldness, Head and face became suddenly warm, warmth extended over rest of body, was more intense in region of stomach, also was accompanied by sweat. (3)
Characteristic
Important characteristic features of Aconitum Napellus
- The symptoms associated with Aconite are primarily derived from cases of poisoning and overdose. While the numbness, tingling, prickling, and heat experienced in Aconite provings are produced by the alkaloid, these sensations are significantly intensified in cases of poisoning.
- Upon local application of Aconite, a sensation of warmth is initially experienced, followed by burning accompanied by sharp pains and itching. Ultimately, this progresses to numbness and anesthesia.
- Furthermore, the symptoms often exhibit an ascending pattern, originating in the lower extremities and moving upwards. For instance, individuals may describe a tingling, prickling sensation ascending from the legs to the spine and head, accompanied by tingling in the fingers. Similarly, an ice-cold sensation may creep upwards from the feet.
- Other characteristic symptoms include an intense fear of death, anguish, profound chilliness, a feeling of sickness, and a constricting burning sensation that extends from the mouth to the stomach. Twitching and spasms may occur throughout the body, particularly in the face.
- Notably, all symptoms tend to improve, especially after vomiting.
Other Characteristic Symptoms
- In one poisoning case "vomiting recurred every 2-3 minutes, with sudden jerking action of abdominal muscles, and a loud shout, probably dependent on a sudden contraction of the diaphragm. Every attempt to swallow caused spasmodic contractions so characteristic of hydrophobia, but they were not renewed by the sight of water. The slightest touch renewed the spasms."
- Aconitine is helpful in cases of hydrophobia, convulsive or the paralytic kind.
- The senses are disordered or lost.
- In poisoning case the blindness was coincident with sudden dilatation of the pupils, also sight partially returned as the pupils contracted.
- A heavy feeling as of lead all over the body.
- All parts except head also stomach feel as if filled with lead.
- 5th nerve neuralgia.
- Creeping on face with feeling of swelling also tension.
- Pains in supraorbital.
- PME show the spleen enlarged, posterior part of liver dark also almost black. Kidneys hyperemic. (3)
Therapeutic Value
Modality
Modalities of Aconitum Napellus
Aggravation:
- At night, Atmospheric changes, North- West wind, Exposure to draft of air while in perspiration, when rising from bed, checked perspiration, Tobacco chewing, Light, Dentition, In warm room, Pressure, touch, During menses, Sleeping in the sun, Music, Inspiration.
Amelioration:
- In open air, Perspiration, lying in bed and especially lying on the back, Wine, Sitting still. (4)
Remedy Relationship
Remedy Relationship of Aconitum Napellus
Complimentary
- Arn, Coff, Sulph
Follows Well
- Abrot, Arn, Ars, Bell, Bry, Cact, Calc, Cocc, Canth, Coff, Hep, Ipec, Kali-brom, Merc, Puls, Rhus, Sep, Spig, Spong, Sulph, Sil.
Antidoted By
- Acet-ac, Cham, Cimic, Coff, Nux-v, Par, Petr, Sep, Sulph
It Antidotes
- Arn, Aspin, Astac, Bell, Bry, Cact, Canth, Cham, Chel, Cit-v, Coff, Croc, Dol, Glon, Graph, Kalm, Kreos, Lyc, Merc-p, Mez, Morph, Nux-v, Petr, Sep, Sol, Spong, Stry, Sulph, Ther, Verat, Vib-p.
Comparison
- Bell, Cann-i, Cham, Cocc, Con, Dulc. (4)
Dose
Dosage of Aconitum Napellus
Potency
- Sixth potency for sensory affections; first to third for congestive conditions and inflammatory fevers.
- Must be repeated frequently in acute diseases. Acon is a rapid worker.
- Sixth potency for neuralgias, 12 and 30 when there is nervous excitement and fear of death.(4)
Repetition
- It must be repeated frequently in an acute condition.
Duration of action
- 1 Hour to Several Weeks.(4)(5)
Terminology
Terminology of Aconitum Napellus
Let’s break down some of the homeopathic terminologies used in the article about Aconitum Napellus:
Key Homeopathic Terms and Meanings:
Ailments from:
Indicates the potential causes or triggers of the symptoms Aconitum Napellus is used to address (e.g., exposure to dry cold air, fright, shock).
Amelioration:
Factors or conditions that improve or relieve the symptoms of a remedy (e.g., open air, perspiration).
Aggravation:
Factors or conditions that worsen the symptoms of a remedy (e.g., warmth, evening/night).
Characteristic Symptoms:
Key symptoms that are particularly indicative of a specific remedy (e.g., intense fear of death, restlessness).
Complementary:
Remedies that often work well together, enhancing each other’s effects.
Concomitants:
Symptoms that accompany the main complaint and are important for choosing the correct remedy.
Constitution:
The overall physical and mental characteristics of a person, which help guide remedy selection.
Diathesis:
A predisposition to certain types of diseases.
Doctrine of Signatures:
A belief that the appearance of a plant can indicate its medicinal properties (e.g., Aconitum’s hood-like flowers suggesting protection).
Generalities:
Symptoms that affect the entire body rather than a specific part.
Guiding Symptoms:
The most prominent and characteristic symptoms of a remedy that guide its use.
Inimical:
Remedies that should not be used together because they may interfere with each other’s action.
Keynotes:
The most essential and unique symptoms of a remedy.
Materia Medica:
A collection of information about the symptoms and therapeutic uses of homeopathic remedies.
Miasm:
A deep-seated disturbance in the body’s energy that predisposes a person to certain chronic diseases.
Modalities:
Factors that modify or change the intensity of symptoms (e.g., better or worse in certain conditions).
Potency: The number of times a remedy has been diluted and succussed, indicating its strength.
Prover:
The person who takes a substance in a proving to record its effects on the body.
Repertory:
An index of homeopathic symptoms and the remedies associated with them.
Rubric:
A specific symptom category in a repertory.
Sanguine Temperament:
A personality type characterized by being optimistic, cheerful, and social.
Therapeutic Value:
The conditions or diseases for which a remedy is commonly used.
Let me know if you’d like any further clarification on these terms or others!
Reference
Reference of Aconitum Napellus
- Synoptic Memorizer of MM- 2001 Vol I-Chap-1,2 > Aconite
- A Manual of MM, Therapeutics and Pharmacology by Blackwood, Alexander Leslie
- Dictionary of practical MM (All 3 Vol.) by Clarke J.H
- MM by Boericke W Chap -Aconite
- J.D. Patil Materia Medica -1st edition 2013 Chapter- Aconite
- https://www.theconsciousnest.com/monkshood-and-the-doctrine-of-signatures/
- Synoptic Memorizer of MM-2001 Vol II Part-1 > Aconite
- Synoptic Memorizer of MM-2001 Vol II Part-2 > Aconite
- Tempraz MM by Dr. Parinaz Humranwala
Also search as
Aconitum Napellus also search as
Specific Terms:
- Aconitum Napellus
- Aconite
- Monkshood
- Wolf’s Bane
- Aconitum napellus homeopathic medicine
- Aconite homeopathic remedy
General Terms:
- Homeopathic medicine for fear
- Homeopathy for anxiety
- Homeopathic remedies for fever
- Homeopathic treatment for colds and flu
- Homeopathy for inflammation
- Homeopathy for pain
Symptom-Based Terms:
- Homeopathic remedy for restlessness
- Homeopathic medicine for sudden onset of illness
- Homeopathy for dry, hot skin
- Homeopathic treatment for intense thirst
- Homeopathic remedy for fear of death
Long-Tail Keywords:
- Homeopathic treatment for panic attacks
- Homeopathic remedies for children’s ailments
- Homeopathy for acute conditions
- Natural remedies for sudden onset of illness
- Homeopathic remedies for high fever
Questions:
- What is Aconitum Napellus used for in homeopathy?
- What are the symptoms of Aconitum Napellus?
- Who should take Aconitum Napellus?
- What are the side effects of Aconitum Napellus?
- Where can I buy Aconitum Napellus?
Additional Tips:
- Use synonyms and variations of keywords to capture a wider audience.
- Include relevant hashtags on social media to increase visibility (e.g., #homeopathy, #aconite, #naturalremedies).
- Share the article on homeopathic forums and groups.
- Optimize the article for search engines by including keywords in the title, meta description, and throughout the content.
By using a combination of these search terms, people interested in Aconitum Napellus homeopathic medicine should be able to find this article easily.
People can search for this article on Aconitum Napellus homeopathic medicine using various methods:
Direct Search:
- Use the full name: "Aconitum Napellus homeopathic medicine" in search engines like Google, Bing, or DuckDuckGo.
Synonym Search:
- Use alternative names: "Monkshood homeopathic remedy," "Wolfsbane homeopathy," or "Aconite remedy" in search engines.
Symptom-Based Search:
- Search for specific symptoms: "Homeopathic remedy for fear and anxiety," "Homeopathy for sudden fever," or "Homeopathic medicine for restlessness."
Homeopathic Resources:
- Online Materia Medica/Repertories: Search for "Aconitum Napellus" in online homeopathic resources like Materia Medica by William Boericke or John Henry Clarke.
- Homeopathic Forums/Websites: Look for discussions and articles about Aconitum Napellus on homeopathic forums and websites.
Social Media:
- Use relevant hashtags: Search for hashtags like #homeopathy, #aconite, or #naturalremedies on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, or Instagram.
Book Search:
- Look for books on homeopathic materia medica or remedies at libraries or online retailers. Search for titles containing "Aconitum Napellus" or "Aconite."
Expert Consultation:
- Seek guidance from a qualified homeopathic practitioner who can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and symptoms.
Tips for Effective Searching:
- Combine keywords: Combine different terms related to Aconitum Napellus and your specific interest (e.g., "Aconitum Napellus homeopathic remedy for anxiety").
- Use quotation marks: Use quotation marks around specific phrases to search for exact matches (e.g., "Aconite fear of death").
- Exclude terms: Use the minus sign (-) before a word to exclude results containing that word (e.g., "Aconitum Napellus -poison").
- Try different platforms: Explore different search engines, online resources, and social media platforms to find a wide range of information.
By using these strategies, you can easily find reliable information about Aconitum Napellus homeopathic medicine and its potential benefits for various health conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Aconitum Napellus safe to use?
It is a highly diluted and potentized remedy in homeopathy, making it safe when used under the guidance of a qualified homeopathic practitioner. However, the raw plant is toxic and should never be ingested directly.
In which stage of disease Aconite is called for?
Aconite for the congestive stage of inflammation before localisation takes place.
What is the key-note of Aconite?
Tension’ is the key-note of Aconite.
What is the facial expression of an Aconite patient?
The countinance is expressive of fear. The face represents the great fear and anxiety of mind. On rising from a recumbent position, the red face becomes deathly pale.
Who can benefit from Aconitum Napellus?
Individuals experiencing sudden and intense physical or emotional symptoms, particularly those triggered by cold, shock, or fright, may find relief with Aconitum Napellus.
FAQ Related to Symptoms of Medicine
What are the common names of Aconite?
i) Monkshood,
ii) Wolfs bane,
iii) Helmet flower.
Who is the chronic of Aconite?
Sulphur.
What are the mental symptoms of Aconite?
Mental Symptoms
i) Introduction-
Mental symptoms are characterized by acute onset.
ii) Fear
Great fear of death; fear to go out; to go into a crowd; to go into where there are many people or excitement to cross the street: fear of death during pregnancy: fear of darkness; fear of ghost.
iii) Prediction
Predicts the day & time of death.
iv) Restlessness
Constant restlessness both physically and mentally. Must change position often; everything startles him.
v) Anxiety
Great anxiety of mind; does everything in great haste.
vi) Agony
Tosses about in agony with great nervous excitability.
vii) Over sensitiveness
Mentally oversensitive.
viii) Relation with music
Music is unbearable and makes her sad.
Differentiate Aconite and Ars. alb. in fear of death.
Remedy Differentiate
Aconite
Fear of death predicts the day even the time or moment of death. Patient thinks that unless proper medicine is taken, he would die, therefore wants the doctor to be called at once.
Arsenic alb.
Fear of death but never predicts the time of death. He thinks that his sease is incurable. Therefore, no use of taking medicine and doctor need not be called.
What are the constant concomitants of Aconite?
Constant concomitants
i) Firstly, Mental anxiety.
ii) Secondly, Worry
iii) Thirdly, Fear- these accompanies the most trivial ailment.
State the cough symptoms of Aconite.
Cough Symptoms
a) Causation i.e.: –
i) Firstly, Exposure to dry cold air,
ii) Secondly, Dry north or west winds.
iii) Thirdly, Exposure to draught of cold air,
iv) Fourthly, After checked perspiration.
b) Character of the cough i.e.:
- It is croupy, dry, hoarse, suffocating, rough, loud, croaking, hard, ringing & whistling.
c) Modalities i.e.: –
Agg. i) Firstly, On expiration, ii) Secondly, Towards evening & night.
Amel. i) In open air.
d) Concomitants i.e.: –
i) Firstly, Constant mental & physical restlessness., ii) Secondly, Thirst for large quantities of cold water.
State the indications of Aconite in cholera.
Cholera
a) Causation i.e.:
i) Firstly, From fear,
ii) Secondly, From fright, from shock excitement.
iii) Thirdly, From checked perspiration,
iv) Fourthly, From heat of the sun, etc.
b) Mode of onset i.e.:
Sudden and violent.
c) Ch. of stool i.e.:
i) Firstly, Severe vomiting and purging in profuse quantity.
ii) Secondly, Rice watery stool, contains bright-red blood.
iii) Thirdly, Frequent desire for stool & vomiting.
d) Modalities i.e.: –
Agg. in evening and towards night.
e) Concomitants i.e.:
- Severe precordial pain
- Great fear of death, even predicts the day and moment of death.
- Intense nervousness and restlessness with great anxiety.
- Thirst for large quantities of cold water.
Discuss the paralytic symptoms of Aconite.
Paralaytic Symptoms
a) Causation i.e.: –
i) Firstly, Due to exposure of cold air, ii) Secondly, Due to draught of north, west wind etc.
b) Onset i.e.: – Sudden and violent.
c) Ch. symptoms i.e.:
i) Firstly, Paralysis accompanied by coldness, ii) Secondly, Numbness and tingling of the parts.
State Aconite in convulsion.
Convulsion of Aconite
a) Adoptability i.e.: –
i) Firstly, Acon. is esp. suitable for rosy, chubby and plethoric baby.
ii) Secondly, Convulsion esp. of teething children.
b) Convulsive symptoms i.e.: –
i) Firstly, Jerks and twitches of single muscle with heat,
ii) Secondly, Child gnaws its fist.
iii) Thirdly, Frets and screams-restlessness,
iv) Fourthly, Skin dry and hot esp. with high fever.
What is the other medicine in your course having convulsion of single muscle?
Ignatia
What are the indications of Aconite in fever?
Fever Condition
a) Mode of onset i.e.:
Acute onset; sudden and violent like storm.
b) Causation i.e.: –
i) Firstly, From exposure to dry cold air,
ii) Secondly, From exposure to draught of cold air.
iii) Thirdly, From bad effect of checked perspiration, iv) From fear, fright, shock.
v) Fourthly, From heat of the sun.
c) Period of prodrome i.e.:
- High rise of temperature, whole body burning hot
d) Period of progress i.e.:
- High fever but of short and sharp attack.
- Severe chill in the evening
e) Period of decline i.e.:
- There is no periodicity, recovery is quick.
f) Physical symptoms i.e.:
i) Firstly, Skin i.e.: – Dry and hot.
ii) Secondly, Sweat i.e.: -Drenching sweat on the parts laid on, which ameliorates the complaints.
iii) Thirdly, Thirst i.e.: -Burning thirst for large quantity of cold water.
iv) Fourthly, Pulse i.e.: -Full, frequent, both tense and hard.
v) Lastly, Face: –
- Face red or pale also red alternately
- On rising from a recumbent position, the red face becomes deathly pale or he becomes faint or giddy and falls and he fears to rise again; often accompanied by vanishing of sight also unconsciousness.
- The countenance is expressive of fear.
g) Mental symptoms i.e.:
i) Firstly, Fear-Great fear of death; predicts the day and moment of death.
ii) Secondly, Restlessness-Intense nervous restlessness; tossing about in agony.
iii) Thirdly, Anxiety-Anxiety with nervous excitability.
h) Modalities i.e.:
Agg.: In evening and towards night; in warm room.
Amel: In open air; by perspiration.
i) Cautions i.e.:
- Acon, should never be given simply to control the fever, never alternated with other drugs for that purpose. If it be a case requiring Acon. no other medicine is needed; Acon. will cure the case.
- Rarely indicated in eruptive fever.
- Unless indicated by the exciting cause, is nearly always injurious in first stages of typhoid fever.
.
What is the master’s warning regarding Aconite?
Master Hahnemann says about Aconitum Napellus
"Whenever Aconite is chosen homeopathically, you must. above all. observe the moral symptoms, also be careful that it closely resembles them: the anguish of mind also body: the restlessness; the disquiet not to be allayed."
Name six characteristic symptoms of Acon.
Arranged in grade/order
- Is generally indicated in acute or recent cases which starts suddenly also violently.
- ‘Tension’ is the key-note of Acon.
- It is one of the members of the trios of ‘restless family’ of Dr. Nash. The anxiety also impatience make the patient mentally restless.
- Great fear also anxiety of mind. Fear of death with prediction of day also moment of death.
- It is one of the members of the ‘trios of pain remedy of Dr. Nash. Pains are intolerable also is often associated with numbness.
- Either Unquenchable thirst or burning thirst for large quantities of cold water.(7)
State the menstrual symptom of Aconite
Menstrual symptoms
Amenorrhoea- suppression of menses after fright.(1)
Note i.e.
1. Firstly, Aconite is the acute of Sulphur.
2. Secondly, Sulphur is the chronic of Aconite.(7)
FAQ Realated to Trio of Medicine
Name three medicines those are easily affected by atmospheric changes.
Aconite.
Sulphur.
Hepar sulph.
What are the A B C of Clarke’s nurseries?
A B C of Clarke’s nurseries
A-Aconite.
B-Belladonna.
C-Chamomilla.
Name four medicines where tonsils become inflamed after riding in a cold wind.
Aconite.
Belladonna.
Hepar sulph.
Rhus tox.
Four medicines having plethoric habit.
Aconite.
Belladonna.
Calc. carb.
Sulphur.
Name three medicines for bad effect of checked perspiration.
Aconite.
Bryonia.
Dulcamara.
Three medicines for acute conditions.
Aconite nap.
Belladonna.
Dulcamara.
Name three medicines who lead ‘sedentary life’.
Trio of sedentary life
- Aconite.
- Aloe soc
- Nux vom.
Name three medicines those are easily affected by atmospheric changes.
Aconite.
Sulphur.
Hepar sulph.
Name three medicines where pleurisy or pneumonia occurs from sudden exposure while overheated.
Aconite.
Arnica
Ranunculus bulb.
Three medicines for bad effects from having the hair-cut.
Aconite.
Belladonna.
Glonoinum.
Nash’s trio of restless medicine and differentiate them.
Restlessness Trio
i) Firstly, Aconite.
ii) Secondly, Ars. alb.
iii) Thirdly, Rhus tox.
- Aconite-Aconite is mentally restless
- alb.-Ars. alb. is restless both physically and mentally.
- Rhus tox is physically restless.
Name four medicines for fear of death.
i) Firstly, Aconite.
ii) Secondly, Arsenic. alb.
iii) Thirdly, Arg. Nitricum.
iv) Fourthly, Gelsemium.
Nash’s trio of pain remedies.
Nash’s trio
i) Firstly, Aconite-Pains are intolerable and makes the patient restless esp. at night. Pain is often associated with numbness.
ii) Secondly, Chamomilla-Pain is accompanied by intense irritability.
iii) Thirdly, Coffea-Pain is accompanied by excitement.
Name three remedies where music is unbearable.
Aconite-Music is unbearable -makes the patient sad.
Graphites-Music makes her weep.
Thuja-Music makes her weep.
Name two medicines for complete aphonia after exposure to north-west wind.
i) Firstly- Aconite.
ii) Secondly-Hepar sulph.
Three medicines for bad effects of fear which is still remaining.
i) Firstly, Aconite
ii) Secondly, Opium
iii) Thirdly, Hyoscyamus.
